The Characteristics of Granite Associated with Tin and Mineralization in Northwest China
-
摘要:
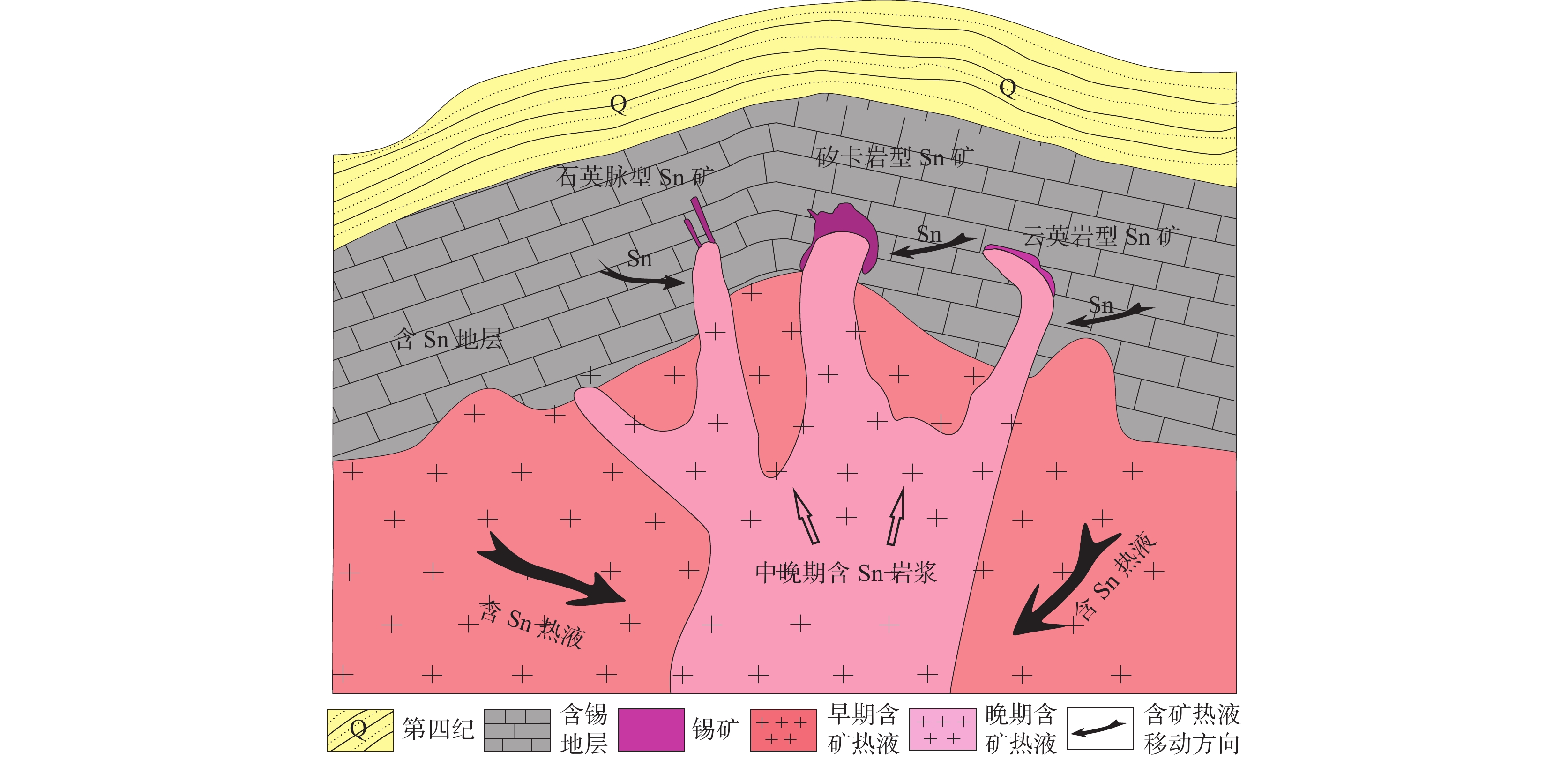
西北地区是国内成矿条件优越、矿产资源集中区域之一,但锡产出不足全国的2%,且分布零散、规模较小,所以西北地区锡矿并没有得到很多关注,且已有研究主要偏重典型矿床的地球化学分析和矿床成因,对区域成矿特征和成矿规律少有总结。笔者选择西北地区与锡有关的花岗岩为研究对象,通过分析此类花岗岩的特征提出锡矿找矿新认识。分析显示,Sn元素易富集于晚期熔体,且易由地幔向地壳富集,花岗岩浆源区地壳物质越多对形成锡矿越有利,A型花岗岩对锡成矿有更为明显的专属性,尤其在大陆碰撞、俯冲和洋陆转换环境下形成的过铝质和钙碱性花岗岩更有利于锡富集。同时,与锡成矿有关的花岗岩普遍具有较高锡丰度,如东准和天山地区达到7×10−6,远远高于地壳Sn丰度值(1.7×10−6),加之成矿区地层锡值普遍偏高,锡经过不断的迁移、富集、岩浆结晶分异并在一定的温度下最终成矿。文中简述了西北地区的6个锡矿成矿区带特征,为西北地区锡矿找矿提供参考。
Abstract:Northwest China is one of superior conditions area for tin ore formation and rich mineral resources in China, but tin ore output is less than 2%, and scattered distribution and small scale in the area. Because tin is not a dominant mineral, it has not received much attention. Previous research mainly focused on the geochemical and genesis of typical deposits, lacking a summary and understanding of regional mineralization characteristics and patterns. This paper selects the granite related to tin ore as the research object. The authors put forward some new comprehension of tin prospecting by analyzing the characteristics of the granite. The paper shows that tin is not only enriched in late melt but also from mantle to crust. The more crustal material in granulite basement, it is the more favorable for tin mineralization. A-type granite has a more obvious specificity to tin mineralization. It found that granites related to tin mineralization generally have higher Sn abundance, especially the peraluminous and calc-alkaline granites formed in the environment of continental collision, oceanic or crust subduction and ocean-continent transition are more conducive to tin enrichment. The high Sn abundance is also an essential factor for tin mineralization. For example, in the East Junggar and Tianshan regions, the tin abundance is reached 7×10−6, higher than the crustal tin abundance value of (1.7×10−6). Tin ore is finally formed at a certain temperature, continuous mobilized, migrated, enriched, and magmatic crystallization differentiation. Based on the above views, the paper describes the characteristics of the 6 tin metallogenic belts in Northwest China, which are considered to be tin prospecting potential area.
-
Key words:
- tin ore /
- granite related to tin /
- metallogenic conditions /
- metallogenic environment /
- NW China
-

-
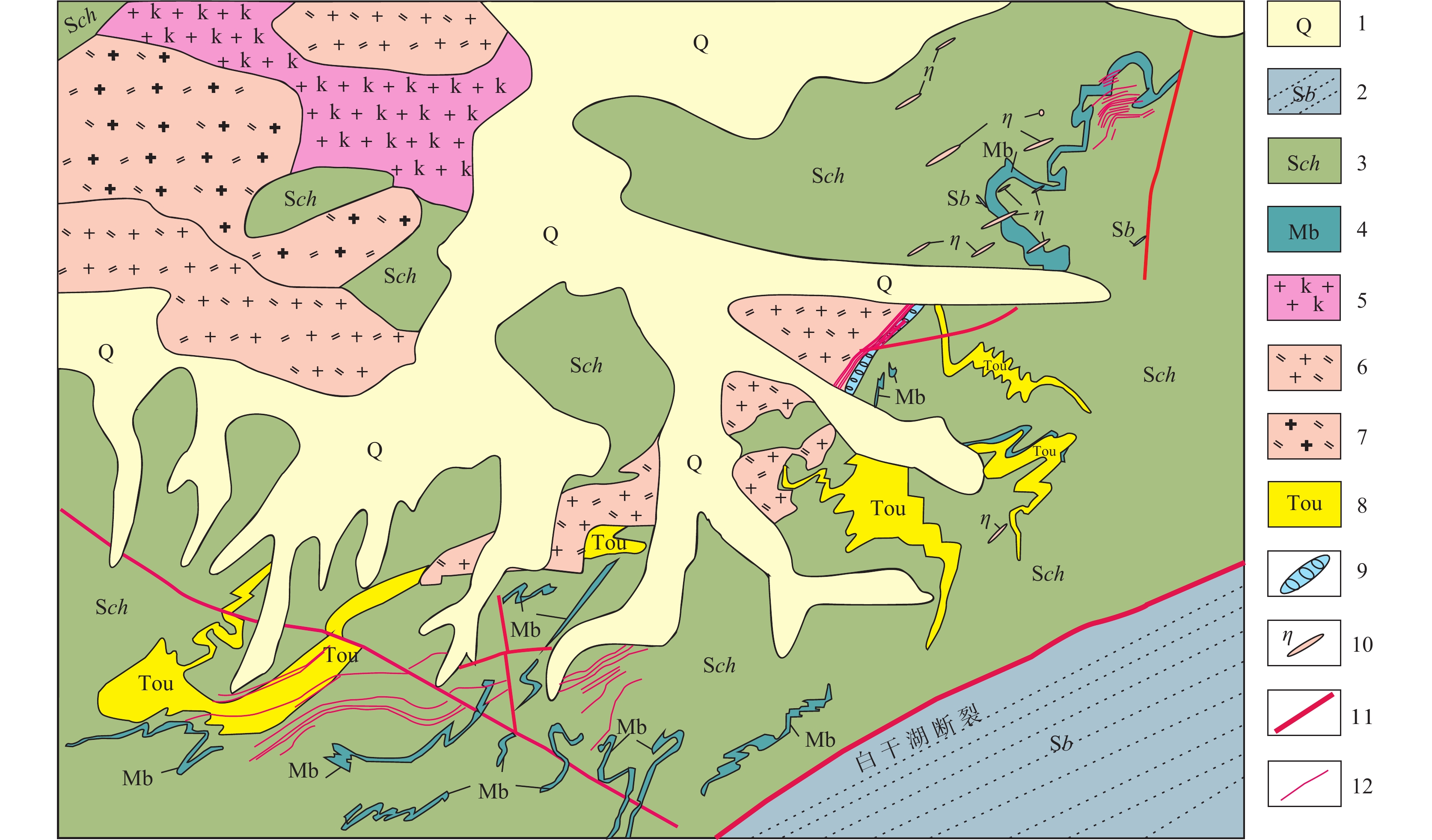
图 2 白干湖矿田地质略图(据李大新等,2013修)
Figure 2.
图 3 萨惹什克锡矿床地质图(据林锦富等,2008修)
Figure 3.
表 1 西北地区重要锡矿床地质特征表
Table 1. Geological characteristics of important tin deposits in Northwest China
矿床名称 矿床规模 成矿元素 矿床类型 围岩 矿体产
出位置矿石矿物 含矿岩体地球
化学特征与成矿有关岩体及时代 参考文献 奇台县萨惹什克锡矿床 中型 Sn 石英脉型 富碱花岗岩 锡石石英脉和含锡
花岗岩锡石 高碱、贫Ca、富Rb、Sn、K,强烈亏损Ba, Sr, Eu, δEu= 0.01~0.03, A型花岗岩 锡石石英脉(324.2±3.4) Ma;富碱花岗岩(306±3) Ma、(313±2) Ma、314±5) Ma 唐红峰等,2007;林锦富等,2008 温泉县喀孜别克锡矿床 中型 Sn、W、Cu 云英岩型 上泥盆统碎屑岩建造 喀孜别克岩体内 锡石、黑钨矿、磁铁矿、辉钼矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、蓝铜矿 SiO2>70%,K2O>Na2O,σ=1.62%~2.07%,属钙碱岩系列,出现刚玉分子(>l%),富Rb、Sn,δEu=0.15,S型花岗岩 喀孜别克岩体,290 Ma 兰天佑等,1994 兴海县日龙沟锡矿床 中型 Sn、Cu、Pb、Zn 海相火
山岩型下二叠统浅变质滨海-浅海相碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩夹火山沉积岩建造 围岩含矿 锡石、黄铁矿、方铅矿、自然铜 — — 王移生,1990;路远发,1990 都兰县小卧龙铁钨锡
矿床中型 W、Sn、Fe 矽卡岩型 奥陶系—志留系中-基性火山沉积变质岩 角岩化泥质砂岩及矽
卡岩磁铁矿、锡石、白钨矿、黄铜矿 富SiO2、K、Sn,属高钾钙碱性系列 似斑状二长花岗岩,印支期 马慧英等,2009 彻依布拉克锡多金属
矿床中型 Sn、Au、Zn、Cu 矽卡岩型 碱长花岗岩 矽卡岩 锡石、黄铜矿、白钨矿、黄铁矿等 富Si、富碱、富轻稀土,贫Mg、Al,Ga/Al值大,具强Eu负异常,A型花岗岩 塔木岩体,(261.5±2.7) Ma 杨富全等,2003 独山锡矿 中型 Sn 热液型 钾长花岗斑岩 钾长花岗斑岩体 锡石、
磁铁矿A2型花岗岩 钾长花岗斑岩,(264.6±1.2)~
(259.9±2.6) Ma张子敏等,2001 若羌县白干湖钨锡矿床 大型 W、Sn 矽卡岩型 古元古界金水口群小庙岩组陆源碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩沉积建造 二长花岗岩、更长花岗岩及其与围岩接触带中 锡石、白钨矿、黑钨矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿 高碱高钾,富SiO2、Rb、Sn,亏损Ba,Sr,Eu,A型花岗岩 二长花岗岩(430.5±1.2) Ma、(421±4) Ma;含矿更长花岗岩(429.5±3.2) Ma 高永宝等,2011;李大新等,2013 表 2 西北地区大中型主要锡矿床与成矿有关的花岗岩体主量元素(%)测试数据
Table 2. Major element compositions (%) of the metallogenic granite of the main tin deposits in Northwest China
矿床名称
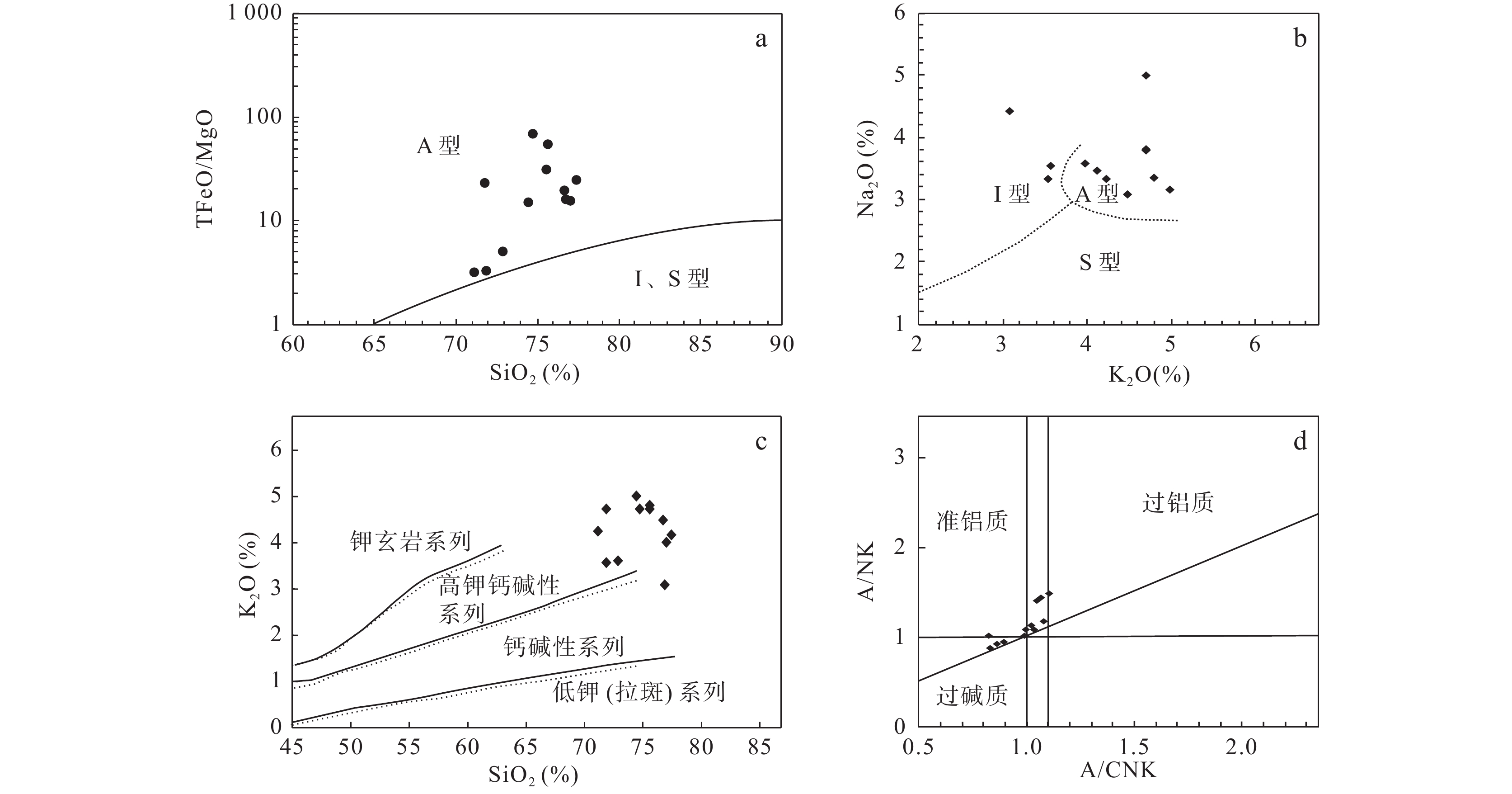
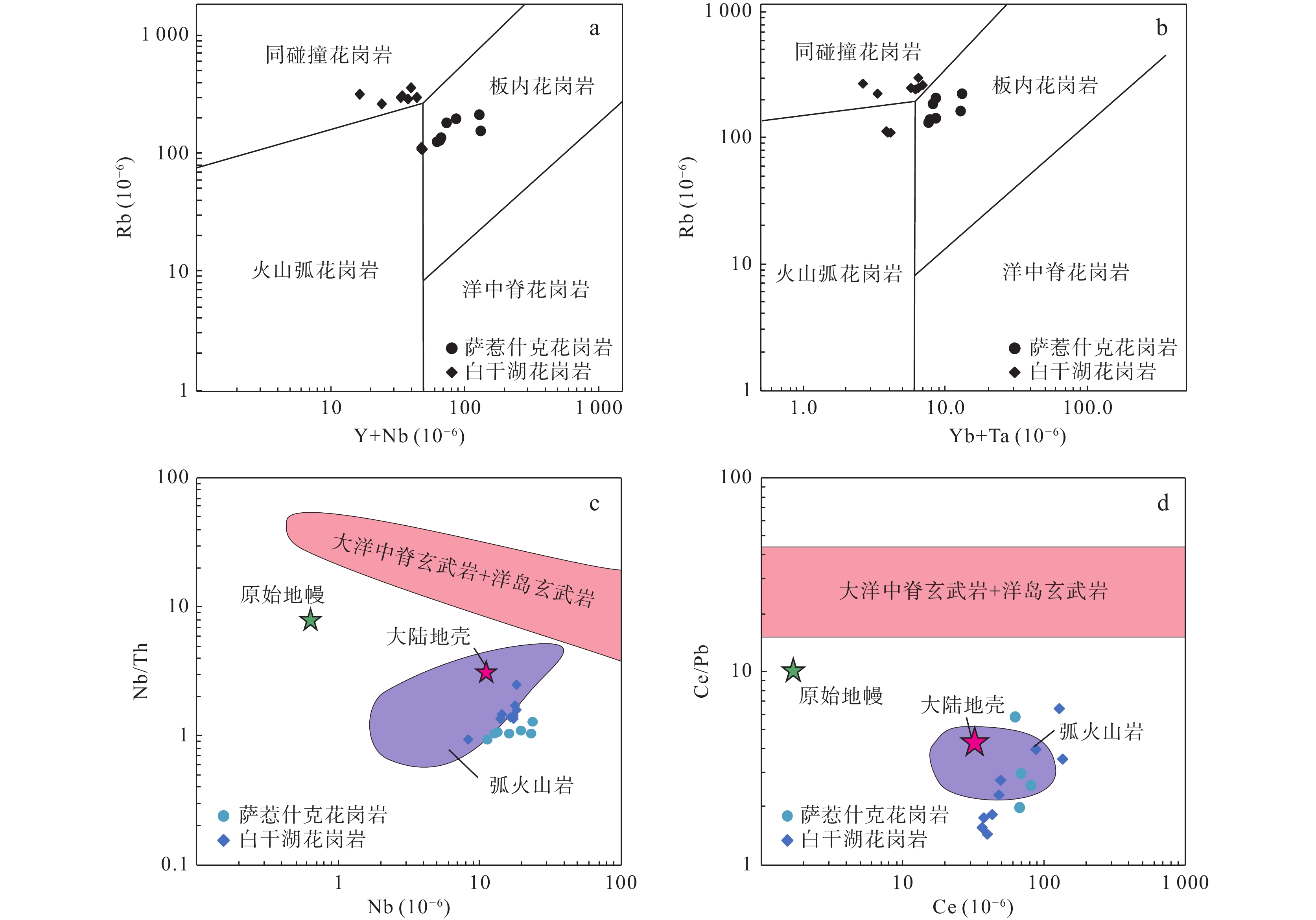
岩体白干湖 萨惹什克 小卧龙 彻依布拉克 似斑状二长花岗岩 细粒二长花岗 萨北岩体碱性花岗岩 似斑状二长花岗岩 塔木碱长花岗岩 SiO2 71.10 71.88 76.98 77.36 76.68 76.77 72.88 74.46 71.81 Al2O3 14.55 13.84 9.74 9.00 9.27 10.86 13.61 12.00 13.57 Fe2O3 0.19 0.69 0.83 1.81 1.61 1.87 1.00 0.49 1.10 FeO 1.85 1.70 0.95 1.05 0.71 0.70 1.63 0.90 1.30 MnO 0.10 0.12 0.16 0.18 0.16 0.18 0.05 0.05 0.04 CaO 1.97 1.79 0.40 0.38 0.47 0.20 1.82 0.64 1.75 MgO 0.64 0.71 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.15 0.51 0.09 0.10 K2O 4.23 3.54 3.98 4.13 4.48 3.08 3.57 4.99 4.71 Na2O 3.33 3.32 3.58 3.46 3.07 4.41 3.53 3.15 4.98 P2O5 0.11 0.13 0.20 0.21 0.28 0.22 0.08 0.01 0.01 TiO2 0.26 0.30 0.48 0.53 0.53 0.51 0.01 0.10 0.11 Na2O+K2O 7.56 6.86 7.56 7.59 7.55 7.49 7.10 8.14 9.69 TFeO/MgO 3.16 3.27 15.43 24.35 19.62 15.88 4.96 14.90 22.90 A/CNK 1.07 1.10 0.89 0.83 0.86 0.99 1.05 1.02 0.82 A/NK 1.45 1.49 0.96 0.89 0.94 1.03 1.41 1.13 1.02 注:白干湖数据据李大新等(2013);萨惹什克数据据唐红峰等(2007);小卧龙数据据马慧英等(2009);彻依布拉克数据据杨富全等(2003)。 -
[1] 曹华文. 滇西腾-梁锡矿带中-新生代岩浆岩演化与成矿关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015, 1−349. CAO Huawen. Research on Mesozoic-Cenozoic magmatic evolution and its relation with metallogeny in Tengchong-Lianghe tin ore belt, western Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing): 2015, 1−349. [2] 陈郑辉, 王登红, 盛继福, 等 . 中国锡矿成矿规律概要[J]. 地质学报,2015 ,89 (6 ):1026 −1037 .CHEN Zhenghui, WANG Denghong, SHENG Jifu, et al . The Metallogenic Regularity of Tin Deposits in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2015 ,89 (6 ):1026 −1037 .[3] 陈骏, 王汝成, 周建平, 等. 锡的地球化学[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 2000, 116−154. CHEN Jun, WANG Rucheng, ZHOU Jianping, et al. Geochemistry of Tin[M]. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 2000, 116−154. [4] 高晓峰, 校培喜, 谢从瑞, 等 . 东昆仑阿牙克库木湖北巴什尔希花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报,2010 ,29 (7 ):1001 −1008 .GAO Xiaofeng, XIAO Peixi, XIE Congrui, et al . Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and geological significance of Bashierxi granite in the eastern Kunlun area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2010 ,29 (7 ):1001 −1008 .[5] 高永宝, 李文渊 . 东昆仑造山带祁漫塔格地区白干湖含钨锡矿花岗岩: 岩石学、年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 地球化学,2011 ,40 (4 ):324 −336 .GAO Yongbao, LI Wenyuan . Petrogenesis of granites containing tungsten and tin ores in the Baiganhu deposit, Qimantage, NW China: Constraints from petrology, chronology and geochemistry[J]. Geochimica,2011 ,40 (4 ):324 −336 .[6] 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 姜海, 等 . 中国钨锡矿床时空分布规律、地质特征与成矿机制研究进展[J]. 科学通报,2020 ,65 (33 ):3730 −3745 .JIANG Shaoyong, ZHAO Kuidong, JIANG Hai, et al . Spatiotemporal distribution, geological characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of tungsten and tin deposits in China: An overview[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2020 ,65 (33 ):3730 −3745 .[7] 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 姜耀辉, 等 . 华南与花岗岩有关的一种新类型的锡成矿作用: 矿物化学、元素和同位素地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报,2006 ,22 (10 ):2509 −2516 .JIANG Shaoyong, ZHAO Kuidong, JIANG Yaohui, et al . New type of tin mineralization related to granite in South China: evidence from mineral chemistry, element and isotope geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2006 ,22 (10 ):2509 −2516 .[8] 兰天佑, 岳书仓 . 新疆喀孜别克锡矿床地质地球化学研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),1994 ,17 (1 ):160 −164 .LAN Tianyou, YUE Shucang . Studies on geology and geochemistry of the KEZBIKE tin deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology,1994 ,17 (1 ):160 −164 .[9] 李聪, 梁婷, 陈永康, 等 . 青海省锡矿成矿特征及成矿规律[J]. 地质与资源,2019 ,28 (6 ):526 −534 .LI Cong, LIANG Ting, CHEN Yongkang, et al . Metallogenic characteristics and regularities of tin deposits in qinghai province[J]. Geology and Resources,2019 ,28 (6 ):526 −534 .[10] 李大新, 丰成友, 周安顺, 等 . 东昆仑祁漫塔格西段白干湖超大型钨锡矿田地质特征及其矿化交代岩分类[J]. 矿床地质,2013 ,32 (1 ):37 −54 .LI Daxin, FENG Chengyou, ZHOU Anshun, et al . Geological characteristics and mineralization-metasomatite classification of superlarge Baiganhu tungsten-tin orefield in western Qimantag, East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Mineral Deposits,2013 ,32 (1 ):37 −54 .[11] 李国臣, 丰成友, 王瑞江等 . 新疆白干湖钨锡矿田东北部花岗岩锆石SIMS U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地球学报,2012a ,33 (2 ):216 −226 .LI Guochen, FENG Chengyou, WANG Ruijiang, et al . SIMS Zircon U-Pb Age, Petrochemistry and Tectonic Implications of Granitoids in Northeastern Baiganhue W-Sn Orefield, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2012a ,33 (2 ):216 −226 .[12] 李国臣, 丰成友, 王瑞江, 等 . 新疆若羌县柯可卡尔德钨锡矿床地质特征与流体包裹体研究[J]. 地质学报,2012b ,86 (1 ):209 −218 .LI Guochen, FENG Chengyou, WANG Ruijiang, et al . Study on Geological Characteristics and Fluid Inclusion of the Kekekaerde W-Sn Deposit in Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2012b ,86 (1 ):209 −218 .[13] 黎彤, 袁怀雨, 吴胜昔 . 中国花岗岩类和世界花岗岩类平均化学成分的对比研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,1998 ,22 (1 ):29 −34 .LI Tong, YUAN Huaiyu, WU Shengxi . On the average chemical composition of granitoids in china and the world[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,1998 ,22 (1 ):29 −34 .[14] 林锦富, 喻亨祥, 吴昌志, 等 . 东准噶尔萨北锡矿SHRIMP 锆石U-Pb测年及地质意义[J]. 中国地质,2008 ,35 (6 ):1197 −1205 .LIN Jinfu, YU Hengxiang, WU Changzhi, et al . Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating and geological implication of the Sabei Tin ore-deposit from Eastern Junggar of Xinjiang, China[J]. Geology in China,2008 ,35 (6 ):1197 −1205 .[15] 刘家远, 喻亨祥, 吴郭泉 . 新疆北部卡拉麦里富碱花岗岩带的碱性花岗岩与锡矿[J]. 有色金属矿产与勘查,1997 ,6 (3 ):129 −135 .LIU Jiayuan, YU Hengxiang, WU Guoquan . Alkali granites and tin deposits of the Kalamaili area,northern xinjiang[J]. Geological exploration for non-ferrous metals,1997 ,6 (3 ):129 −135 .[16] 刘义茂, 王昌烈, 胥友志, 等 . 柿竹园超大型钨多金属矿床的成矿条件与成矿模式[J]. 中国科学(D辑),1998 ,28 (Suppl ):49 −56 .LIU Yimao, WANG Changlie, XU Youzhi, et al . Metallogenic condition and model of the giant Shizhuyuan tungsten polymetallic deposit[J]. Science in China (Series D),1998 ,28 (Suppl ):49 −56 .[17] 刘子峰, 崔雅茹, 魏微 . 新疆东昆仑白干湖钨锡矿床地球化学特征[J]. 吉林地质,2007 ,26 (4 ):54 −60 .LIU Zifeng, CUI Yaru, WEI Wei . The geochemical characteristics of the Baiganhu W Sn deposit, Dongkunlun, Xinjiang[J]. Jilin Geology,2007 ,26 (4 ):54 −60 .[18] 路远发 . 赛什塘-日龙沟矿带成矿地球化学特征及矿床成因[J]. 西北地质,1990 , (3 ):20 −26 .[19] 马慧英, 刘继顺, 尹利君, 等 . 青海省都兰小卧龙锡、铁、钨多金属矿地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 矿产与地质,2009 ,23 (4 ):311 −315 .MA Huiying, LIU Jishun, YIN Lijun, et al . Geological feature and exploration sign of Xiaowolong tin-iron-tungsten polymeallic deposit in Dulanxian in Qinghai province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology,2009 ,23 (4 ):311 −315 .[20] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 袁顺达, 等 . 环太平洋成矿带斑岩-矽卡岩型铜矿和与花岗岩有关的锡多金属矿研究现状与展望[J]. 岩石学报,2018 ,34 (9 ):2501 −2517 .MAO Jingwen, XIE Guiqing, YUAN Shunda, et al . Current research progress and future trends of porphyry-skarn copper and granite-related tin polymetallic deposits in the Circum Pacific metallogenic belts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2018 ,34 (9 ):2501 −2517 .[21] 苏玉平, 唐红峰, 刘丛强, 等 . 新疆东准噶尔苏吉泉铝质A型花岗岩的确立及其初步研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2006 ,25 (3 ):175 −184 .SU Yuping, TANG Hongfeng, LIU Congqiang, et al . The determination and a preliminary study of Sujiquan aluminous A-type granites in East Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2006 ,25 (3 ):175 −184 .[22] 隋清霖, 祝红丽, 孙赛军, 等 . 锡的地球化学性质与华南晚白垩世锡矿成因[J]. 岩石学报,2020 ,36 (1 ):23 −34 .SUI Qinglin, ZHU Hongli, SUN Saijun, et al . The geochemical behavior of tin and Late Cretaceous tin mineralization in South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2020 ,36 (1 ):23 −34 .[23] 唐红峰, 屈文俊, 苏玉平, 等 . 新疆萨惹什克锡矿与萨北碱性A型花岗岩成因关系的年代学制约[J]. 岩石学报,2007 ,23 (8 ):1989 −1997 .TANG Hongfeng, QU Wenjun, SU Yuping, et al . Genetic connection of Sareshike tin deposit with the alkaline A-type granites of Sabei body in Xinjiang: constraint from isotopic ages[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinaca,2007 ,23 (8 ):1989 −1997 .[24] 王永和, 高晓峰, 孙吉明, 等. 西北地区大地构造环境与成矿[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2020, 1−281. [25] 王移生 . 青海日龙沟锡-多金属矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 西北地质,1990 ,23 (2 ):43 −48 .[26] 吴宏恩, 杨高学, 李永军, 等 . 东准噶尔锡矿北花岗斑岩地球化学特征[J]. 新疆地质,2008 ,26 (4 ):325 −329 .WU Hongen, YANG Gaoxue, LI Yongjun, et al . Characteristic of Geochemistry of the Xikuangbei granite-porphyry in Kalamaili area, east junggar[J]. Xinjiang Geology,2008 ,26 (4 ):325 −329 .[27] 肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等, 花岗岩研究思维与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002, 12−52. [28] 杨富全, 邓会娟, 夏浩东, 等 . 新疆阿图什彻依布拉克锡多金属矿点地质特征[J]. 新疆地质,2003 ,21 (4 ):426 −432 .YANG Fuquan, DENG Huijuan, XIA Haodong, et al . Geological characteristics of Qieyibulake tin-polymetallic ore spot in Atushi city, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology,2003 ,21 (4 ):426 −432 .[29] 杨合群 . 钨锡矿与地球演化的关系[J]. 西北地质,2007 ,40 (4 ):108 −108 .[30] 张子敏, 马汉峰, 蔡根庆 . 南天山独山锡矿床的成矿特征及成矿模式[J]. 新疆地质,2001 ,19 (1 ):49 −53 .ZHANG Zimin, MA Hanfeng, CAI Genqing . Mineralization characteristics and metallogenetic model of Dushan Sn deposit in the eastern part of the south Tianshan mountain[J]. Xinjiang Geology,2001 ,19 (1 ):49 −53 .[31] 朱金初, 陈骏, 王汝成, 等 . 南岭中西段燕山早期北东向含锡钨A型花岗岩带[J]. 高校地质学报,2008 ,14 (4 ):474 −484 .ZHU Jinchu, CHEN Jun, WANG Rucheng, et al . Early Yanshanian NE Trending Sn/W-Bearing A-Type Granites in the Western-Middle Part of the Nanling Mts Region[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2008 ,14 (4 ):474 −484 .[32] 周建厚, 丰成友, 李大新, 等 . 东昆仑白干湖钨锡矿床成矿岩体岩石学、年代学和地球化学[J]. 岩石学报,2015 ,31 (8 ):2277 −2293 .ZHOU Jianhou, FENG Chengyou, LI Daxin, et al . Petrology, geochronology and geochemistry of metallogenetic granite in Baiganhu W-Sn deposit, East Kunlun[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2015 ,31 (8 ):2277 −2293 .[33] Blevin P L , Chappell BW . Chemistry, origin, and evolution of mineralized granites in the Lachlan fold belt, Australia: The metallogeny of I- and S-type granites[J]. Economic Geology,1995 ,90 (6 ):1604 −1619 .[34] Bonin B . A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos,2007 ,97 (1−2 ):1 −29 .[35] Boztug D, Harlavan Y, Arehart G, et al . K-Ar age, whole-rock and isotope geochemistry of A-type granitoids in the Divrigi-Sivas region, eastern-central Anatolia, Turkey[J]. Lithos,2007 ,97 (1−2 ):193 −218 .[36] Chen Y X, Li H, Sun W D, et al . Generation of Late Mesozoic Qianlishan A2-type granite in Nanling Range, South China: Implications for Shizhuyuan W-Sn mineralization and tectonic evolution[J]. Lithos,2016 ,266−267 :435 −452 .[37] Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al . Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1982 ,80 (2 ):189 −200 .[38] Eby G N . Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology,1992 ,20 (7 ):641 −644 .[39] Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, Zhao K D, et al . Petrogenesis of Late Jurassic Qianlishan granites and mafic dykes, Southeast China: Implications for a back-arc extension setting[J]. Geological Magazine,2006 ,143 (4 ):457 −474 .[40] Jochum K P, Hofmann A W, Seufert H M . Tin in mantle-derived rocks: Constraints on Earth evolution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1993 ,57 (15 ):3585 −3595 .[41] Kamilli R J, Kimball B E, Carlin J F Jr. Tin. In: Schulz K J, DeYoung J H Jr, Seal R R , Bradley D C (eds.). Critical Mineral Resources of the United States: Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply[M]. US: USGS, 2017, S1−S53. [42] Lehmann B. Metallogeny of Tin[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1990, 1−210. [43] Li H, Palinkas L A, Watanabe K, et al . Petrogenesis of Jurassic A-type granites associated with Cu-Mo and W-Sn deposits in the central Nanling region, South China: Relation to mantle upwelling and intra-continental extension[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2018 ,92 :449 −462 .[44] Linnen R L, Pichavant M, Holtz F . The combined effects of fO2 and melt composition on SnO2solubility and tin diffusivity in haplogranitic melts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1996 ,60 (24 ):4965 −4976 .[45] Liu P, Mao J W, Santosh M, et al . Geochronology and petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous A-type granite from the Feie'shan W-Sn deposit in the eastern Guangdong Province, SE China: Implications for W-Sn mineralization and geodynamic setting[J]. Lithos,2018 ,300−301 :330 −347 .[46] Mania P D, Piccoli P M . Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1989 ,101 :635 −643 .[47] Mao J W, Cheng Y B, Chen M H, et al . Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings[J]. Mineralium Deposita,2013 ,48 (3 ):267 −294 .[48] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G . Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology,1984 ,25 (4 ):956 −983 .[49] Rickwood P C . Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos,1989 ,22 (4 ):247 −263 .[50] Rudnick R L, Gao S . Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry,2003 ,3 :1 −64 .[51] Romer R L, Kroner U . Phanerozoic tin and tungsten mineralization: Tectonic controls on the distribution of enriched protoliths and heat sources for crustal melting[J]. Gondwana Research,2016 ,31 :60 −95 .[52] Sato K, Vrublevsky A A, Rodionov S M, et al . Mid-cretaceous episodic Magmatism and tin mineralization in Khingan-Okhotsk volcano-plutonic belt, Far East Russia[J]. Resource Geology,2002 ,52 (1 ):1 −14 .[53] Schwartz M O, Rajah S S, Askury A K, et al . The southeast Asian tin belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,1995 ,38 (2−4 ):95 −293 .[54] Shu X J, Wang X L, Sun T, et al . Trace elements, U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of zircons from Mesozoic granites in the western Nanling Range, South China: Implications for petrogenesis and W-Sn mineralization[J]. Lithos,2011 ,127 (3−4 ):468 −482 .[55] Sylvester P J. Post-collisional alkaline granites[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1989, 97(3): 261−280. [56] Whalen J B, Jenner G A, Longstaffe F J, et al . Geochemical and isotopic (O, Nd, Pb and Sr) constraints on A-type granite petrogenesis based on the Topsails igneous suite, Newfoundland Appalachians[J]. Journal of Petrology,1996 ,37 (6 ):1463 −1489 .[57] Yan Q H, Wang H, Qiu Z W, et al . Origin of Early Cretaceous A-type granite and related Sn mineralization in the Sanjiaowo deposit, eastern Guangdong, SE China and its tectonic implication[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2018 ,93 :60 −80 .[58] Yao Y, Chen J, Lu J J, et al . Geology and genesis of the Hehuaping magnesian skarn-type cassiterite-sulfide deposit, Hunan Province, southern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2014 ,58 :163 −184 .[59] Zhang L P, Zhang R Q, Hu Y B, et al . The formation of the Late Cretaceous Xishan Sn-W deposit, South China: Geochronological and geochemical perspectives[J]. Lithos,2017 ,290−291 :253 −268 . -



 下载:
下载: