GEOCHEMISTRY AND EVALUATION OF ATMOSPHERIC DRY AND WET DEPOSITION IN JINGDE-NINGGUO AREA, ANHUI PROVINCE
-
摘要:
以安徽旌德-宁国地区大气干湿沉降物为研究对象,共采集6处干湿沉降物样品24件,对大气干湿沉降元素含量特征、通量特征进行对比分析,对干湿沉降元素含量及分布特征加以统计研究,并开展大气干湿沉降环境地球化学评价.结果显示:1)大气干湿沉降元素主要以矿物相形式存在或吸附在固体颗粒上,且受周边环境影响;2)干沉降中Cd、Se的高含量会对研究区土壤污染造成较大影响,湿沉降中部分样点pH超灌溉水水质标准,所有点均达到地表水Ⅱ类环境质量标准;3)区内重金属元素年沉降通量密度为,As年沉降通量低,Hg、Ni、Pb、Cr、Cu、Cd偏低,Zn偏高;4)大气干湿沉降重金属元素通量一般表现为丘陵山区小于城镇及工矿区,主要受燃煤燃烧、尾气排放及人为活动等影响;5)大气干湿沉降物环境地球化学单指标和综合指标评价结果均为一等.
Abstract:Taking the atmospheric dry and wet deposition in Jingde-Ningguo area of Anhui Province as study object, a total of 24 samples are collected from 6 sites to comparatively analyzes the element content and flux characteristics of atmospheric dry and wet deposition, statistically study the element content and distribution features of dry and wet deposition, and carry out the environmental geochemical evaluation as well. The results show that atmospheric dry and wet deposition elements mainly exist in the form of mineral facies or adsorbed on solid particles, and they are affected by surrounding environment. The high Cd and Se contents in dry deposition have great impact on soil pollution in the study area, the pH values of some wet deposition sampling sites exceed the irrigation water quality criteria, and all sites reach the Grade Ⅱ surface water environmental quality standard. As to the annual deposition flux density of heavy metal elements, the deposition flux of As is low, Hg, Ni, Pb, Cr, Cu and Cd lower, and Zn higher. The flux of heavy metal elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition is generally smaller in hilly areas than in towns and industrial/mining areas, mainly affected by coal combustion, exhaust gas emission and human activities. The evaluation results of environmental geochemistry single index and comprehensive index for atmospheric dry and wet deposition are both Grade Ⅰ.
-

-
表 1 干湿沉降滤液分析方法
Table 1. Analysis methods of atmospheric dry and wet deposition filtrate
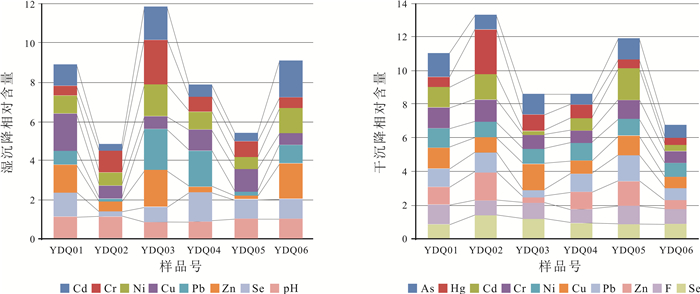
测定项目 处理方法 分析方法 As、Hg 1+1王水溶样 AFS Se 高氯酸冒烟 AFS F 直接取样 ISE Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn 直接取样 ICP-MS 表 2 研究区大气干湿沉降中元素含量特征
Table 2. Element contents of atmospheric dry and wet deposition in the study area
元素 湿沉降/(μg/L) 干沉降/10-6 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 As < 0.4 9.1 13.2 5.8 Hg < 0.05 0.381 1.035 0.149 Cd 0.233 0.430 0.075 4.699 8.723 0.877 Cr 5.35 12.17 2.69 151.7 196.4 106.3 Ni 0.30 0.49 0.18 54.2 62.4 47.1 Cu 1.92 3.56 1.13 179.2 261.8 101.1 Pb 1.86 3.99 0.13 301.0 456.6 133.5 Zn 107.81 199.25 15.65 567.2 955.4 183.0 Se 0.49 0.72 0.38 4.91 6.94 3.95 F < 0.1 0.10 369 444 310 pH 6.14 7.22 5.26 表 3 研究区湿沉降元素含量特征
Table 3. Characteristics of wet deposition element content in the study area
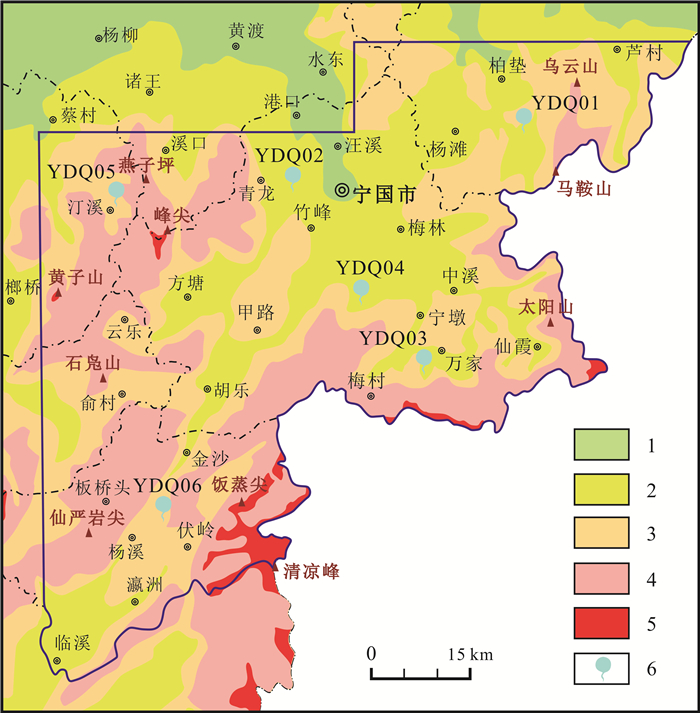
大气沉降点号 地理位置 灌溉水水质标准 地表水环境质量标准 YDQ01 广德市四合乡张家湾 Zn Ⅱ类水 YDQ02 宁国市青龙乡 Zn Ⅱ类水 YDQ03 宁国市万家乡云山村 pH超标 Cd、Zn Ⅱ类水,pH超标 YDQ04 宁国市霞西镇山门村 pH超标 pH超标 YDQ05 泾县汀溪乡棋盘村 YDQ06 绩溪县杨溪镇牛皮石达 Zn Ⅱ类水 表 4 研究区大气干湿沉降物元素年沉降通量密度地球化学参数统计表
Table 4. Geochemical parameters of annual deposition flux density of atmospheric dry and wet deposition elements
元素 算术均值 标准偏差 最大值 最小值 几何均值 全国几何均值 区内均值/全国均值 所处百分位数 As 0.2247 0.0790 0.3740 0.1350 0.2150 2.4500 0.09 0.5~10 Hg 0.0108 0.0107 0.03120 0.0031 0.0076 0.0360 0.21 0.5~50 Cd 0.2332 0.0960 0.3740 0.1150 0.2160 0.4820 0.45 10~75 Cr 5.9190 1.4900 8.1880 4.4160 5.7690 15.0800 0.38 10~50 Ni 1.5315 0.3500 2.0730 1.1250 1.4990 5.9000 0.25 0.5~25 Cu 5.5534 1.969 8.9070 2.9940 5.3500 13.0900 0.41 10~50 Pb 8.2050 2.8220 12.3010 5.2820 7.8130 22.9900 0.34 5~50 Zn 71.9156 54.8600 150.7050 23.7680 55.8710 70.1100 0.80 10~80 Se 0.3605 0.1450 0.5580 0.2090 0.3360 F 15.5980 15.7600 47.4070 7.3330 11.8250 注:①区内均值/全国均值中的均值为几何均值;②所处百分位数是指区内大气干湿沉降重金属元素年沉降通量密度位于全国大气干湿沉降物重金属元素年沉降通量密度频率统计中位置;③通量密度单位:mg/(m2·a). 表 5 不同地区大气干湿沉降重金属元素沉降通量对比统计表
Table 5. Comparison of deposition flux of heavy metal elements in atmospheric dry and wet deposition among different regions
地区 As Hg Cd Cr Ni Cu Pb Zn 资料来源 研究区 城镇及工矿区 0.2357 0.0156 0.2443 6.5532 1.5796 5.6303 7.2231 83.8201 本文 研究区 丘陵山区 0.2137 0.0060 0.2221 5.2848 1.4834 5.4765 9.1869 60.0111 本文 研究区 全区 0.2247 0.0108 0.2332 5.9190 1.5315 5.5534 8.2050 71.9156 本文 北京平原区 2.9000 0.0240 0.2400 11.8600 6.6000 14.2000 21.0000 54.4900 文献[13] 河北南部 3.1690 0.0700 0.8550 15.6520 7.2410 13.7110 30.4880 168.9720 文献[10] 成都经济区 2.7700 0.1000 1.7700 - - - 45.9500 147.8300 文献[8] 南京市 4.0500 0.0400 0.7000 16.9000 - 46.0000 48.5000 248.0000 文献[30] 长江三角洲 1.5700 0.0300 0.4100 13.2000 4.6000 13.9000 35.9000 89.5000 文献[31] 全国均值 2.4500 0.0360 0.4800 15.0800 5.9000 13.0900 22.9900 70.1100 通量单位:mg/(m2·a). 表 6 大气干湿沉降通量环境地球化学等级分级标准值
Table 6. Environmental geochemical grading values of atmospheric dry and wet deposition flux
评价指标 年通量/(mg/m2·a) 等级 一等 二等 Cd ≤3 >3 Hg ≤0.5 >0.5 -
[1] 王梦梦, 原梦云, 苏德纯. 我国大气重金属干湿沉降特征及时空变化规律[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(11): 4085-4096. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.11.010
Wang M M, Yuan M Y, Su D C. Characteristics and spatial-temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition of China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(11): 4085-4096. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.11.010
[2] 秦先燕, 彭苗枝, 焦团理, 等. 基于GIS的环巢湖地区地质环境承载能力评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(2): 180-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.010 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10190.shtml
Qin X Y, Peng M Z, Jiao T L, et al. Assessment of GIS-based geological environment carrying capacity in circum-Chaohu Lake area, Anhui, China[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(2): 180-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.010 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10190.shtml
[3] 黄春雷, 宋金秋, 潘卫丰. 浙东沿海某地区大气干湿沉降对土壤重金属元素含量的影响[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(9): 1434-1441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.013
Huang C L, Song J Q, Pan W F. Impact of dry and wet atmospheric deposition on content of heavy metals in soils along coastal areas of eastern Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(9): 1434-1441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.013
[4] 李延生. 黑龙江省松嫩平原南部大气降尘地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(4): 536-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201104024.htm
Li Y S. Geochemical characteristics of atmospheric dust in southern Songnen Plain, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(4): 536-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201104024.htm
[5] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 等. 石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(2): 683-690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.02.027
Cui X T, Luan W L, Song Z F, et al. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(2): 683-690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.02.027
[6] Kelly J, Thornton I, Simpson P R. Urban geochemistry: A study of the influence of anthropogenic activity on the heavy metal content of soils in traditionally industrial and non-industrial areas of Britain[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1996, 11(1/2): 363-370. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-0883292795000844&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1436958159&md5=31b5fadb6df08d0bae6119307f8fbaf4
[7] Lawlor A J, Tipping E. Metals in bulk deposition and surface waters at two upland locations in northern England[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2003, 121(2): 153-167. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00228-2
[8] 汤奇峰, 杨忠芳, 张本仁, 等. 成都经济区As等元素大气干湿沉降通量及来源研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(3): 213-222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.03.020
Tang Q F, Yang Z F, Zhang B R, et al. A study of elements flux and sources from atmospheric bulk deposition in the Chengdu economic region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(3): 213-222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.03.020
[9] 庞绪贵, 王晓梅, 代杰瑞, 等. 济南市大气降尘地球化学特征及污染端元研究[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1): 285-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.023
Pang X G, Wang X M, Dai J R, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution sources identification of the atmospheric dust-fall in Jinan City[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1): 285-293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.023
[10] 李随民, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 等. 河北省南部平原区大气降尘来源及分布特征[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(6): 1769-1774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.024
Li S M, Luan W L, Song Z F, et al. The distribution and source of atmospheric dust fall in the southern plain of Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(6): 1769-1774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.024
[11] 刘国栋, 杨泽, 戴慧敏, 等. 黑龙江省海伦市长发镇土地质量地球化学评价及开发建议[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 533-542. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10242.shtml
Liu G D, Yang Z, Dai H M, et al. Geochemical evaluation of land quality and development suggestion of land in Hailun City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 533-542. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10242.shtml
[12] 刘鹏, 胡文友, 黄标, 等. 大气沉降对土壤和作物中重金属富集的影响及其研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(5): 1048-1059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201905003.htm
Liu P, Hu W Y, Huang B, et al. Advancement in researches on effect of atmospheric deposition on heavy metals accumulation in soils and crops[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(5): 1048-1059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201905003.htm
[13] 丛源, 陈岳龙, 杨忠芳, 等. 北京平原区元素的大气干湿沉降通量[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(2): 257-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.02.014
Cong Y, Chen Y L, Yang Z F, et al. Dry and wet atmospheric deposition fluxes of elements in the Plain area of Beijing Municipality, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2): 257-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.02.014
[14] 刘国栋, 张立, 杨泽, 等. 嫩江流域水体及悬浮物重金属元素分布特征及环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(1): 53-61. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10265.shtml
Liu G D, Zhang L, Yang Z, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the water and suspended substance of Nenjiang River basin: Environmental implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(1): 53-61. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10265.shtml
[15] 戴彬, 吕建树, 战金成, 等. 山东省典型工业城市土壤重金属来源、空间分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(2): 507-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201502021.htm
Dai B, Lü J S, Zhan J C, et al. Assessment of sources, spatial distribution and ecological risk of heavy metals in soils in a typical industry-based city of Shandong Province, eastern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(2): 507-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201502021.htm
[16] 赵君, 汪月华, 张哲寰. 多目标地球化学调查数据在松嫩平原油气藏远景预测的应用[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 635-640, 626. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10258.shtml
Zhao J, Wang Y H, Zhang Z H. Application of multi-target geochemical survey data in prospect prediction of the oil-gas reservoirs in Songnen Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 635-640, 626. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10258.shtml
[17] 王卫星, 曹淑萍, 李攻科, 等. 津北大气干湿沉降重金属元素通量与评价研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2017, 42(5): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2017.05.011
Wang W X, Cao S P, Li G K, et al. Sedimentation flux and its evaluation of dry and wet atmospheric deposition of heavy metal elements in North Tianjin[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2017, 42(5): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2017.05.011
[18] 王琦. 辽东湾北部浅海沉积物铅地球化学评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(5): 477-481. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.010 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8423.shtml
Wang Q. Geochemical evaluation of lead in the neritic sediments of northern Liaodong Bay[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(5): 477-481. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.010 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8423.shtml
[19] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 李随民, 等. 石家庄市大气降尘重金属元素来源分析[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(4): 1108-1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.04.028
Cui X T, Luan W L, Li S M, et al. An analysis of the sources of heavy metals in atmospheric dust fall of Shijiazhuang city[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(4): 1108-1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.04.028
[20] 孙雪菲, 张丽霞, 董玉龙, 等. 典型石化工业城市土壤重金属源解析及空间分布模拟[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1093-1104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103007.htm
Sun X F, Zhang L X, Dong Y L, et al. Source apportionment and spatial distribution simulation of heavy metals in a typical petrochemical industrial city[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1093-1104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103007.htm
[21] Nriagu J O. Changing metal cycles and human health[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1984: 113-141.
[22] 王增辉. 鲁西南平原区大气干湿沉降元素输入通量及来源浅析: 以巨野县为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4): 839-846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202004020.htm
Wang Z H. An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong: A case study of Juye County[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4): 839-846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202004020.htm
[23] 魏明辉, 许江, 李秋燕, 等. 内蒙古鄂伦春旗土壤钼元素的分布特征及主要影响因素[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 609-613. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10254.shtml
Wei M H, Xu J, Li Q Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and main influencing factors of soil molybdenum in Oroqen Qi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 609-613. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10254.shtml
[24] 徐宏林, 李定远, 杨军, 等. 湖北省云梦县重金属元素大气干湿沉降通量初探[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2015, 29(6): 816-821. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201506013.htm
Xu H L, Li D Y, Yang J, et al. Preliminary study on flux of atmospheric dry and wet deposition of heavy metal elements in Yunmeng County, Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2015, 29(6): 816-821. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201506013.htm
[25] 王锐, 张风雷, 徐姝姝, 等. 土壤重金属污染风险筛选值划分方法: 以Cd为例[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 5082-5089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201911039.htm
Wang R, Zhang F L, Xu S S, et al. Method of dividing the value of soil heavy metal pollution risk screening: Using Cd as an example[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(11): 5082-5089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201911039.htm
[26] 李锋, 刘思源, 李艳, 等. 工业发达城市土壤重金属时空变异与源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2): 934-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201902054.htm
Li F, Liu S Y, Li Y, et al. Spatiotemporal variability and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a industrially developed city[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(2): 934-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201902054.htm
[27] 王硕, 蔡立梅, 王秋爽, 等. 中国城市地表灰尘中重金属的富集状况及空间分布特征[J]. 地理研究, 2018, 37(8): 1624-1640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201808013.htm
Wang S, Cai L M, Wang Q S, et al. Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in urban surface dust of China[J]. Geographical Research, 2018, 37(8): 1624-1640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201808013.htm
[28] 龚香宜, 祁士华, 吕春玲, 等. 福建省兴化湾大气重金属的干湿沉降[J]. 环境科学研究, 2006, 19(6): 31-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.06.006
Gong X Y, Qi S H, Lv C L, et al. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals to Xinghua Bay, Fujian Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(6): 31-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.06.006
[29] 刘娜, 余晔, 马学谦. 西宁市大气污染来源和输送季节特征[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1268-1279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103027.htm
Liu N, Yu Y, Ma X Q. Seasonal characteristics of air pollutant sources and transport pathways in Xining City[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1268-1279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103027.htm
[30] Hu W Y, Wang H F, Dong L R, et al. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 650-661. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.070
[31] Huang S S, Tu J, Liu H Y, et al. Multivariate analysis of traceelement concentrations in atmospheric deposition in the Yangtze River Delta, East China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2009, 43(36): 5781-5790. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.07.055
[32] 严晓瑜, 缑晓辉, 武万里, 等. 银川地区大气颗粒物输送路径及潜在源区分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(5): 1727-1738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201805005.htm
Yan X Y, Gou X H, Wu W L, et al. Analysis of atmospheric particulate transport path and potential source area in Yinchuan[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(5): 1727-1738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201805005.htm
[33] 杨忠平, 卢文喜, 龙玉桥. 长春市城区重金属大气干湿沉降特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2009, 22(1): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200901006.htm
Yang Z P, Lu W X, Long Y Q. Atmospheric dry and wet deposition of heavy metals in Changchun City, China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 22(1): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200901006.htm
-



 下载:
下载: