PRIMARY HALO CHARACTERISTICS AND DEEP PROSPECTING PREDICTION OF NARAN TOLGOI GOLD DEPOSIT IN MONGOLIA
-
摘要:
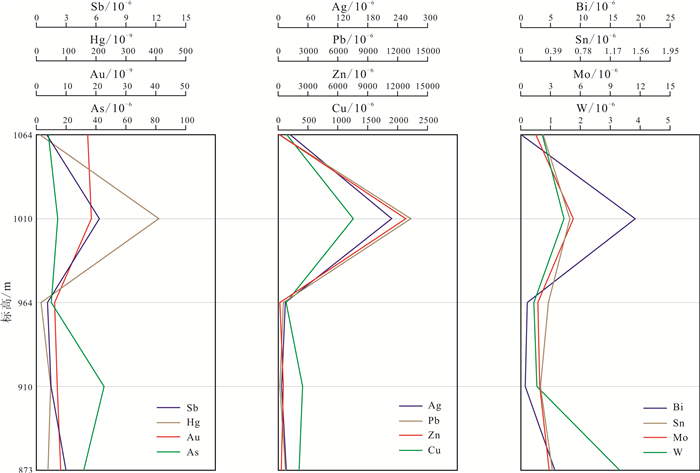
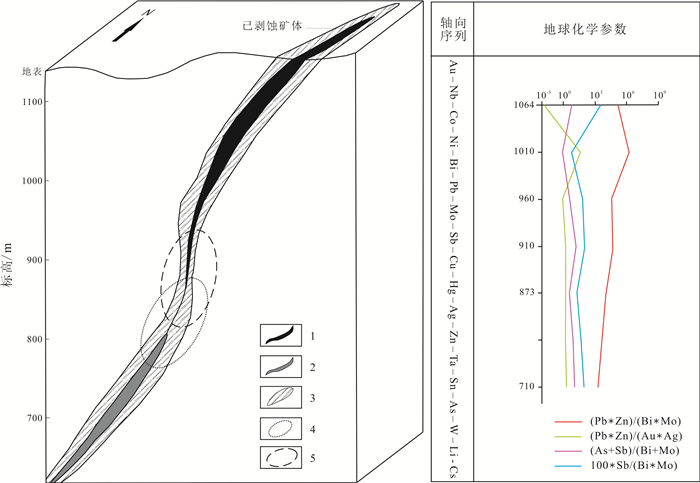
为预测和评价那仁陶勒盖金矿的成矿潜力,运用多元统计方法,结合地球化学各参数信息,对那仁陶勒盖金矿原生晕进行系统研究.结果显示: 那仁陶勒盖金矿赋矿花岗闪长岩中Au、Ag、Bi等元素浓集克拉克值明显偏高,与那仁陶勒盖金成矿作用关系密切; 矿石中Au与Sb、Cu、Pb、Ag、Hg、Zn、As、Bi等关系最为密切; 矿体原生晕轴向分带序列出现尾晕元素W、Sn等与前缘晕元素As叠加的现象,同时(As+Sb)/(Bi+Mo)、100Sb/(Bi·Mo)等分带性指数出现转折,指示深部存在盲矿体.依据上述矿体原生晕特征,建立矿体叠加晕预测模型,预测盲矿体赋存位置在海拔710m以下的岩体与地层接触带附近.
Abstract:To predict and evaluate the metallogenic potential, the primary halo of Naran Tolgoi gold deposit is systematically studied by using multivariate statistical method combined with geochemical parameter information. The results show that the Clarke values of Au, Ag and Bi in the host rock granodiorite of the deposit are obviously high, which is closely related to the gold mineralization. Au is most closely correlated to Sb, Cu, Pb, Ag, Hg, Zn, As and Bi in the ores. There exists the superposition of rear halo elements(W and Sn) with front halo element(As) in the axial zoning sequence of primary halo. Besides, the turning of zonation indexes such as(As+Sb)/(Bi+Mo) and 100Sb/(Bi·Mo) indicates the existence of blind orebody in the deep. Based on the characteristics of primary halo, the prediction model of superimposed halo is established that the blind orebody is probably located near the contact zone between rock mass and strata below 710 m altitude.
-
Key words:
- primary halo /
- axial zoning /
- concealed orebody /
- Naran Tolgoi gold deposit /
- Mongolia
-

-
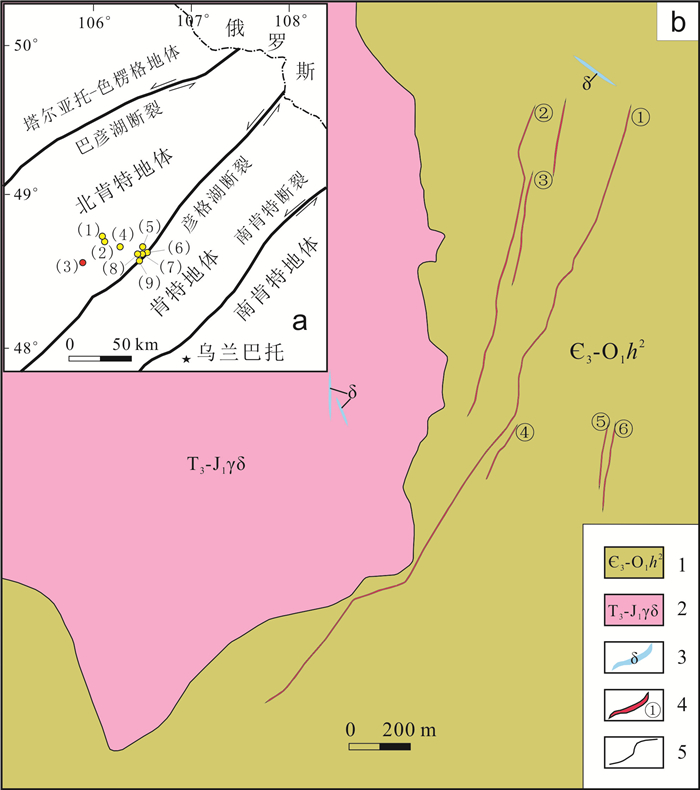
图 1 那仁陶勒盖金矿大地构造位置及矿区地质图(据文献[8])
Figure 1.
表 1 那仁陶勒盖金矿围岩中指示元素含量特征
Table 1. Contents of indicator elements in the wall rock of Naran Tolgoi gold deposit
元素 花岗闪长岩(4件) 变质沉积岩(8件) 全部样品(12件) 地壳克拉克值 几何平均值 浓集克拉克值 几何平均值 浓集克拉克值 几何平均值 浓集克拉克值 Au 55.70 13.93 30.18 7.54 38.68 9.67 4 Ag 0.56 6.97 0.22 2.78 0.33 4.18 0.08 Bi 0.05 11.88 0.26 65.00 0.19 47.29 0.004 Cu 67.13 1.07 38.19 0.61 47.83 0.76 63 Zn 56.45 0.60 106.36 1.13 89.73 0.95 94 Pb 22.18 1.85 27.01 2.25 25.40 2.12 12 W 5.88 5.35 5.03 4.57 5.31 4.83 1.1 Mo 0.57 0.43 2.40 1.85 1.79 1.38 1.3 Sn 1.10 0.65 2.27 1.34 1.88 1.11 1.7 Sb 0.38 0.63 0.44 0.73 0.42 0.69 0.6 Hg 15.38 0.19 10.41 0.13 12.07 0.15 80 As 3.98 1.81 3.68 1.67 3.78 1.72 2.2 Co 6.70 0.27 20.41 0.82 15.84 0.63 25 Ni 17.85 0.20 53.21 0.60 41.43 0.47 89 Nb 3.85 0.20 10.64 0.56 8.38 0.44 19 Ta 0.35 0.22 0.72 0.45 0.60 0.37 1.6 Li 10.50 0.50 30.64 1.46 23.93 1.14 21 Cs 3.80 2.71 5.53 3.95 4.95 3.54 1.4 Mn 463.25 0.36 870.00 0.67 734.42 0.56 1300 ①含量单位:Au、Hg为10-9,其余元素均为10-6;②浓集克拉克值=几何平均值/地壳克拉克值,其中克拉克值引自文献[13]. 表 2 那仁陶勒盖金矿不同中段微量元素含量
Table 2. Contents of trace elements in Naran Tolgoi gold deposit at different elevations
样品编号 NR3-2-4 NR3-3-3 NR3-4-4 NR3-5-1 YH003 标高/m 1064 1010 964 910 873 样品长度/m 1 0.95 0.95 0.4 0.7 Cu 137.6 1254.1 124.9 401.1 344.6 Zn 83.3 12800 137.1 486.1 289.9 Pb 63.2 13300 480.5 147.8 708.4 W 0.72 1.44 0.43 0.53 3.32 Mo 1.5 5.26 1.69 1.87 2.85 Ag 23.396 227.776 13.528 6.553 16.206 Sn 0.29 0.64 0.36 0.25 0.41 Bi 0.02 19.15 1.04 0.71 5.66 Sb 1.05 6.33 1.11 1.48 3 Hg 12.2 411.5 15.6 49 39.6 As 8.1 14.3 10 45.4 31.8 Au 17260 18490 6060 7020 8160 Co 1.6 3.9 1.4 1.4 3.2 Ni 8 20.7 7.7 9.2 19.4 Nb 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.2 0.3 Ta 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 Li 3.2 2.6 4.8 2.6 26.6 Cs 0.5 1.9 0.9 1 14.2 Mn 113 200 263 121 200 含量单位:10-6. -
[1] 李惠, 张国义, 禹斌. 金矿区深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕模型及找矿效果[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 1-146.
Li H, Zhang G Y, Yu B. The structural superimposed halo model for the prediction of deep blind deposits in gold mining areas and its prospecting effect[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 1-146. (in Chinese)
[2] 李惠, 禹斌, 魏江, 等. 热液型矿床深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕实用理想模型及其意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(5): 889-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202005001.htm
Li H, Yu B, Wei J, et al. A new practical ideal model of structural superimposed halos for prediction of deep blind hydrothermal deposits and its significance[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(5): 889-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202005001.htm
[3] 李惠, 张国义, 禹斌, 等. 构造叠加晕找盲矿法及其在矿山深部找矿效果[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1): 287-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001028.htm
Li H, Zhang G Y, Yu B, et al. Structural superimposed halos method for prospecting blind ore-body in the deep of ore-districts[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(1): 287-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001028.htm
[4] 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 程文斌, 等. 内蒙古柳坝沟金矿床原生晕地球化学特征及深部成矿远景评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2): 209-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002027.htm
Zhang Y M, Gu X X, Cheng W B, et al. The geochemical features of primary halo and the evaluation of deep mineralization prospect of Liubagou gold deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2): 209-221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002027.htm
[5] 曹强, 刘家军, 吴杰, 等. 秦岭西部铧厂沟金矿床主矿带原生晕分带特征及深部预测[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(1): 27-36, 98. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10262.shtml
Cao Q, Liu J J, Wu J, et al. Primary halo zoning and deep prediction of the main ore belt in Huachanggou gold deposit, western Qinling Mountains[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(1): 27-36, 98. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10262.shtml
[6] 梁科伟, 赵忠海, 郭艳. 原生晕在深部成矿预测中的应用——以黑河地区永新金矿为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(6): 512-518. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.06.002 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9526.shtml
Liang K W, Zhao Z H, Guo Y. Application of primary halo in deep metallogenic prediction: A case study of Yongxin gold deposit in Heihe area[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(6): 512-518. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.06.002 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9526.shtml
[7] 俞炳, 曾庆栋, 夏凡, 等. 辽宁五龙金矿构造叠加晕研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(5): 898-914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202005002.htm
Yu B, Zeng Q D, Xia F, et al. Structural superimposed halo of the Wulong gold deposit in Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(5): 898-914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202005002.htm
[8] 张帅, 张义波, 石传军. 蒙古国北部那仁陶勒盖金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 黄金, 2019, 40(8): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201908006.htm
Zhang S, Zhang Y B, Shi C J. Geological characteristics and genesis of Naran Tolgoi gold deposit in northern Mongolia[J]. Gold, 2019, 40(8): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201908006.htm
[9] 王鸿祯, 何国琦, 张世红. 中国与蒙古之地质[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 1-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.003
Wang H Z, He G Q, Zhang S H. The geology of China and Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(6): 1-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.003
[10] 聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等. 蒙古矿产勘查与开发现状评述[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(1): 105-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201001017.htm
Nie F J, Jiang S H, Bai D M, et al. An overview of present exploration and exploitation on mineral resources of Mongolia[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(1): 105-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201001017.htm
[11] 李俊建. 蒙古地质矿产概况[M]. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 2013: 1-273.
Li J J. General situation of Mongolian geology and mineral resources[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 2013: 1-273. (in Chinese)
[12] 吴涛涛, 周永恒, 陈聪, 等. 蒙古国铀矿地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(6): 1247-1255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201806018.htm
Wu T T, Zhou Y H, Chen C, et al. Geological features and resource potential of uranium deposits in Mongolia[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(6): 1247-1255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201806018.htm
[13] 黎彤. 化学元素的地球丰度[J]. 地球化学, 1976(3): 167-174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1976.03.004
Li T. Chemical element abundances in the earth and it's major shells[J]. Geochimica, 1976(3): 167-174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1976.03.004
[14] 朴寿成, 杨永强, 连长云. 原生晕分带序列研究方法综述[J]. 世界地质, 1996, 15(1): 44-48, 53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ601.007.htm
Piao S C, Yang Y Q, Lian C Y. A summary of studying methods in primary halo zoning sequence[J]. Global Geology, 1996, 15(1): 44-48, 53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ601.007.htm
[15] 王建新, 臧兴运, 郭秀峰, 等. 格里戈良分带指数法的改良[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37(5): 884-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200705005.htm
Wang J X, Zang X Y, Guo X F, et al. The improved Gregorian's zoning index calculating method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2007, 37(5): 884-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200705005.htm
[16] 李惠, 张文华, 常凤池, 等. 大型?特大型金矿盲矿预测的原生叠加晕模型[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998: 1-125.
Li H, Zhang W H, Chang F C, et al. Primary halo superposition model for blind ore prediction of large and super-large gold deposits[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998: 1-125. (in Chinese)
[17] 朴寿成, 李绪俊, 师磊, 等. 赤峰-朝阳金矿化集中区元素分带特征及其应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2006, 42(1): 17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2006.01.004
Piao S C, Li X J, Shi L, et al. Element zoning and its application in the Chifeng-Chaoyang auriferous province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2006, 42(1): 17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2006.01.004
[18] 吴松洋, 侯林, 丁俊, 等. 贵州泥堡金矿床原生晕特征及深部找矿预测——以Ⅲ-1号矿体为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(4): 674-686. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201804012.htm
Wu S Y, Hou L, Ding J, et al. Primary halo characteristics and deep ore body prospecting of the Nibao gold deposit, Guizhou Province: Illustrated with the example of Ⅲ-1 orebody[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2018, 37(4): 674-686. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201804012.htm
[19] Clure J K, Kotlyar B, Gantsetseg O, et al. Geology of the Boroo gold deposit, Northern Mongolia[J]. Seg-Iagod Guidbook Series 11: Cercams/Nhm Longon, 2005, 105-117.
[20] 侯万荣, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等. 蒙古国博洛大型金矿区花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年及地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(3): 331-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201003009.htm
Hou W R, Nie F J, Jiang S H, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of ore-bearing granite in the Boroo large-size gold deposit, Mongolia and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 331-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201003009.htm
-



 下载:
下载: