BIMODAL INTRUSIVE ROCKS IN XIAOHONGSHAN VANADIUM-TITANIUM MAGNETITE OREFIELD IN BEISHAN AREA OF INNER MONGOLIA: Petrology, Geochronology, Geochemistry and Geological Implication
-
摘要:
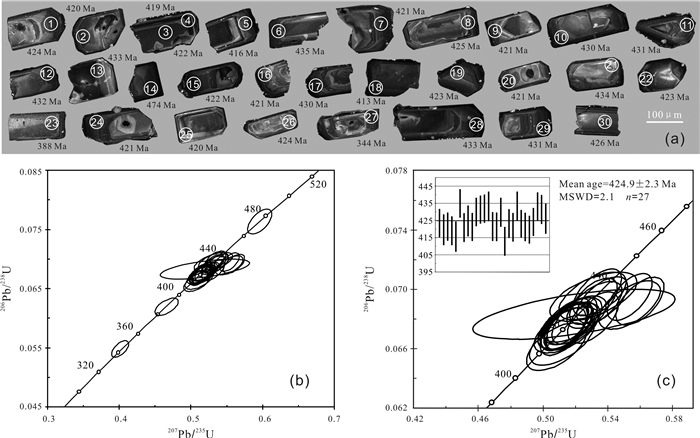
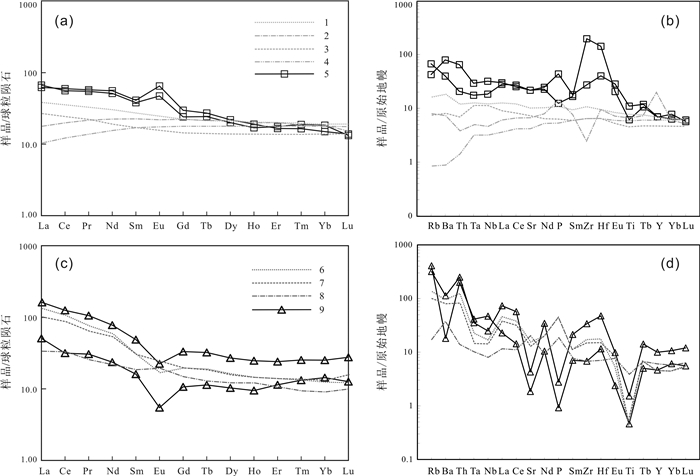
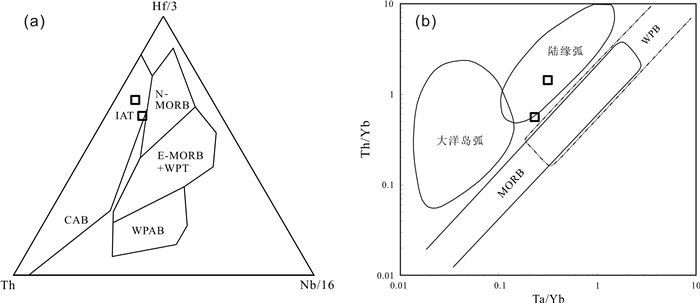
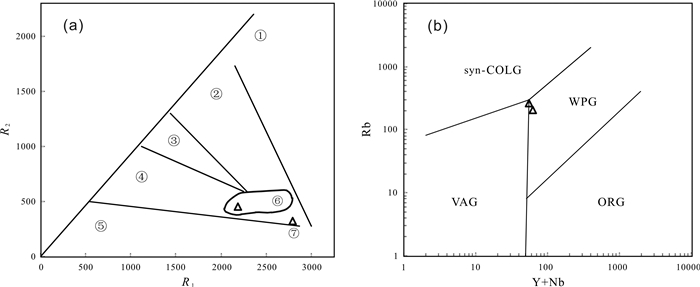
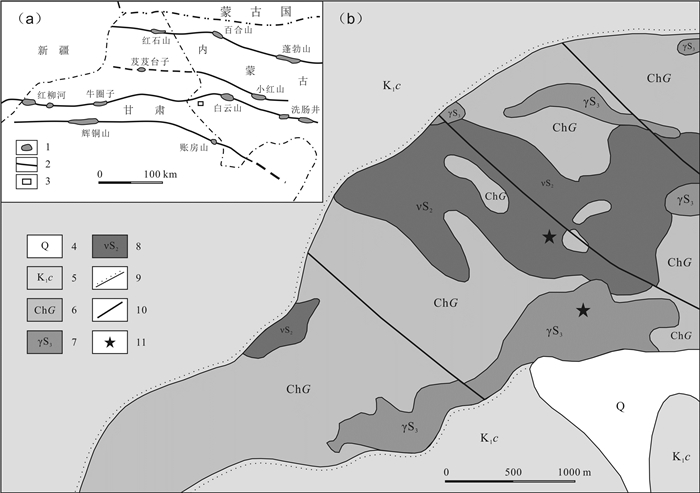
对内蒙古北山地区小红山钒钛磁铁矿区内侵入岩的岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学和全岩地球化学资研究显示,该岩体岩性为辉长岩和花岗岩,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果表明成岩年龄分别为431.1±2.4 Ma和424.9±2.3 Ma,形成时代相近,属同一构造岩浆作用事件. 该套侵入岩的SiO2含量呈双峰式,稀土、微量元素特征表明它们具有岛弧岩浆岩地球化学特征,其源区可能受到了俯冲流体交代作用的影响. 地球化学特征指示小红山花岗岩源于下地壳物质在高温条件下的部分熔融,辉长岩为富集地幔部分熔融的产物. 结合区域地质背景及构造判别,认为小红山中晚志留世双峰式岩浆组合是北山洋南向俯冲诱导大陆边缘伸展环境下的产物.
Abstract:Study on the petrology, zircon U-Pb chronology and whole-rock geochemistry of intrusive rocks in Xiaohongshan vanadium-titanium magnetite orefield of Beishan area in Inner Mongolia shows that the lithology of the intrusion is gabbro and granite with the diagenetic age of 431.1±2.4 Ma and 424.9±2.3 Ma respectively. The two types of rocks were formed at a similar time of the same tectono-magmatism event. The SiO2 content in the intrusive rocks shows double peaks, and the characteristics of rare earth and trace elements indicate that they have the geochemical features of island-arc magmatic rocks, with the source area metasomatized by subduction-related fluid. The geochemical characteristics reflect Xiaohongshan granite is originated from the partial melting of lower crust materials at high temperature while the gabbros resulted from the partial melting of enriched mantle. Combined with the regional geological background and tectonic discrimination, it is concluded that the Middle and Late Silurian bimodal magmatic assemblage in Xiaohongshan area is the product of continental margin extension induced by the southward subduction of Beishan ocean.
-

-
[1] 陈超, 滕学建, 潘志龙, 等. 内蒙古北山造山带中段石板井地区A型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及对北山洋闭合时间的限定[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(9): 1448-1460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202009011.htm
Chen C, Teng X J, Pan Z L, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of A-type granite from the Shibanjing area of middle Beishan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia, and its constraint on closure time of Beishan Ocean[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(9): 1448-1460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202009011.htm
[2] 严忠, 金海宽, 范泽. 内蒙古小红山钒钛磁铁矿地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 有色矿冶, 2009, 25(2): 10-11, 9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2009.02.003
Yan Z, Jin H K, Fan Z. Discussion about geological characteristics of vanadium-titanium magnetite and its causes of formation in Xiaohongshan of Inner Mongolia[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2009, 25 (2): 10-11, 9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2009.02.003
[3] 杨福新, 李为民, 陈岱, 等. 内蒙古小红山钒钛磁铁矿床成矿特征及成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2010, 43(3): 66-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2010.03.009
Yang F X, Li W M, Chen D, et al. Discussion on the deposit features and genetic characteristics of vanadium-titanium magnetite ore in Xiaohongshan, western Inner Mongolia[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(3): 66-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2010.03.009
[4] 杨建国, 王磊, 王小红, 等. 内蒙古北山额济纳旗小红山钒钛磁铁矿床SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34 (9): 1699-1705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.011
Yang J G, Wang L, Wang X H, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the Xiaohongshan vanadium-titanium magnetite deposit, Ejin Banner, Beishan, Inner Mongolia, and its geological implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(9): 1699-1705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.011
[5] 张国鹏, 谢春林, 赵寒森, 等. 内蒙古北山地区小红山钒钛磁铁矿成岩成矿过程探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2017, 50(1): 63-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.01.007
Zhang G P, Xie G C, Zhao H S, et al. The diagenetic mineralization process of the Xiaohongshan vanadium-bearing titanometite in the Beishan area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2017, 50 (1): 63-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.01.007
[6] 王硕, 潘志龙, 张欢, 等. 内蒙古小红山钒钛磁铁矿赋矿岩石的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 西部资源, 2017(3): 172-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-562X.2017.03.077
Wang S, Pan Z L, Zhang H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of ore-bearing rocks in Xiaohongshan Vanadium-titanium magnetite deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Western Resources, 2017(3): 172-173. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-562X.2017.03.077
[7] 潘志龙, 张欢, 陈超, 等. 内蒙古北山敖包呼图仁斑状正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Lu-Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2017, 52(1): 301-316.
Pan Z L, Zhang H, Chen C, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope compositions of porphyritic syenite granite from Aobaohuturen in Beishan, Inner Mongolia and its tectonic implication [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2017, 52(1): 301-316.
[8] 郝增元, 高鉴, 王晨, 等. 北山造山带风雷山地区二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造背景[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47 (4): 1204-1219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202004020.htm
Hao Z Y, Gao J, Wang C, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and tectonic setting of the monzogranites in the Fengleishan area of Beishan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(4): 1204-1219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202004020.htm
[9] 牛文超, 辛后田, 段连峰, 等. 内蒙古北山地区百合山蛇绿混杂岩带的厘定及其洋盆俯冲极性——基于1∶ 5万清河沟幅地质图的新认识[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5): 977-994. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201905004.htm
Niu W C, Xin H T, Duan L F. The identification and subduction polarity of the Baiheshan ophiolite mélanges belt in the Beishan area, Inner Mongolia: New understanding based on the geological map of Qinghegou Sheet (1∶ 50000)[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(5): 977-994. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201905004.htm
[10] 任邦方, 段连峰, 李敏, 等. 内蒙古北山哈珠地区晚古生代花岗岩类年代学与地球化学测试数据集[J]. 中国地质, 2020. 47(S1): 40-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI2020S1006.htm
Ren B F, Duan L F, Li M, et al. Geochronological and geochemical dataset of Late Paleozoic granitoids in the Hazhu area of Beishan, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 47(S1): 40-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI2020S1006.htm
[11] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571.
[12] Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]// Holland D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2003, 3: 1-64.
[13] Leat P T, Livermore R A, Millar I L, et al. Magma supply in back-arc spreading centre segment E2, East Scotia Ridge[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41(6): 845-866. doi: 10.1093/petrology/41.6.845
[14] 王治淇. 西秦岭同仁县兰采地区三叠纪擦拉更复式花岗岩地球化学特征、时代及其地质意义[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2018.
Wang Z Q. Geochemical characteristics, ages and geological significance of Triassic Chalageng composite granite in the Lancai area, Tongren County of the west Qinling orogenic belt[D]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou University, 2018.
[15] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes [C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
[16] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1985.
[17] Fretzdorff S, Livermore R A, Devey C W, et al. Petrogenesis of the back-arc East Scotia Ridge, South Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2002, 43(8): 1435-1467.
[18] 吴宜翰, 刘博, 韩宝福, 等. 大兴安岭北部兴隆地区寒武纪侵入岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(10): 3346-3360. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201910013.htm
Wu Y H, Liu B, Han B F, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Cambrian plutons in Xinglong area of Northern Da-Hinggan Mountains: Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(10): 3346-3360. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201910013.htm
[19] 杨鑫朋, 田粉英, 王硕, 等. 内蒙古横峦山组类高镁安山岩年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质调查, 2018, 5(5): 58-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201805008.htm
Yang X P, Tian F Y, Wang S, et al. Geochronological and geochemical characteristics of analogy high-magnesium andesite in Henluanshan Formation of Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2018, 5 (5): 58-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201805008.htm
[20] 李守奎, 张世涛, 赵庆红, 等. 滇西兰坪皂角场新生代富碱斑岩体锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(1): 169-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202101013.htm
Li S K, Zhang S T, Zhao Q H, et al. Zircon U-Pb chronology and petrogeochemistry of Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyry in Zaojiaochang, Lanping, Western Yunnan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(1): 169-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202101013.htm
[21] Wilson M. Igneous petrogenesis: A global tectonic approach[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1989: 1-446.
[22] Perfit M R, Gust D A, Bence A E, et al. Chemical characteristics of island-arc basalts: Implications for mantle sources[J]. Chemical Geology, 1980, 30(3): 227-256.
[23] Hergt J M, Peate D W, Hawkesworth C J. The petrogenesis of Mesozoic Gondwana low-Ti flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 105(1/3): 134-148.
[24] 贠杰. 西昆仑北带晚古生代火山岩成因及构造背景研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
Yun J. Petrogenesis and the tectonic setting of the Lower Paleozoic volcanic rocks in the Northern Belt of West Kunlun[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
[25] Atherton M P, Petford N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362(6416): 144-146.
[26] Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931.
[27] Rapp R P, Shimizu N, Norman M D, et al. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(4): 335-356.
[28] 李强, 程学芹, 陈伟, 等. 额尔古纳地块早—中三叠世安山岩的发现及其对蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋南向俯冲的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(8): 2768-2785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202108007.htm
Li Q, Cheng X Q, Chen W, et al. Discovery of Early-Middle Triassic andesite in Erguna Massif and its indication of southward subduction of Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean Plate[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(8): 2768-2785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202108007.htm
-



 下载:
下载: