DISTRIBUTION OF SOIL SELENIUM AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH SOIL PROPERTIES IN WANJINSHAN OF BAOQING COUNTY, HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE
-
摘要:
在宝清县万金山乡耕地区和林区按4个点/km2的密度采集了628件表层土壤样品, 分析包括Se在内的28项化学元素指标. 结果表明: 万金山乡表土中Se元素平均含量为0.28×10-6, 波动范围0.065×10-6~0.51×10-6; 富硒土地占全区3.16%, 足硒土地占92.3%, 硒潜在不足土地占4.3%, 缺硒土地占0.24%, 不存在硒中毒区域. 黑土类型Se元素含量最高, 沼泽土类型Se元素含量最低; Se元素含量在不同土地利用方式下表现为旱田>水田>灌木林地>乔木林地>草地及其他土地. 相关性分析显示: 土壤TOC、土壤黏粒含量对Se元素的富集有促进作用, pH对Se元素含量影响有限, 但对Se元素有效性具有显著影响.
Abstract:The study collects 628 topsoil samples at a density of 4 points/km2 in farm and forest areas of Wanjinshan Township, Baoqing County, to analyze 28 chemical indexes including Se etc. The results show that the average Se content in the topsoil is 0.28×10-6, ranging from 0.065×10-6 to 0.51×10-6, with the Se-rich land accounting for 3.16%, Se-sufficient land 92.3%, potential Se-deficient land 4.3%, Se-deficient land 0.24% and no Se poisoning area. Black soil type has the highest Se content, while swamp soil type has the lowest Se content. The Se contents in different land use patterns are ranked as follows: dry field > paddy field > shrub land > arbor land > grassland and other land. Correlation analysis indicates that soil TOC and clay content promote the enrichment of Se, while pH has a limited influence on Se content but significant effect on Se availability.
-
Key words:
- Se content /
- soil type /
- land use pattern /
- soil TOC /
- soil clay /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
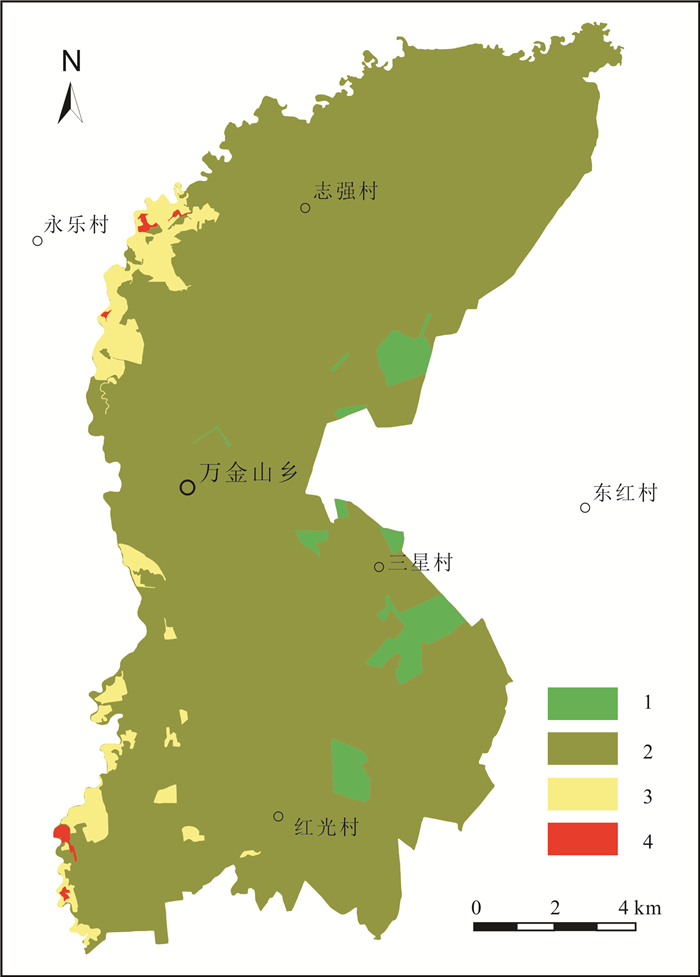
表 1 万金山乡土壤Se元素含量划分界限值及统计结果
Table 1. Threshold values and statistical results of soil Se content in Wanjinshan area
Se等级 Se含量/10-6 硒效应 面积/km2 占比/% 过剩 > 3.0 硒中毒 0 0 高 0.4~3.0 富硒 5.75 3.16 适中 0.175~0.4 足硒 167.98 92.30 边缘 0.125~0.175 硒潜在不足 7.83 4.30 缺乏 < 0.125 缺硒 0.43 0.24 表 2 不同土壤类型Se元素含量参数统计表
Table 2. Parameter statistics of Se content by soil types
土壤类型 样品数 平均值 最大值 最小值 标准差 变异系数 暗棕壤 44 0.23 0.37 0.14 0.05 0.23 白浆土 69 0.30 0.44 0.13 0.08 0.26 草甸土 210 0.28 0.50 0.12 0.07 0.26 黑土 160 0.31 0.51 0.10 0.09 0.29 水稻土 53 0.26 0.45 0.14 0.06 0.24 沼泽土 85 0.22 0.43 0.07 0.06 0.29 含量单位: 10-6. 表 3 不同土地利用方式Se元素含量参数统计表
Table 3. Parameter statistics of Se content by land use patterns
土地利用 样本数 平均值 最大值 最小值 标准差 变异系数 草地 1 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.00 0.00 灌木林地 4 0.22 0.27 0.15 0.05 0.24 旱地 288 0.30 0.51 0.10 0.09 0.29 其他土地 1 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.00 0.00 乔木林地 23 0.21 0.30 0.13 0.04 0.21 水田 304 0.26 0.50 0.07 0.07 0.28 含量单位: 10-6. 表 4 表层土壤各种成分与土壤Se相关系数
Table 4. Correlation coefficients of surface soil compositions and soil Se
成分 Al2O3 CaO MgO Na2O SiO2 Fe2O3 TOC SOM CEC 相关系数(r) 0.116** 0.152** 0.340** -0.532** -0.411** 0.210** 0.368** 0.354** 0.540** 成分 K N P 全盐量 水解性氮 速效钾 有效磷 有效硒 As 相关系数(r) -0.242** 0.324** 0.123** 0.304** 0.336** 0.355** 0.172** 0.779** 0.410** 成分 Cd Cr Cu Hg Mn Ni Pb Zn pH 相关系数(r) 0.066 0.202** 0.461** 0.115** 0.059 0.265** 0.285** 0.190** 0.197** **为p < 0.01, 相关性显著. -
[1] Milner J A. Diet and cancer: Facts and controversies[J]. Nutrition and Cancer, 2006, 56(2): 216-224. doi: 10.1207/s15327914nc5602_13
[2] 张哲寰, 赵君, 宋运红, 等. 黑龙江省克山县土壤-作物系统硒元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 585-591, 555. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10250.shtml
Zhang Z H, Zhao J, Song Y H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in the soil-crop system of Keshan Country, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 585-591, 555. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10250.shtml
[3] 杨立国, 马志超, 王鑫. 内蒙古通辽市科尔沁区土壤硒地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(4): 383-388. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8364.shtml
Yang L G, Ma Z C, Wang X. Geochemical characteristics of Selenium in the soil of Horqin District, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(4): 383-388. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8364.shtml
[4] 梁帅, 戴慧敏, 刘国栋, 等. 黑龙江双阳河流域土壤-作物-人体系统中硒元素及生态环境与人体健康评价[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49 (4): 1064-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202204003.htm
Liang S, Dai H M, Liu G D, et al. Geochemical characteristics and evaluation of ecological environment and human health of selenium in soil-crop-human system in Shuangyang River Basin, Heilongjiang[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(4): 1064-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202204003.htm
[5] 夏飞强, 张祥, 杨艳, 等. 安徽省宁国市土壤和农产品硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(3): 585-593.
Xia F Q, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of Selenium in soils and agricultural products in Ningguo City, Anhui Province[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(3): 585-593.
[6] 周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究: 以青塘-梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32 (6): 1292-1301.
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of Selenium in soils of south Jiangxi Province: A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1292- 1301.
[7] 朱建明, 左维, 秦海波, 等. 恩施硒中毒区土壤高硒的成因: 自然硒的证据[J]. 矿物学报, 2008, 28(4): 397-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200804010.htm
Zhu J M, Zuo W, Qin H B, et al. An investigation on the source of soil Se in Yutangba, Enshi: Evidence from native selenium[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2008, 28(4): 397-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200804010.htm
[8] 王仁琪, 张志敏, 晁旭, 等. 陕西省安康市西部稻田土壤硒形态特征与水稻富硒状况研究[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(2): 398-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202202004.htm
Wang R Q, Zhang Z M, Chao X, et al. A study of the selenium speciation in paddy soil and status of selenium-enriched rice in western part of Ankang City, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49 (2): 398-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202202004.htm
[9] 杨泽, 刘国栋, 戴慧敏, 等. 黑龙江兴凯湖平原土壤硒地球化学特征及富硒土地开发潜力[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10): 1773-1782.
Yang Z, Liu G D, Dai H M, et al. Selenium geochemistry of soil and development potential of Se-rich soil in Xingkai Lake Plain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(10): 1773-1782.
[10] 尹昭汉, 崔剑波, 马晓丽, 等. 东北地区生态环境中的Se及其生态效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 1995, 6(3): 308-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB503.016.htm
Yin Z H, Cui J B, Ma X L, et al. Selenium in eco-environment of Northeast China and its ecological effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1995, 6(3): 308-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB503.016.htm
[11] 余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125.
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1119-1125.
[12] 杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 837-849.
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26 (5): 837-849.
[13] 王美珠, 章明奎. 我国部分高硒低硒土壤的成因初探[J]. 浙江农业大学学报, 1996, 22(1): 89-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNY601.020.htm
Wang M Z, Zhang M K. A discussion on the cause of high-Se and low-Se soil formation[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University, 1996, 22(1): 89-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNY601.020.htm
[14] 王松山, 梁东丽, 魏威, 等. 基于路径分析的土壤性质与硒形态的关系[J]. 土壤学报, 2011, 48(4): 823-830. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201104018.htm
Wang S S, Liang D L, Wei W, et al. Relationship between soil physico-chemical properties and selenium species based on path analysis[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011, 48(4): 823-830. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201104018.htm
[15] 李杰, 杨志强, 刘枝刚, 等. 南宁市土壤硒分布特征及其影响因素探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(5): 1012-1020. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201205021.htm
Li J, Yang Z Q, Liu Z G, et al. Distribution of selenium in soils of Nanning City and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(5): 1012-1020. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201205021.htm
[16] 迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274.
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274.
[17] 牛雪, 何锦, 庞雅婕, 等. 三江平原西部土壤硒分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1): 223-229. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2021.2596.
Niu X, He J, Pang Y J, et al. Distribution feature of soil selenium in west Sanjiang Plain and its influencing factors[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 223-229, doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2021.2596.
[18] 王月平, 张立, 崔玉军, 等. 宝清县东部土壤硒含量特征及其与土壤性质的关系[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(4): 904-911, doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2019.0020.
Wang Y P, Zhang L, Cui Y J, et al. Characteristics of selenium content in soil of eastern Baoqing County and its relationship with soil properties[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43 (4): 904-911, doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2019.0020.
[19] 戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6): 1356-1364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201506015.htm
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in the Northeast China Plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6): 1356-1364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201506015.htm
[20] 谭见安. 环境生命元素与克山病——生态化学地理研究[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 1996: 1-13.
Tan J A. Environmental life elements and Keshan disease: A study on ecological chemicogeography[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 1996: 1-13.
-



 下载:
下载:

