Enhancement Effects of Anionic and Cationic Species in Sulfide Flotation of Copper, Lead, and Zinc Oxide Ores: Current Research Status and Future Perspectives
-
摘要:
硫化浮选法是回收铜、铅、锌氧化矿常用的浮选工艺。为获得更高的回收率,研究人员常使用一些阴阳离子对硫化过程进行强化。文章通过对近些年铜、铅、锌氧化矿强化硫化浮选相关研究成果的梳理,阐述了铜、铅、锌氧化矿硫化浮选机制,讨论了铵根离子、铅离子、铜离子、锌离子、氟离子、氯离子、碳酸根离子等阴阳离子的强化机理,综述了其强化硫化基础理论研究的进展,并对未来发展方向进行了展望,以期对铜、铅、锌氧化矿强化硫化浮选的研究提供一定的帮助。
Abstract:Vulcanization flotation is a common flotation process for copper, lead and zinc oxidation ores. To achieve higher recovery rates, a few ions are used to strengthen the vulcanization process. The intensified sulfide flotation of copper, lead, and zinc oxide ores was reviewed, were discussed. The mechanisms of intensification by anionic and cationic species such as ammonium ions, lead ions, copper ions, zinc ions, fluoride ions, chloride ions, carbonate ions, and others. The article provides an overview of fundamental theoretical research on strengthening sulfidation and offers insights into future research directions, to contribute to the advancement of intensified sulfide flotation research for copper, lead, and zinc oxide ores.
-
Key words:
- copper oxide /
- lead oxide /
- zinc oxide /
- sulphidizing flotation /
- strengthening of sulfidization /
- cation /
- anion
-

-
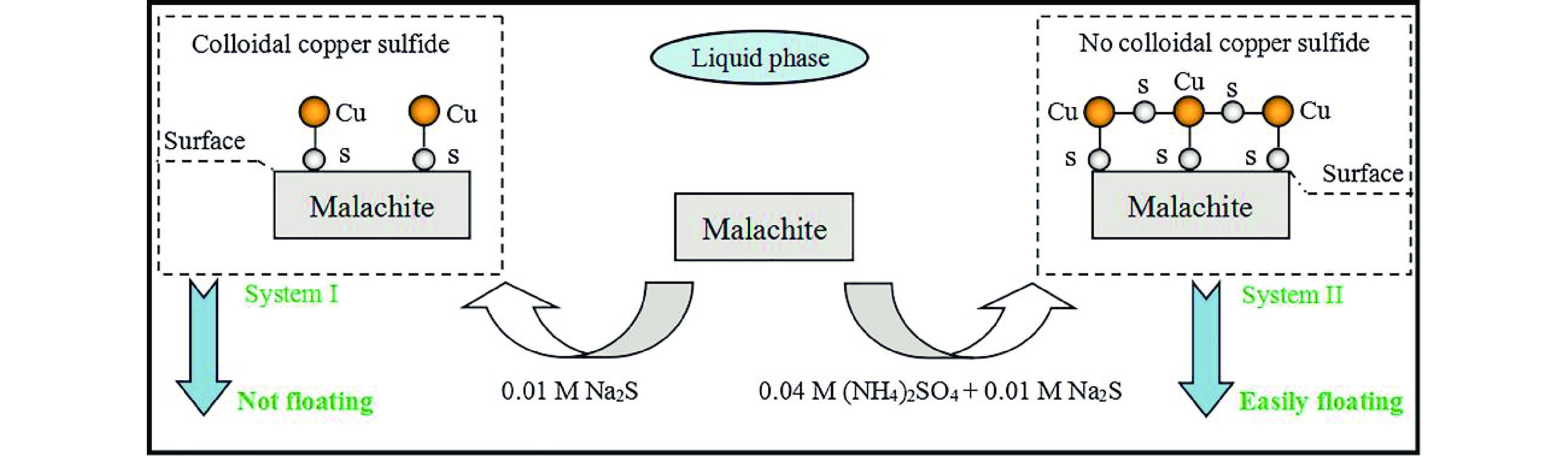
图 1 孔雀石浮选模型[17]
Figure 1.
图 2 铅离子改性增强菱锌矿硫化强化浮选机理示意图[34]
Figure 2.
表 1 常见的铜、铅、锌氧化矿矿物
Table 1. Common copper, lead and zinc oxide minerals
矿物 化学式 理论品位 晶系 孔雀石 Cu2(OH)2CO3 57.47% 单斜 硅孔雀石 —— —— 非晶 菱锌矿 ZnCO3 52.15% 三方 异极矿 Zn4SiO7(OH)2·2H2O 52.36% 斜方 白铅矿 PbCO3 77.54% 三方 -
[1] 陈代雄, 刘梦飞, 等. 氧化铜矿活化硫化浮选机理及其工业应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(8): 2393−2404.
CHEN D X, LIU M F, et al. Mechanism of activated vulcanization flotation of copper oxide and its industrial application[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(8): 2393−2404.
[2] KONG Y, LI F, et al. Application of magnetization treatment in flotation[C]//Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2021, 1748(6): 062005.
[3] BEHERA S K, MULABA−BAFUBIANDI A F. Microbes assisted mineral flotation a future prospective for mineral processing industries: A review[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2017, 38(2): 96−105. doi: 10.1080/08827508.2016.1262861
[4] 季登会, 罗文波, 等. 高铁低品位氧化锌矿的水热硫化试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2023, 42(2): 199−204.
JI D H, LUO W B, et al. Experimental study on hydrothermal vulcanization of low grade zinc oxide ore with high iron[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2023, 42(2): 199−204.
[5] HUANG Y, YIN W, et al. Strengthening sulfidation flotation of hemimorphite via pretreatment with Pb2+[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(8): 463. doi: 10.3390/min9080463
[6] ZHANG S, WEN S, et al. Pb ion pre−modification enhances the sulfidization and floatability of smithsonite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 170: 107003. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107003
[7] 张覃, 张文彬. 硫酸铵在石菉孔雀石纯矿物浮选中的活化作用及机理探讨[J]. 云南冶金, 1993(10): 16−21.
ZHANG Q, ZHANG W B. The activation effect and mechanism of ammonium sulfate to the flotation of Shi Luofmalachite pure mineral[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 1993(10): 16−21.
[8] 胡岳华, 王淀佐. 金属离子在氧化物矿物/水界面的吸附及浮选活化机理[J]. 中南矿冶学院学报, 1987(5): 501−508+590-591.
HU Y H, WANG D Z. Mechanism of adsorption and flotation activation of metal ions at oxide mineral/water interface[J]. Journal of Central South University of Mining and Metallurgy, 1987(5): 501−508+590-591.
[9] 李佳磊. 孔雀石浮选中的硫化及其铵盐强化机制探究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019.
LI J L. Vulcanization in Malachite flotation and its strengthening mechanism of ammonium salt[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[10] 高跃升, 高志勇, 等. 金属离子对矿物浮选行为的影响及机理研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(4): 859−868.
GAO Y S, GAO Z Y, et al. Effect of Metal ions on mineral flotation behavior and mechanism research progress[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(4): 859−868.
[11] 韩广. 赤铜矿预氧化−强化硫化黄药浮选试验与理论研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2022.
HAN G. Experimental and theoretical study on pre−oxidation and enhanced vulcanization xanthode flotation of copper ores[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2022.
[12] 刘殿文, 李佳磊, 等. 典型氧化铜铅锌矿物浮选的硫化及其强化研究新进展[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 35(6): 885−894.
LIU D W, LI J L, et al. Research progress on vulcanization and strengthening of typical copper−lead−zinc oxide minerals by flotation[J]. Science Foundation of China, 2019, 35(6): 885−894.
[13] GeorgeW, Poling, 王鹏程, 等. 在硫化过程中用硫酸铵作活化剂用黄药浮选孔雀石[J]. 有色矿山, 1990(6): 55−59.
GEORGEW, POLING, WANG P C, et al. Flotation of malachite with xanthate using ammonium sulfate as activator in vulcanization process[J]. Nonferrous Metals Mines, 1990(6): 55−59.
[14] 张覃, 张文彬, 等. 硫酸铵对黄药在孔雀石表面吸附的促进作用[J]. 昆明理工大学学报, 1997(4): 7−10.
ZHANG Q, ZHANG W B, et al. Effect of ammonium sulfate on the adsorption of xanthate on malachite surface[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1997(4): 7−10.
[15] LIU D W, ZHANG W B, et al. The improvment of flotation performance of difficult−to−float copper oxide ore[C]//Proceedings of ⅩⅩⅣ international mineral processing congress, Beijng China. 2012: 24−28.
[16] LIU D W, FANG J J, et al. Sulfidisation promotion effect of ammonium sulfate on flotation of copper oxide ore[C]//Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2012, 524: 1109−1114.
[17] SHEN P, LIU D, et al. Effect of (NH4)2SO4 on eliminating the depression of excess sulfide ions in the sulfidization flotation of malachite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 137: 43−52. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.03.015
[18] 胡波, 刘梦飞, 等. 铜铵络合物强化硫化钠硫化作用的机理及应用[J]. 金属矿山, 2021(4): 119−124.
HU B, LIU M F, et al. Mechanism and application of sodium sulfide enhanced by copper ammonium complex[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(4): 119−124.
[19] 胡绍彬. 乙二胺磷酸盐浮选东川氧化铜矿的生产实践[J]. 云南冶金, 1981(2): 27−29+45.
HU S B. Production practice of ethylenediamine phosphate flotation of Dongchuan copper oxide[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 1981(2): 27−29+45.
[20] 徐晓军, 刘邦瑞. 用乙二胺磷酸盐和D−2药剂活化难浮氧化铜矿物的研究[J]. 有色金属, 1991(3): 28−33.
XU X J, LIU B R. Study on the activation of refractory copper oxide minerals by ethylenediamine phosphate and D−2 reagent[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 1991(3): 28−33.
[21] 孙忠梅, 龙翼, 等. 氧化铜矿硫化强化浮选研究与应用分析[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2019(1): 26−30+42.
SUN Z M, LONG Y, et al. Research and application analysis of copper oxide vulcanization enhanced flotation[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2019(1): 26−30+42.
[22] 蒋太国, 方建军, 等. 铵(胺)盐对孔雀石硫化浮选行为的影响[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2015(4): 31−37.
JIANG T G, FANG J J, et al. Effect of ammonium (amine) salt on sulfidation flotation behavior of malachite[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2015(4): 31−37.
[23] 戈保梁, 张文彬. 硅孔雀石的活化浮选[J]. 云南冶金, 1995(4): 15−19.
GE B L, ZHANG W B. Activation flotation of malachite[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 1995(4): 15−19.
[24] 申培伦. 孔雀石硫化浮选过程中磷酸乙二胺作用机理探讨[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2016.
SHEN P L. Discussion on mechanism of ethylenediamine phosphate in sulfidation flotation of malachite[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2016.
[25] 徐晓会, 申培伦, 等. 磷酸乙二胺对硅孔雀石浮选的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(7): 2291−2296.
XU X H, SHEN P L, et al. Effect of ethylenediamine phosphate on flotation of silicomachite[J]. Bulletin of Silicate, 2018, 37(7): 2291−2296.
[26] 沈同喜. 氧化铅矿硫化浮选强化技术研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2013.
SHEN T X. Research on vulcanization flotation strengthening technology of lead oxide ore[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2013.
[27] 王瑜. 菱锌矿表面硫化层稳定性及硫化机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019.
WANG Y. Study on the stability and mechanism of vulcanization layer on the surface of magnesite[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[28] 王涵. 孔雀石硫化浮选体系中金属离子在矿物表面吸附特性及其对浮选的影响[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2021.
WANG H. Adsorption characteristics of metal ions on mineral surface and its effect on flotation in malachite vulcanization flotation system[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[29] 赵文娟. 基于铜−铵协同活化的菱锌矿强化硫化浮选理论研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2021.
ZHAO W J. Research on theory of enhanced vulcanization flotation of zinzite based on co−activation of copper and ammonium[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[30] 蒋世鹏, 张国范, 等. 金属离子对菱锌矿硫化浮选影响研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2016(2): 23−28.
JIIANG S P, ZHANG G F, et al. Study on effect of metal ions on vulcanization flotation of zinc ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing), 2016(2): 23−28.
[31] WANG H, WEN S, et al. Modification of malachite surfaces with lead ions and its contribution to the sulfidization flotation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 550: 149350. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149350
[32] 张国范, 张凤云. 浮选过程中金属离子对异极矿硫化的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(7): 1689−1696.
ZHANG G F, ZHANG F Y. Effect of metal ions on sulfide of hemimeric ore in flotation process[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 48(7): 1689−1696.
[33] 黄裕卿, 邓荣东, 等. 黄药体系下铅离子诱导异极矿强化硫化浮选及其机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020, 30(9): 2224−2233.
HUANG Y Q, DENG R D, et al. Lead ion induced enhanced vulcanization flotation and its mechanism in xanthate system [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 20, 30(9): 2224−2233.
[34] DENG R, WANG Y, et al. Induced crystallization of Pb2+ on smithsonite surface during sulfidation−xanthate flotation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 650: 129576. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129576
[35] XING D, HUANG Y, et al. Strengthening of sulfidization flotation of hemimorphite via fluorine ion modification[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 269: 118769.
[36] HU Y, SUN W, et al. Electrochemistry of flotation of sulphide minerals[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2010.
[37] FENG Q, WEN S, et al. Contribution of chloride ions to the sulfidization flotation of cerussite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 83: 128−135. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2015.08.020
[38] PEREIRA C A, PERES A E C. Reagents in calamine zinc ores flotation[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(2): 275−277. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2004.09.011
[39] 李明晓. 基于循环经济的低品位难处理氧化锌矿选冶联合新工艺研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2011.
LI M X. Research on new combined process for separation and smelting of low−grade refractory zinc oxide ore based on circular economy[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2011.
-



 下载:
下载:

