Study on the Vortex−driven Floatation of Fine Cassiterite and CFD Numerical Simulation
-
摘要:
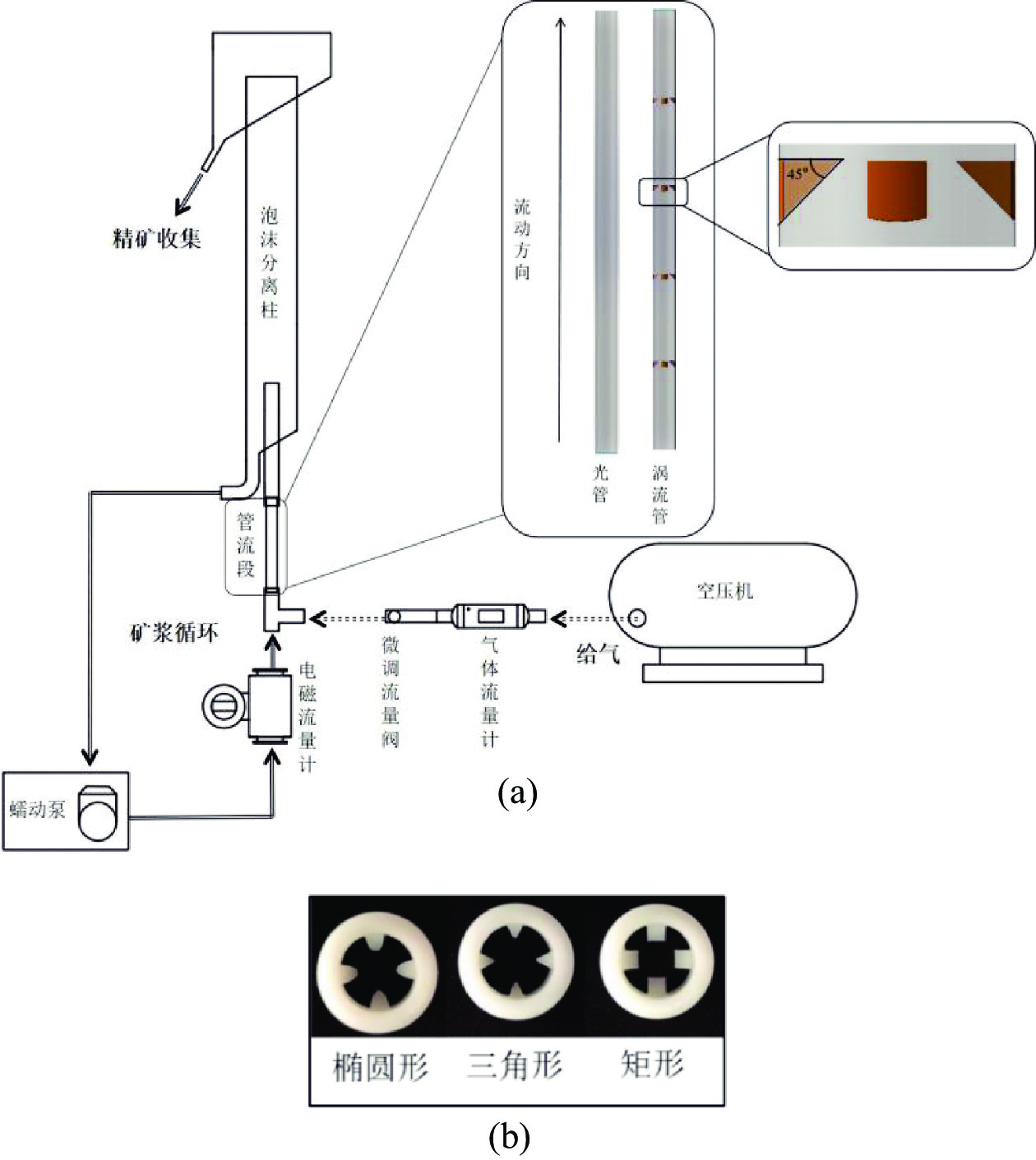
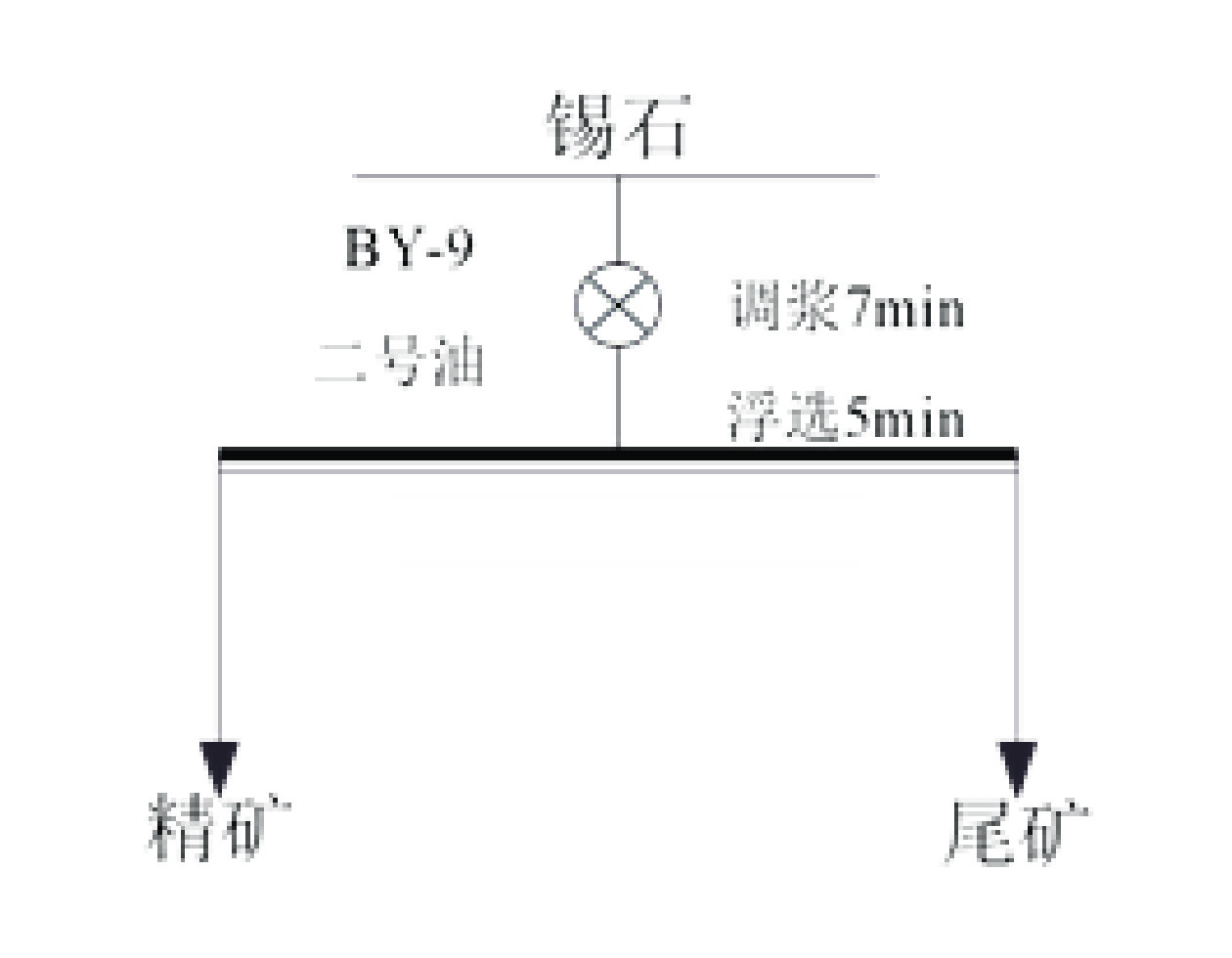
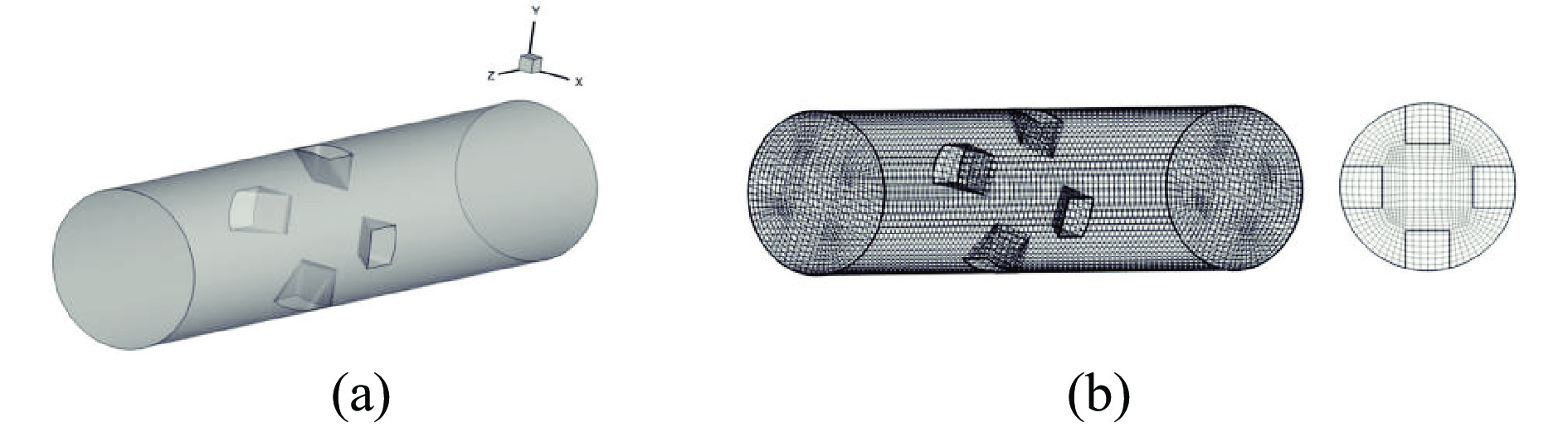
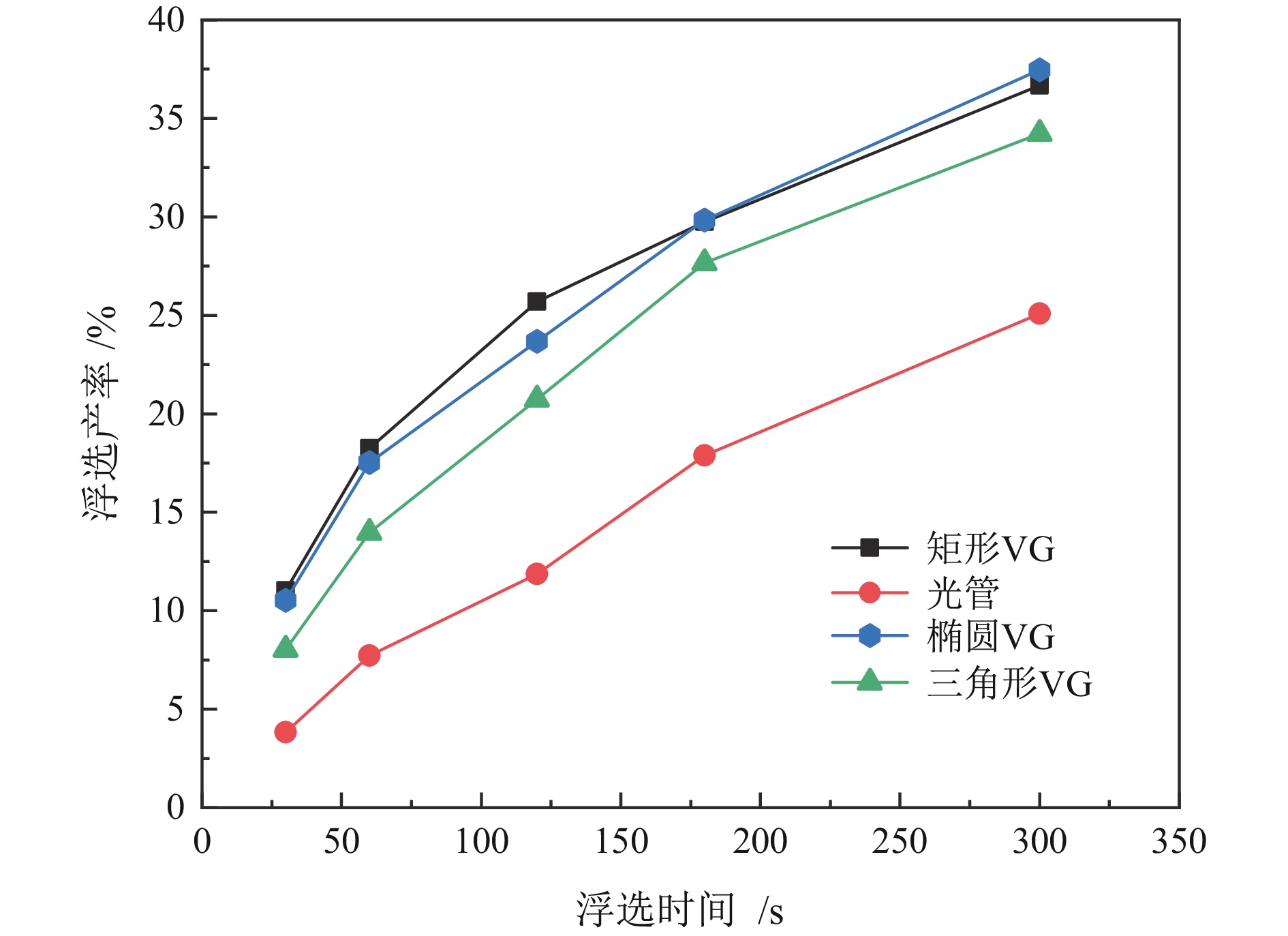
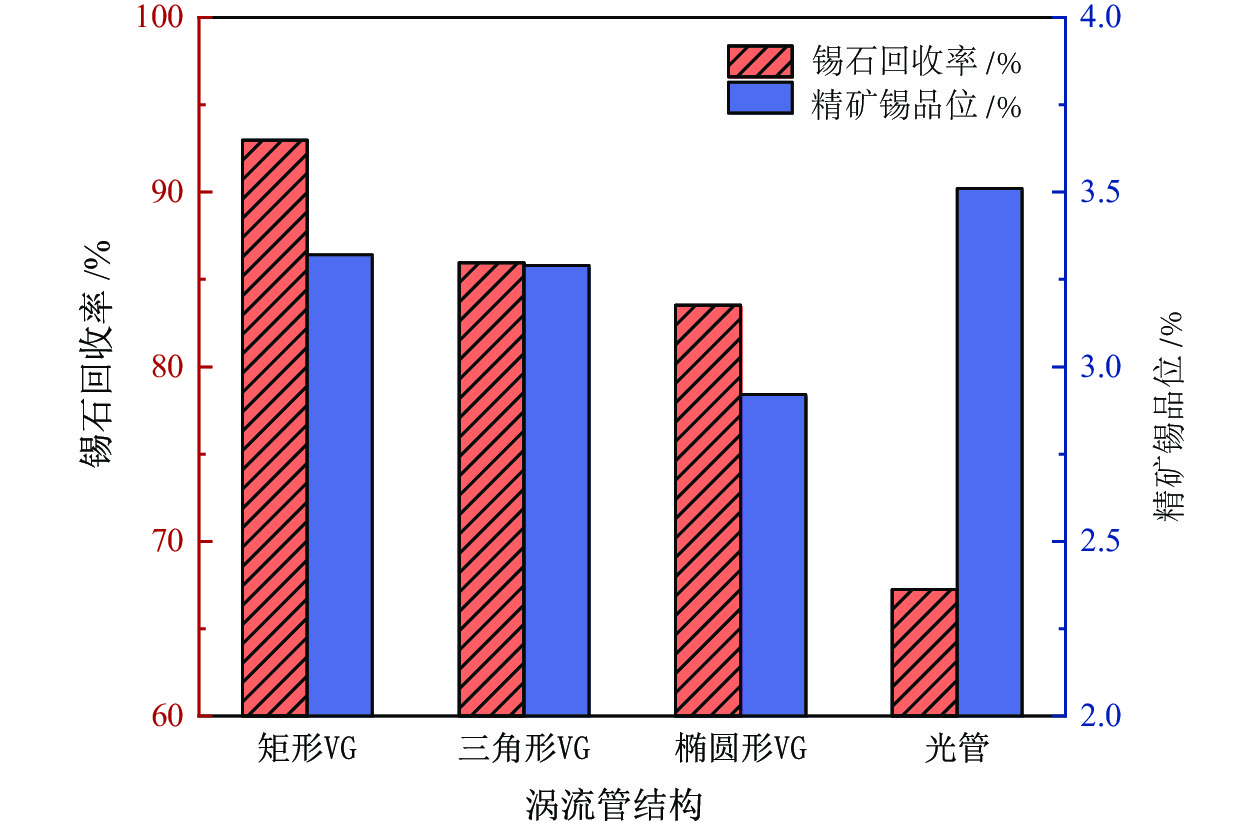
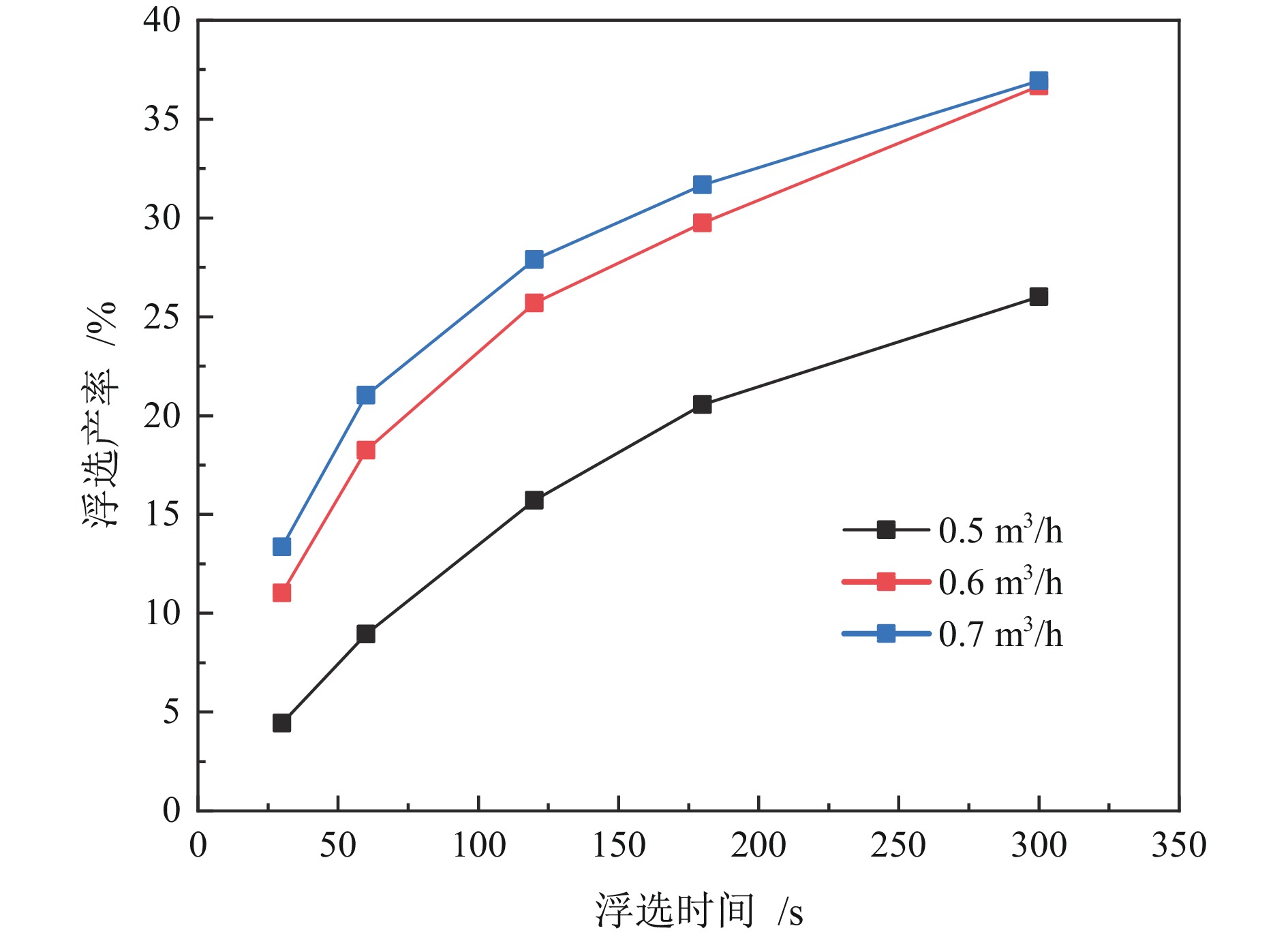
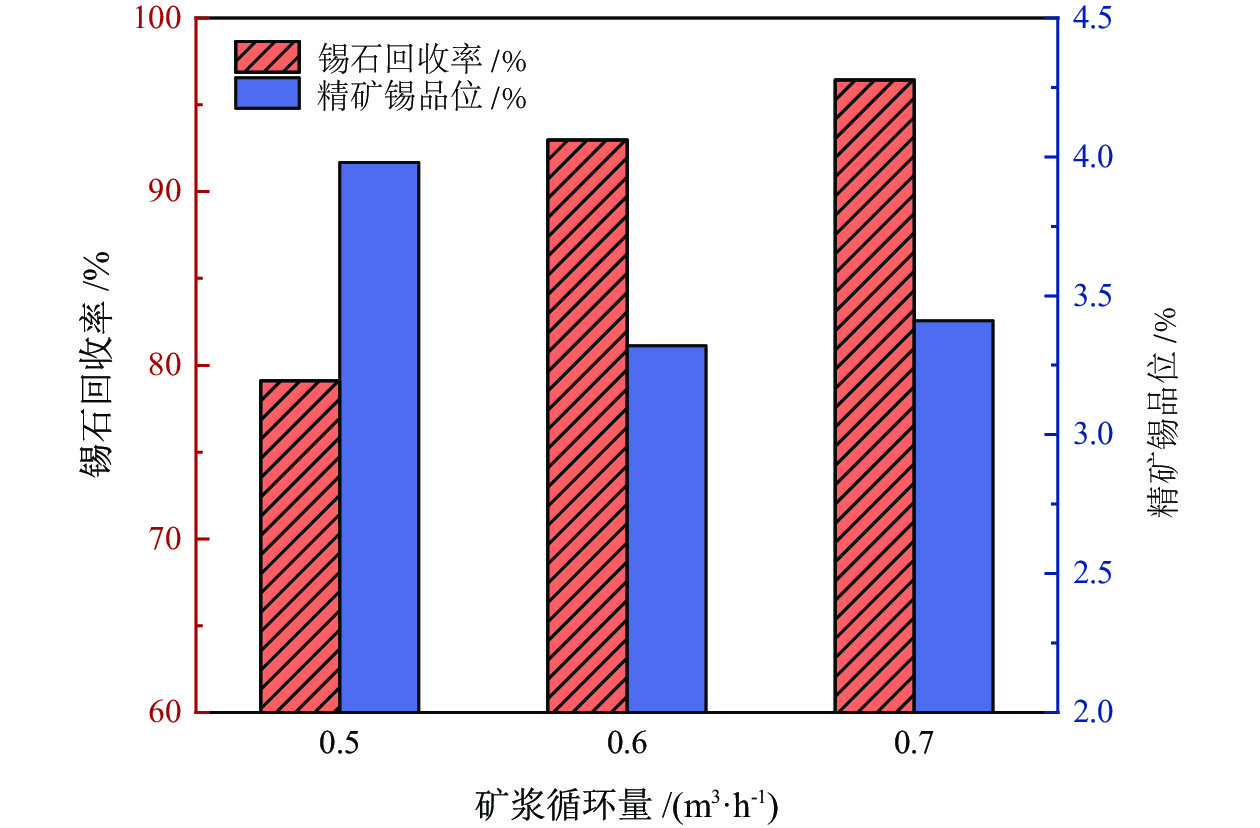
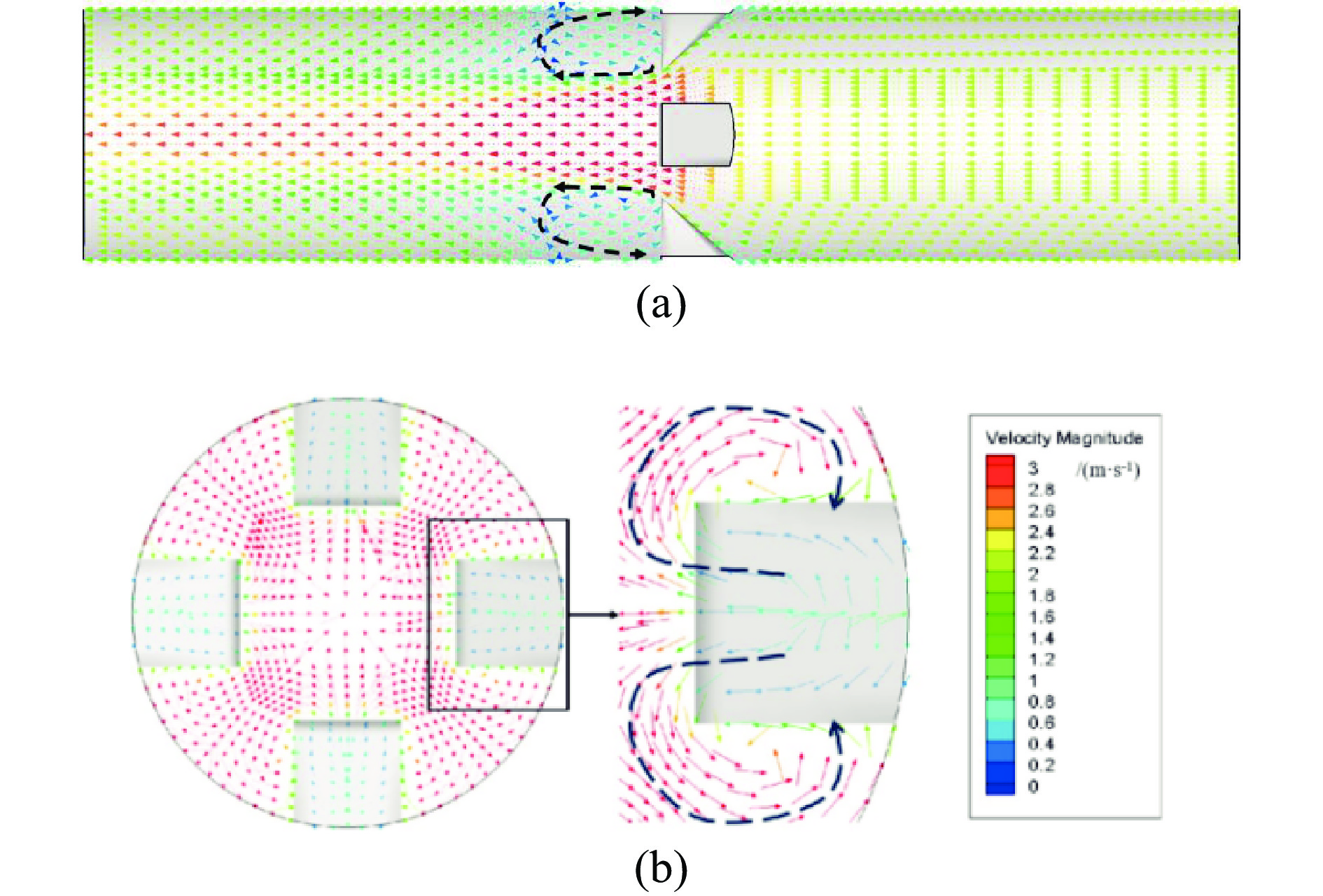
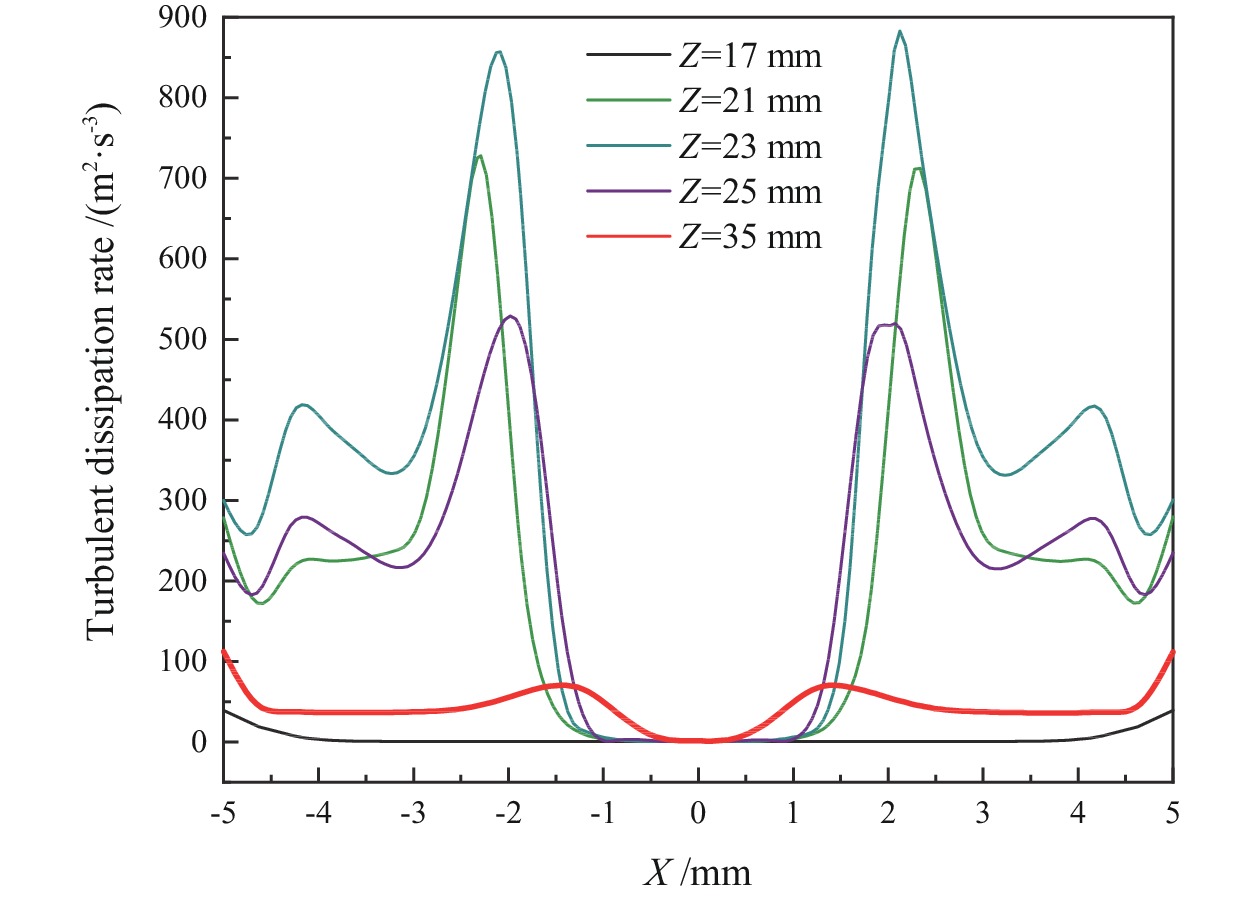
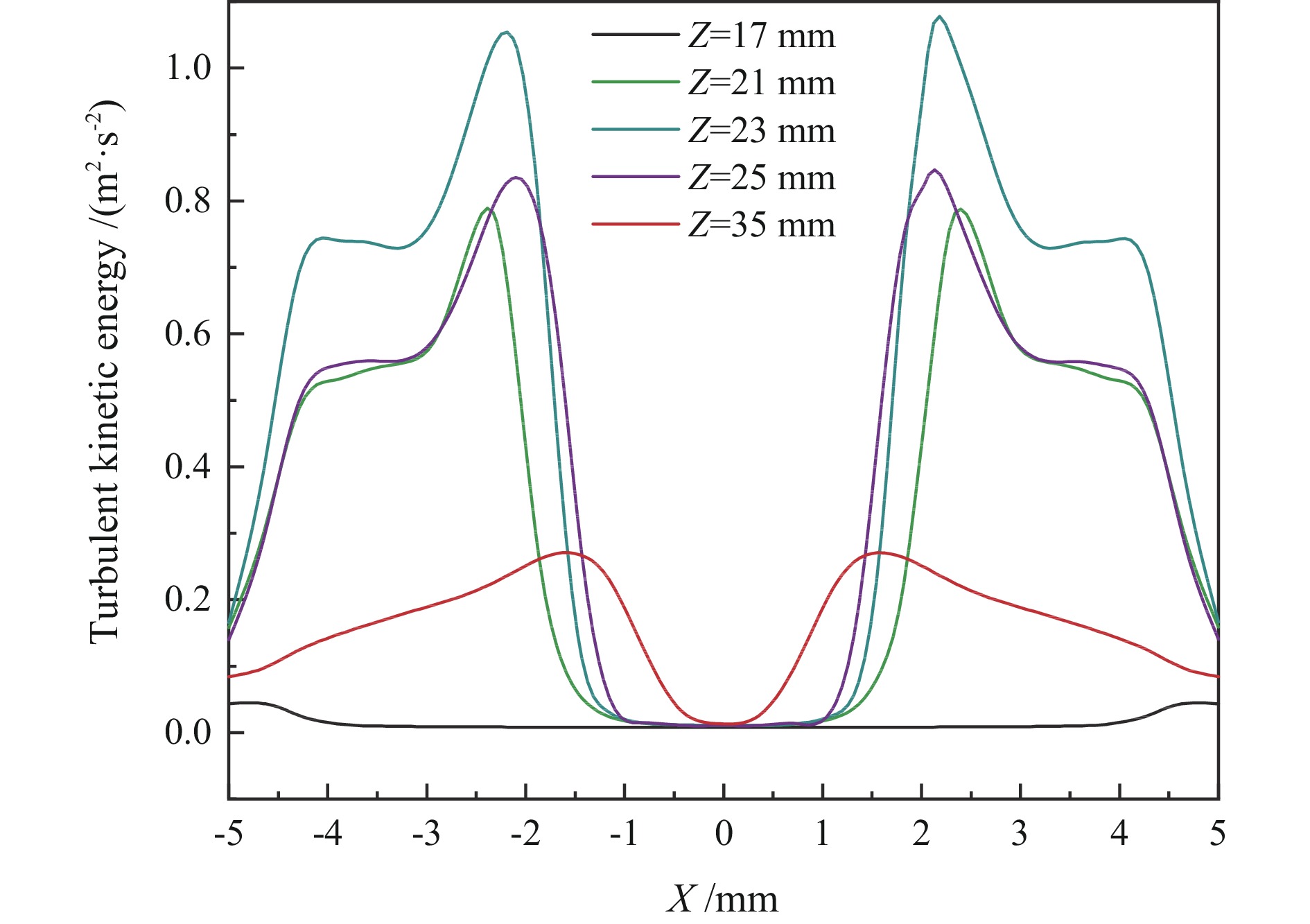
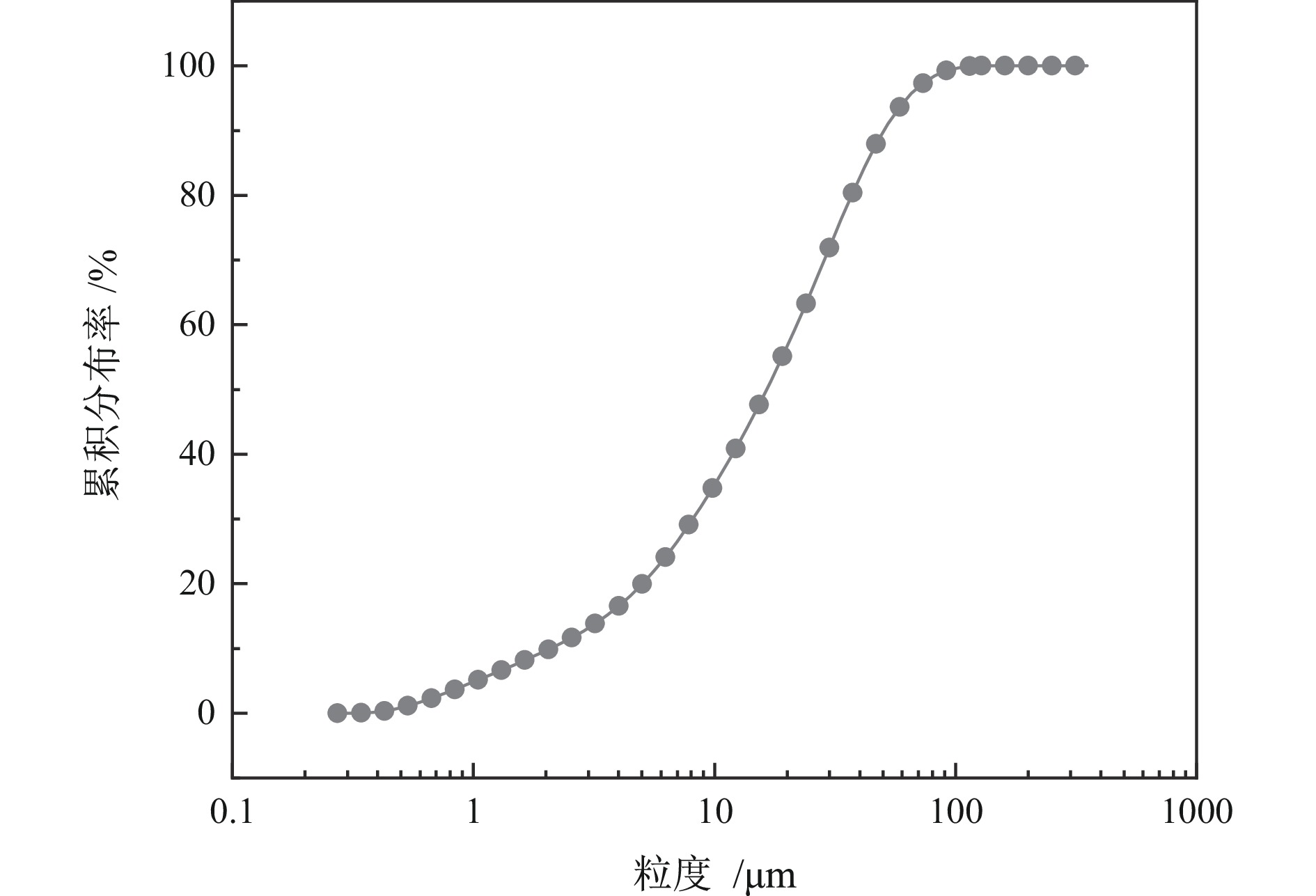
为提高微细粒锡石矿物的浮选回收效果,采用基于湍流涡调控技术的新型涡流浮选装置对微细粒锡石(d50=16.45 µm)进行了浮选实验研究,考察了涡流发生器结构及矿浆循环量对微细粒锡石浮选的影响。通过涡流矿化管内部流场CFD数值模拟,分析了涡流矿化改善微细粒浮选效果的原因。浮选实验表明,使用矩形涡流发生器诱导方式且在循环量0.6 m3/h(Re=21220)时锡石的回收率为92.96%,精矿锡品位为3.32%。在获得精矿锡品位几乎相同的情况下,回收率相较于光管提高了25.73个百分点;CFD模拟分析结果表明内置矩形涡流发生器的矿化管内平均湍流耗散率和平均湍流动能最高,分别是光管的13.01倍和7.03倍,碰撞概率从1.07%提高到2.32%,矩形涡流发生器能显著改善矿化管的湍流环境,增大了微细颗粒−气泡的碰撞概率,从而起到强化微细粒锡石浮选的作用。
Abstract:In order to improve the recovery efficiency of fine−grained cassiterite minerals, a new type of vortex−driven flotation device based on turbulent control technology was used for flotation experiments of fine−grained cassiterite(d50=16.45 µm), and the influence of the structures and slurry circulation flow rate of vortex generators and slurry circulation flow rate on the flotation efficiency of fine−grained cassiterite was investigated. Meanwhile, the internal flow field of the vortex mineralization tube was calculated through CFD numerical simulation, and the reasons for improving the flotation efficiency of fine particles through vortex mineralization was analyzed. The flotation experiment results show that using a induction method, the concentrate recovery rate of cassiterite was 92.96% at a circulation rate of 0.6 m3/h (Re=21220), the tin grade of concentrate was 3.32%. With almost the same tin grade, the recovery rate increased by 25.73 percentage points compared to the empty tube; The CFD simulation analysis results show that the average turbulence dissipation rate and averageturbulence kinetic energy inside the mineralization tube with rectangular vortex generator are the highest, which are 13.01 times and 7.03 times higher than that of the empty tube, respectively, and the collision probability increases from 1.07% to 2.32%. The rectangular vortex generator can significantly improve the turbulent environment of the vortex mineralization tube, increase fine particles−bubbles collision probability, and thus enhance the flotation recovery of fine−grained cassiterite.
-
Key words:
- cassiterite /
- fine minerals /
- flotation /
- vortex generator /
- numerical simulation
-

-
表 1 不同管流段结构0.6 m3/h下湍流参数
Table 1. Turbulent flow parameters of different pipe flow section structures at 0.6 m3/h
结构 湍流耗散率/(m2·s−3) 湍流动能/(m2·s−2) 碰撞概率/% 平均值 极大值 平均值 极大值 光管 4.696 20.41 0.0189 0.0154 1.07 矩形VG管 61.11 907.4 0.1329 0.9919 2.32 椭圆形VG管 43.12 768.75 0.0794 0.6538 2.09 三角形VG管 25.32 575.70 0.0433 0.3096 1.77 表 2 不同循环量下矩形VG管内湍流参数
Table 2. Turbulent flow parameters in rectangular VG tube under different circulation
矿浆循环量 湍流耗散率/(m2·s−3) 湍流动能/(m2·s−2) 碰撞概率/% 平均值 极大值 平均值 极大值 0.5 m3/h 35.94 493.7 0.0941 0.7435 1.97 0.6 m3/h 61.11 907.4 0.1329 0.9919 2.32 0.7 m3/h 95.84 1431.7 0.1780 1.396 2.67 -
[1] 吕中海, 胡卫波, 张俊, 等. 锡矿石选矿工艺研究现状与进展[J]. 现代矿业, 2009, 25(10): 19−22.
LV Z H, HU W B, ZHANG J, et al. Study status and progress of tin ore dressing process[J]. Modern Mining, 2009, 25 (10): 19−22.
[2] 宫贵臣, 韩跃新, 刘杰, 等. 油酸钠在锡石(211)表面吸附的量子化学研究[J]. 东北大学学报 (自然科学版), 2018, 5(9): 639−644.
GONG G C, HAN Y X, LIU J, et al. Quantum chemical study on adsorption of sodium oleate on cassiterite (211) surface[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natu−ral Science), 2018, 5(9): 639−644.
[3] 李宏建, 李新冬. 国内外锡选矿进展[J]. 中国矿山工程, 2006(5): 10−13.2006(5): 10−13.
LI H J, LI X D. Domestic and foreign tin dressing progress[J]. China Mine Engineering.
[4] 张文杰, 华中宝, 谢贤, 等. 锡石选别工艺和药剂研究进展[J]. 金属矿山, 2021(8): 116−121.
ZHANG W J, HUA Z B, XIE X, et al. Research progress of cassiterite separation process and reagent[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(8): 116−121.
[5] 李亚超, 张怀瑶, 贾凯, 等. 锡石浮选药剂研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2023, 43(5): 62−70.
LI Y C, ZHANG H Y, JIA K, et al. Research development of cassiterite flotation reagents[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2023, 43(5): 62−70.
[6] U. S. Department of the Interior, U. S. Geological Survey. Mineral commodity summaries 2020[R]. Reston, Virginia: U. S. Geological Survey, 2020.
[7] 刘杰, 韩跃新, 朱一民, 等. 细粒锡石选矿技术研究进展及展望[J]. 金属矿山, 2014, 10: 76−81.
LIU J, HAN Y X, ZHU Y M, et al. Research status and prospective on separation technology of fine cassiterite[J]. Metal Mine, 2014, 10: 76−81.
[8] 陈文岳. 细粒锡石表面特性及可浮性研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2014.
CHEN W Y. Study on surface characteristics and floatability of fine−grained cassite[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014.
[9] 郑恺昕. 湍流中颗粒−气泡碰撞概率模型修正及微细粒矿物分选过程流动强化[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2022.
ZHENG K X. Modification of particle−bubble turbulent collision probability model and hydrodynamic enhancement of fine mineral particles separation process[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021.
[10] WANG G, ZHOU S, JOSHI J, et al. An energy model on particle detachment in the turbulent field[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 69: 165−169. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2014.07.018
[11] ZHENG K X, YAN X K, WANG L J, et al. Turbulent effects of vortex generators on the separation of fine particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 418(11-13): 129373.
[12] 王超, 孙春宝, 寇珏. 浮选过程中颗粒−气泡黏附作用机理及研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(12): 1423−1433.
WANG C, SUN C B, KOU J, Mechanism and research progress of the bubble−particle attachment in flotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(12): 1423−1433.
[13] WANG L J, WANG Y H, YAN X K, et al. A numerical study on efficient recovery of fine−grained minerals with vortex generators in pipe flow unit of a cyclonic−static micro bubble flotation column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 158: 304−313. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2016.10.037
[14] 王海楠, 杨文清, 李丹龙, 等. 冲击流强化浮选调浆的数值模拟与试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(S1): 443−450.
WANG H N, YANG W Q, LI D L, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study of impact flow enhancing flotation pulp conditioning[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(S1): 443−450.
[15] 张海军, 王海楠, 陈瑞丰, 等. 煤泥调浆湍流强化作用机理与新型涡流强化调浆过程[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(2): 934−944.
ZHANG H J, WANG H N, CHENG R F, et al. Turbulence enhancement mechanism of coal slime pulp conditioning and new type vortex enhancing pulp conditioning process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(2): 934−944.
[16] 闫小康, 苏子旭, 王利军, 等. 基于湍流涡调控的煤气化渣炭−灰浮选分离过程强化[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(3): 1318−1328.
YAN X K, SU Z X, WANG L J, et al. Process intensification on flotation separation of carbon and ash from coal gasification slag using turbulent eddy regulation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(3): 1318−1328.
[17] 苏子旭. 微细粒分选的湍流过程强化及涡流矿化管优化设计[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021.
SU Z X. Process intensification on turbulence for fine particle separation and the optimization design of a vortex mineralization tube[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021.
[18] A. Nguyen, D.−A. An−Vo, T. Tran−Cong, et al. A review of stochastic description of the turbulence effect on bubble−particle interactions in flotation[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 156: 75−86. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2016.05.002
-



 下载:
下载: