Differences of Flocculating Characteristics of Difficult−to−settle Coal Slime Water Between Polyacrylamide−grafted Starch Copolymer and Polyacrylamide
-
摘要:
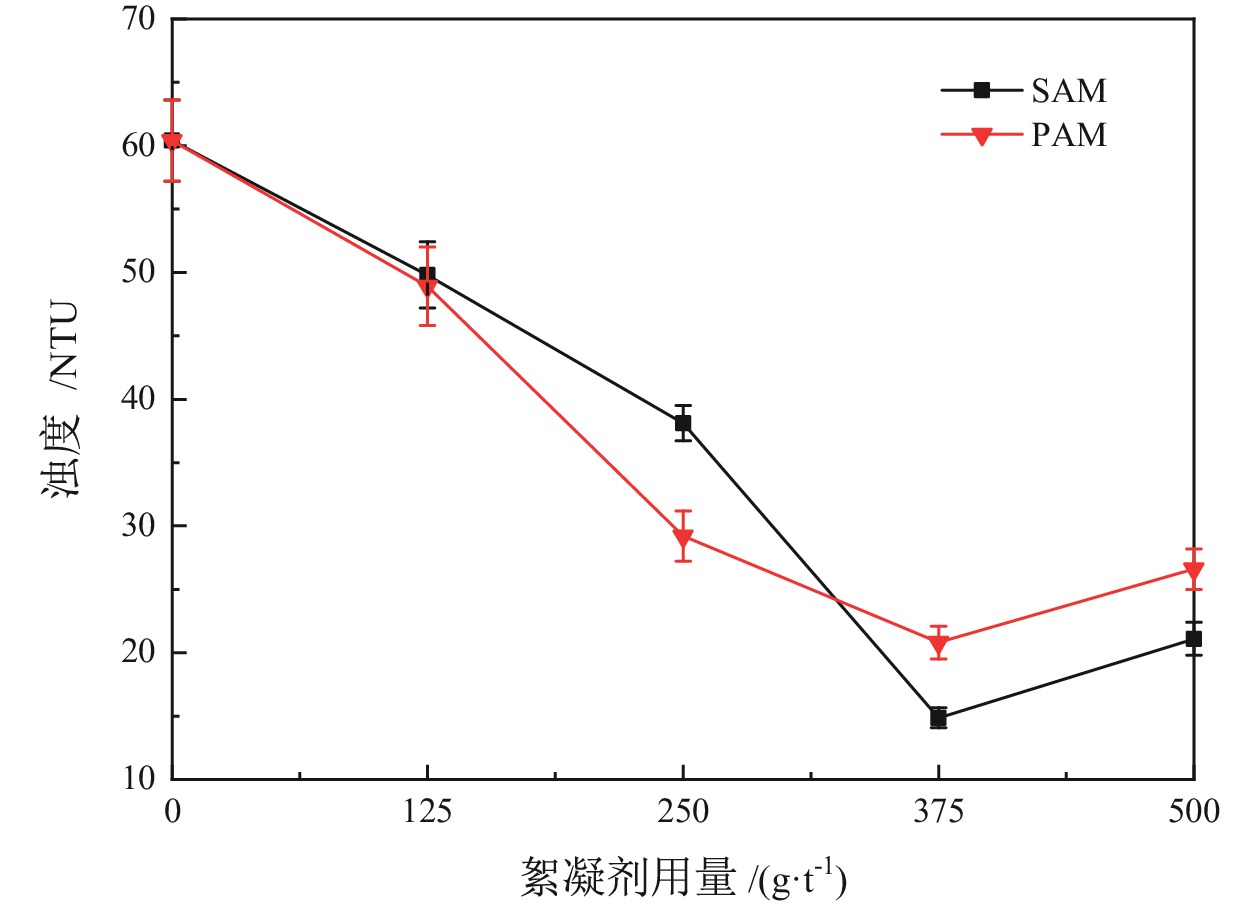
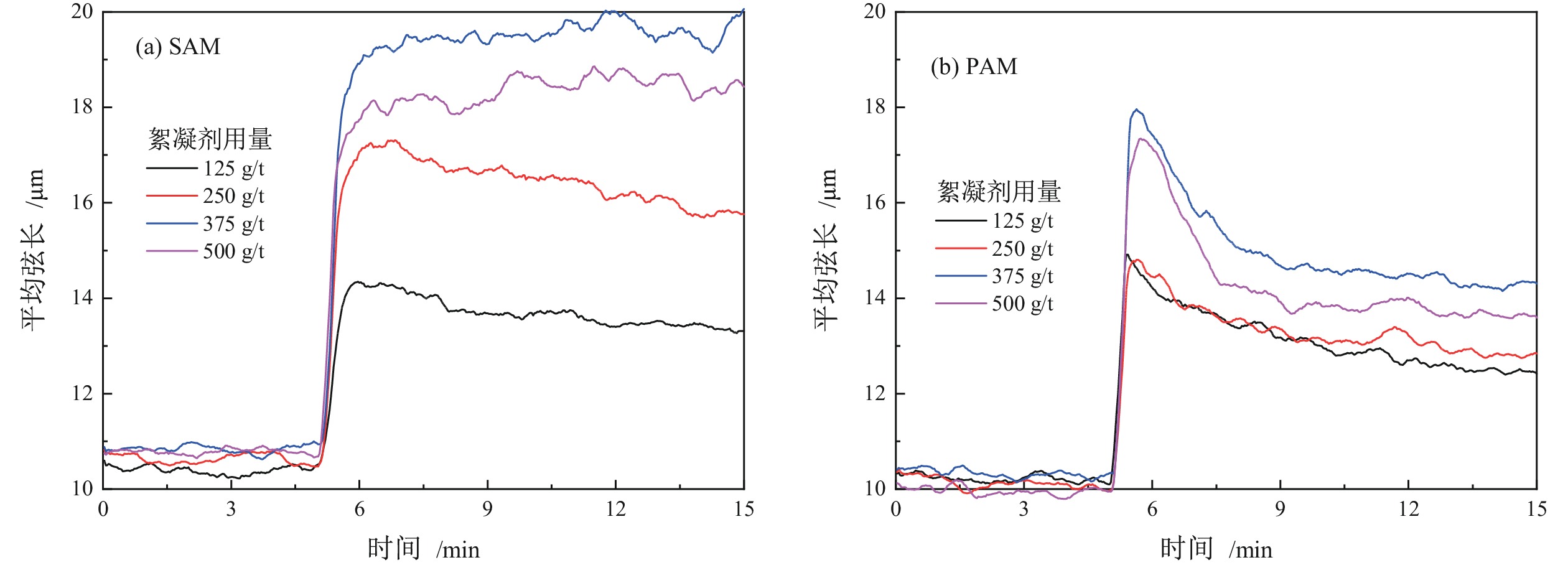
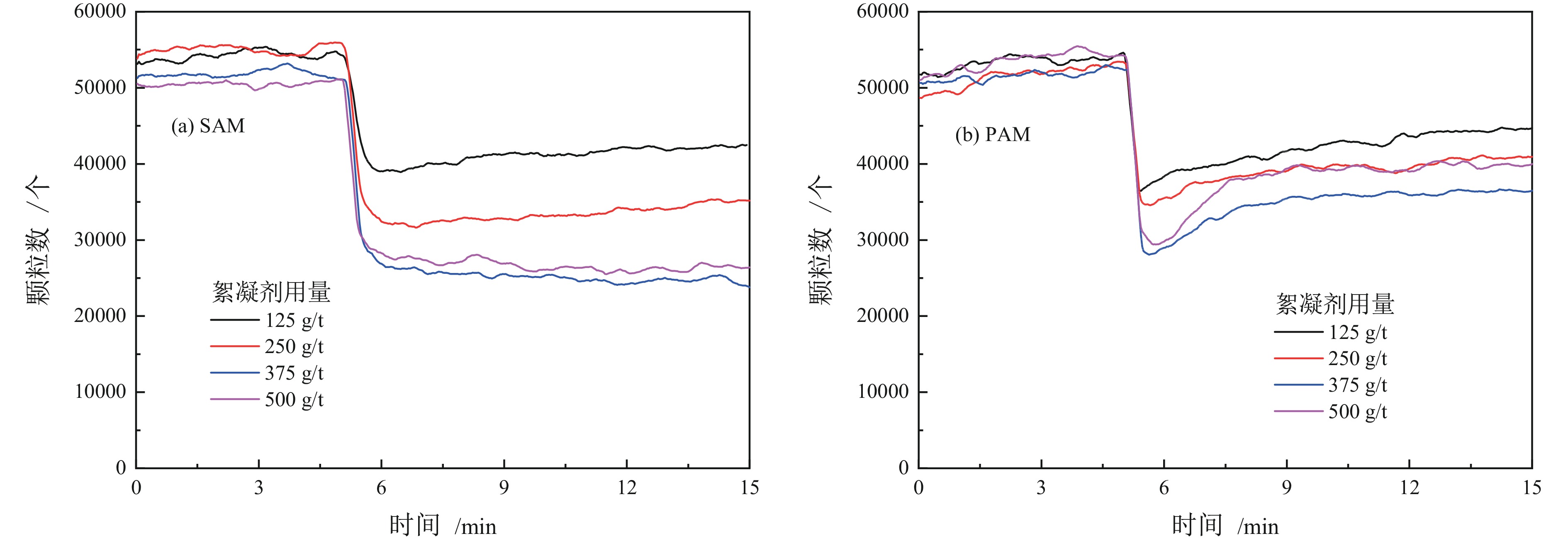
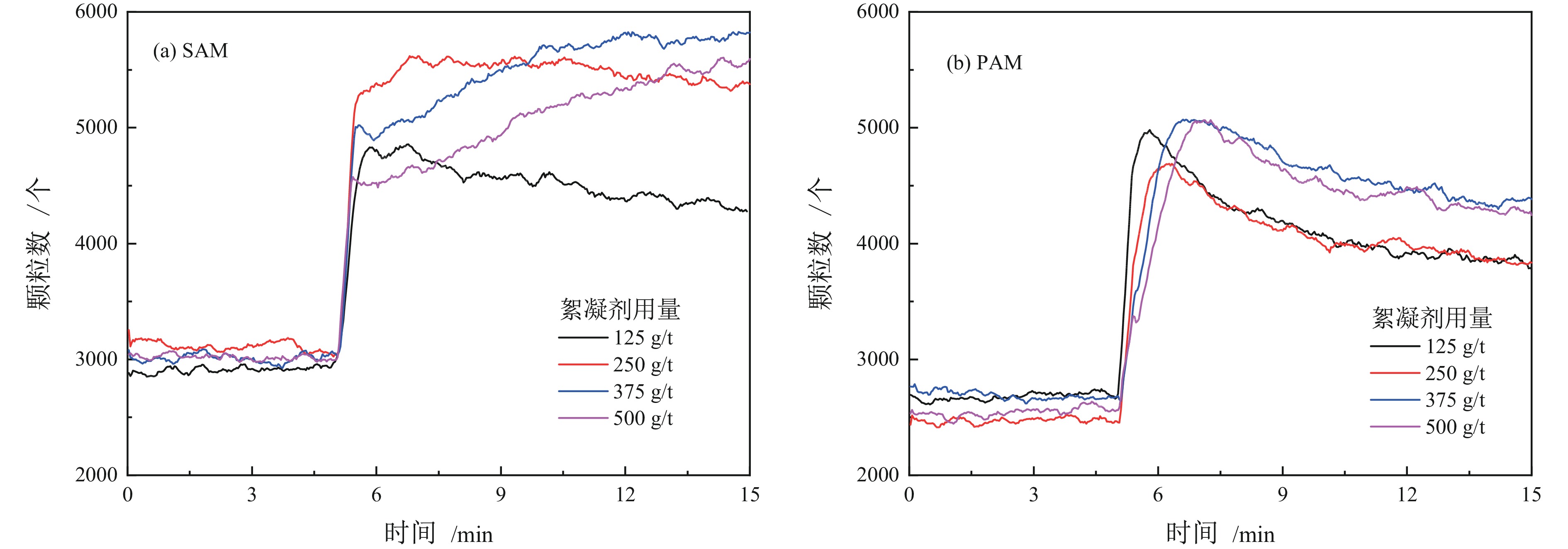
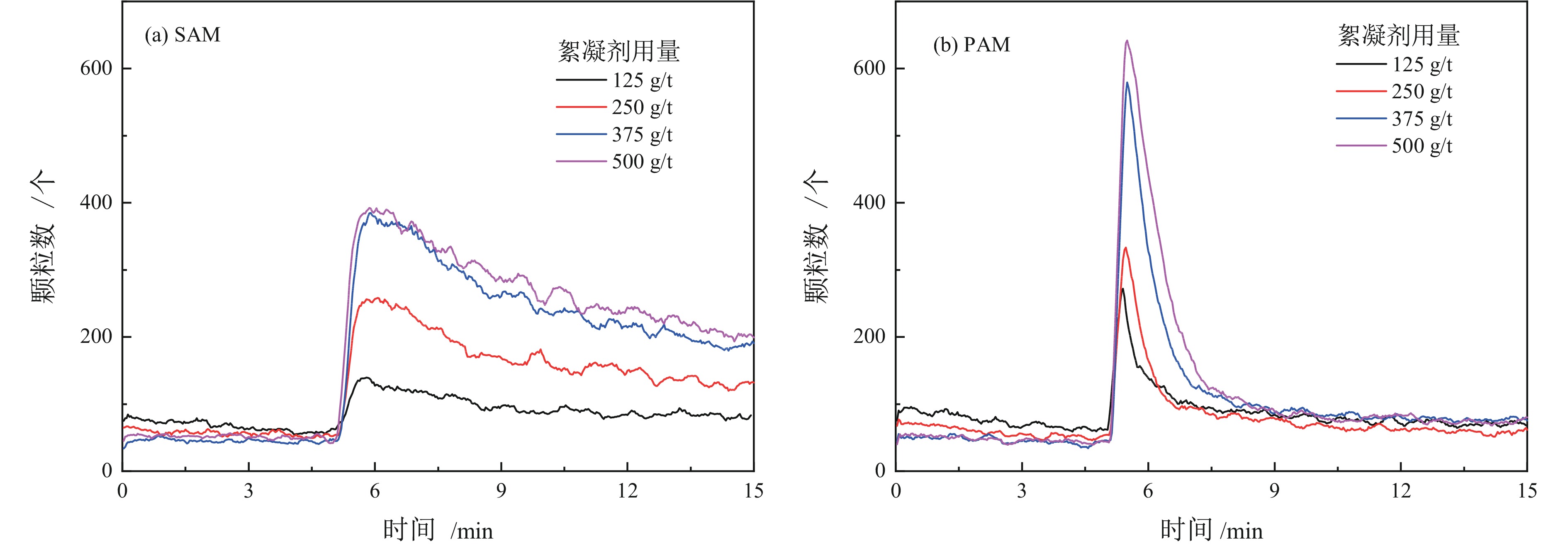
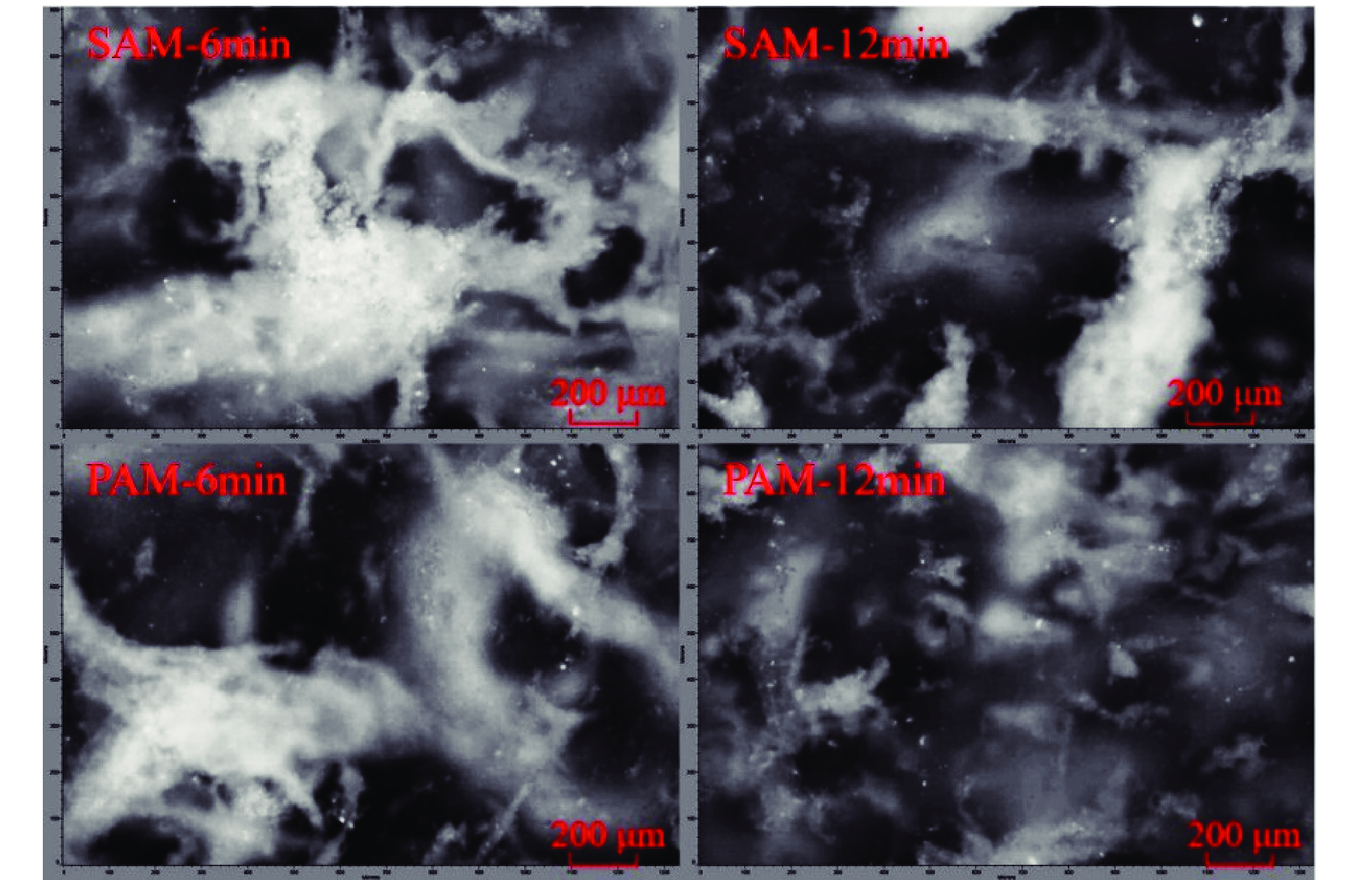
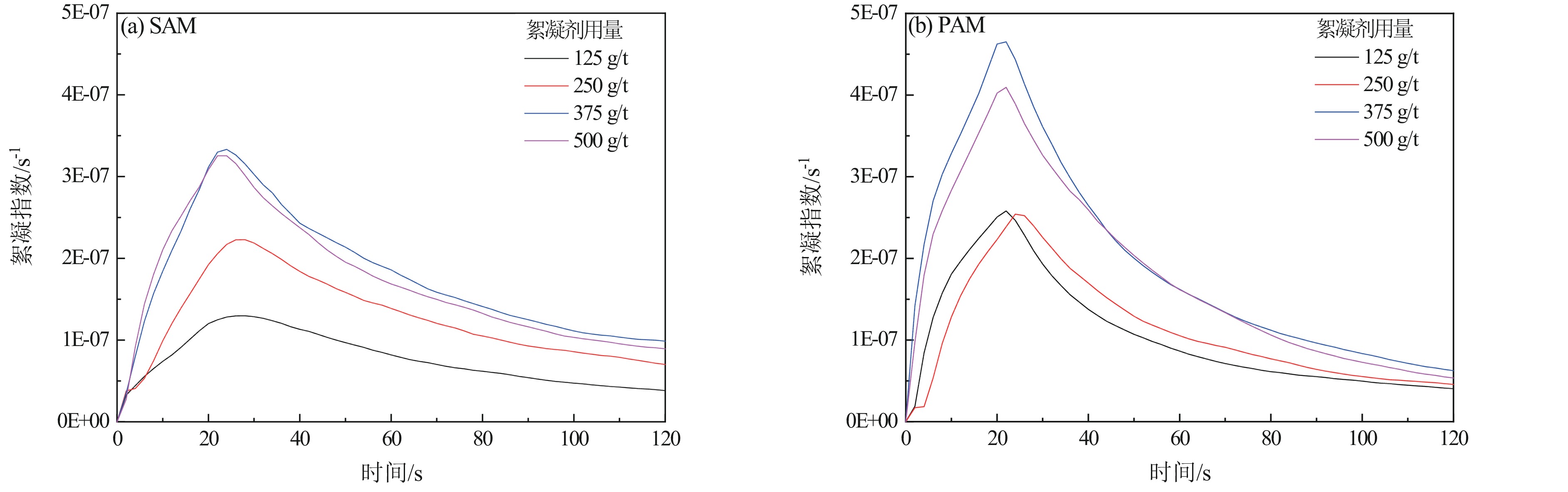
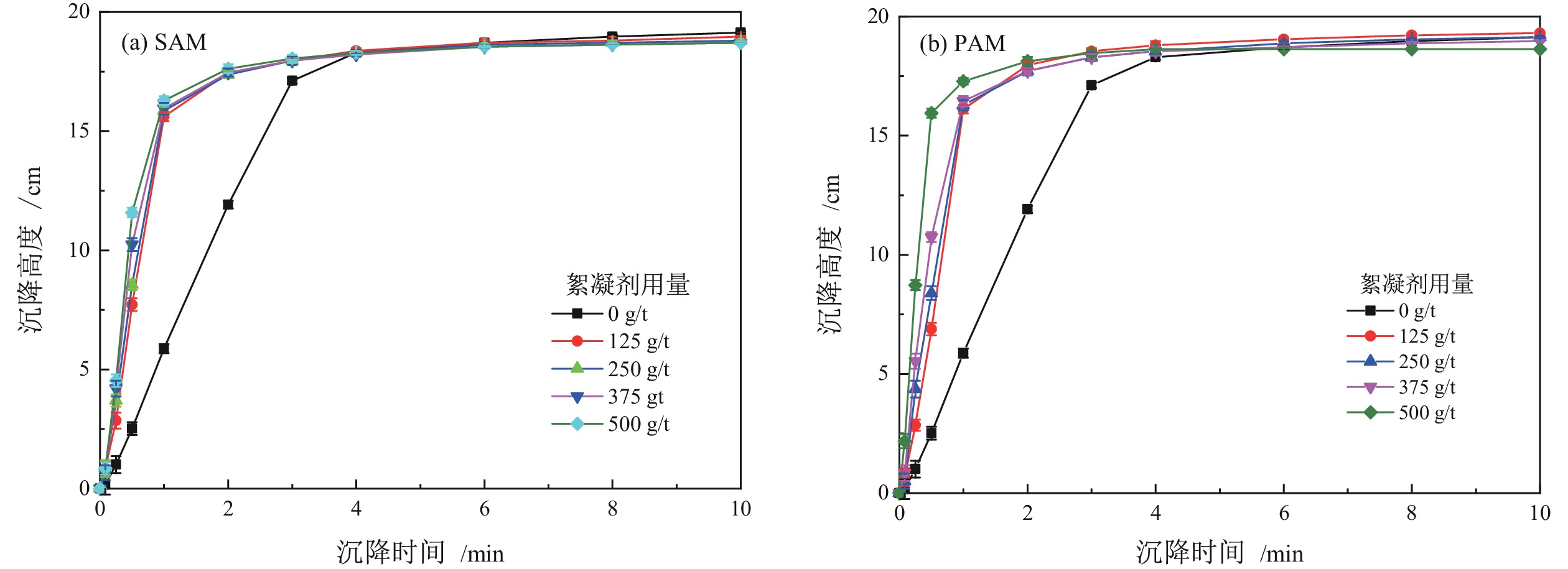
高岭土等黏土矿的存在是煤泥水沉降效果差的主要原因,目前尚未有关于难沉降煤泥水动态絮凝过程的研究。相较于聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)合成单体的毒性,淀粉接枝丙烯酰胺(SAM)合成的单体可降解性好。为此,以高岭土为研究对象,系统对比了SAM与PAM对高岭土动态絮凝过程的影响。首先,考察了不同SAM与PAM用量下的沉降速度和絮凝效果。随后,通过聚焦光束反射测量(FBRM)和颗粒录影显微镜(PVM)技术研究了高岭土悬浮液在SAM和PAM作用下的不同粒级颗粒数量变化。沉降实验和FBRM−PVM测试结果表明,PAM能够形成更多的+100 μm大絮团,使得PAM具有更好的沉降效果;SAM形成的絮团更稳定,对细颗粒的絮凝效果更好。最后,通过FBRM获得的数据,基于Smoluchowski模型计算了PAM和SAM作用下高岭土的絮凝动力学参数,发现PAM作用下的絮凝指数明显高于SAM,同时−30 μm和30~60 μm颗粒数量的动态变化主导了絮凝动力学中絮团的形成过程。总体而言,PAM可以形成更多的、松散的大絮团,有利于高岭土的快速沉降,但对微细颗粒絮凝效果不佳。相较于PAM,SAM独特的多链立体网状结构,有利于微细颗粒絮凝和形成稳定的絮团,从而避免选煤厂洗水系统中细泥的循环积聚。
Abstract:There is currently no research on the dynamic flocculation process of difficult−to−settle coal slurry water. The presence of clay minerals such as kaolin is the main reason for the poor settling effect of coal slurry water. Compared to the toxicity of polyacrylamide (PAM) synthesized monomers, starch−grafted acrylamide (SAM) synthesized monomers have better degradability.Therefore, the effects of SAM and PAM on the dynamic flocculation process of kaolin were systematically compared. Firstly, the sedimentation rate and flocculation performance were investigated under different dosages of SAM and PAM. Subsequently, the changes in the number of different particle sizes of kaolin suspension under the action of SAM and PAM were studied using focused beam reflectance measurement (FBRM) coupled with particle video microscopy (PVM). The settlement and FBRM−PVM results indicate that PAM can form more large flocs of +100 μm, which leads to a better settling effect using PAM. The flocs formed by SAM are more stable, resulting in a better flocculation performance for ultrafine particles. Finally, the flocculation kinetic parameters of kaolin using PAM and SAM were calculated by fitting the data obtained from FBRM to Smoluchowski’s model. It was found that PAM produced a significantly higher flocculation index compared to SAM. Meanwhile, the changes in the number of −30 μm and 30−60 μm particles dominated the formation process of flocs in flocculation kinetics. In conclusion, PAM can form more loose and large flocs, which is beneficial for the rapid settlement of kaolin. However, SAM has a superior flocculation performance of ultrafine particles than that of PAM. Compared to PAM, the unique multi−chain three−dimensional network structure of SAM is conducive to the flocculation of fine particles and the formation of stable flocs, which can avoid the cyclic accumulation of fine mud in the washing water system of coal preparation plants.
-
Key words:
- starch /
- graft copolymer /
- polyacrylamide /
- FBRM−PVM /
- flocculation kinetics /
- kaolin
-

-
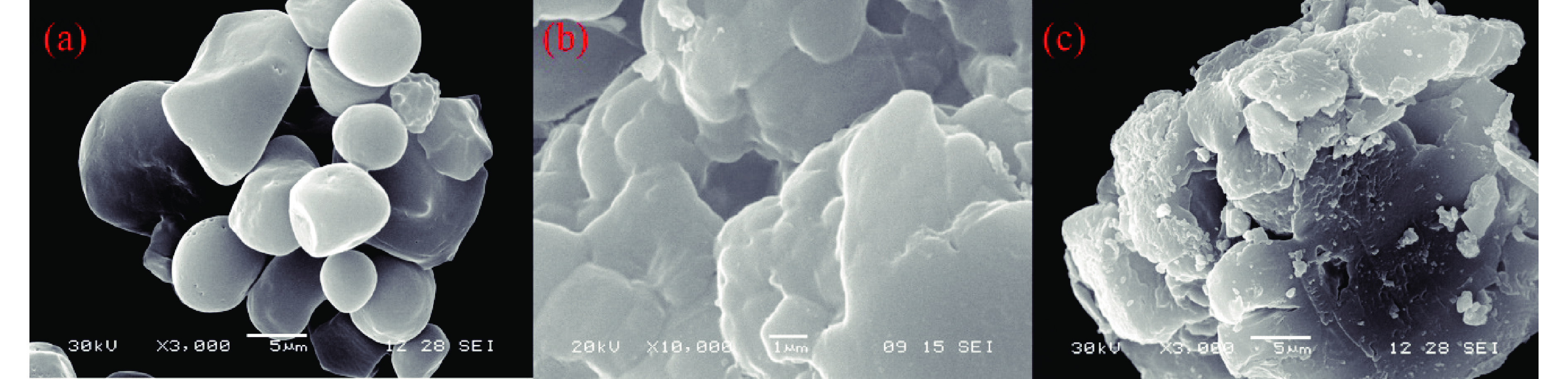
图 3 不同絮凝剂的SEM图片:(a) 淀粉;(b) PAM;(c) SAM[27]
Figure 3.
-
[1] 王兆印, 王旭昭, 胡世雄. 利用粘土絮凝网处理钼矿尾液技术探索[J]. 泥沙研究, 2002(2): 36−39.
WANG Z Y, WANG X Z, HU S X. Treatment of gangue suspension with clay suspension[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2002(2): 36−39.
[2] 陈忠杰, 闵凡飞, 朱金波, 等. 高泥化煤泥水絮凝沉降试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2010, 38(9): 117−120.
CHEN Z J, MIN F F, ZHU J B, et al. Experiment research on flocculation settlement of high muddied coal slurry water[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2010, 38(9): 117−120.
[3] 孙景丹, 李涛, 朱莹莹. 联合助滤剂对高泥化煤泥水助滤效果影响研究[J]. 黑龙江工业学院学报(综合版), 2023, 23(1): 98−103.
SUN J D, LI T, ZHU Y Y. Study on the effect of combined filter aid on extremely sliming coal slime water[J]. Journal of HeilongJiang University of Technology (Comprehensive Edition), 2023, 23(1): 98−103.
[4] 闵凡飞, 张明旭, 朱金波. 高泥化煤泥水沉降特性及凝聚剂作用机理研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2011, 31(4): 55−58,62.
MIN F F, ZHANG M X, ZHU J B. Settling property of highly−argillized coal slurry and reaction mechanism of coagulants[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2011, 31(4): 55−58,62.
[5] 孙浩, 李茂林, 崔瑞, 等. 不同絮凝剂对铅锌尾矿沉降效果的影响[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(1): 66−72.
SUN H, LI M L, CUI R, et al. Influence of different flocculants on settling effect of lead−zinc tailings[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(1): 66−72.
[6] 石从众, 王成, 刘清涛, 等. 高分子复合絮凝剂在废水处理中的研究进展[J]. 毛纺科技, 2023, 51(7): 104−110.
SHI C Z, WANG C, LIU Q T, et al. Research progress of polymer composite flocculants in treatment of textile wastewater[J]. Wool Textile Journal, 2023, 51(7): 104−110.
[7] ZHANG W, TANG M, LI D, et al. Effects of alkalinity on interaction between EPS and hydroxy−aluminum with different speciation in wastewater sludge conditioning with aluminum based inorganic polymer flocculant[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 100(2): 257−268.
[8] OZKAN A, YEKELER M. Coagulation and flocculation characteristics of celestite with different inorganic salts and polymers[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing:Process Intensification, 2004, 43(7): 873−879. doi: 10.1016/S0255-2701(03)00107-7
[9] 孙英娟, 杨永利. 淀粉接枝丙烯酰胺絮凝剂在煤泥水处理中的应用[J]. 中国煤炭, 2017, 43(2): 86−91.
SUN Y J, YANG Y L. Application of polyacrylamide−grafted starch copolymer flocculant in coal slurry wastewater treatment[J]. China Coal, 2017, 43(2): 86−91.
[10] 王啸天, 骆禹璐, 高敏, 等. 天然高分子絮凝剂处理重金属废水研究的进展[J]. 化学世界, 2023, 64(2): 65−72.
WANG X T, LUO Y L, GAO M, et al. Progress in heavy metal wastewater treatment by natural polymer flocculants[J]. Chemical World, 2023, 64(2): 65−72.
[11] 骆禹璐, 王啸天, 高敏, 等. 改性天然高分子絮凝剂制备的研究进展[J]. 高分子通报, 2022(8): 1−11.
LUO Y L, WANG X T, GAO M, et al. Research progress in preparation of modified natural polymer flocculants[J]. Chinese Polymer Bulletin, 2022(8): 1−11.
[12] 赵长青, 赵阳, 杨秦欢, 等. 两性淀粉改性生物絮凝剂的优化及其去除制革废水中总氮的研究[J]. 中国皮革, 2023, 52(6): 1−6+11.
ZHAO C Q, ZHAO Y, YANG Q H, et al. Optimization of amphoteric starch modified bioflocculant and removal of total nitrogen from tanning wastewater[J]. China Leather, 2023, 52(6): 1−6+11.
[13] 屈佳, 曹宝月, 张梦萌, 等. 改性淀粉絮凝剂在选矿废水处理中的应用[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(4): 135−139.
QU J, CAO B Y, ZHANG M M, et al. Modified starch flocculants used in beneficiation wastewater treatment[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(4): 135−139.
[14] 张昊, 郑瑶瑶, 王海涛, 等. 淀粉基絮凝剂的制备及废水应用的研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2022, 53(2): 2012−2018.
ZHANG H, ZHENG Y Y, WANG H T, et al. Research progress on the preparation of starch−based flocculants and wastewater application[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2022, 53(2): 2012−2018.
[15] 陆曦, 刘鉴雯, 周晟葆, 等. 基于重金属去除功能的改性淀粉絮凝剂的研究进展[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(5): 547−552.
LU X, LIU J W, ZHOU S B, et al. Research progress of starch modified flocculant based on heavy metal removal function[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 43(5): 547−552.
[16] 丁淑芳, 潘凤娇, 邹洪顺达. 天然淀粉接枝改性絮凝剂的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2023, 52(2): 633−638.
DING S F, PAN F J, ZOU H S D. Recent advances in natural starch graft modified flocculant[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2023, 52(2): 633−638.
[17] 丁淑芳, 潘凤娇, 邹洪顺达. 羟丙基淀粉接枝丙烯酰胺制备及其强化煤泥水沉降的作用机制[J]. 煤炭工程, 2023, 55(6): 169−175.
DING S F, PAN F J, ZOU H S D. Preparation of hydroxypropyl starch−grafted acrylamide and its mechanism of action to enhance coal slime water sedimentation[J]. Coal Engineering, 2023, 55(6): 169−175.
[18] 聂容春, 贾荣仙, 徐初阳, 等. 阳离子型PAM絮凝剂的光引发合成表征及絮凝效果[J]. 煤炭学报, 2006, 31(5): 631−634.
NIE R C, JIA R X, XU C Y, et al. Photo−initiation synthesis and flocculation property of cationic PAM flocculant[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2006, 31(5): 631−634.
[19] 降林华, 朱书全, 邹立壮, 等. 天然改性淀粉絮凝剂的合成与应用[J]. 环境化学, 2008, 27(4): 449−453.
JIANG L H, ZHU S Q, ZOU L Z, et al. Application and developing of natural modified starch flocculent[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 27(4): 449−453.
[20] 邸传耕, 乔军强. 布尔台选煤厂煤泥水特性的研究[J]. 选煤技术, 2016(6): 21−24.
DI C G, QIAO J Q. A study on the characteristics of the slurry water at Burtai coal preparation plant[J]. Goal Preparation Technology, 2016(6): 21−24.
[21] 高明, 徐志强. 两性型淀粉−丙烯酰胺接枝共聚物的合成与在煤泥水处理中的应用[J]. 中国煤炭, 2013(11): 90−93,107.
GAO M, XU Z Q. Preparation of amphoteric polyacrylamide−grafted starch copolymer and its application in coal slurry wastewater treatment[J]. China Coal, 2013(11): 90−93,107.
[22] 张方东, 李国栋, 裴继诚, 等. 利用FBRM研究阳离子聚丙烯酰胺对高岭土的动态絮凝过程[J]. 中国造纸, 2013, 32(10): 15−20.
ZHANG F D, LI G D, PEI J C, et al. Study on the dynamic flocculation process of kaolin suspensions induced by cationic polyacrylamide by using FBRM[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2013, 32(10): 15−20.
[23] GAO J, BU X, ZHOU S, et al. Graphite flotation by β−cyclodextrin/kerosene Pickering emulsion as a novel collector[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2022, 178: 107412.
[24] GAO J, BU X, ZHOU S, et al. Pickering emulsion prepared by nano−silica particles – A comparative study for exploring the effect of various mechanical methods[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2022, 83: 105928.
[25] LI S, WANG X, ZHANG Q. Dynamic experiments on flocculation and sedimentation of argillized ultrafine tailings using fly−ash−based magnetic coagulant[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(7): 1975−1984. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64308-X
[26] ZHOU S, BU X, ALHESHIBRI M, et al. Floc structure and dewatering performance of kaolin treated with cationic polyacrylamide degraded by hydrodynamic cavitation[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 2022, 209(6): 798−807. doi: 10.1080/00986445.2021.1919652
[27] 康巍. 酸变性水包水型淀粉接枝聚丙烯酰胺的合成及性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2011.
KANG W. Synthesis and properties of acid modified water in water starch grafted polyacrylamide[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2011.
[28] DING S, ZOU H, ZHOU S, et al. The preparation of hydroxypropyl starch grafted acrylamide and its enhancement on flocculation of coal slime water[J]. Energy Sources, Part A:Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2022, 44(3): 7934−7948. doi: 10.1080/15567036.2022.2118904
[29] NEGRO C, FUENTE E, BLANCO A, et al. Flocculation mechanism induced by phenolic resin/PEO and floc properties[J]. AIChE Journal, 2005, 51(3): 1022−1031. doi: 10.1002/aic.10352
-



 下载:
下载: