Treatment and Reuse of Lead−Zinc Flotation Overflow Water Through an In−situ Catalytic Ozonation Treatment Process
-
摘要:
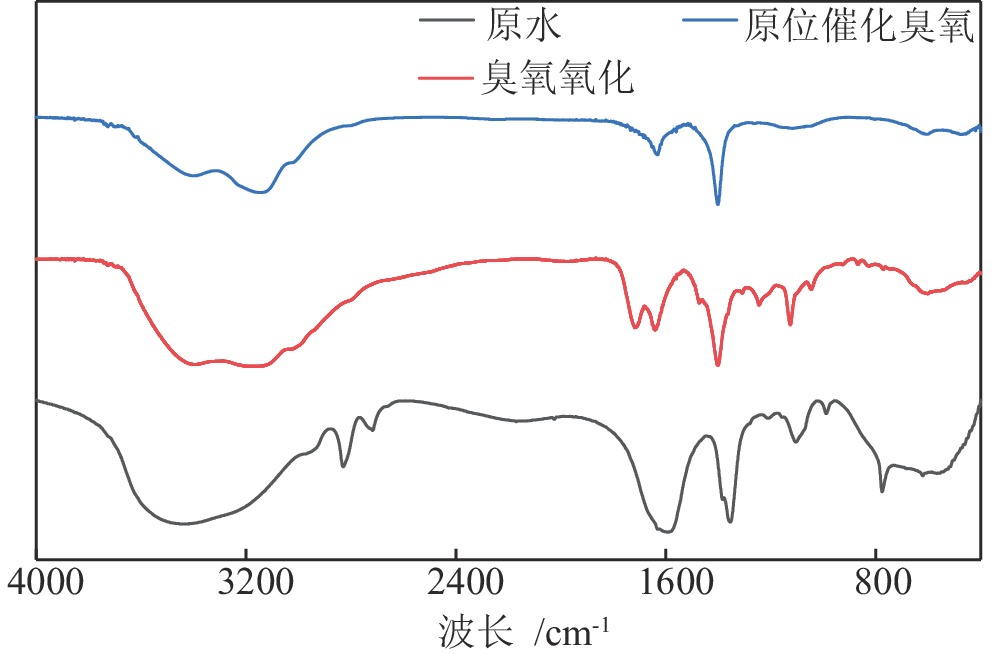
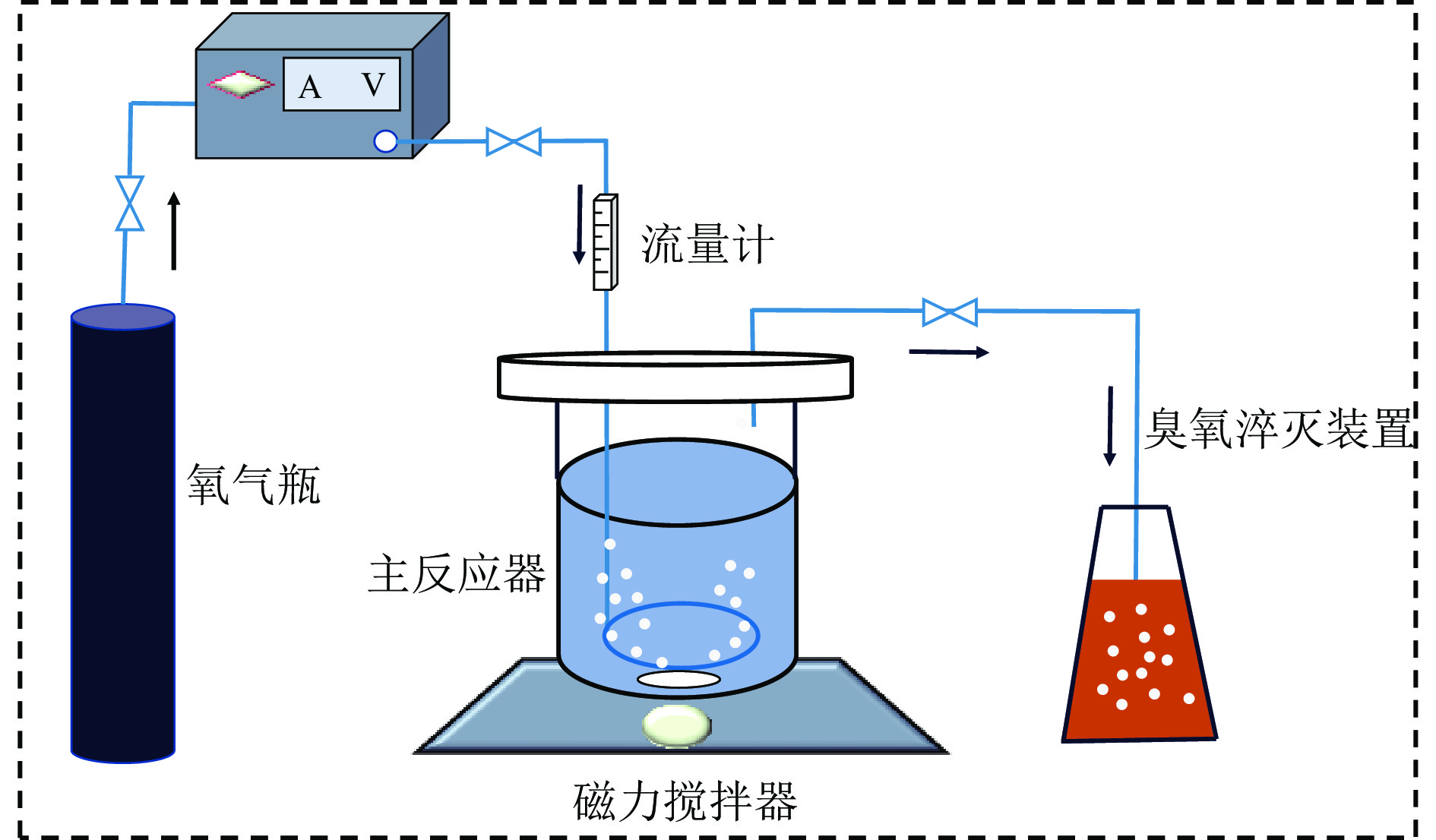
针对铅锌浮选溢流水中有机物含量高、未经处理直接回用时残余的浮选药剂影响选别指标、直接排放威胁矿山周边环境的问题,研究利用溢流水中所含的矿物颗粒原位催化臭氧降解其中有机物。结果表明,由于溢流水中矿物对臭氧具有原位催化能力,臭氧直接处理溢流水对其中有机物的去除效果优于过滤后处理,且矿物催化臭氧顺序为铅精矿>尾矿>锌精矿。最佳条件下臭氧直接处理溢流水对其中COD和TOC的去除率分别可达51.85%和46.30%,与过滤后臭氧处理相比去除率分别提高了0.78和0.62倍。矿物表面富含的活性点可原位催化臭氧产生强氧化性的·OH,将有机物中羟基和长链烃转化为CS2等小分子有机物后矿化为CO2和H2O去除。处理后溢流水返回浮选时,得到铅精矿含Pb 69.93百分点、Zn 2.31百分点,回收率分别为92.51%和2.69%,与未处理溢流水和过滤后臭氧处理溢流水相比,铅回收率分别提高4.56百分点和2.8百分点;得到锌精矿含Zn 43.69百分点、Pb 0.88百分点,回收率分别为92.14%和2.01%,锌回收率分别提高8.24百分点和4.88百分点。利用溢流水中矿物原位催化臭氧处理其中有机物可有效降低回水浮选精矿中铅锌互含,提升精矿品位和回收率。研究结果可为浮选废水的高质量回用提供借鉴。
Abstract:This study focused on utilizing mineral particles in lead−zinc flotation overflow water to catalyze the ozone for the degradation of organic matter, aiming to address issues of separation index deterioration and environment threaten when directly returned to flotation or discharge. The results showed that the direct ozone treatment for the overflow water resulted in a higher removal efficiency of organic matter compared to filtration, attributed to the in−situ catalytic capacity of minerals in the overflow water. Furthermore, it was observed that the order of ozone catalysis by minerals was lead concentrate > tailings > zinc concentrate. Under the optimal conditions, removal efficiency of 51.85% for COD and 46.30% for TOC were achieved representing improvements of 0.78 and 0.62 times, respectively, compared to that ozone treatment without minerals after filtration. The active sites on the mineral surface could catalyze ozone to generate highly reactive ·OH, resulting in the conversion of hydroxyl and long chain hydrocarbons in organic matter to smaller molecular organic compounds such as CS2, which were subsequently mineralized into CO2 and H2O. When the treated overflow water through the direct ozone treatment was recycled to flotation the lead concentrate exhibited a Pb content of 69.93% and a Zn content of 2.31%, with corresponding recoveries of 92.51% and 2.69%, respectively. In comparison to the untreated overflow water and the filtered ozone−treated overflow water, there were increases in lead recoveries by 4.56% and 2.8%, respectively. The zinc concentrate contained 43.69% Zn and 0.88% Pb, achieving recoveries of 92.14% and 2.01%, respectively, with improvements in zinc recoveries of 8.24% and 4.88%, respectively. The application of in situ catalytic ozone treatment on organic matter in the overflow water effectively reduced the lead−zinc interpenetration in the concentrate and improved the grade and recovery of concentrate. The research results can serve as a valuable reference for achieving high−quality reuse of flotation wastewater.
-
Key words:
- lead−zinc ore /
- flotation /
- overflow water /
- minerals /
- ozone /
- in situ catalytic
-

-
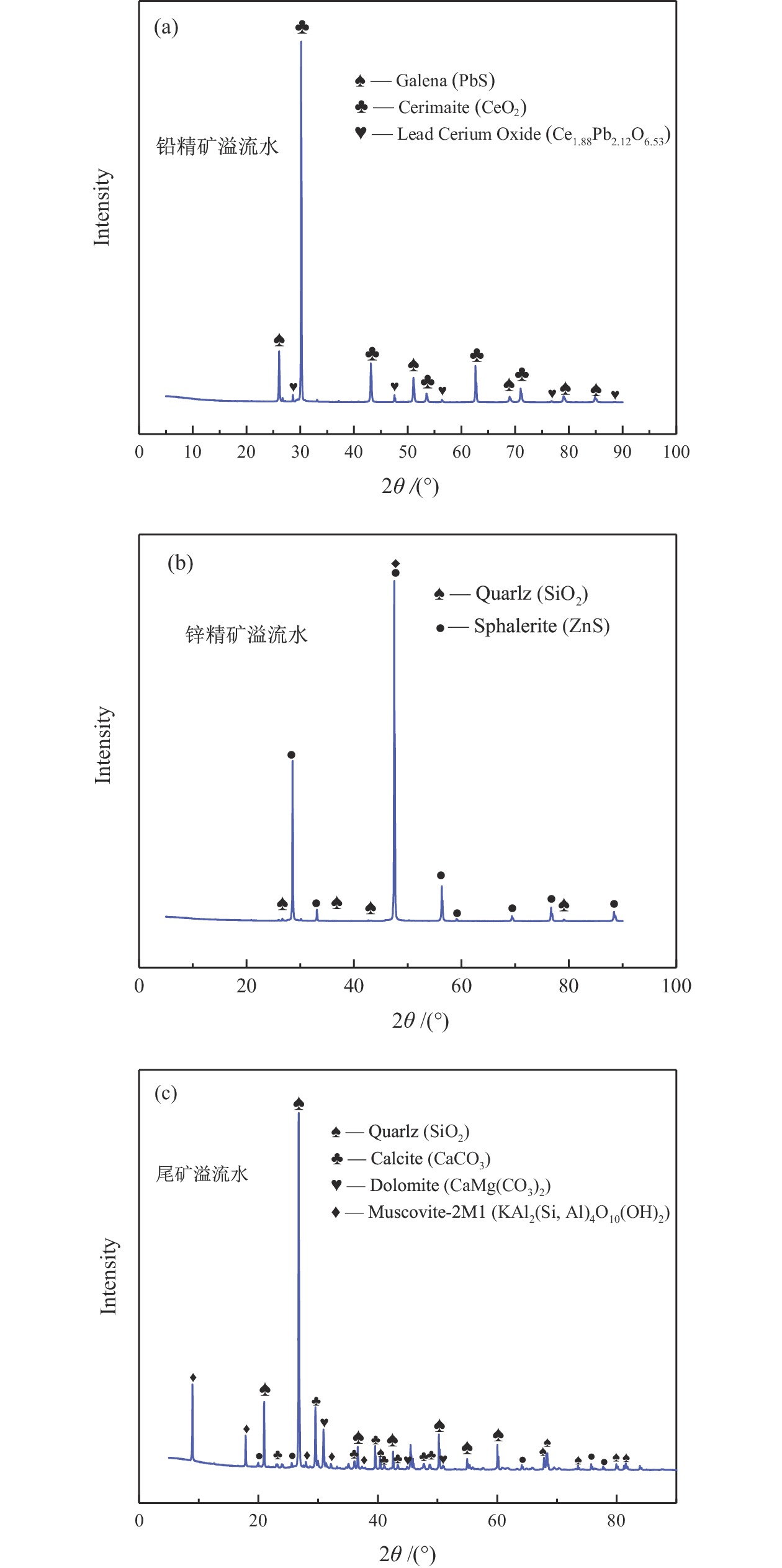
表 1 实验用铅锌浮选溢流水水质特征
Table 1. Characteristics of the lead−zinc flotation overflow water
水质指标 铅精矿溢流水 锌精矿溢流水 尾矿溢流水 COD/(mg·L−1) 374.33 341.26 324.94 TOC/(mg·L−1) 30.78 27.07 32.92 SS/(mg·L−1) 8530 8520 8640 pH 11.70 13.01 10.78 NH4+−N/(mg·L−1) 1.17 1.04 2.13 TN/(mg·L−1) 44.53 40.71 39.57 TP/(mg·L−1) 98.92 57.90 16.62 总硬度/(mg·L−1) 650.90 813.61 497.83 表 2 不同溢流水中矿物的原位催化臭氧处理有机物效能对比
Table 2. Comparison of in−situ catalytic ozonation efficiency of minerals in different overflow water for organic matter removal
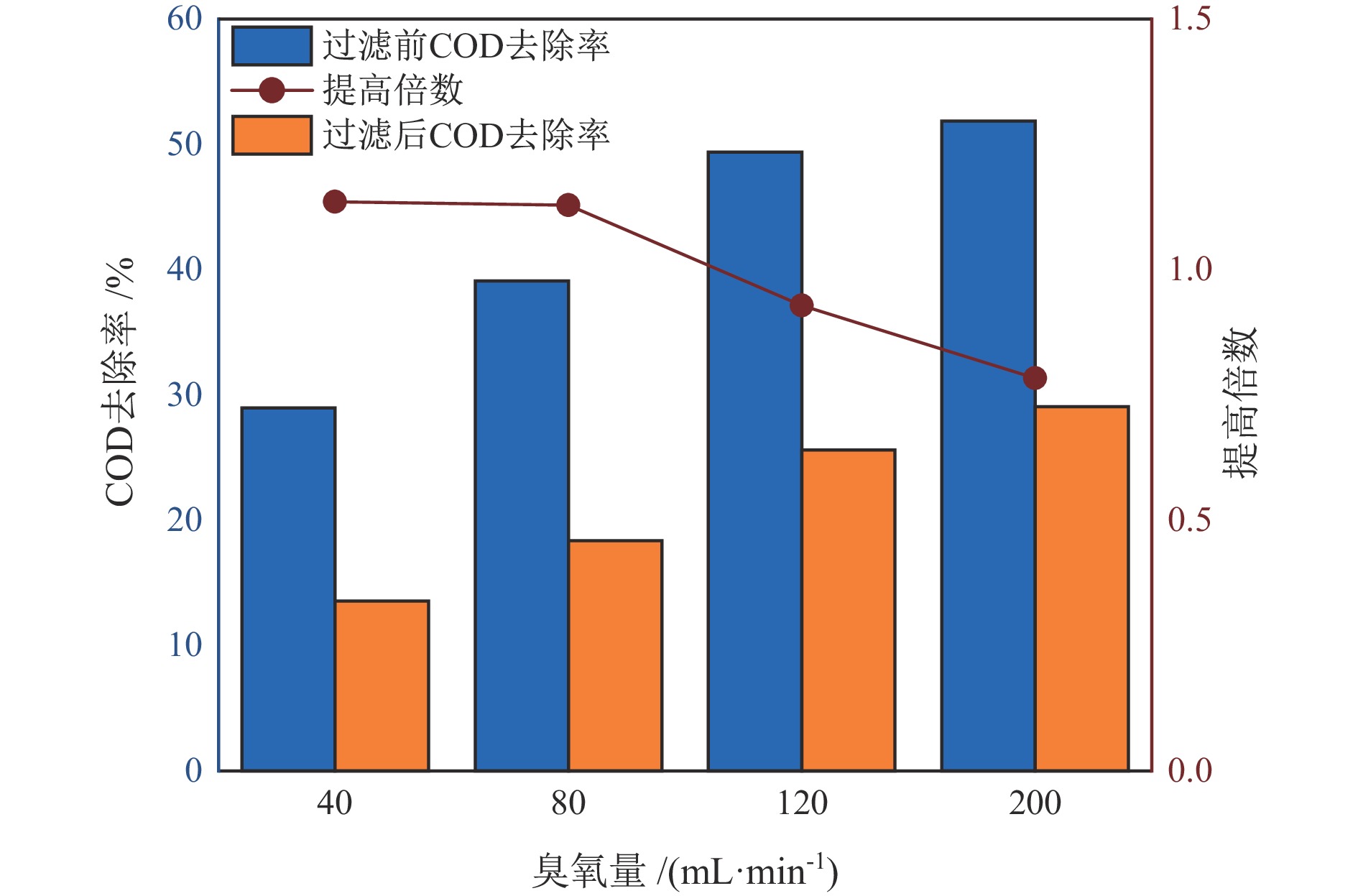
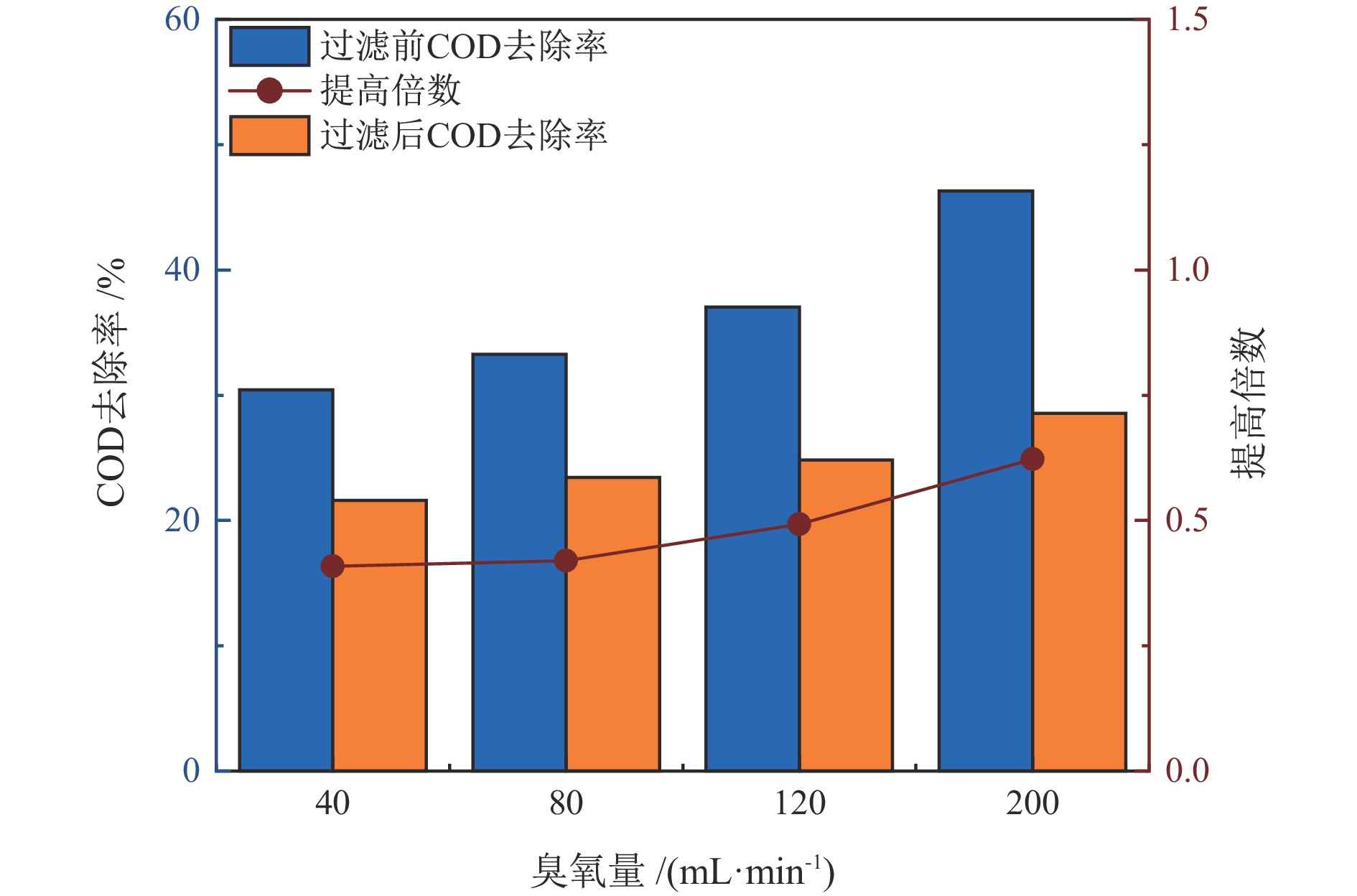
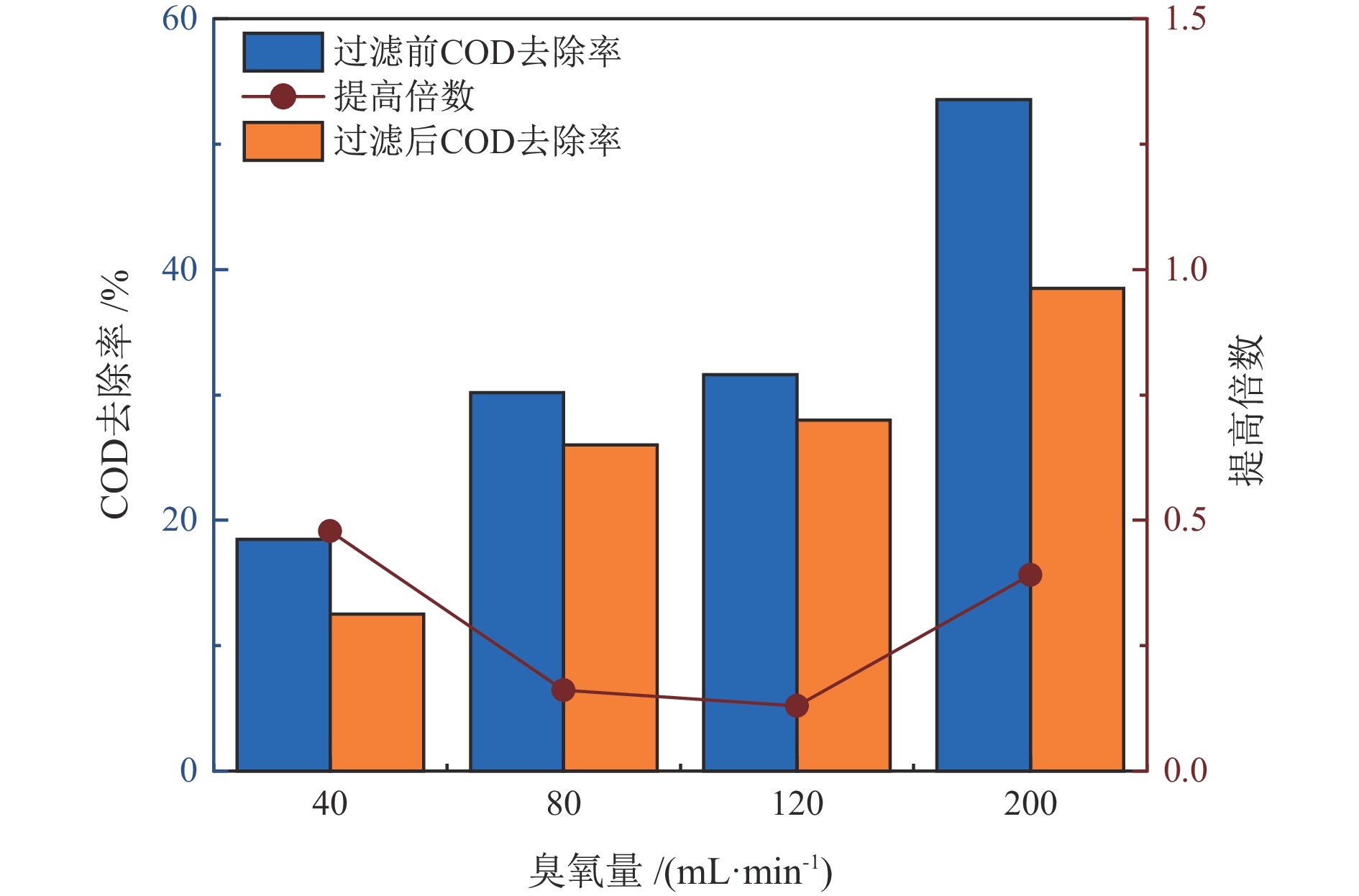
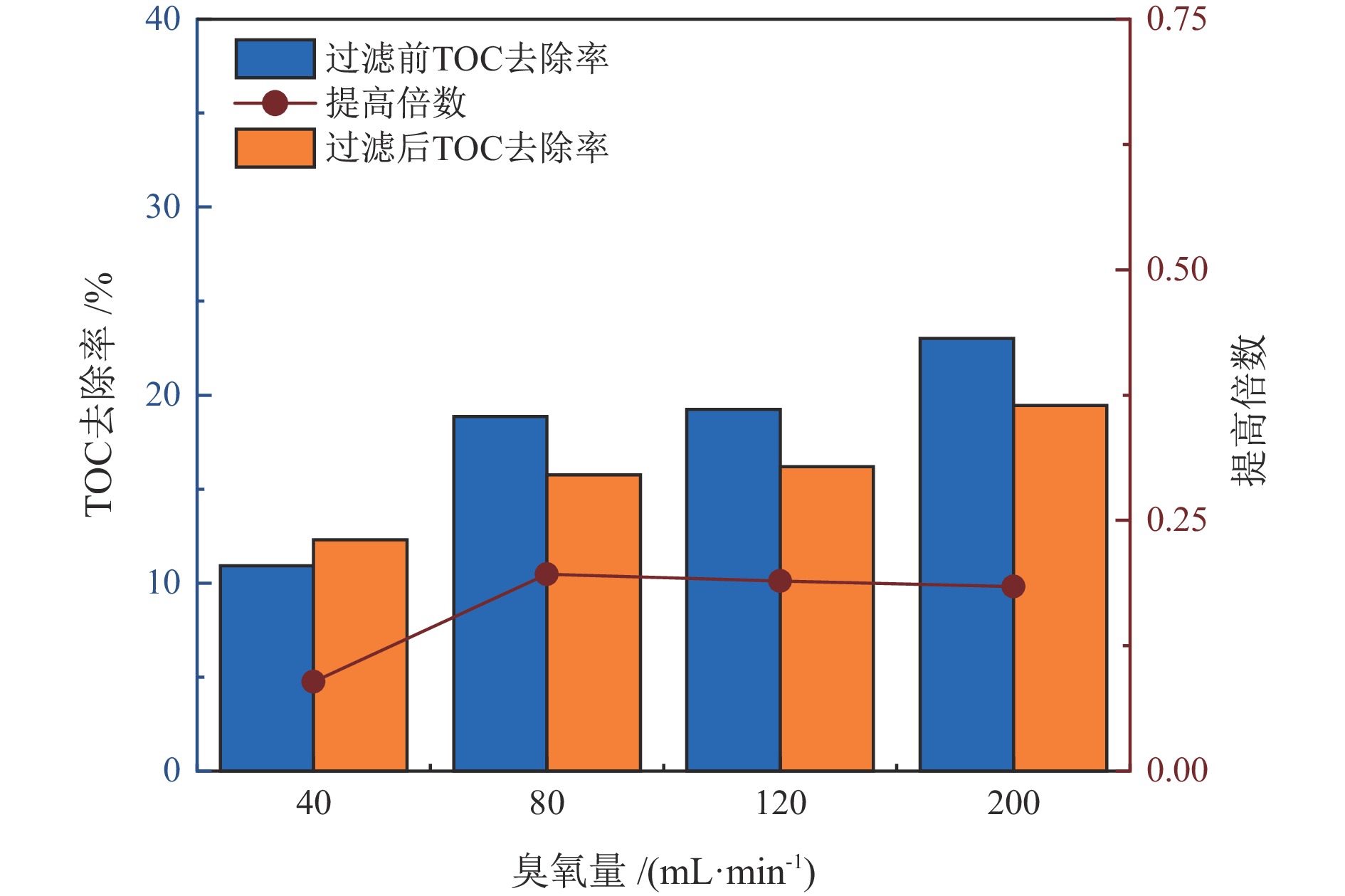
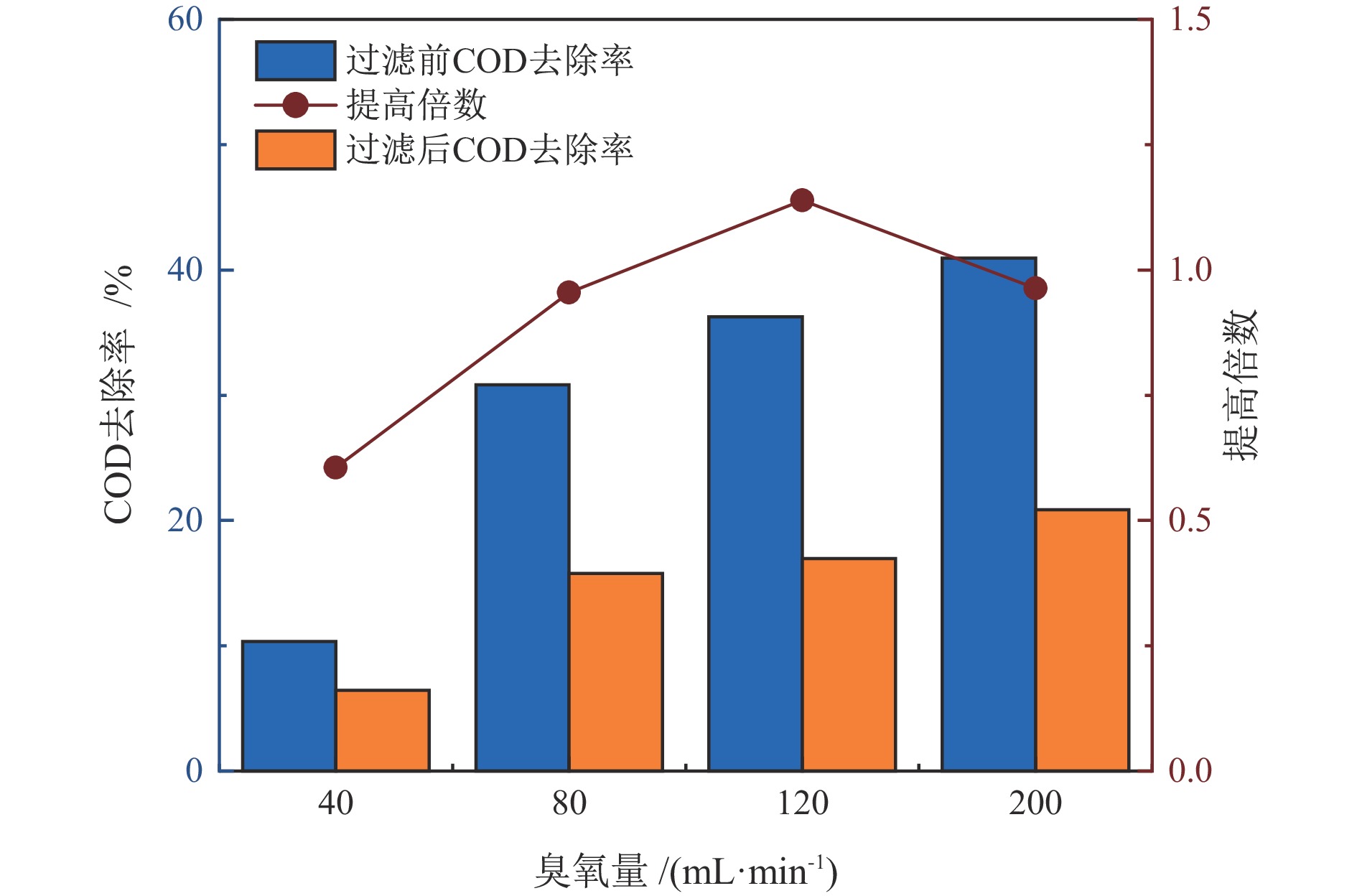
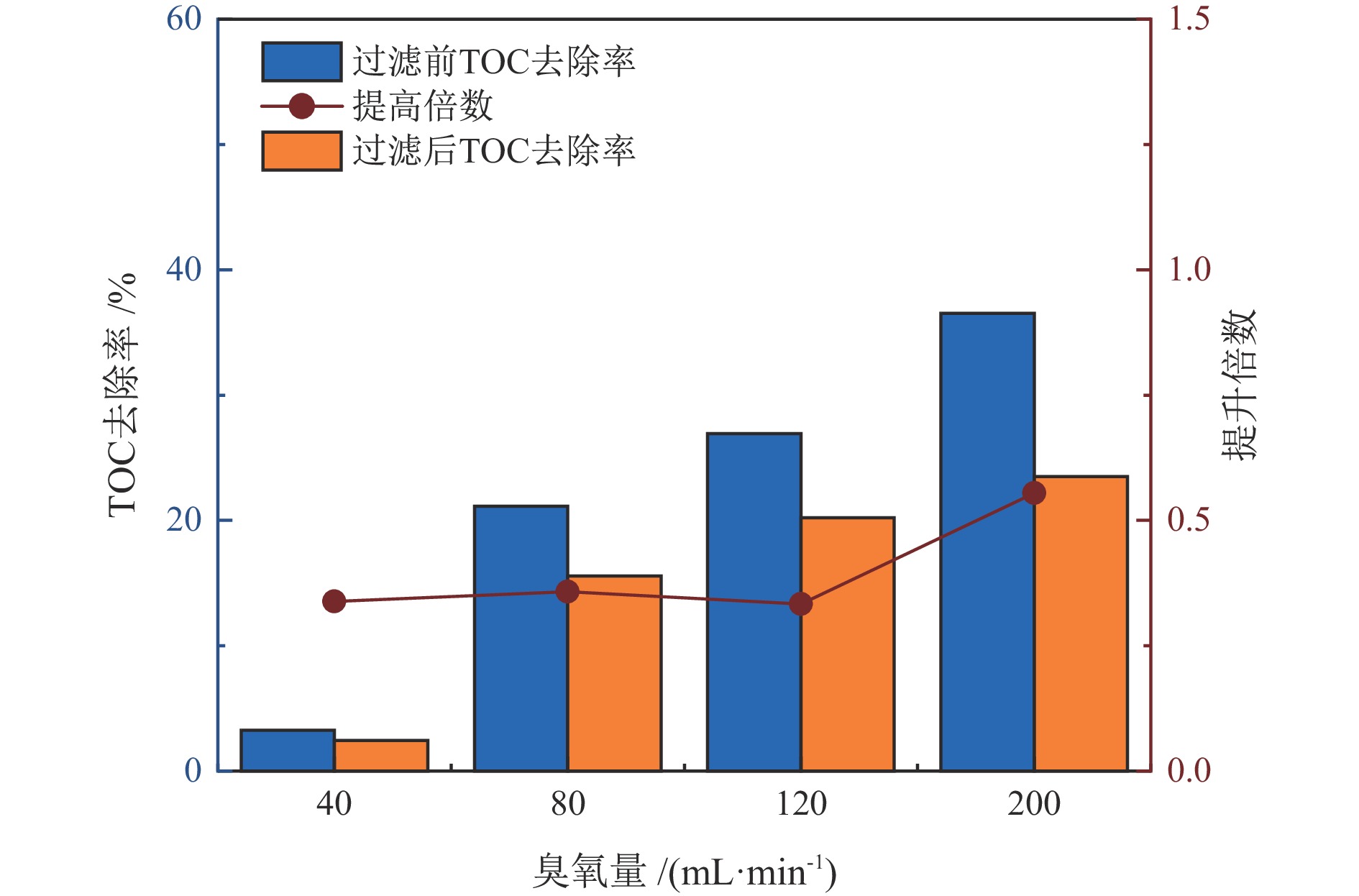
臭氧量/
(mL·min−1)COD去除提高倍数 TOC去除提高倍数 铅精矿 锌精矿 尾矿 铅精矿 锌精矿 尾矿 40 1.13 0.48 0.60 0.41 0.09 0.34 80 1.12 0.17 0.95 0.42 0.20 0.36 120 0.93 0.13 0.14 0.49 0.19 0.33 200 0.78 0.39 0.96 0.62 0.18 0.55 表 3 处理后水回用闭路实验结果
Table 3. Results of closed−circuit experimental by using the treated overflow water
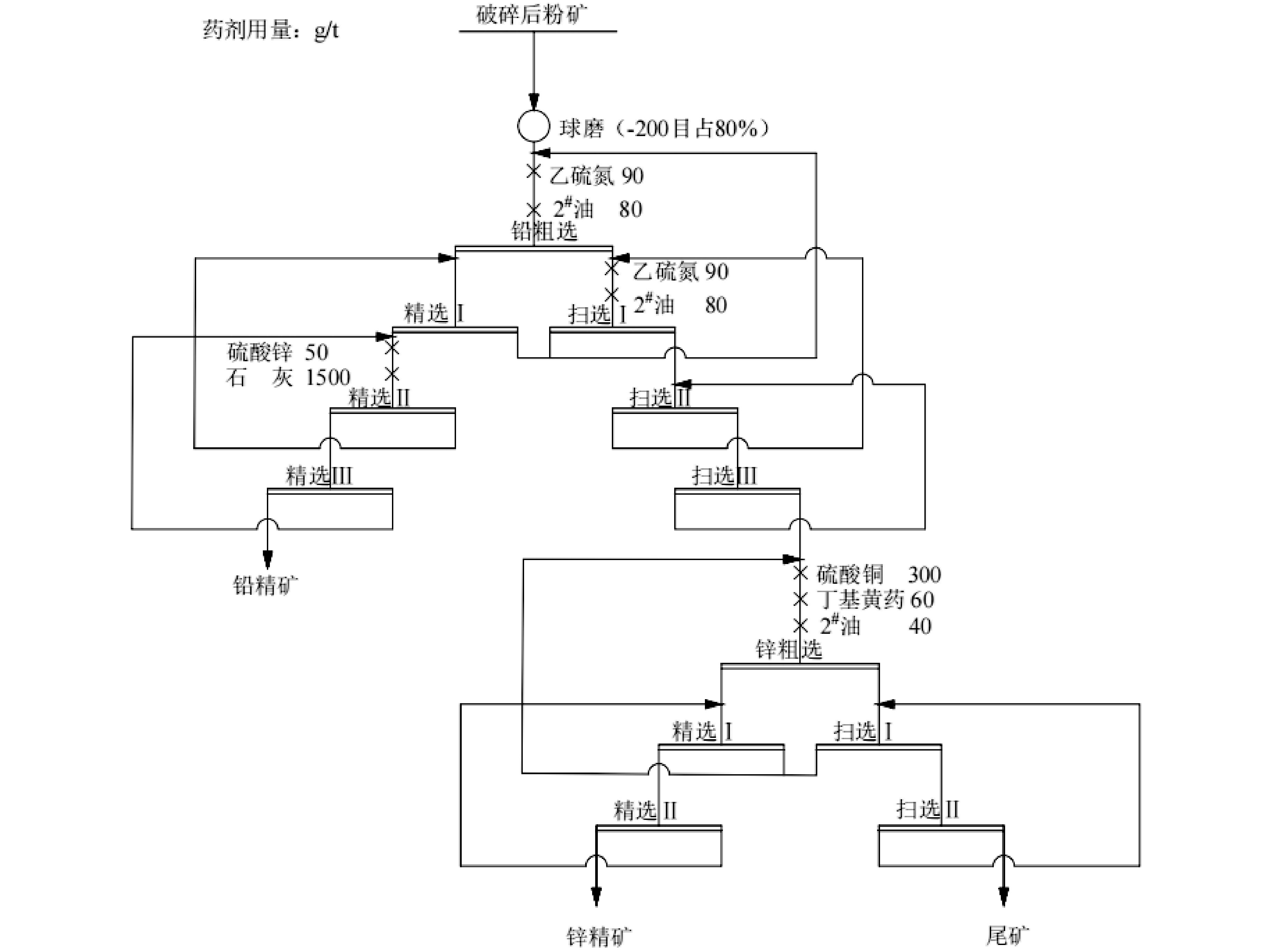
/% 水样 产品 产率 品位 回收率 Pb Zn Pb Zn 清水 铅精矿 5.83 70.95 2.58 92.74 2.98 锌精矿 10.42 0.83 45.35 1.94 93.57 尾矿 83.75 0.28 0.21 5.32 3.44 原矿 100.00 4.46 5.05 100.00 100.00 臭氧直接处理 铅精矿 5.90 69.93 2.31 92.51 2.69 锌精矿 10.65 0.88 43.69 2.10 92.14 尾矿 83.45 0.29 0.31 5.39 5.16 原矿 100.00 4.46 4.05 100.00 100.00 过滤后臭氧处理 铅精矿 6.32 63.31 3.42 89.71 4.28 锌精矿 10.83 1.01 40.69 2.45 87.26 尾矿 82.85 0.42 0.52 7.83 8.46 原矿 100.00 4.46 5.05 100.00 100.00 溢流水直接回用 铅精矿 6.95 56.59 3.81 88.18 5.24 锌精矿 11.39 1.42 39.21 3.62 85.33 尾矿 81.66 0.48 0.58 8.19 9.42 原矿 100 0.46 5.05 100.00 100.00 -
[1] ZENG P, WANG C, LI M, et al. Volatilization behavior of lead, zinc and sulfur from flotation products of low−grade Pb−Zn oxide ore by carbothermic reduction[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 433: 119185. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2023.119185
[2] PAN Z, XIONG J, CUI Y, et al. Effect mechanism of carbonaceous materials on the flotation separation of lead–zinc ore[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 294: 121101. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121101
[3] 杨富垒, 周毅, 杨波. 我国铅锌矿尾矿的资源特征及综合利用研究进展[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2024, 44(4): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2024.04.001
YANG F L, ZHOU Y, YANG B. Research progress on resource characteristics and comprehensive utilization of lead−zinc mine tailings in China[J]. Environmental Protection and Circular Economy, 2024, 44(4): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2024.04.001
[4] LI G, ZHANG Z, WEI Q, et al. Study on flotation recovery of typical carbon−bearing lead−zinc sulphide ore in Guizhou with pre−decarbonization[J]. Geochemistry, 2024: 126096.
[5] JO K, JE J, LEE D, et al. Prediction of multi−stage froth flotation efficiency of complex lead–zinc sulfide ore using an integrated ensemble neural network–random forest model[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2024, 210: 108669. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2024.108669
[6] 吕超, 张晶, 谢峰, 等. 难选高硫低品位硫化铅锌矿分选工艺研究与探讨[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2024(4): 77−84.
LYU C, ZHANG J, XIE F, et al. Research and discussion on a separation process of refractory high−sulfur low−grade lead−linc sulfide ore[J] Nonferrous Metals(Mineral Processing Section), 2024(4): 77−84.
[7] FALCONI I B A, BOTELHO A B, BALTAZAR M D P G, et al. An overview of treatment techniques to remove ore flotation reagents from mining wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(6): 111270. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111270
[8] 谢宝俊, 李兴东, 夏楷. 应用异相金属催化剂去除浮选废水中TOC试验[J]. 金属矿山, 2023(6): 255−261.
XIE B J, LI X D, XIA K. Study on removal of TOC from flotation circulating water by heterogeneous metal catalyst[J]. Metal Mine, 2023(6): 255−261.
[9] CHEN W, HE H, LIANG J, et al. A comprehensive review on metal based active sites and their interaction with O3 during heterogeneous catalytic ozonation process: Types, regulation and authentication[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 443: 130302. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130302
[10] YANG C, JIN X, GUO K, et al. Simultaneous removal of organics and ammonia using a novel composite magnetic anode in the electro−hybrid ozonation−coagulation (E−HOC) process toward leachate treatment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 439: 129664. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129664
[11] 袁少鹏, 吴念鹏, 陈翔, 等. 臭氧催化氧化系统在膜法有机浓水深度处理中的应用[J]. 净水技术, 2024, 43(1): 89−94.
YUAN S P, WU N P, CHEN X, et al. Application of catalytic ozonation system in advanced treatment of organic concentrated water by membrane method[J] Water Purification Technology, 2024, 43(1): 89−94.
[12] WU Y, LI Y, ZHANG H, et al. Application of natural mineral materials in advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(2): 111885. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.111885
[13] FU P F, WANG L, LIN X, et al. Ozonation of recalcitrant O−isopropyl−N−ethylthionocarbamate catalyzed by galena in flotation effluents and its dissolution behaviors[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 165: 106859. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106859
[14] HU J, WANG Q, WANG Y, et al. Enhanced ozonation of nitrobenzene in water using natural iron ores: Efficiencies, mechanisms and stability[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2024, 61: 105315. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.105315
[15] 林小凤, 傅平丰, 马艳红, 等. 矿物催化臭氧氧化乙硫氨酯的效率和矿化行为研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(1): 1−7.
LIN X F, FU P F, MA Y H, et al. Removal efficiency and mineralization in catalytic ozonation of O−isopropyl−N−ethyl thionocarbamate minerals in flotation wastewaters[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(1): 1−7.
[16] JING G G, MENG X, Chen J, et al. Electrocoagulation in a packed aluminium scraps anode reactor for mineral processing wastewater treatment[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2023, 202: 108231. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2023.108231
[17] WANG X J, CHEN M X, MA L Y, et al. Degradation of residual xanthates in mineral processing wastewater−A review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2024, 212: 108717.
[18] 刘楚玉, 黄自力, 袁晨光, 等. 磁性活性炭的制备及其对选矿废水中丁基黄药的去除研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2022, 42(3): 70−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2022.03.016
LIU C Y, HUANG Z L, YUAN C G, et al. Preparation of magnetic activated carbon and its application in removal of butyl xanthate from mineral processing wastewater[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2022, 42(3): 70−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2022.03.016
-



 下载:
下载: