Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Industrial Land and Farmland Soils of Tianjin with Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure
-
摘要:
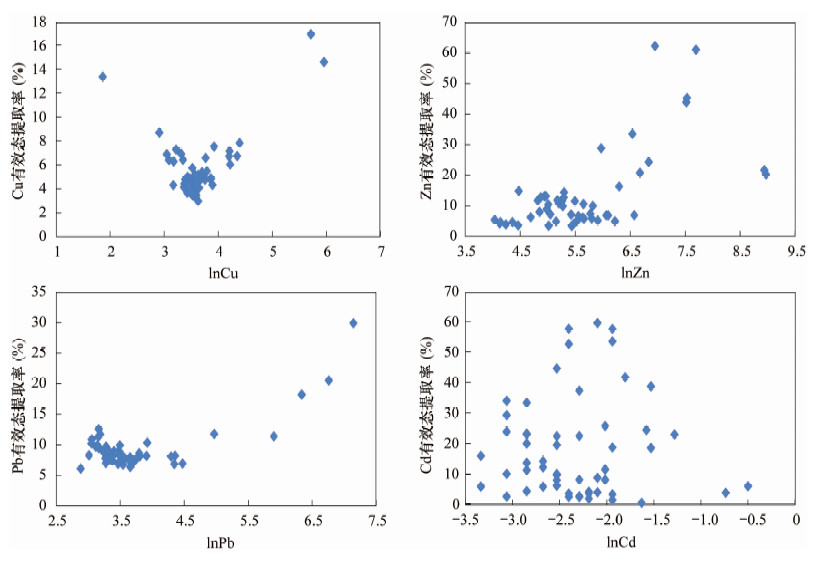
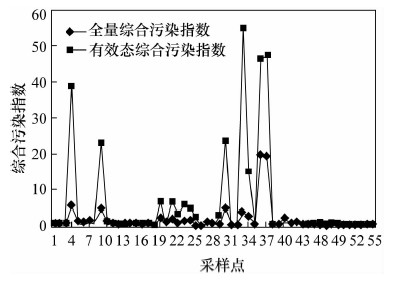
毒性淋溶提取法(TCLP)是美国法定的一种生态环境风险评价方法, 通过提取土壤中的重金属有效态判断土壤重金属污染状况和评估污染区域生态风险。本文应用TCLP法提取天津市某工业园区内及周围农田土壤中的有效态Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd, 采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法和原子吸收光谱法分别测定重金属全量和有效态, 结合单项污染指数和内梅罗综合污染指数评价了重金属生态风险。结果表明:研究区Zn是首要污染物, 主要来源于镀锌厂、金属制品厂和电镀厂, 其次是Pb和Cu污染, Cd无污染; Pb、Zn可能具有同源性或伴生关系; 大部分土壤处于安全水平, 重金属污染率不到30%, 但农田土壤出现了Zn的轻度污染。重金属全量是影响重金属有效态含量较大的因素, 当Zn全量大于环境质量标准限值(300 mg/kg), Pb全量大于80 mg/kg时, 有效态Zn、Pb与其全量均呈正相关。因此, 可以使用TCLP法将土壤重金属全量与有效态进行量化评价重金属生态风险。
-
关键词:
- 毒性淋溶提取法(TCLP) /
- 土壤 /
- 重金属有效态 /
- 生态风险
Abstract:Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) is a currently recognized method by the USA for evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soils, by extracting the effective state of heavy metals in soils to evaluate the degree of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk of the pollution area. In this study, the TCLP method was used for extracting the effective state of heavy metals in industrial land and farmland in Tianjin. The total heavy metals and the effective state of heavy metals were measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) and Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS), respectively. Single Pollution Index and Comprehensive Pollution Index were used for the ecological risk assessment of heavy metal. Results show that Zn is the primary pollutant, which comes from galvanizing and metal products factories, and electroplating plants. Secondary to Zn pollution is the Pb and Cu pollution but no pollution of Cd. Pb and Zn may have the same source or alternatively Pb is associated with Zn. Most of the soil is safe with heavy metal pollution rates of less than 30%, but the farmland is slightly polluted by Zn. Total heavy metals is the main influence for the effective state of heavy metal. When Zn concentration is more than the environmental quality standard limits (300 mg/kg) and Pb concentration is more than 80 mg/kg, effective states of Zn and Pb show a positive correlation with total metals. Therefore, TCLP method can be used to quantify the total and effective state of heavy metals in soil.
-

-
表 1 重金属全量和有效态含量分析结果
Table 1. Anlaytical results of total heavy metals and their bioavailable states
统计项目 Cu
全量Pb
全量Zn
全量Cd
全量有效态
Cu有效态
Pb有效态
Zn有效态
Cd平均值(mg/kg) 48.8 90.2 637 0.108 3.90 15.7 155 0.019 标准差(mg/kg) 60.5 213 1455 0.096 9.99 56.9 376 0.021 变异系数(%) 124 236 229 88.8 256 362 242 113 偏度 4.84 4.40 4.43 3.46 5.01 5.51 3.06 1.49 峰度 24.0 20.3 20.0 14.3 24.4 32.8 8.73 1.16 最小值(mg/kg) 6.45 17.9 56.8 0.030 0.866 1.09 2.60 0.001 最大值(mg/kg) 388 1268 7820 0.590 57.0 379 1644 0.078 百分位数
(mg/kg)25% 30.6 26.6 140 0.050 2.31 12.4 2.31 4.38×10 -3 50% 35.2 32.1 227 0.080 2.67 19.2 2.67 9.80×10 -3 75% 42.8 44.2 431 0.120 3.59 49.7 3.59 3.11×10 -2 表 2 单项污染指数评价结果
Table 2. The evaluation results of single pollution index
重金属元素 超标率
(%)重污染
比重(%)中度污染
比重(%)轻度污染
比重(%)轻微污染
比重(%)Cu全量 3.64 - 100 - - Pb全量 5.46 33.3 33.3 33.4 - Zn全量 34.5 21.1 10.5 15.8 52.6 Cd全量 0 - - - - 有效态Cu 3.64 - 100 - - 有效态Pb 10.0 40 10 - 50 有效态Zn 38.2 42.9 14.3 9.5 33.3 有效态Cd 0 - - - - 注:重金属全量的评价标准依据《土壤环境质量标准》(GB15618—1995) 二级标准;重金属TCLP有效态的评价标准依据国际标准。 表 3 重金属有效态与土壤理化性质和重金属全量之间的相关性分析结果
Table 3. The correltionship between bioavailability of heavy metals with total content and the physical-chemical properties of soil
元素 Pb全量 Cu全量 Zn全量 Cd全量 有效态Cu 有效态Zn 有效态Pb 有效态Cd 有机质 pH值 Pb全量 1 0.056 0.398** 0.192 0.007 0.419** 0.974** 0.269* 0.443** -0.243 Cu全量 1 0.082 0.013 0.987** 0.196 0.062 0.192 0.180 -0.008 Zn全量 1 0.127 0.054 0.910** 0.319* 0.200 -0.027 -0.029 Cd全量 1 0.010 0.146 0.123 0.365** 0.433** 0.148 有效态Cu 1 0.160 0.015 0.163 0.120 0.007 有效态Zn 1 0.371** 0.129 0.082 -0.090 有效态Pb 1 0.208 0.435** -0.280* 有效态Cd 1 0.182 -0.149 有机质 1 -0.145 pH 1 注:标注“**”表示在0.01置信水平内相关;标注“*”表示0.05置信水平内相关。 -
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] -



 下载:
下载: