Speciation and Translocation Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metals in the Water Level Fluctuating Zone of Pengxi River in Three Gorges Reservoir Area
-
摘要: 消落带是水域与陆地的过渡地带,对水环境有着至关重要的影响。本文以三峡库区消落带面积最大的澎溪河流域作为研究区域,采集消落带土壤及其沿岸土壤样品,分析重金属形态分布特征,并使用地质累积指数法和风险评价准则(RAC)对重金属污染程度及生态风险进行评价。研究表明,消落带土壤中Pb、Cu、Cr、Cd、Zn和Ni平均含量分别为68.70、36.96、55.10、0.68、108.26、31.68 mg/kg,污染程度依次为Cd > Pb > Zn > Cu > Ni > Cr,以Cd和Pb污染较为突出,普遍高于长江干流土壤,远高于重庆地区土壤。Cd的RAC值为20.62%,呈中等环境风险;其形态稳定性最差,以可还原态和酸提取态为主。Pb、Cu、Cr、Zn、Ni的RAC值为5.45%~10.0%,环境风险较低;且均以残渣态为主,占总量的54.69%~83.05%。以消落带沿岸土壤为对照,消落带形成后土壤中各重金属总量均有不同程度升高,且不同重金属在其增量部分的形态存在差异,Cr和Ni的增量部分以残渣态为主,Cd、Pb、Zn的增量以非残渣态为主。研究发现,由于受到水域与陆地污染源的双重影响,澎溪河流域重金属具有由沿岸向消落带沉积富集的趋势。Abstract: The water level fluctuating zone (WLFZ) is a transition belt between the water area and the terrestrial habitat that plays an indispensable role in the water environment. Pengxi River basin with the largest WLFZ area was chosen as the study area. The soils in the WLFZ and the coastal soil samples were collected to analyze the speciation characteristics of heavy metals. Besides, we have evaluated the pollution degree of such metal contaminants as well as the levels of the potential ecological risks with the methods of geo-accumulation index and the risk assessment code (RAC). The average contents of Pb, Cu, Cr, Cd, Zn and Ni in the soils of WLFZ were 68.70, 36.96, 55.10, 0.68, 108.26 and 31.68 mg/kg, respectively. The pollution degree is in the order of Cd > Pb > Zn > Cu > Ni > Cr, among which Cd and Pb pollution were prominent, generally higher than that in soils of mainstream of the Yangtze River and much higher than that in soils of Chongqing area. The RAC value of Cd was 20.62%, showed moderate pollution, and was mainly found in exchangeable and carbonates fraction. The RAC value of Pb, Cu, Cr, Zn and Ni were 5.45%-10.0%, showed low pollution, and were mainly found in residual fraction, accounting for 54.69%-83.05% in the total amount. Compared with the coastal soils, the content of heavy metals was increased in WLFZ soil, but the increased amount of each heavy metal was different. According to fractionation studies, residual fraction was the main part of the increased Cr and Ni. Nevertheless, the main part of the increased Cd, Pb and Zn were found in non-residual fractions. The results of our investigation indicated that under the effect of the terrestrial and aquatic pollution sources, the heavy metals contaminants in the Pengxi River basin were translocated from the coastal soil to the WLFZ, then deposited and enriched.
-

-
表 1 澎溪河流域土壤中重金属的平均含量
Table 1. Average content of heavy metals in soils of Pengxi river
采样区域 项目 Pb Cu Cr Cd Zn Ni 消落带沿岸土壤 含量范围(mg/kg) 45.00~82.51 16.74~37.57 30.57~55.01 0.42~0.57 73.85~101.11 21.93~29.69 含量均值(mg/kg) 64.44 27.18 43.03 0.51 86.61 25.81 标准差(mg/kg) 13.20 7.84 9.60 0.05 8.64 2.24 变异系数 20.48 28.83 22.30 10.33 9.97 8.70 消落带 土壤 含量范围(mg/kg) 51.61~83.16 24.49~51.12 37.19~72.82 0.55~0.93 89.81~127.51 28.79~35.02 含量均值(mg/kg) 68.70 36.96 55.10 0.68 108.26 31.68 标准差(mg/kg) 11.76 8.19 10.63 0.13 12.10 2.58 变异系数 17.12 22.16 19.30 19.66 11.18 8.14 土壤环境 质量标准 Ⅰ级(mg/kg) 35 35 90 0.2 100 40 Ⅱ级(mg/kg) 300 100 200 0.3 250 50 Ⅲ级(mg/kg) 500 400 300 1 500 200 重庆地区 土壤[17] 背景值(mg/kg) 28.2 24.5 76.7 0.269 90.7 34.8 三峡库区 消落带土壤[8] 背景值(mg/kg) 42.89 35.70 44.72 0.49 88.09 - 表 2 土壤中重金属地质累积指数(Igeo)评价特征值
Table 2. Geo-accumulation index (Igeo) of heavy metals in soils
采样点 Pb Cu Cr Cd Zn Ni 沿岸 消落带 沿岸 消落带 沿岸 消落带 沿岸 消落带 沿岸 消落带 沿岸 消落带 渠马 0.88 0.98 -0.10 0.45 -1.56 -1.22 1.16 1.65 -0.33 0.13 -0.57 -0.34 猫爪子 1.18 1.22 -0.06 0.23 -1.13 -0.93 1.50 2.21 -0.43 0.21 -0.74 -0.35 高阳 0.33 0.53 -1.16 -0.61 -1.94 -0.68 1.30 2.07 -0.51 0.28 -0.82 -0.51 张王庙 1.20 1.21 -0.72 0.03 -1.44 -1.65 1.31 1.54 -0.30 -0.22 -1.01 -0.61 康家沟 0.66 0.74 0.00 0.01 -1.80 -1.00 1.40 1.44 -0.05 0.05 -0.80 -0.52 黄石 0.60 0.68 -0.79 -0.32 -1.70 -1.26 1.07 1.59 -0.10 -0.01 -0.84 -0.57 彭桥 0.99 1.10 -0.60 -0.19 -1.16 -1.20 1.47 1.80 -0.23 0.02 -0.69 -0.37 河口 0.71 0.91 -0.71 -0.02 -1.09 -0.95 1.45 1.65 -0.30 -0.17 -0.78 -0.62 Igeo平均值 0.82 0.92 -0.52 -0.05 -1.48 -1.11 1.33 1.74 -0.28 0.04 -0.78 -0.48 表 3 消落带土壤中重金属各形态对其总量增量的贡献值
Table 3. The contribution of different fractions to the increased amount of heavy metals in WFLZ soils
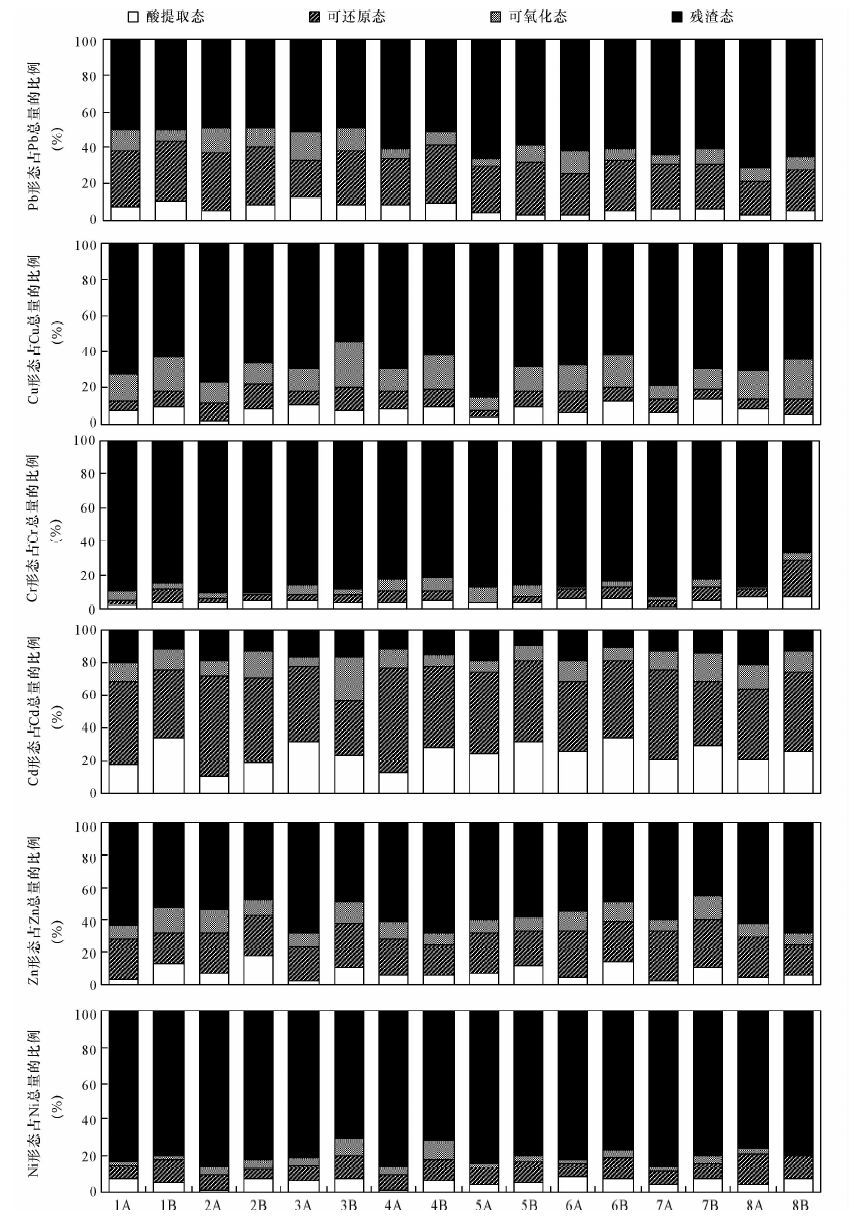
形态 重金属各形态对其总量增量的贡献值(%) Pb Cu Cr Cd Zn Ni 酸提取态 23.07 18.17 7.15 47.53 34.75 15.12 可还原态 82.06 16.19 22.00 24.42 16.78 22.56 可氧化态 -3.52 31.95 5.60 27.98 16.00 10.33 残渣态 -1.62 33.69 65.25 0.08 32.48 51.99 注:表中的负值表示此形态金属相比对照是减少的。 -
[1] Soodana R K,Pakadeb Y B,Nagpala A,et al.Analytical Techniques for Estimation of Heavy Metals in Soil Ecosystem:A Tabulated Review[J].Talanta,2014,125:405-410. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.02.033
[2] Shao X X,Huang B,Zhao Y C,et al.Impacts of Human Activities and Sampling Strategies on Soil Heavy Metal Distribution in a Rapidly Developing Region of China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2014,104:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.02.007
[3] Yao Z,Li J H,Xie H H,et al.Review on Remediation Technologies of Soil Contaminated by Heavy Metals[J].Procedia Environmental Sciences,2012,16:722-729. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.099
[4] Bao Y H,Gao P,He X B.The Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of Three Gorges Reservoir-A Unique Geomor-phological Unit[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2015,150:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.07.005
[5] 王图锦,胡学斌,吉芳英,等.三峡库区淹没区土壤重金属形态分布及其对水质影响[J].环境科学研究,2010,23(2):158-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201002004.htm
Wang T J,Hu X B,Ji F Y,et al.Chemical Fraction Composition Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Submerged Soil of Three Gorges Reservoir Area and Effect on Water Quality[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2010,23(2):158-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201002004.htm
[6] 曹琳,吉芳英.三峡库区消落带干湿交替表层沉积物磷分布特征[J].地球与环境,2013,41(2):126-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201302006.htm
Cao L,Ji F Y.Phosphorus Distribution Characteristics in Dry-Wet Alteration Sediment of Fluctuation Zone in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J].Earth and Environ-ment, 2013,41(2):126-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201302006.htm
[7] 朱宏伟,贺秀斌,胡云华,等.三峡库区消落带土壤磁性变化规律及成因探讨[J].现代地质,2014,28(4):859-866. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201404024.htm
Zhu H W,He X B,Hu Y H,et al.Discussion of Characteristics and Origin of Soil Magnetism Changes in the Three-Gorge Reservoir Riparian Zone[J].Geoscience,2014,28(4):859-866. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201404024.htm
[8] Chen Y,Li S Y,Zhang Y L,et al.Assessing Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Water-Level-Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir,China[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,191:366-372. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.090
[9] 胥焘,王飞,郭强,等.三峡库区香溪河消落带及库岸土壤重金属迁移特征及来源分析[J].环境科学,2014,305(4):1502-1508. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201404049.htm
Xu T,Wang F,Guo Q,et al.Transfer Characteristic and Source Identification of Soil Heavy Metals from Water-Level-Fluctuating Zone along Xiangxi River,Three-Gorges Reservoir Area[J].Environmental Science,2014,305(4):1502-1508. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201404049.htm
[10] 张成,陈宏,孙荣国,等.三峡水库消落带不同水位高程土壤汞风险评价[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(1):242-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201401046.htm
Zhang C,Chen H,Sun R G,et al.Risk Assessment of Mercury in Soil at Different Water-Level Altitudes in Drawdown Areas of Three Gorges Reservior[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,28(1):242-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201401046.htm
[11] 余杨,王雨春,周怀东,等.三峡库区蓄水初期大宁河重金属食物链放大特征研究[J].环境科学,2013,34(10):3847-3853. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201310018.htm
Yu Y,Wang Y C,Zhou H D,et al.Biomagnification of Heavy Metals in the Aquatic Food Chain in Daning River of the Three Gorges Reservoir during Initial Impoundment[J].Environmental Science,2013,34(10):3847-3853. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201310018.htm
[12] 张晨光,徐德星,张乃明,等.大宁河回水区消落带土壤磷释放动力学研究[J].土壤通报,2011,42(5):1159-1164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201105024.htm
Zhang C G,Xu D X,Zhang N M,et al.Phosphorus Release Kinetics of the Soils from the Backwater-Fluctuating Zones of Daning River[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2011,42(5):1159-1164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201105024.htm
[13] 许超,夏北成,吴海宁,等.酸性矿山废水污灌区水稻土重金属的形态分布及生物有效性[J].环境科学,2009,30(3):900-906. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200903050.htm
Xu C,Xia B C,Wu H N,et al.Speciation and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Paddy Soil Irrigated by Acid Mine Drainage[J].Environmental Science,2009,30(3):900-906. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200903050.htm
[14] Forstner U.Sediments and Environmental Geochemistry:Selected Aspects and Case Histories[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag,1990:311-338.
[15] 唐将,钟远平,王力.三峡库区土壤重金属背景值研究[J].中国生态农业学报,2008,16( 4) :848-852. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00848
Tang J,Zhong Y P,Wang L.Background Value of Soil Heavy Metal in the Three Gorges Reservoir District[J].Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2008,16(4):848-852. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00848
[16] Saleem M,Iqbal J,Shah M H.Geochemical Speciation,Anthropogenic Contamination,Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Selected Metals in Freshwater Sediments-A Case Study from Mangla Lake,Pakistan[J].Environmental Nanotechnology,Monitoring & Management,2015,4:27-36. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2047769469&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] Chen H Y,Teng Y G,Lu S J,et al.Contamination Features and Health Risk of Soil Heavy Metals in China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2015,512-513:143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
[18] Zhao S,Feng C H,Wang D X,et al.Salinity Increases the Mobility of Cd,Cu,Mn,and Pb in the Sediments of Yangtze Estuary:Relative Role of Sediments' Properties and Metal Speciation[J].Chemosphere,2013,91:977-984. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.001
[19] Yang Z F,Wang Y,Shen Z Y,et a1.Distribution and Speciation of Heavy Metals in Sediments from the Mainstream,Tributaries,and Lakes of the Yangtze River Catchment of Wuhan,China[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,166:1186-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.034
[20] Wei X,Han L F,Gao B,et a1.Distribution,Bioavai-lability,and Potential Risk Assessment of the Metals in Tributary Sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir:The Impact of Water Impoundment[J].Ecological Indicators,2016,61:667-675. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.018
[21] 钟晓兰,周生路,黄明丽,等.土壤重金属的形态分布特征及其影响因素[J].生态环境学报,2009,18 (4):1266-1273. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200904016.htm
Zhong X L,Zhou S L,Huang M L,et al.Chemical Form Distribution Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metals and Its Influencing Factors[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2009,18(4):1266-1273. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200904016.htm
[22] 陈媛,郭秀锐,程水源,等.基于SWAT模型的三峡库区流域污染物来源分析及重点控制区域识别[J].北京工业大学学报,2013,39(5):761-768. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201305019.htm
Chen Y,Guo X R,Cheng S Y,et al.Pollutant Source Analysis and Identification of Prior Control Areas in Three Gorges Reservoir Based on SWAT Model[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2013,39(5):761-768. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201305019.htm
[23] 高银超,鲍玉海,唐强,等.基于AnnAGNPS模型的三峡库区小江流域非点源污染负荷评价[J].长江流域资源与环境,2012,21(1):119-126. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY2012S1022.htm
Gao Y C,Bao Y H,Tang Q,et al.Applying AnnAGNPS to Estimate Non-point Pollution Loading from Xiao Jiang Basin in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J].Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2012,21(1):119-126. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY2012S1022.htm
-



 下载:
下载:
