Study on Accuracy of Quantitative Analysis of Minerals under Rotating Stage Microscopy
-
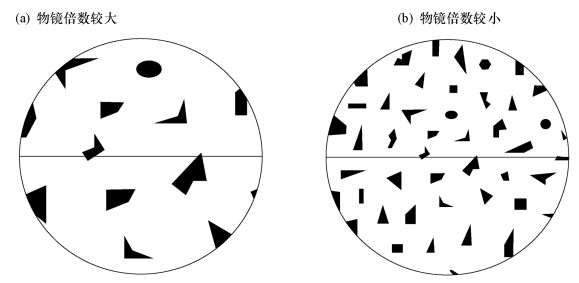
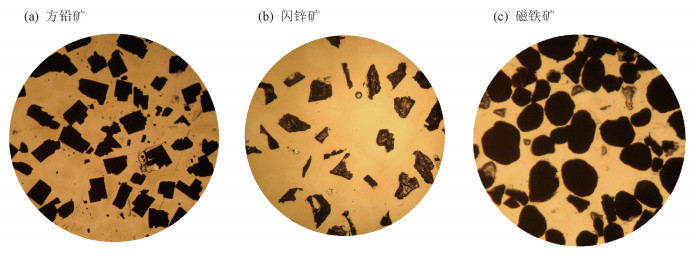
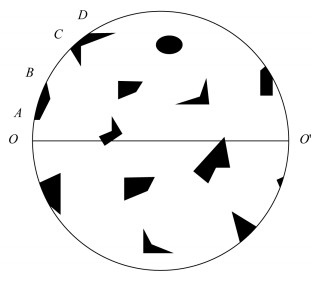
摘要: 光学显微镜矿物定量方法简单、结果可靠,被广泛应用于工艺矿物学和岩矿鉴定工作中。“线测法”测试速度快,效率高,并且适用于细粒矿物颗粒,在应用中占有重要的地位。但是常规的测试线具有方向同一性的特征,不能很好地处理待测矿物颗粒“择优取向”的问题。针对该问题,本文阐述了一种通过旋转载物台进行镜下矿物定量的方法。主要工作原理为:系列圆周线穿切各待测矿物颗粒截线长度比等于其体积比。主要测试过程为:转动载物台一周,测定待测矿物颗粒与视域周边相交的各段圆周截线所占的包含角之和(ΔK)。观测一定数量的视域(N),计算质量百分含量(W)=[∑ΔK/(N×360)]·(δ/Δ)×100%。经理论分析,并对方铅矿、闪锌矿和磁铁矿光片进行了检验,结果表明:旋转载物台矿物定量工作量低、简单易行、精度较高,与传统“线测法”测试结果差值小于±5%,并且可以有效地解决待测矿物颗粒“择优取向”对测试结果的不利影响。Abstract: Mineral quantitative analysis by optical microscope is simple and reliable, and has been widely used in process mineralogy and rock-mineral determination. The line measurement method is fast and efficient, and is suitable for fine-grained mineral particles, which plays an important role in the application. However, the conventional test line has the characteristics of directional identity, and cannot deal with the problem of 'preferential orientation' of the analyzed mineral particles. To solve this problem, a new mineral quantitative method by rotating the platform of an optical microscope was conducted. The main principle is that the length ratio of the circular cutting lines of different mineral particles is equal to their volume ratio. The main test process of the method is as follows:rotating the objective table for a circle and testing the angles (ΔK) that the circular cutting line contained, which is intersected by the mineral particles and the visual field under the microscope. By testing a certain number of visual fields (N) and calculating weight percentage (W), the percent content is acquired by the equation W=[∑ΔK/(N×360)]·(δ/Δ)×100%. After theoretical analysis, the galena, sphalerite, and magnetite thin sections were examined. The results show that the new mineral quantitative method is simple, accurate, and the difference value of the test results is less than ±5% compared with the conventional line measurement method. In addition, this method can be used to effectively solve the negative effect of 'preferential orientation' on the test results.
-
Key words:
- rotate the objective table /
- microscope /
- mineral quantitation /
- accuracy
-

-
表 1 显微镜下矿物定量观测统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of mineral quantitative observation under the microscope
观测方法 方铅矿 闪锌矿 磁铁矿 体积
(%)质量
(%)体积
(%)质量
(%)体积
(%)质量
(%)线测法 36.2 78.0 16.8 41.4 55.5 84.6 旋物法 32.5 75.1 14.7 37.6 56.5 85.2 差值 3.7 2.9 2.1 3.8 -1.0 -0.6 -
[1] Baum W.Ore characterization, process mineralogy and lab automation a roadmap for future mining[J].Minerals Engineering, 2014, 60:69-73. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.11.008
[2] Lotter N O, Kormos L J, Oliveira J, et al.Modern process mineralogy:Two case studies[J].Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24:638-650. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2011.02.017
[3] 黄凌云, 杨波, 童雄.贵州某铅锌尾矿工艺矿物学研究[J].昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 42(4):25-37. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98519X/201102/39102342.html
Huang L Y, Yang B, Tong X.Process mineralogy of lead-zinc tailings in Guizhou Province[J].Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 42(4):25-37. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98519X/201102/39102342.html
[4] 蒋先强, 熊文良, 曾令熙.国外某铁尾矿中稀土赋存状态研究[J].稀土, 2016, 37(6):32-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL503.001.htm
Jiang X Q, Xiong W L, Zeng L X.Study on low grade rare earth occurrences in a foreign iron tailings[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(6):32-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL503.001.htm
[5] Zheng X, Yan L, Shuang L, et al.The characteristics study of sphalerite tailings by using MLA[J].Procedia Engineering, 2015, 102:278-286. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.144
[6] 杜谷, 王坤阳, 冉敬, 等.红外光谱/扫描电镜等现代大型仪器岩石矿物鉴定技术及其应用[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(9):625-632. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/3980f0fc-b8e1-4632-be00-cf45aba72902
Du G, Wang K Y, Ran J, et al.Application of IR/SEM and other modern instruments for mineral identification[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(9):625-632. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/3980f0fc-b8e1-4632-be00-cf45aba72902
[7] Dirk S. Method Development in Automated Mineralogy[D]. Freiberg: TU Bergakademie, 2015.
Method Development in Automated Mineralogy [8] Lotter N O.Modern process mineralogy:An integrated multi-disciplined approach to flowsheeting[J].Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24:1229-1237. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2011.03.004
[9] 赵海波, 黄俊玮, 马驰, 等.河南某钨钼矿石工艺矿物学研究[J].金属矿山, 2016(9):122-126. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98519A/201401/48667647.html
Zhao H B, Huang J W, Ma C, et al.Process mineralogy research of tungsten-molybdenum ore in Henan[J]. Metal Mine, 2016(9):122-126. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98519A/201401/48667647.html
[10] 马驰, 王守敬, 海东婧, 等.内蒙古赵井沟钽铌矿工艺矿物学研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2017(6):75-78. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YKCS201305010.htm
Ma C, Wang S J, Hai D J, et al.Process mineralogy of the Zhaojinggou tantalum-niobium ore deposit in Inner Mongolia Province[J].Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(6):75-78. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YKCS201305010.htm
[11] 周姣花, 汪建宇, 顾茗心, 等.利用X射线衍射和岩矿鉴定等技术研究河南汤家坪钼矿区主要矿物标型特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(1):82-90. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.011
Zhou J H, Wang J Y, Gu M X, et al.The main mineral typomorphic characteristics of the Henan Tangjiaping molybdenum district using X-ray diffraction and rock mineral identification technology[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(1):82-90. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.011
[12] 彭艳华, 彭光菊, 贾利攀, 等.湖南宝山铅锌矿西部矿带银的工艺矿物学研究[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(5):729-737. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/6bb5114d-8c90-4b13-888f-f8006ed17d80
Peng Y H, Peng G J, Jia L P, et al.Technological mineralogy research of silver in the lead-zinc ore deposit in West Baoshan, Hunan Province[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5):729-737. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/6bb5114d-8c90-4b13-888f-f8006ed17d80
[13] Goodwin P C, Johnson B, Frevert C W.Microscopy, Im-muno-histochemistry, Digital Imaging, and Quantitative Microscopy[M].Elsevier Press, 2018:53-66.
[14] Ueda T, Oki T, Koyanaka S.Stereological correction me-thod based on sectional texture analysis for the liberation distribution of binary particle systems[J].Advanced Powder Technology, 2017, 28:1391-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2017.03.007
[15] Ueda T, Oki T, Koyanaka S.Stereological bias for sph-erical particles with various particle compositions[J].Advanced Powder Technology, 2016, 27:1828-1838. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2016.06.016
[16] de Souza D S, da Silva Assis W L, Rios P R, et al.Ste-reological analysis of the microstructure of pure iron with random nucleation[J].Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2014, 3(4):349-353. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2014.08.002
-



 下载:
下载: