Study on the Pore Structure Characteristics of Shale by Atomic Force Microscope and Energy Spectrum-Scanning Electron Microscope
-
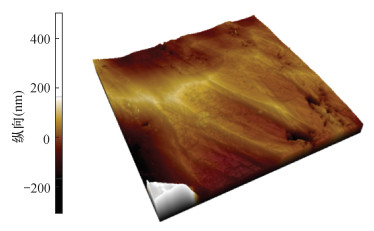
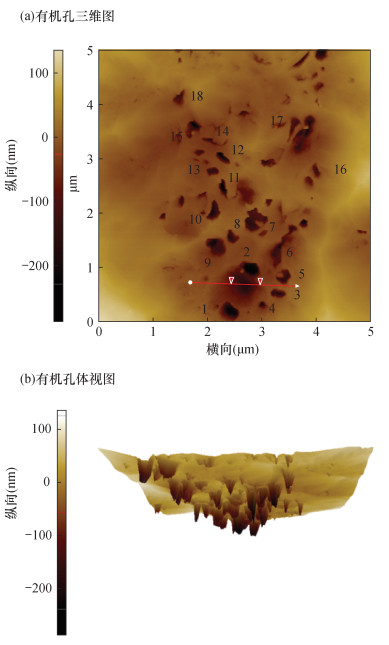
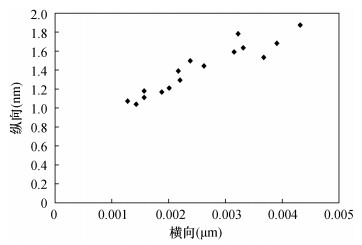
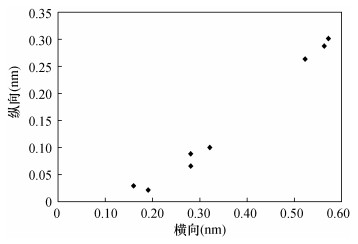
摘要: 已有研究表明页岩中纳米孔隙与组成导电膜的金颗粒处在同一量级,使得页岩中纳米孔隙在一定程度上被金颗粒掩埋,导致页岩中纳米孔隙被“二次改造”,从而无法真实观察到页岩中孔隙的形态特征;其次,由于受仪器分辨率、景深等因素的制约,无法观察到孔隙的三维展布特征。因此,如何真实地揭示纳米孔隙的空间结构特征,以及如何有效避免金颗粒对页岩储层中纳米孔隙的“二次改造”一直是微区分析的难点。本文通过扫描电镜(SEM)与原子力显微镜(AFM)方法组合观察到四川盆地龙马溪组黑色页岩中有机孔与无机孔在二维平面的分布存在较强的非均值性,孔径与孔隙的空间延展性呈现明显的正相关关系。有机孔呈蜂窝状分布,孔径主要分布在微米量级0.1~0.4μm,孔隙在三维空间呈现明显的“一体化”特征,具有较好的空间连通性;无机孔主要发育黏土矿物的层间孔隙,孔径主要分布在纳米量级16~57nm,此外见少量的矿物粒内不规则状溶蚀孔。研究认为,页岩中孔隙在二维平面的非均值性导致孔隙、喉道的分布会发生突变,从而影响储层的储集性能;页岩中孔隙在三维空间的非均值性导致页岩储层的渗透率在纵向上出现较大的差异,从而影响储层的物性特征。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDStudies have shown that the nano-pores in shale are at the same magnitude as the gold particles that make up the conductive film, and thus the pore size of nano-pores is blocked and buried by gold particles. The planar morphological characteristics of nano-pores cannot be observed due to the 'secondary transformation' of pores. Moreover, limited by the resolution and depth of field of the instrument, the spatial ductility and other structural characteristics of nano-pores cannot be observed. Therefore, how to truly reveal the spatial structure characteristics of nano-pores and how to effectively avoid the 'secondary modification' of nano-pores in shale reservoirs by gold particles has always been a difficulty in microanalysis. OBJECTIVESTo characterize the two/three dimensional structural characteristics of nano-pores in shale. METHODSAtomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to observe the pore features. RESULTSThe distribution of organic and inorganic pores in the black shale of the Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin has strong non-meanness, and the pore size and spatial ductility of the pores were significantly positively correlated. The organic pores were distributed in a honeycomb shape, with the pore size from 0.1 to 0.4μm. The pores show an obvious 'integrated' feature in the three-dimensional space and have good spatial connectivity. Inorganic pores mainly develop interlayer pores of clay minerals, and the pore size was mainly distributed between 16 and 57nm. In addition, there were a few irregular dissolution pores in mineral grains. CONCLUSIONSThe non-meanness of pores in the 2D plane of shale leads to abrupt changes in the distribution of pores and throats, which affects the reservoir performance. The non-meanness of pores in shale in three-dimensional space leads to the great difference of permeability of shale reservoir in the longitudinal direction, which affects the physical characteristics of the reservoir. -

-
表 1 原子力显微镜参数
Table 1. Parameters of atomic force microscope
扫描模式 接触模式 扫描频率
(Hz)扫描范围 Z Gain SetPoint 成像信号 快速扫描 非接触模式
(NCM)0.5 20μm×20μm 1.5 20nm Z Height 精细扫描 轻敲模式
(Taping)0.4 5μm×5μm 2 15nm Z Drive -
[1] 高波, 刘忠宝, 舒志国, 等.中上扬子地区下寒武统页岩气储层特征及勘探方向[J].石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(2):284-294.
Gao B, Liu Z B, Shu Z G, et al.Reservoir characteristics and exploration of the Lower Cambrian shale gas in the Middle-Upper Yangtze area[J].Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(2):284-294.
[2] 肖佃师, 赵仁文, 杨潇, 等.海相页岩气储层孔隙表征、分类及贡献[J].石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6):1215-1225.
Xiao D S, Zhao R W, Yang X, et al.Characterization, classification and contribution of marine shale gas reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6):1215-1225.
[3] 姜振学, 唐相路, 李卓, 等.川东南地区龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构全孔径表征及其对含气性的控制[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(2):126-134.
Jiang Z X, Tang X L, Li Z, et al.The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the southeastern Sichuan Basin[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2):126-134.
[4] 朱炎铭, 王阳, 陈尚斌, 等.页岩储层孔隙结构多尺度定性-定量综合表征:以上扬子海相龙马溪组为例[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(1):154-163.
Zhu Y M, Wang Y, Chen S B, et al.Qualitative-quantitative multiscale characterization of pore structures in shale reservoirs:A case study of Longmaxi Formation in the Upper Yangtze area[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1):154-163.
[5] 蒋裕强, 付永红, 谢军, 等.海相页岩气储层评价发展趋势与综合评价体系[J].天然气工业, 2019(10):1-9.
Jiang Y Q, Fu Y H, Xie J, et al.Development trend of marine shale gas reservoir evaluation and a suitable comprehensive evaluation system[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2019(10):1-9.
[6] Zhen X J, Yan S, Xiang L T, et al.Controlling factors of marine shale gas differential enrichment in southern China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3):661-673.
[7] 蔡潇, 靳雅夕, 叶建国, 等.一种页岩有机孔与无机孔定量表征的方法[J].油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(1):30-36.
Cai X, Jin Y X, Ye J G, et al.A quantitative characterization method for organic and inorganic pores in shale[J].Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(1):30-36.
[8] Nelson P H.Pore-throat sizes in sandstones, tight sand-stones, and shales[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93:329-340.
[9] 范家维, 陈孔全, 沈均均, 等.中扬子地区当阳复向斜奥陶系五峰组-志留系龙马溪组页岩储层特征[J].石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1):69-78.
Fan J W, Chen K Q, Shen J J, et al.Shale reservoir characteristics of Ordovician Wufeng-Silurian Longmaxi Formations in Dangyang synclinorium, Middle Yangtze Region[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1):69-78.
[10] 贾成业, 贾爱林, 韩品龙, 等.四川盆地志留系龙马溪组优质页岩储层特征与开发评价[J].天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(9):1406-1415.
Jia C Y, Jia A L, Han P L, et al.Reservoir characterization and development evaluation of organic-rich gas-bearing shale layers in the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(9):1406-1415.
[11] 何顺, 秦启荣, 范存辉, 等.川东南丁山地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩储层特征及影响因素[J].油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(4):61-69.
He S, Qin Q R, Fan C H, et al.Shale reservoir characteristics and influencing factors of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Dingshan area, southeast Sichuan[J].Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2019, 9(4):61-69.
[12] 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等.页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(2):301-311.
Yang F, Ning Z H, Hu C P, et al.Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2):301-311.
[13] 聂海宽, 张金川.页岩气储层类型和特征研究——以四川盆地及其周缘下古生界为例[J].石油实验地质, 2011, 33(3):219-225.
Nie H K, Zhang J C.Types and characteristics of shale gas reservoir:A case study of Lower Paleozoic in and around Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2011, 33(3):219-225.
[14] 陈居凯, 朱炎铭, 崔兆帮, 等.川南龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构综合表征及其分形特征[J].岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(1):55-62.
Chen J K, Zhu Y M, Cui Z B, et al.Pore structure and fractal characteristics of Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan Basin[J].Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(1):55-62.
[15] 方新焰, 王鹏, 吴亮亮, 等.神农架及其周缘地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构特征及其含气性评价[J].地球化学, 2019, 48(6):590-601.
Fang X Y, Wang P, Wu L L, et al.Characteristics of microscopic pore distribution and gas-bearing evaluation of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale around the Shennongjia region[J].Geochimica, 2019, 48(6):590-601.
[16] 焦堃, 姚素平, 张科, 等.树皮煤的原子力显微镜研究[J].地质论评, 2012, 58(4):775-782.
Jiao K, Yao S P, Zhang K, et al.An atomic force microscopy study on "Barkinite" liptobiolith[J].Geological Review, 2012, 58(4):775-782.
[17] Can M F, Cinar M, Benli B, et al.Determining the fiber size of nano structured sepiolite using atomic force microscopy[J].Applied Clay Science, 2010, 47(34):217-222.
[18] 王羽, 汪丽华, 王建强, 等.基于聚焦离子束-扫描电镜方法研究页岩有机孔三维结构[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3):235-243.
Wang Y, Wang L H, Wang J Q, et al.Three-dimension characterization of organic matter pore structures of shale using focused ion beam-scanning electron microscope[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3):235-243.
[19] 戚明辉, 李君军, 曹茜.基于扫描电镜和JMicroVision图像分析软件的泥页岩孔隙结构表征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(3):260-269.
Qi M H, Li J J, Cao Q.The pore structure characterization of shale based on scanning electron microscopy and JMicroVision[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(3):260-269.
[20] Zou C N, Zhao Q, Dong D Z, et al.Geological characteristics, main c hallenges and future prospect of shale gas[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(12):1781-1796.
[21] 蒋裕强, 董大忠, 漆麟, 等.页岩气储层的基本特征及其评价[J].天然气工业, 2010, 30(10):7-12.
Jiang Y Q, Dong D Z, Qi L, et al.Basic features and evaluation of shale gas reservoirs[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(10):7-12.
[22] 曹涛涛, 宋之光, 王思波, 等.上扬子区古生界页岩的微观孔隙结构特征及其勘探启示[J].海相油气地质, 2015, 20(1):71-78.
Cao T T, Song Z G, Wang S B, et al.Characteristics of microscopic pore structure in Paleozoic shales in Upper Yangtze Region and its enlightenment for shale gas exploration[J].Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2015, 20(1):71-78.
[23] 高之业, 范毓鹏, 胡钦红, 等.川南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质孔隙差异化发育特征及其对储集空间的影响[J].石油科学通报, 2020, 5(1):1-16.
Gao Z Y, Fan Y P, Hu Q H, et al.Differential development characteristics of organic matter pores and their impact on reservoir space of Longmaxi Formation shale from the south Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2020, 5(1):1-16.
[24] 张成林, 张鉴, 李武广.等.渝西大足区块五峰组-龙马溪组深层页岩储层特征与勘探前景[J].天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(12):1794-1804.
Zhang C L, Zhang J, Li W G, et al.Deep shale reservoir characteristics and exploration potential of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Dazu area, western Chongqing[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(12):1794-1804.
-




 下载:
下载: