Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils from Jiulong Li-Be Mining Area, Western Sichuan Province, China
-
摘要:
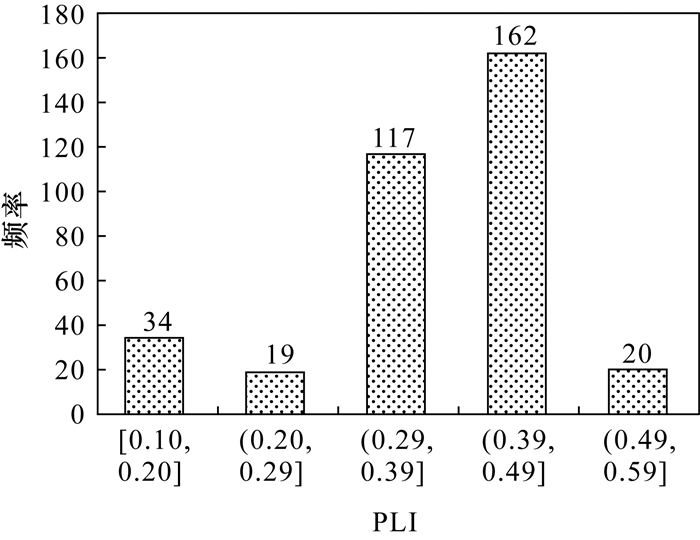
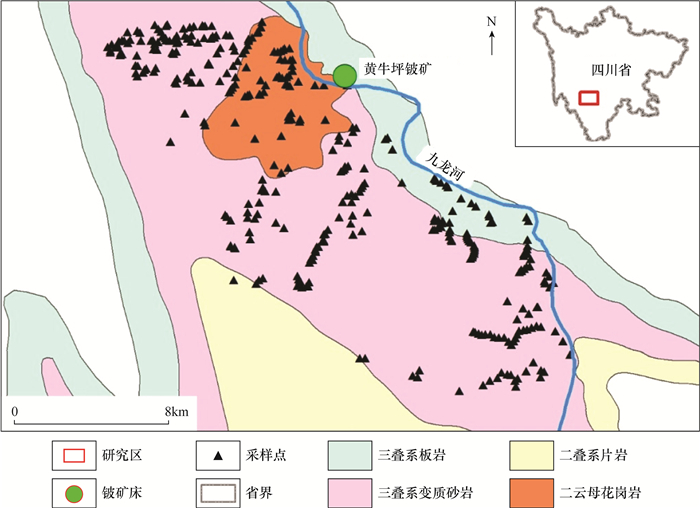
川西九龙地区是近年来中国关键矿产资源勘查的热点地区之一,区内锂铍等稀有金属矿产资源优势突出,有望逐步发展成为国家级大型资源基地。作为长江上游生态保护屏障,该区生态环境脆弱,面对矿业开发的巨大机遇,在当前“环保优先”的现实情况下,急需摸清该区环境家底,支撑国家能源战略发展。本文用ICP-MS方法检测了该区352件土壤样品中7种重金属元素(Cd、As、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn)的含量,运用地累积指数法、污染负荷指数法、潜在生态风险指数法和健康风险评价模型,结合GIS空间分析,综合研究了该区土壤中重金属的空间分布特征和生态风险。结果表明:①研究区土壤7种重金属元素浓度的平均值均没有超过国家农用土壤污染风险筛选值。As和Pb平均含量低于四川省土壤背景值,Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni和Zn含量高于背景值,分别是背景值的2.44、1.04、1.15、1.28和1.17倍。②Cd、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni和Zn六种重金属元素浓度的空间分布特征明显受到区内黑云母花岗岩的影响,Pb的高浓度中心以及Cr、Cu、Ni和Zn的低浓度中心与岩体的空间位置对应关系明显。③地累积指数法评价结果显示,研究区土壤区域整体上不存在重金属异常累积;污染负荷指数法评价结果显示污染负荷指数均小于1,不存在重金属的污染;除Cd存在轻微的潜在生态风险外,其余6种元素均不存在潜在生态风险。④健康风险评价模型分析结果显示,空间上,Cd元素的单元素潜在生态风险指数空间分布规律与岩体存在一定联系,无生态风险区域与黑云母花岗岩岩体位置对应。土壤中的重金属可以通过手口、呼吸和皮肤直接接触三种途径进入人体,其中手口途径是产生健康风险的最主要途径。在全部重金属元素产生的健康风险中,除Cr的手口途径会产生可以接受的正常的自然致癌风险外,其余元素均不存在致癌性和非致癌性。研究表明,当前研究区土壤不存在重金属污染,潜在危害程度较低,且不存在非致癌和致癌性风险。但基于土壤中重金属存在一定的累积效应,在今后矿业开发过程中要密切关注土壤重金属浓度的变化,防止重金属污染带来的风险。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The Jiulong area in western Sichuan is an important rare metal production area in China, which has a large resource potential. As an ecological protection barrier on the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, the ecological environment of this area is fragile. Facing the huge opportunities of mining development and under the current situation of 'environmental protection first', it is urgent to investigate the environmental background of this area to support the development of national energy strategy.
OBJECTIVES To evaluate the ecological risk of heavy metals in soils from the Jiulong Li-Be mining area.
METHODS A total of 352 soil samples were collected. The concentration of 7 heavy metals (Cd, As, Pb, Cr, Cu, Ni, Zn) in soil was analyzed by NexION 300x inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). The comprehensive assessment methods including geoaccumulation index, pollution load index, potential ecological risk index, and health risk model, combined with GIS spatial analysis were used to study the spatial distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in the soil.
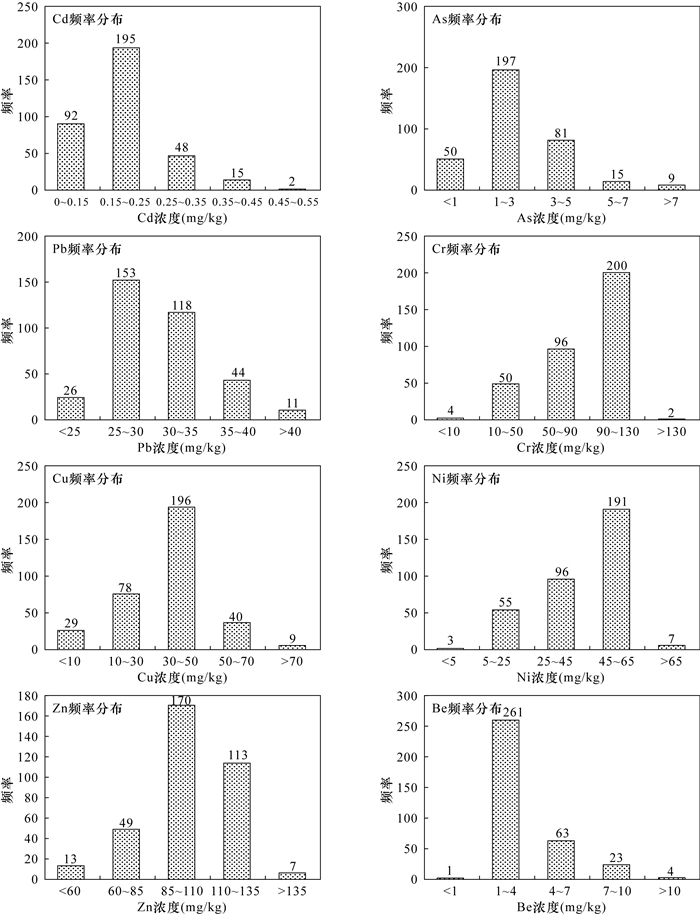
RESULTS The average concentration of all 7 heavy metals in the soil in Jiulong did not exceed the Chinese national standard. There was no soil heavy metals pollution in the studied area. Compared with the soil background value of Sichuan Province, the average concentrations of As and Pb were lower than the background; the concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn were higher than the background, which were 2.44, 1.04, 1.15, 1.28, and 1.17 times the background values, respectively. The spatial distribution characteristics of these elements except As were affected by biotite granite in the study area. The high concentration center of Pb and the low concentration center of Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn had an obvious correspondence with the spatial position of the rock mass. Except for the weak accumulation indicated by Cd Igeo, there was no accumulation of other heavy metals. Similarly, there was no potential ecological risk in the study area, except for the slight potential ecological risk of Cd. Spatially, the distribution of Cd single element potential ecological risk index was related to the rock mass, and the area without potential ecological risk corresponded to the location of the biotite granite rock mass. Heavy metals in the soil can enter the human body through direct contact with hands, mouth, and skin, and through inhalation. The hand-to-mouth approach is the most important way to generate health risks among all 3 approaches. Except hand-to-mouth approach of Cr, which has an acceptable and normal natural carcinogenic risk, there is no carcinogenic risk for other metals.
CONCLUSIONS At present, there is no pollution of heavy metals in the soil in the studied area. The potential risk of heavy metals is low, and there are no non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks. However, due to the cumulative effect of heavy metals in the soil, close attention must be paid to changes in the concentration of heavy metals in the soil in the future mining development process, to prevent the risk caused by heavy metals pollution.
-

-
表 1 暴露健康评价模型参数值
Table 1. Parameter values of exposure assessment models
参数 中文含义(单位) 成人 儿童 IngR 摄入土壤的频率(mg/d) 100 200 InhR 呼吸频率(m3/d) 20 5 EF 暴露频率(d/a) 180 180 ED 暴露年限(a) 24 6 BW 平均体质量(kg) 62.4 15 AT 平均暴露时间(d) 365×ED(非致癌) 365×ED(非致癌) 365×70(致癌) 365×70(致癌) PEF 灰尘排放因子(m3/kg) 1.36×109 1.36×109 CF 转换系数(kg/mg) 1.0×10-6 1.0×10-6 SL 皮肤黏着度[mg/(d·cm2)] 0.07 0.2 ABS 皮肤吸收因子(无量纲) 0.001 0.001 SA 暴露皮肤表面积(cm2) 2011 1078 表 2 土壤重金属不同暴露途径的RfD和SF值
Table 2. RfD and SF values of heavy metals in the soil of different exposure pathways
非致癌暴露参考剂量和致癌风险斜率 Cd As Pb Cr3+ Cu Zn RfDing(mg/kg·d) 1.00×10-3 3.00×10-4 3.50×10-3 3.00×10-3 4.00×10-2 0.3 RfDinh(mg/kg·d) 1.00×10-3 3.01×10-4 3.52×10-3 2.86×10-5 4.00×10-2 - RfDderm(mg/kg·d) 1.00×10-5 1.23×10-4 5.25×10-4 6.00×10-5 1.20×10-2 0.3 SFing(kg·d/mg) 6.30 15.1 - 1.5 - - SFinh(kg·d/mg) 6.40 15.1 - - - - SFderm(kg·d/mg) 6.30 7.5 - 1.95×10-2 - - 注:“-”表示无相关数据。 表 3 研究区土壤重金属浓度描述性统计
Table 3. Concentrations of heavy metals in soils of the research area
重金属元素 浓度范围
(mg/kg)平均值
(mg/kg)标准差
(mg/kg)变异系数
(%)偏度 峰度 筛选值
(mg/kg)四川省土壤背景值
(mg/kg)Cd 0.05~0.49 0.19 0.07 0.39 0.88 1.52 0.3 0.079 As 0.34~12.21 2.50 1.74 0.70 1.92 5.33 40 10.4 Pb 6.05~47.28 30.36 4.60 0.15 0.27 2.25 90 30.9 Cr 8.11~133.79 81.98 28.21 0.34 -1.56 1.20 150 79 Cu 4.86~109.89 35.86 15.77 0.44 0.47 1.90 50 31.1 Ni 3.99~75.49 41.65 15.85 0.38 -1.04 0.35 70 32.6 Zn 33.94~157.02 101.35 18.81 0.19 -0.84 0.89 200 86.5 Be 0.98~18.86 3.79 2.09 0.55 3.09 14.81 - 1.80 表 4 研究区土壤重金属Igeo分级统计
Table 4. Statistical classification of heavy metals Igeo in soils of the research area
重金属元素 Igeo平均值 各分级中样品数占总样品数比例(%) 第0级 第1级 第2级 第3级 第4级 第5级 第6级 Cd 0.59 13.92 62.50 23.30 0.28 0 0 0 As -2.95 100 0 0 0 0 0 0 Pb -0.63 99.72 0.28 0 0 0 0 0 Cr -0.72 99.43 0.57 0 0 0 0 0 Cu -0.57 79.55 19.89 0.57 0 0 0 0 Ni -0.44 62.50 37.50 0 0 0 0 0 Zn -0.39 96.88 3.13 0 0 0 0 0 表 5 研究区土壤重金属单元素潜在生态风险等级统计
Table 5. Statistics of Eri in soils of the research area
等级 各分级中样品数占总样品数比例(%) Cd As Pb Cr Cu Ni Zn 无 9.94 100 100 100 100 100 100 轻微 56.53 0 0 0 0 0 0 中等 32.39 0 0 0 0 0 0 强烈 1.14 0 0 0 0 0 0 极强 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 6 研究区不同途径土壤重金属日均暴露量、非致癌风险指数和致癌风险指数
Table 6. Daily exposure doses, non-carcinogenic risk index and carcinogenic risk index of heavy metals in soils of the research area
参数 Cd As Pb Cr Cu Ni Zn 合计 LADDing
(mg·kg-1·d-1)1.61×10-7 2.09×10-6 2.24×10-4 6.84×10-5 2.64×10-4 3.07×10-4 7.46×10-4 1.61×10-3 LADDinh
(mg·kg-1·d-1)9.66×10-12 1.25×10-10 2.63×10-6 4.12×10-9 3.10×10-6 3.60×10-6 8.77×10-6 1.81×10-5 LADDderm
(mg·kg-1·d-1)1.90×10-10 2.47×10-9 2.49×10-7 8.11×10-8 2.94×10-7 3.42×10-7 8.31×10-7 1.80×10-6 ΣLADD
(mg·kg-1·d-1)1.61×10-7 2.09×10-6 2.27×10-4 6.85×10-5 2.68×10-4 3.11×10-4 7.56×10-4 1.63×10-3 HQing 1.61×10-4 6.95×10-3 6.39×10-2 2.28×10-2 6.60×10-3 - 2.49×10-3 1.03×10-1 HQinh 9.66×10-9 4.17×10-7 7.46×10-4 1.44×10-4 7.76×10-5 - - 9.68×10-4 HQderm 1.90×10-5 2.01×10-5 4.74×10-4 1.35×10-3 2.45×10-5 - 2.77×10-6 1.89×10-3 HI 1.80×10-4 6.97×10-3 6.51×10-2 2.43×10-2 6.71×10-3 - 2.49×10-3 1.06×10-1 Risking 1.01×10-6 3.15×10-5 - 1.0×10-4 - - - 1.35×10-4 Riskinh 6.19×10-11 1.89×10-9 - - - - - 1.96×10-9 Riskderm 1.20×10-9 1.85×10-8 - 1.58×10-9 - - - 2.13×10-8 CR 1.01×10-6 3.15×10-5 - 1.0×10-4 - - - 1.35×10-4 注:“-”表示无相关数据。 -
[1] 况琴, 黄庭, 向京, 等. 鄂西北某农田保护区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(5): 45-49, 55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201905009.htm
Kuang Q, Huang T, Xiang J, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of a farmland protection area in northwest Hubei[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(5): 45-49, 55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201905009.htm
[2] 张建东, 赖建清, 范舟, 等. 理想点法在太原盆地土壤重金属污染等级评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(2): 161-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902013.htm
Zhang J D, Lai J Q, Fan Z, et al. The application of the ideal point method to the grade evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soils of Taiyuan Basin[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(2): 161-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902013.htm
[3] 吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(7): 971-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDE201606007.htm
Lv J S, Zhang Z L, Liu Y, et al. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(7): 971-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDE201606007.htm
[4] 张菊, 陈诗越, 邓焕广, 等. 山东省部分水岸带土壤重金属含量及污染评价[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(10): 3144-3153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201210021.htm
Zhang J, Chen S Y, Deng H G, et al. Heavy metal concentrations and pollution assessment of riparian soils in Shandong Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(10): 3144-3153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201210021.htm
[5] 石占飞, 王力. 神木矿区土壤重金属含量特征及潜在风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(6): 1150-1158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201306012.htm
Shi Z F, Wang L. Contents of soil heavy metals and evaluation on the potential pollution risk in Shenmu mining area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(6): 1150-1158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201306012.htm
[6] 郭笑笑, 刘丛强, 朱兆洲, 等. 土壤重金属污染评价方法[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(5): 889-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201105007.htm
Guo X X, Liu C Q, Zhu Z Z, et al. Evaluation methods for soil heavy metals contamination: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(5): 889-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201105007.htm
[7] 赵科理, 傅伟军, 戴巍, 等. 浙江省典型水稻产区土壤-水稻系统重金属迁移特征及定量模型[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(2): 226-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN201602011.htm
Zhao K L, Fu W J, Dai W, et al. Characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metal transfer in soil-rice systems in typical rice production areas of Zhejiang Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(2): 226-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN201602011.htm
[8] 洪涛, 孔祥胜, 岳祥飞. 滇东南峰丛洼地土壤重金属含量、来源及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(10): 4620-4627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201910036.htm
Hong T, Kong X S, Yue X F. Concentration characteristics, source analysis, and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in a peak-cluster depression area, southeast of Yunnan Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(10): 4620-4627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201910036.htm
[9] 王玉军, 吴同亮, 周东美, 等. 农田土壤重金属污染评价研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(12): 2365-2378. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1317
Wang Y J, Wu T L, Zhou D M, et al. Advances in soil heavy metal pollution evaluation based on bibliometrics analysis[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(12): 2365-2378. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1317
[10] 周国华. 土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6): 1097-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201406001.htm
Zhou G H. Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6): 1097-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201406001.htm
[11] 孟敏, 杨林生, 韦炳干, 等. 我国设施农田土壤重金属污染评价与空间分布特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(11): 1019-1026. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.11.009
Meng M, Yang L S, Wei B G, et al. Contamination assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metals in greenhouse soils in China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2018, 34(11): 1019-1026. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.11.009
[12] 周永超, 孙慧兰, 陈学刚, 等. 绿洲城市伊宁市表层土壤重金属污染特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(2): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201902019.htm
Zhou Y C, Sun H L, Chen X G. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soil of Yining in Oasis City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(2): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201902019.htm
[13] 叶宏萌, 李国平, 郑茂钟, 等. 茶园土壤重金属空间分异及风险评价[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2016, 36(2): 209-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLB201602013.htm
Ye H M, Li G P, Zheng M Z. Spatial variation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the tea garden soils[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2016, 36(2): 209-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLB201602013.htm
[14] 王蕊, 陈明, 陈楠, 等. 基于总量及形态的土壤重金属生态风险评价对比: 以龙岩市适中镇为例[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10): 4348-4359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201710043.htm
Wang R, Chen M, Chen N, et al. Comparison of ecological risk assessment based on the total amount and speciation distribution of heavy metals in soil: A case study for Longyan City, Fujian Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10): 4348-4359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201710043.htm
[15] 何博, 赵慧, 王铁宇, 等. 典型城市化区域土壤重金属污染的空间特征与风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2869-2876. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201906044.htm
He B, Zhao H, Wang T Y, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from a typical urbanized area[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2869-2876. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201906044.htm
[16] 王斐, 黄益宗, 王小玲, 等. 江西某铜矿冶炼厂周边土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(7): 1066-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201407002.htm
Wang F, Huang Y Z, Wang X L, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surrounding soils of a copper smelting plant in Jiangxi Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(7): 1066-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201407002.htm
[17] 王斐, 黄益宗, 王小玲, 等. 江西钨矿周边土壤重金属生态风险评价: 不同评价方法的比较[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(2): 225-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201502004.htm
Wang F, Huang Y Z, Wang X L, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surrounding soils of tungsten ores: Comparison of different evaluation method[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(2): 225-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201502004.htm
[18] 罗改, 谭晓莲. 金阳县丝窝土地开发区土壤重金属污染现状及生态风险评价[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2019, 39(10): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2019.10.012
Luo G, Tan X L. Pollution situation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil in Siwo land development zone, Jinyang County[J]. Environmental Protection and Circular Economy, 2019, 39(10): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2019.10.012
[19] 方晓波, 史坚, 廖欣峰, 等. 临安市雷竹林土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(6): 1883-1891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201506039.htm
Fang X B, Shi J, Liao X F, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk analysis for soil in Phyllostachy spraecox stands of Lin'an[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(6): 1883-1891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201506039.htm
[20] 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 阿吉古丽·马木提, 艾尼瓦尔·买买提, 等. 博斯腾湖流域绿洲农田土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(9): 1680-1694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201709013.htm
Eziz M, Mamut A, Mohammad A, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and its potential ecological risks of farmland soils of oasis in Bosten Lake Basin[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(9): 1680-1694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201709013.htm
[21] 李一蒙, 马建华, 刘德新, 等. 开封城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(3): 1037-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201503043.htm
Li Y M, Ma J H, Liu D Z, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of urban soils in Kaifeng City, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(3): 1037-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201503043.htm
[22] 王小莉, 陈志凡, 魏张东, 等. 开封市城乡交错区农田土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 513-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201803015.htm
Wang X L, Chen Z F, Wei Z D, et al. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment in agricultural soils located in the peri-urban area of Kaifeng City[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 513-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201803015.htm
[23] 赵庆令, 李清彩, 谢江坤, 等. 应用富集系数法和地累积指数法研究济宁南部区域土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(1): 129-137. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.017
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, Xie J K, et al. Characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and its ecological risk assessment in south Jining District using methods of enrichment factor and index of geoaccumulation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(1): 129-137. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.017
[24] 李有文, 曹春, 巨天珍, 等. 白银市不同区域蔬菜地土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(11): 3205-3213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201511031.htm
Li Y W, Cao C, Ju T Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of different vegetable soils of Baiyin, Gansu, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(11): 3205-3213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201511031.htm
[25] 张倩, 陈宗娟, 彭昌盛, 等. 大港工业区土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(11): 4232-4240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201511042.htm
Zhang Q, Chen Z J, Peng C S, et al. Heavy metals pollution in topsoil from Dagang industry area and its ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(11): 4232-4240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201511042.htm
[26] 虞敏达, 张慧, 何小松, 等. 典型农业活动区土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(3): 1500-1507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201603080.htm
Yu M D, Zhang H, He X S, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in typical agricultural soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(3): 1500-1507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201603080.htm
[27] 秦鱼生, 喻华, 冯文强, 等. 成都平原北部水稻土重金属含量状况及其潜在生态风险评价[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 6335-6344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201319047.htm
Qin Y S, Yu H, Feng W Q, et al. Assessment on heavy metal pollution status in paddy soils in the northern Chengdu Plain and their potential ecological risk[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(19): 6335-6344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201319047.htm
[28] 赵曦, 黄艺, 李娟, 等. 大型垃圾焚烧厂周边土壤重金属含量水平、空间分布、来源及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(6): 1013-1021. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201506016.htm
Zhao X, Huang Y, Li J, et al. Environmental levels, spatial distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soils surrounding a large solid waste in cinerator[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(6): 1013-1021. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201506016.htm
[29] 郑杰, 王志杰, 王磊, 等. 贵州草海流域不同土地利用方式土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(6): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201906022.htm
Zheng J, Wang Z J, Wang L, et al. Risk potentials of soil heavy metals under different land use patterns in Caohai Basin of Guizhou Province[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(6): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201906022.htm
[30] 陆泗进, 王业耀, 何立环. 湖南省某冶炼厂周边农田土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(3): 77-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.03.014
Lu S J, Wang Y Y, He L H. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of the paddy soils near a smelting area in Hunan Province[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(3): 77-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.03.014
[31] 陆泗进, 王业耀, 何立环. 会泽某铅锌矿周边农田土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(11): 1832-1838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.11.017
Lu S J, Wang Y Y, He L H. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of the paddy soilsaround a Pb-Zn mine in Huize Country[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(11): 1832-1838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.11.017
[32] 杨净, 王宁. 夹皮沟金矿开采区土壤重金属污染潜在生态风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(3): 595-600. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201303031.htm
Yang J, Wang N. Assessment of potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soils from Jia-Pi-Gou gold mine area, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(3): 595-600. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201303031.htm
[33] 黄顺红, 杨伊, 李倩, 等. 铅锌矿区土壤重金属空间分布及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(2): 186-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201602034.htm
Huang S H, Yang Y, Li Q, et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around lead-zinc mining area[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 39(2): 186-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201602034.htm
[34] 李仕群, 朱静媛, 崔留欣, 等. 沙颍河沈丘段底泥、土壤中砷及重金属污染与潜在生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2013, 8(2): 275-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201302022.htm
Li S Q, Zhu J Y, Cui L X, et al. Pollution and risk assessment of arsenic and heavy metals in sediments and soils from Shenqiu Section of Shaying River[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2013, 8(2): 275-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL201302022.htm
[35] 戴彬, 吕建树, 战金成, 等. 山东省典型工业城市土壤重金属来源、空间分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(2): 507-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201502021.htm
Dai B, Lv J S, Zhan J C, et al. Assessment of sources, spatial distribution and ecological risk of heavy metalsin soils in a typical industry-based city of Shandong Province, eastern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(2): 507-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201502021.htm
[36] 蔡怡敏, 陈卫平, 彭驰, 等. 顺德水道土壤及沉积物中重金属分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(5): 1763-1770. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201605022.htm
Cai Y M, Chen W P, Peng C, et al. Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals insoils and sediments in Shunde Waterway, southern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(5): 1763-1770. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201605022.htm
[37] 高鹏, 刘勇, 苏超. 太原城区周边土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5): 866-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201505009.htm
Gao P, Liu Y, Su C. Distribution and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in area surrounding Taiyuan City[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(5): 866-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201505009.htm
[38] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 等. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201806045.htm
Zhou Y, Chen Q, Deng S P, et al. Principal component analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around a Pb-Zn mine in southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201806045.htm
[39] 海米提·依米提, 祖皮艳木·买买提, 李建涛, 等. 焉耆盆地土壤重金属的污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(6): 1523-1530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201406031.htm
Hamid Y, Zulpiya M, Li J T, et al. Sources explanation, pollution and assessment of potential ecological hazards of heavy metals in the soils of Yanqi Basin, China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(6): 1523-1530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201406031.htm
[40] 冉秀芝, 吴爽, 谢相尉, 等. 重庆市某区果蔬基地土壤重金属污染及其风险评价研究[J]. 食品与发酵科技, 2019, 55(6): 115-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKSF201906022.htm
Ran X Z, Wu S, Xie X W, et al. Evaluation of heavy metals pollution risk of fruit and vegetable bases in the suburbs of Chongqing[J]. Food and Fermentation Sciences & Technology, 2019, 55(6): 115-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKSF201906022.htm
[41] 崔勇, 柏连阳, 龙岳林, 等. 长沙市近郊莲花镇土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(5): 202-209. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC202005035.htm
Cui Y, Bai L Y, Long Y L, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of Lianhua Town in the suburbs of Changsha[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2020, 38(5): 202-209. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC202005035.htm
[42] 张广胜, 徐文彬, 李俊翔, 等. 一个未开采的铅锌矿周边土壤重金属含量及生态安全评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(3): 522-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201503024.htm
Zhang G S, Xu W B, Li J X, et al. Heavy metals pollution and eco-security evaluation in the surrounding soil of an untapped lead-zinc mining[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(3): 522-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201503024.htm
[43] 张学礼, 徐乐昌, 张辉. 某铀尾矿库周围农田土壤重金属污染潜在生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境监测, 2016, 32(6): 76-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201606012.htm
Zhang X L, Xu L C, Zhang H. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in farmland soils near an uranium tailings pond[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2016, 32(6): 76-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201606012.htm
[44] Pardo T, Clemente R, Epelde L, et al. Evaluation of the phytostabilisation efficiency in a trace elements contaminated soil using soil health indicators[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 268: 68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.003
[45] Lee C S L, Li X, Shi W, et al. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 356: 45-61. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.03.024
[46] 王小宇, 周忠发, 黄登红, 等. 喀斯特山区茶园土壤重金属污染损失率模型评价研究[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(3): 169-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201803035.htm
Wang X Y, Zhou Z F, Huang D H, et al. Study on evaluation model of heavy metal pollution loss rate in teagarden soils in Karst mountainous region[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(3): 169-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201803035.htm
[47] 李飞, 黄瑾辉, 李雪, 等. 基于随机模糊理论的土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价及溯源分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(4): 1233-1240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201504039.htm
Li F, Huang J H, Li X, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment based on stochastic-fuzzy simulation for soils and pollution source identification[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(4): 1233-1240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201504039.htm
[48] 罗厚枚, 王宏康. 用灰色聚类法综合评价土壤中重金属污染程度[J]. 北京农业大学学报, 1994(2): 197-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYDX199402020.htm
Luo H M, Wang H K. Application of gray cluster method in comperhensive evalution of heavy matel pollusion in soil[J]. Acta Agriculaturae Universitatis Pekinensis, 1994(2): 197-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYDX199402020.htm
[49] 岑静, 陈家玮, 杨忠芳, 等. 层次分析法在四川省通江县广纳镇土地评估中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 2008, (2): 277-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.02.017
Cen J, Chen J W, Yang Z F, et al. Application of the analytic hierarchy process in the evaluation of land quality of Guangna Town, Tongjiang County, Sichuan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2): 277-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.02.017
[50] 疏志明, 王雄军, 赖健清, 等. 分形理论在太原盆地土壤重金属元素分析中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(2): 157-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902012.htm
Shu Z M, Wang X J, Lai J Q, et al. The application of fractal theory to soil heavy trace metal analysis in Taiyuan Basin, Shanxi Province[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(2): 157-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902012.htm
[51] 范拴喜, 甘卓亭, 李美娟, 等. 土壤重金属污染评价方法进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(17): 310-315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201017070.htm
Fan S X, Gan Z T, Li M J, et al. Progress of assessment methods of heavy metal pollution in soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(17): 310-315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201017070.htm
[52] 周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1358-1366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906025.htm
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1358-1366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906025.htm
[53] 高娟琴, 于扬, 王登红, 等. 川西甲基卡锂资源富集区根系土壤重金属含量水平及时空分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 681-692. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201812190137
Gao J Q, Yu Y, Wang D H, et al. The content and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in root soil in Jiajika lithium-bearing area, western Sichuan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 681-692. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201812190137
[54] 王刚. 四川省九龙县土地利用变化特征及生态系统服务价值分析[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2019.
Wang G. Analysis of land use characteristics and ecosystem service value in Jiulong County, Sichuan Province[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019.
[55] 王伟, 刘图强, 袁蔺平, 等. 川西九龙黄牛坪铍矿床地质特征及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质调查, 2019, 6(6): 72-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201906009.htm
Wang W, Liu T Q, Yuan L P, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Huangniuping beryllium deposit in Jiulong of West Sichuan[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2019, 6(6): 72-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201906009.htm
[56] Ji Y Q, Fengy C, Wu J H, et al. Using geoaccumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(5): 571-578. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62096-3
[57] Loska K, Wiechuła D, Korus I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry[J]. Environment International, 2004, 30(2): 159-165. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00157-0
[58] 赵兵, 王玉云, 徐德江, 等. 四川石棉工业园区周边土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价研究[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(6): 138-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201906027.htm
Zhao B, Wang Y Y, Xu D J, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk of soils near a industrial park in Shimian Sichuan Province[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2019, 38(6): 138-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201906027.htm
[59] 王玉云, 赵兵, 徐德江, 等. 四川雅安工业园区周边土壤重金属空间分布及污染评价研究[J]. 四川环境, 2019, 38(6): 133-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201906026.htm
Wang Y Y, Zhao B, Xu D J, et al. Study on the spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of soil heavy metals around a industrial park in Ya'an, Sichuan Province[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2019, 38(6): 133-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ201906026.htm
[60] Tomlinson D, Wilson J, Harris C, et al. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index[J]. Helgoländer Meeresunter Suchungen, 1980, 33(1): 566-575. http://hmr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1007/BF02414780
[61] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[62] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008(2): 112-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Tuo X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008(2): 112-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
[63] Lai H Y, Hseu Z Y, Chen T C, et al. Health risk-based assessment and management of heavy metals-contaminated soil sites in Taiwan[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2010, 7(10): 3595-3614. doi: 10.3390/ijerph7103596
[64] Wu K, Zhang L. Progress in the development of envir-onmental risk assessment as a tool for the decision-making process[J]. Journal of Service Science and Management, 2014, 7: 131-143. doi: 10.4236/jssm.2014.72011
[65] Ferreira-Baptista L, de Miguel E. Geochemistr y and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(25): 4501-4512. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.026
[66] Ministry of The Environment. Soil, ground water and sediment standards for use under part XV. 1 of the Environmental Protection Act[R]. Ontario: Ministry of the Environment, Conservation and Parks, 2009.
-



 下载:
下载: