Mineral Composition and Genesis of Black Quartzite Jade from Linwu County, Hunan Province
-
摘要:
石英岩质玉是一种市场上常见且产地较多的玉石品种,本文基于前人石英岩质玉的研究基础,通过常规宝石学测试、红外光谱测试、偏反光显微镜下观察,以及采用X射线粉晶衍射、X射线荧光光谱、电感耦合等离子体质谱仪对样品的宝石学特征、矿物组成进行分析,并对其成因进行讨论。结果表明:该地区黑色石英岩质玉多为中-细粒粒状结构,偏光显微镜观察可见多种变晶/变余结构;成分中主要矿物石英平均含量为44.7%,次要矿物云母、长石平均含量合计31.0%,黏土矿物平均含量为12.7%,另含有有机碳以及红柱石、铁铝榴石、黄铁矿等铁质矿物;结合样品结构、构造特征及矿物化学成分分析可知,样品为典型副变质岩系的中、低温热液交代型区域变质岩,属绿片岩相,原岩为富铝且富含石英、长石的沉积岩,其形成的构造环境属大陆边缘构造。本研究为该地区石英岩质玉的矿物组成鉴定提供了多手段技术支撑。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Black quartzite jade is a type of commonly and commercially available jade. Many areas produce this gem.
OBJECTIVES To analyze the gemological characteristics and mineral composition of the jade samples and to discuss their genesis.
METHODS Conventional gemological tests, infrared spectrum tests, polarizing microscopy, X-ray powder diffraction analysis, X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry were used.
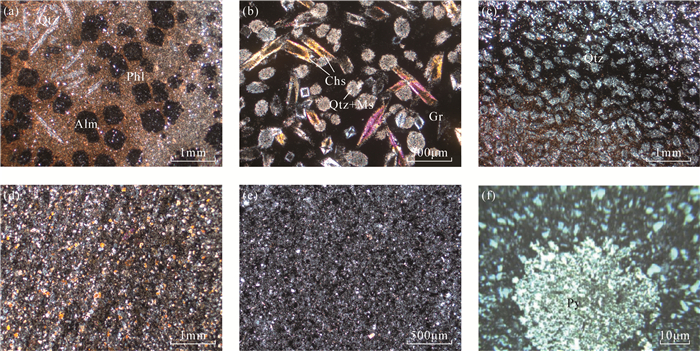
RESULTS Black quartzite jade from the Linwu County, Hunan Province, showed a medium-fine grain texture. The polarizing microscopy results revealed many crytalloblastic or palimpsest textures. The content of the main mineral quartz was 44.7%, the content of secondary minerals (mica and feldspar) was 31.0%, and the content of clay minerals was 12.7%. Minor organic carbon, iron minerals, andalusite, almandine, and pyrite were also observed.
CONCLUSIONS Based on the main textures, structures, configuration features, and chemical compositions, the studied samples are regarded as typical low-to-moderate temperature hydrothermal regional metamorphic rocks, which are classified as greenschist facies. The source rock was composed of sedimentary rocks abundant with aluminum, quartz, and feldspar. The tectonic environment for its formation belonged to the continental margin. This study provides technical support for the identification of the mineral composition of quartzite jades from the Linwu County, Hunan Province.
-

-
图 1 湖南省临武县香花岭地区地质略图(图片来源:袁顺达等[16])
Figure 1.
表 1 湖南临武地区黑色石英岩质玉的矿物相半定量分析结果
Table 1. Semi-quantitative analysis of mineral phases of the black quartzite jade in Linwu District, Hunan Province
样品编号 矿物含量(%) 石英 云母 长石 红柱石 石榴石 黄铁矿 钛铁矿 磷灰石 黏土矿物 LS-1-1 47.1 22.4 9.8 2.2 3.8 2.6 1.1 0.9 10.1 LS-1-2 41.2 15.7 12.2 7.1 2.7 1.1 2.0 1.4 16.6 LS-1-4 43.2 20.3 15.3 1.9 / 2.8 1.3 2.0 13.2 LS-2-3 43.5 17.4 9.8 4.6 6.3 1.2 3.5 2.2 10.5 LS-3-1 45.6 18.4 16.1 1.0 1.1 2.1 1.8 1.5 12.4 LS-3-2 47.5 20.3 8.2 5.3 1.1 2.3 1.3 0.5 13.5 平均值 44.7 19.1 11.9 3.7 3.0 2.0 1.8 1.4 12.7 表 2 湖南临武地区黑色石英岩质玉的主量元素测试结果及变质岩原岩性质判别函数(DF值)计算结果
Table 2. Analytical results of major elements and DF values of the black quartzite jade in Linwu District, Hunan Province
样品编号 含量(%) DF值 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Cr2O3 Fe2O3 MgO MnO CaO Na2O K2O 总量 LS-1-1 70.45 0.58 14.90 0.01 4.02 0.60 0.17 1.33 0.91 2.38 95.35 -2.82 LS-1-2 59.49 0.86 24.68 0.01 7.19 0.56 0.14 0.39 0.32 3.10 96.74 -1.95 LS-1-3 65.47 1.00 22.97 0.01 4.89 0.79 0.16 0.49 0.60 2.67 99.05 -3.07 表 3 湖南临武地区黑色石英岩质玉的地球化学特征
Table 3. Geochemical characteristics of the black quartzite jades in Linwu District, Hunan Province
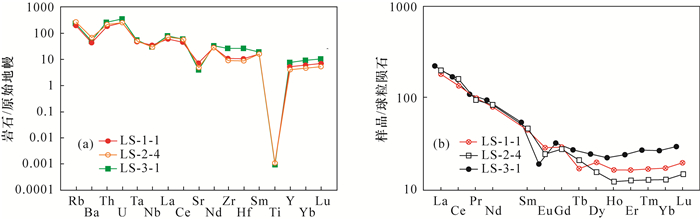
微量元素 微量元素含量测定值(μg/g) LS-1-1 LS-2-4 LS-3-1 Rb 122 170 147 Ba 306 485 346 Th 15.7 18.6 21.6 U 5.41 5.47 7.33 Ta 1.92 2.05 2.21 Nb 23.6 20.8 21.4 La 42.4 46.7 52.0 Ce 82.0 97.1 102 Sr 150 96.4 82.8 Nd 37.1 39.0 43.4 Zr 119 98.0 291 Hf 3.16 2.63 7.91 Sm 6.96 7.18 8.22 Ti 1.37 1.18 1.13 Y 22.8 18.0 32.9 Yb 2.88 2.22 4.51 Lu 0.50 0.38 0.75 稀土元素 稀土元素含量测定值(μg/g)及相关参数 LS-1-1 LS-2-4 LS-3-1 La 42.4 46.7 52.0 Ce 82.0 97.1 102 Pr 9.34 9.10 10.3 Nd 37.1 39.0 43.4 Sm 6.96 7.18 8.22 Eu 1.64 1.41 1.11 Gd 5.93 5.76 6.60 Tb 0.63 0.79 1.02 Dy 5.05 3.96 6.20 Ho 0.93 0.70 1.27 Er 2.71 2.10 3.96 Tm 0.43 0.33 0.68 Yb 2.88 2.22 4.51 Lu 0.50 0.38 0.75 Y 22.8 18.0 32.9 ΣREE 198 216 242 LREE 179 200 217 HREE 19.0 16.2 25.0 LREE/HREE 9.41 12.4 8.69 LaN/YbN 10.6 15.1 8.26 δEu 0.76 0.65 0.44 δCe 0.97 1.08 1.02 -
[1] 张蓓莉. 系统宝石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 374-379.
Zhang B L. Systematic gemmology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 374-379.
[2] 王长秋, 张丽葵. 珠宝玉石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 560-569.
Wang C Q, Zhang L K. Gemology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017: 560-569.
[3] 李胜荣. 结晶学与矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 188-190.
Li S R. Crystallography and mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Geology Publishing House, 2008: 188-190.
[4] 刘晓亮, 孟庆鹏, 陈熙皓, 等. 经变质作用形成的石英质玉的宝石学特征[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志, 2020, 22(1): 33-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB202001005.htm
Liu X L, Meng Q P, Chen X H, et al. Gemmological characteristics of quartzose jade by metamorphism[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2020, 22(1): 33-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB202001005.htm
[5] 周丹怡, 陈华, 陆太进, 等. 广西桂林不同颜色石英质玉的宝石学特征对比研究[C]//中国国际珠宝首饰学术交流会论文集(2017). 2017: 215-219.
Zhou D Y, Chen H, Lu T J, et al. Comparative study on gemmological characteristics of different color quartz jade in Guilin, Guangxi[C]//Proceedings of China International Jewelry Academic Exchange Conference (2017). 2017: 215-219.
[6] 王琦. 石英质玉的分类特征与市场现状[J]. 中国地名, 2020(2): 39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NAME202002019.htm
Wang Q. Classification characteristics and market status of quartz jade[J]. China Place Name, 2020(2): 39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NAME202002019.htm
[7] 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝. 系统矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 169-180.
Wang P, Pan Z L, Weng L B. Systematic mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1984: 169-180.
[8] 姚凤良, 孙丰月. 矿床学教程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 215-227.
Yao F L, Sun F Y. Course in mineral deposits[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 215-227.
[9] 张高鑫, 刘建朝, 张海东, 等. 陕西勉略宁地块车渡磁铁石英岩型金矿床多期成矿作用[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(3): 355-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202003008.htm
Zhang G X, Liu J C, Zhang H D, et al. Multistage mineralization of Chedu magnetite quartzite gold deposit in Mianluening Block of Shannxi, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(3): 355-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202003008.htm
[10] 李孝文, 曹淑云, 刘建华, 等. 北阿尔金余石山含金石英脉地质构造特征与流体作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.05.014:1-33.
Li X W, Cao S Y, Liu J H, et al. Geological structure characteristics and fluid activity of the gold-bearing quartz veins on the Yushishan area, north Altyn Tagh[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 2021. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.05.014:1-33.
[11] 程奋维. 白尖山脉石英矿床成因浅析[J]. 甘肃冶金, 2020, 42(3): 106-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2020.03.031
Cheng F W. Genesis of quartz deposit in Baijian Mountain[J]. Gansu Metallurgy, 2020, 42(3): 106-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2020.03.031
[12] 颜玲亚, 高树学, 陈正国, 等. 我国脉石英矿床类型及成矿规律[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2020(5): 10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2020.05.004
Yan Y L, Gao S X, Chen Z G, et al. Types and metallogenic regularity of vein quartz deposits in China[J]. China Non-Metallic Mining Industry Herald, 2020(5): 10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2020.05.004
[13] Moxon T W, Palyanova G. Agate genesis: A continuing enigma[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(11): 953. doi: 10.3390/min10110953
[14] Moxon T, Reed S. Agate and chalcedony from igneous and sedimentary hosts aged from 13 to 3480Ma: A cathodoluminescence study[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2006, 70(5): 485-498. doi: 10.1180/0026461067050347
[15] 李伟良, 王谦. 临武县通天玉相关特征及成因初探[J]. 国土资源导刊, 2015, 12(4): 46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2015.04.010
Li W L, Wang Q. Preliminary exploration of the characteristics and the genesis of Tongtian Jade in Linwu County[J]. Land & Resources Herald, 2015, 12(4): 46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2015.04.010
[16] 袁顺达, 彭建堂, 李向前, 等. 湖南香花岭锡多金属矿床C、O、Sr同位素地球化学[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(11): 2-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200811008.htm
Yuan S D, Peng J T, Li X Q, et al. Carbon, oxygen and strontium isotope geochemistry of calcites from the Xianghualing tin-polymetallic deposit, Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(11): 2-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200811008.htm
[17] 徐质彬, 张利军, 杨晓弘, 等. 湖南临武通天山石英岩质玉矿床地质特征与成矿规律[J]. 资源信息与工程, 2018, 33(5): 47-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5391.2018.05.021
Xu Z B, Zhang L J, Yang X H, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenic regularity of ore deposits of the black quartzite jade in Tongtian Mountain Linwu District, Hunan Province[J]. Resource Information and Engineering, 2018, 33(5): 47-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5391.2018.05.021
[18] 罗彬, 喻云峰, 廖佳, 等. 珠宝玉石无损检测光谱库及解析[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2019: 216-217.
Luo B, Yu Y F, Liao J, et al. Nondestructive testing spectrum library of jewelry and jade and its solution[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2019: 216-217.
[19] 常丽华, 陈曼云, 金巍, 等. 透明矿物薄片鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 20-151.
Chang L H, Chen M Y, Jin W, et al. A manual for thin section identification of transparent minerals[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 20-151.
[20] 陈曼云, 金巍, 郑常青. 变质岩鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 41-73.
Chen M Y, Jin W, Zheng C Q. Handbook of metamorphic rock identification[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009: 41-73.
[21] 胡玲, 刘俊来, 纪沫. 变形显微构造识别手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015: 23-31.
Hu L, Liu J L, Ji M. Handbook of deformation microstructure identification[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015: 23-31.
[22] 柳生祥, 曾俊杰, 张学奎, 等. 祁连造山带东段皋兰岩群叠加变质作用及其形成环境[J]. 甘肃地质, 2020, 29(增刊2): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ2020Z2004.htm
Liu S X, Zeng J J, Zhang X K, et al. Superimposed metamorphism of the Gaolan Group in the eastern segment of Qilian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gansu Geology, 2020, 29(Supplement 2): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ2020Z2004.htm
[23] Shaw D M. The origin of the Apsley gneiss, Ontario[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Science, 1972: 18-35. http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/doi/abs/10.1139/e72-002
[24] 陶瑞. 滇西凤庆泥盆系"温泉组"岩石特征及变质变形分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019.
Tao R. The analysis of characteristics, metamorphism and deformation of rock in Devonian Wenquan Formation, Fengqing, western Yunnan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019.
[25] Girty G H, Ridge D L. Provenance and depositional setting of Paleozoic chert and argillite, Sierra Nevada, California[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66(1): 107-118. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279710026_Provenance_and_depositional_setting_of_Paleozoic_chert_and_argillite_Sierra_Nevada_California
[26] 孙乾龙, 夏冬, 弓小平. 新疆北山清白山花岗岩体成因及构造环境分析[J]. 新疆地质, 2020, 38(3): 298-304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2020.03.004
Sun Q L, Xia D, Gong X P. Genesis and tectonic environment of Qingbaishan granite in Beishan, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2020, 38(3): 298-304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2020.03.004
[27] 周伟, 曾梦, 王健, 等. 熔融制样-X射线荧光光谱法测定稀土矿石中的主量元素和稀土元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3): 298-305. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706280113
Zhou W, Zeng M, Wang J, et al. Determination of major elements and rare earth elements in rare earth ores by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3): 298-305. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201706280113
[28] Jewell P W, Stallard R F. Geochemistry and paleoceano graphic setting of central Nevada bedded barites[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1991, 99(2): 151-170. doi: 10.1086/629482
[29] 谈昕, 邱振, 卢斌, 等. 华南地区不同时代硅质岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(2): 7-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.02.002
Tan X, Qiu Z, Lu B, et al. Geochemical characteristics for siliceous rocks of different ages in South China and their geological significance[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 7-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.02.002
[30] 王西荣. 安徽省霍邱铁矿含铁岩系中斜长片麻岩黑云母-石榴石地球化学特征及其地质指示意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018(2): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201802010.htm
Wang X R. Biotite garnet geochemistry of plagioclase gneiss in the iron bearing rock series of Huoqiu iron deposit, Anhui Province and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Rock, 2018(2): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201802010.htm
[31] 黄长煌. 福建东山亲营山岩组变质岩石榴石-黑云母地质温度计的应用[J]. 华东地质, 2019, 40(1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2019.01.001
Huang C H. Application of garnet biotite geothermometer in metamorphic rocks of Qinyingshan Formation, Dongshan, Fujian Province[J]. Geology of East China, 2019, 40(1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2019.01.001
[32] 张茜, 余谦, 王剑, 等. 应用ICP-MS研究川西南龙马溪组泥页岩稀土元素特征及沉积环境[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2): 217-224. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201705090078
Zhang Q, Yu Q, Wang J, et al. Study on REE characteristics and sedimentary environment of Longmaxi Formation shale in southwest Sichuan by ICP-MS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2): 217-224. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201705090078
[33] 赵振明, 计文化, 李文明. 北山南部敦煌岩群铁矿化磁铁石英岩的变质成因[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(4): 689-701. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.04.003
Zhao Z M, Ji W H, Li W M. Metamorphic genesis of magnetite quartzite with iron mineralization in the Dunhuang Group of southern Beishan Region[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(4): 689-701. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.04.003
[34] 柳生祥, 曾俊杰, 张学奎, 等. 祁连造山带东段皋兰岩群叠加变质作用及其形成环境[J]. 甘肃地质, 2020, 29(3): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ2020Z2004.htm
Liu S X, Zeng J J, Zhang X K, et al. Superimposed metamorphism of the Gaolan Group in the eastern segment of Qilian orogenic belt[J]. Gansu Geology, 2020, 29(3): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ2020Z2004.htm
-




 下载:
下载: