Improvement of the Method for Determining Total Nitrogen in Water Quality Using Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry
-
摘要:
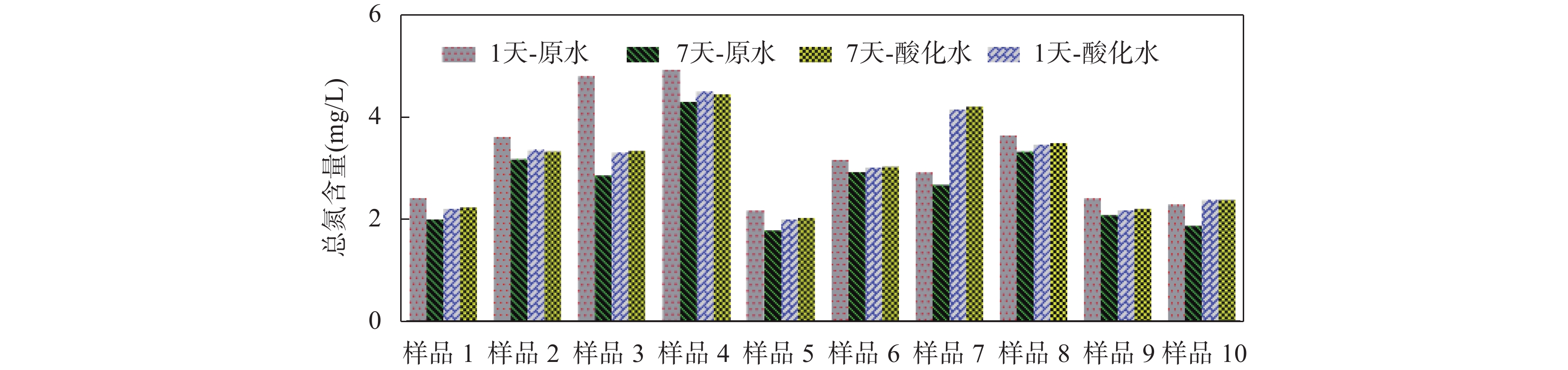
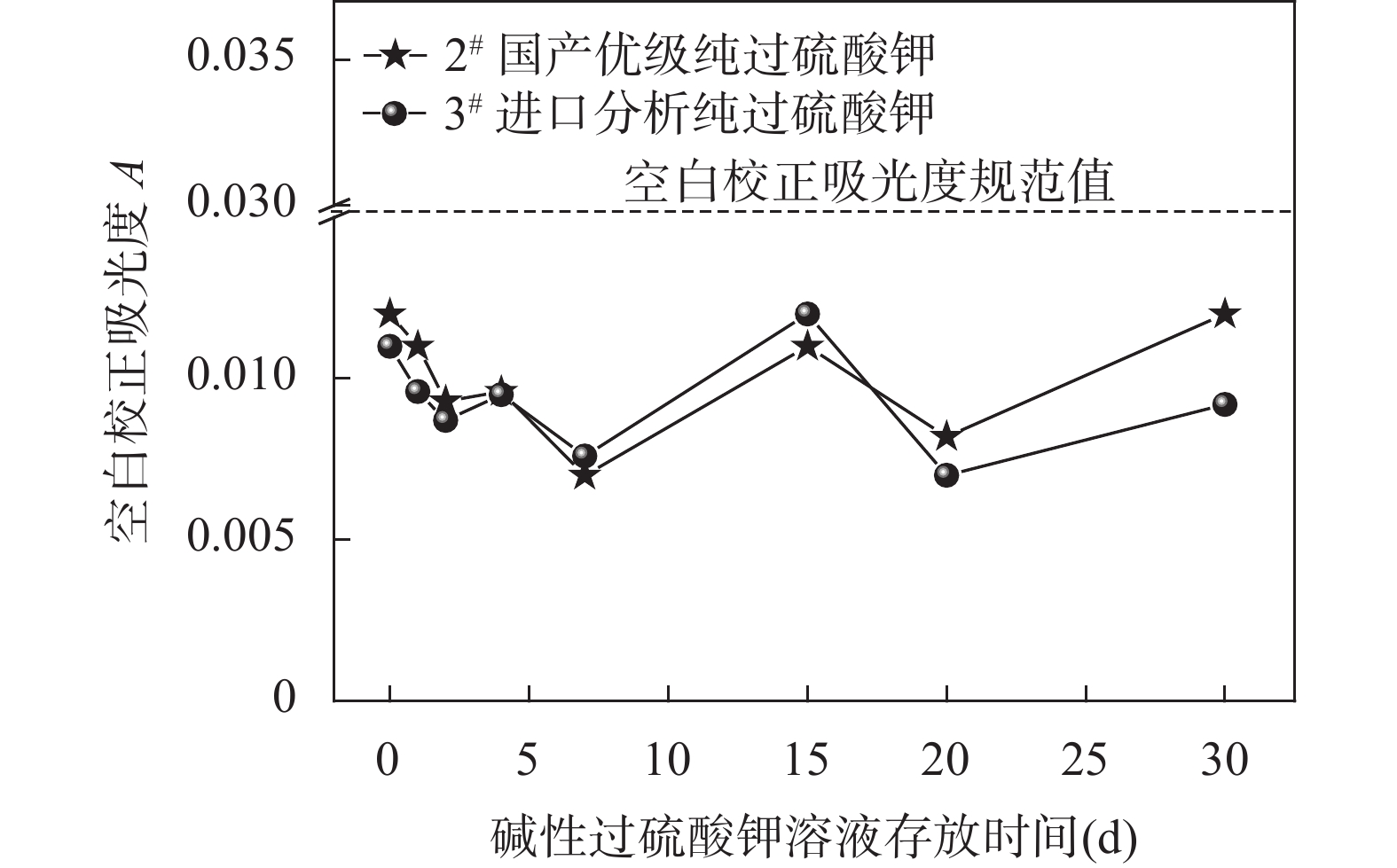
水质总氮是指示水体富营养化的重要标志物,因此,开发测定水体中总氮的准确方法,对研究水体中的污染物来源、污染程度及总氮的地球化学循环过程具有重要意义。测定水质样品中的总氮,通常采用碱性过硫酸钾-紫外分光光度法,但该法对空白吸光度有严苛的要求,空白吸光度一旦超过0.030,就有可能导致测定结果严重偏低,其中,过硫酸钾的纯度和存放时间可能对测定结果影响最大;同时,采用比色管捆绑方式高温高压消解水质样品,导热较慢,消解时间偏长,捆绑时一旦比色管上的标签或记号脱落,容易导致样品混乱;样品保存条件不当也很容易造成测定结果偏低。为提高水质样品中总氮测定结果的准确性和效率,本文通过对国内外不同厂家生产的过硫酸钾进行总氮空白吸光度和存放时间对比实验,然后对两种消解方法进行消解时间对比实验,最后,对比了两种不同水质样品保存方法对测定结果的影响。对比实验结果表明:国产优级纯碱性过硫酸钾存放时间在30天内,其水质总氮空白吸光度均小于0.030;在124℃条件下,使用插置法消解样品,只用20min就能使样品消解完全;对酸化后的水质样品,其保质期从1天延长至7天。研究认为,选用国产优级纯过硫酸钾和改良过的插置法消解水质样品,与捆绑法相比,其水质总氮检出限更低,消解效率更高,且不容易出现互相污染和样品错位等情况,提高了水质总氮测定的准确度。
Abstract:Alkaline potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) ultraviolet (UV) spectrophotometry is the routine method to analyze total nitrogen (TN) in water and is important for studying pollutants in water and the geochemical cycling of TN. However, several analytical conditions can influence the accuracy of the results. (1) The blank, purity, and storage time of K2S2O8. For example, a blank UV of K2S2O8 exceeding 0.030 can lead to a significant underestimation of results. (2) The digestion method of bundling colorimetric tubes in high temperature and high pressure is time-consuming. (3) Improper sample storage conditions can lower measurement results. To improve the accuracy and efficiency of TN measurement in water samples, this study compared the storage times of different K2S2O8, different digestion methods, and sample storage methods. The results show that the domestic premium-grade alkaline K2S2O8 should be stored for <30 days (blank UV<0.03). The insertion digestion method is much more efficient (124°C, 20min). Acidification extends samples’ shelf life from 1 day to 7 days. Therefore, choosing domestic premium-grade K2S2O8 and using the modified insertion method for sample digestion results in lower detection limits, higher digestion efficiency, minimal risk of contamination and misplacement, and improved accuracy of TN measurement in water quality analysis.
-

-
表 1 捆绑法和插置法的准确度和精密度试验统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of accuracy and precision comparison experiments between binding method and insertion method.
消解方法 标准样品
批号测定值
(mg/L)平均值
(mg/L)标准值
(mg/L)准确度RE
(%)精密度RSD
(%)加标量
(mg/L)测定值
(mg/L)回收率
(%)捆绑法 203277 0.52 0.64 0.51 0.59 0.705±0.06 16.5 9.26 1 1.61 1.62 1.64 91 92 94 0.67 0.62 0.58 1.60 1.63 1.67 90 93 97 203278 2.25 2.41 2.65 2.42 2.62±0.16 7.82 8.72 2 4.44 4.48 4.46 91 93 92 2.71 2.35 2.12 4.36 4.46 4.58 87 92 98 203267 3.52 3.95 4.62 3.97 4.43±0.24 10.5 8.92 2 6.25 6.21 6.35 91 89 96 3.61 3.96 4.13 6.31 6.27 6.37 94 92 97 插置法 203277 0.68 0.66 0.71 0.67 0.705±0.06 4.30 3.43 1 1.64 1.69 1.81 96 99 106 0.69 0.64 0.68 1.72 1.76 1.60 101 103 94 203278 2.35 2.38 2.55 2.52 2.62±0.16 3.69 7.65 2 4.57 4.48 4.62 99 97 100 2.36 2.85 2.65 4.76 4.57 4.90 103 99 106 203267 4.28 4.25 4.42 4.36 4.43±0.24 1.62 3.46 2 6.69 6.75 6.37 104 105 99 4.21 4.36 4.63 6.43 6.49 6.62 100 101 103 表 2 捆绑法和插置法的方法检出限对比试验统计结果
Table 2. Comparative experimental statistical results of detection limits between binding method and insertion method.
分析方法 水质总氮空白测定结果
(mg/L)标准偏差
s(mg/L)检出限
(mg/L)方法检出限规范要求
(mg/L)捆绑法 0.048 0.026 0.048 0.048 0.044 0.018 0.029 0.013 0.040 0.050 插置法 0.028 0.036 0.019 0.024 0.026 0.025 0.035 0.006 0.020 表 3 不同厂家生产的不同纯度过硫酸钾与空白吸光度的关系试验统计结果
Table 3. Experimental statistical results on the relationship between potassium persulfate of different purities produced by different manufacturers and blank absorbance.
样品编号 公司名称及规格 总氮量
(%)空白吸光度
(n=6)1# 四川西陇科学有限公司(AR) ≤0.005 0.096 2# 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司(GR) ≤0.005 0.010 3# 德国默克公司(AR) ≤0.0005 0.0095 -
[1] 左航, 徐晋, 王雪娇, 等. 水质总氮在线分析仪器研究与应用现状[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44(14): 173−176.
Zuo H, Xu J, Wang X J, et al. Research and application of instruments for on-line monitoring water quality of total nitrogen[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(14): 173−176.
[2] 王玉功, 王华, 刘建军, 等. 沙棘树干茎流液中总氮总磷联合消解的测定方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(5): 665−669.
Wang Y G, Wang H, Liu J J, et al. Determination method on total nitrogen and total phosphorus in seabuckthorn stem flow liquid with combined digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(5): 665−669.
[3] 任坤, 潘晓东, 彭聪, 等. 氮氧同位素和水化学解析昭通盆地地下水硝酸盐来源及对环境的影响[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(2): 409−419.
Ren K, Pan X D, Peng C, et al. Identification of nitrate sources of groundwaters in the Zhaotong Basin using hydrochemistry, nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and its impact on the environment[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(2): 409−419.
[4] 张华, 王宽, 宋箭, 等. 不同溶解氧水平上覆水中DOM荧光特性及总氮含量评估[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(3): 890−895.
Zhang H, Wang K, Song J, et al. The fluorescent properties of dissolved organic matter and assessment of total nitrogen in overlying water with different dissolved oxygen conditions[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(3): 890−895.
[5] 刘斯文, 黄园英, 赵文博, 等. 赣南北部黄陂河流域离子型稀土矿地区水质与健康风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 120−132.
Liu S W, Huang Y Y, Zhao W B, et al. Water quality and health risk assessment of an ion-adsorption type REE mining area of the Huangpi River Basin, Northern Ganzhou of China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 120−132.
[6] 郭子宁, 王旭升, 向师正, 等. 再生水入渗区典型抗生素分布特征与地下水微生物群落 影响因素研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3): 451−462.
Guo Z N, Wang X S, Xiang S Z, et al. Distribution characteristics of typical antibiotics in reclaimed water infiltration area and influencing factors of groundwater microbial community[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3): 451−462.
[7] 李谨丞, 曹文庚, 潘登, 等. 黄河冲积扇平原浅层地下水中氮循环对砷迁移富集的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3): 488−498.
Li J C, Cao W G, Pan D, et al. Influences of nitrogen cycle on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater from the Yellow River alluvial fan plain[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3): 488−498.
[8] 韩斌, 林法祥, 丁宇, 等. 海州湾近岸海域水质状况调查与风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(4): 429−437.
Han B, Lin F X, Ding Y, et al. Quality survey and risk assessment of the coastal waters of Haizhou Bay[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(4): 429−437.
[9] 王燕, 王艳洁, 赵仕兰, 等. 海水中溶解态总氮测定方法比对及影响因素分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(4): 644−648.
Wang Y, Wang Y J, Zhao S L, et al. Method comparison and analysis of influence factors for determination of dissolved total nitrogen in seawater[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(4): 644−648.
[10] 丁明军, 杨慧中. 水中总磷和总氮含量的离子色谱测定法[J]. 分析化学, 2012, 40(3): 381−385.
Ding M J, Yang H Z. Determination of total phosphorus and nitrogen in water by ion chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 40(3): 381−385.
[11] 欧阳钧. 离子色谱法测定水中总氮[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2014, 50(7): 906−907.
Ouyang J. Determination of total nitrogen in water by ion chromatography[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2014, 50(7): 906−907.
[12] 张国郁. 离子色谱法测定生活饮用水中总氮和总磷[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2014, 50(12): 1577−1578.
Zhang G Y. Determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in drinking water by ion chromatography[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2014, 50(12): 1577−1578.
[13] 杨雪. 离子色谱法测定地表水中总氮和总磷[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2015, 51(11): 1619−1620.
Yang X. Determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in surface water by ion chromatography[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2015, 51(11): 1619−1620.
[14] 唐景静, 黎丽萍, 区一杭. 燃烧氧化-电化学法测定地表水和废水中的总氮[J]. 中国环境监测, 2016, 32(1): 108−111.
Tang J J, Li L P, Qu Y H. The determination of total nitrogen in surface water and waste water samplers by burning oxidation-electrochemical method[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2016, 32(1): 108−111.
[15] 赵洋甬, 赵建平, 黄绍荣, 等. 闭管消解-萘乙二胺分光光度法测定水中总氮[J]. 中国环境监测, 2012, 28(1): 57−59.
Zhao Y Y, Zhao J P, Huang S R, et al. Determination of total nitrogen in water by closed digestion N-(1-naphthyl)ethyle chromogenic reaction[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(1): 57−59.
[16] 梁康甫, 杨慧中. 水质总氮在线检测的光谱数据校正方法[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(12): 7396−7400.
Liang K F, Yang H Z. Calibration method for spectral data of on-line total-nitrogen detection in water[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(12): 7396−7400.
[17] 凌琪, 李组成, 罗梦洋, 等. 智能消解/紫外分光光度法测定高氨氮污水中总氮[J]. 中国给水排水, 2014, 30(16): 117−119.
Ling Q, Li Z C, Luo M Y, et al. Measuring TN in high ammonia nitrogen domestics sewage by smart digester and ultraviolet spectrophotometry[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2014, 30(16): 117−119.
[18] 王中荣, 魏福祥, 王盼盼, 等. 微顺序注射-镉柱还原分光光度法测定海水中总氮[J]. 分析化学, 2016, 44(9): 1328−1334.
Wang Z R, Wei F X, Wang P P, et al. Determination of total nitrogen in seawater by micro sequential injection-cadmium column reduction spectrophotometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 44(9): 1328−1334.
[19] 杨颖, 程祥圣, 刘鹏霞. 紫外光照还原-流动注射分光光度法测定海水中硝酸盐[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2011, 47(5): 514−516.
Yang Y, Cheng X S, Liu P X. FI-spectrophotometric determination of nitrate in seawater by UV irradiation reduction[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2011, 47(5): 514−516.
[20] 贾岳清, 周昊, 殷惠民, 等. 水中总氮测定方法的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2020, 40(2): 1−5.
Jia Y Q, Zhou H, Yin H M, et al. Progress in determination of total nitrogen in water[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2020, 40(2): 1−5.
[21] 周英杰, 王淑梅, 陈少华. 影响总氮测定的关键因素研究[J]. 环境工程, 2012, 30(1): 106−110.
Zhou Y J, Wang S M, Chen S H. Key factors on the accuracy of total nitrogen analysis[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2012, 30(1): 106−110.
[22] 祝旭初, 周雪莲, 雷迅, 等. 对测定总氮新标准( HJ636—2012)的探讨[J]. 中国给水排水, 2013, 29(16): 94−97.
Zhu X C, Zhou X L, Lei X, et al. Discussion on new standard method HJ636—2012 for determining total nitrogen[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2013, 29(16): 94−97.
[23] 郝冬亮. 碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法测定总氮的影响因素[J]. 中国给水排水, 2014, 30(12): 148−150.
Hao D L. Influence factors of alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometry for determination of total nitrogen[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2014, 30(12): 148−150.
[24] 张念, 刘祖文, 郭云, 等. 浸矿废水中总氮测量的影响因素及相关对策[J]. 工业水处理, 2016, 36(5): 102−105.
Zhang N, Liu Z W, Guo Y, et al. Influential factors and related countermeasures of the determination of TN in mine leaching wastewater[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2016, 36(5): 102−105.
[25] 林莉莉, 钟旋, 包思聪, 等. 影响水中总氮检测准确度的关键因素探析[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(Supplement): 119−122.
Lin L L, Zhong X, Bao S C, et al. Research on the key factors influencing on detection of total nitrogen in water[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(Supplement): 119−122.
[26] 蒋然, 柴欣生, 张翠. 影响总氮准确定量的光谱检测因素[J]. 中国环境监测, 2012, 28(4): 45−47.
Jiang R, Chai X S, Zhang C. Effects of spectroscopic uncertainties on total nitrogen quantification[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(4): 45−47.
[27] 罗琼, 刘则华, 尹华, 等. 国产过硫酸钾不能用于水样总氮测定的原因解析和对策[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(4): 110−113.
Luo Q, Liu Z H, Yin H, et al. Analysis and countermeasure of total nitrogen determination failure in water sample with domestic potassium persulfate[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2018, 34(4): 110−113.
[28] 王小剑, 张海霞, 蔡昂祖, 等. 总氮测定过程中空白吸光值偏高的原因分析[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2021, 33(4): 741−748.
Wang X J, Zhang H X, Cai A Z, et al. Cause analysis of high blank absorbance in determination of total nitrogen[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2021, 33(4): 741−748.
[29] 晁雷, 曹雨, 李亚峰. 水质总氮测定时空白值的影响因素[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 37(5): 949−954.
Chao L, Cao Y, Li Y F. Influencing factors of blank value in the determination of total nitrogen in water[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science), 2021, 37(5): 949−954.
[30] 潘忠成, 李敏. HJ636—2012测定总氮时影响空白值因素分析[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(1): 126−129.
Pan Z C, Li M. Analysis of influencing factors on the blank value of total nitrogen determination by HJ636—2012[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(1): 126−129.
[31] 薛程, 吕晓杰, 王允. 水中总氮测定方法存在问题的研究及改进[J]. 中国环境监测, 2018, 34(3): 123−127.
Xue C, Lyu X J, Wang Y. Research on the problems and improvement of total nitrogen determination method in water[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2018, 34(3): 123−127.
[32] 陈松, 梁娟, 蒲宗耀, 等. 碱性过硫酸钾测定总氮的改进[J]. 印染, 2018(1): 54−56.
Chen S, Liang J, Pu Z Y, et al. Improvement for determination of total nitrogen in water with alkaline potassium persulfate[J]. China Dyeing & Finishing, 2018(1): 54−56.
[33] 钟金鸣, 王树谦. 滏阳河总氮测定中水样保存条件的探究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2018, 36(7): 43−46.
Zhong J M, Wang S Q. Prediction model of total nitrogen concentration in Qinghe Reservoir based on grey relational grade and BP neural network[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2018, 36(7): 43−46.
-



 下载:
下载: