Optimization of Cation Exchange Capacity Determination in Soil by Hexamminecobalt Trichloride Method
-
摘要:
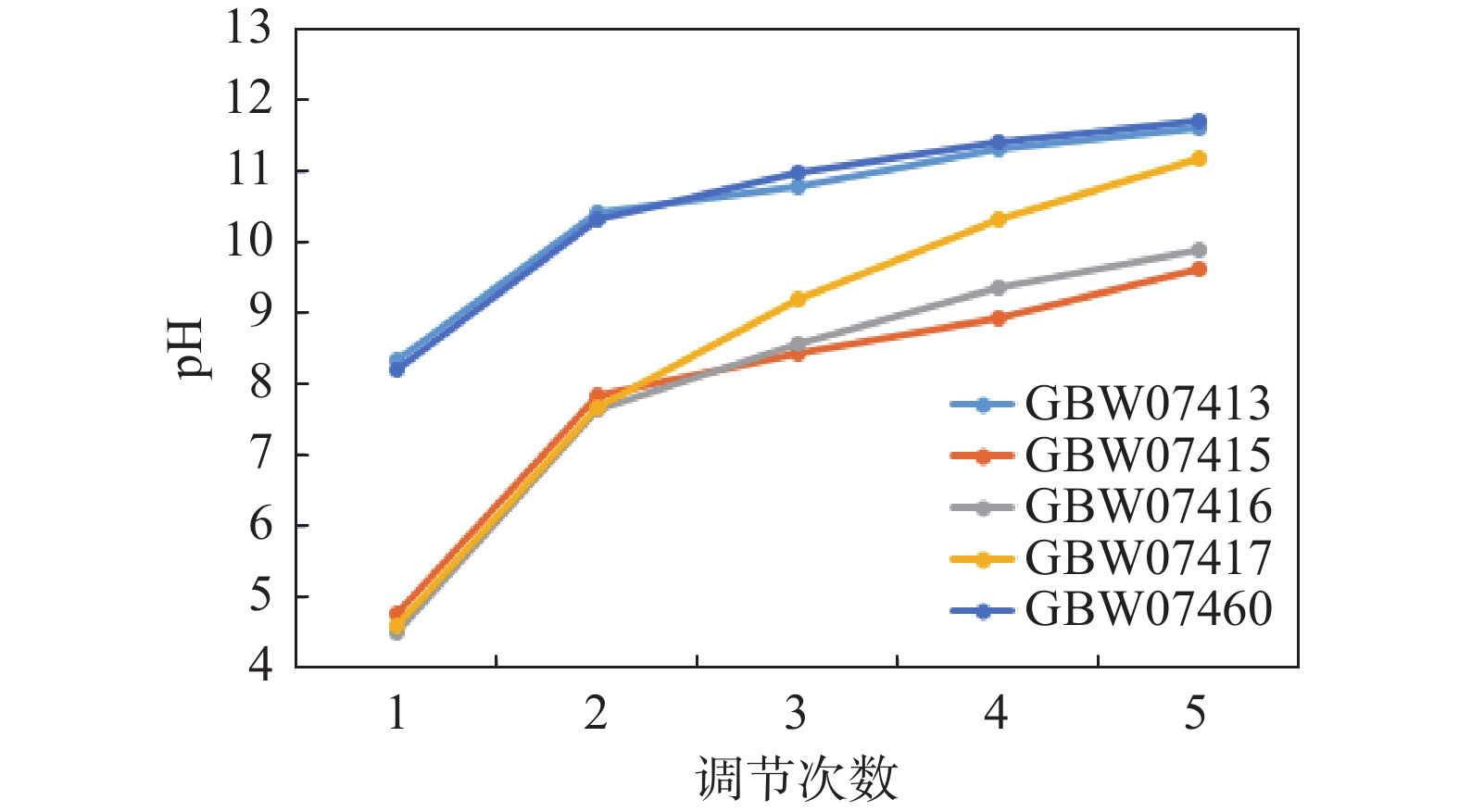
土壤阳离子交换量(CEC)是评价土壤保肥能力和改良土壤、合理施肥的重要依据,同时也能影响土壤中污染物的迁移转化。与传统的乙酸铵交换法、乙酸钙交换法测定CEC的方法相比,三氯化六氨合钴法的操作步骤简洁,检测效率高,试剂消耗量小,对大批量样品的分析有明显优势。但该方法的适用范围较小,对中性和碱性样品检测结果好,而对酸性样品的检测结果偏低至50%。为解决以上问题,本文以2mol/L氢氧化钠溶液调节pH至碱性,样品的CEC测定值有显著提高,酸性和碱性样品测定结果均可达到标准值范围内。通过绘制pH调节曲线,得到不同pH范围的土壤样品中加入2mol/L氢氧化钠溶液体积,以此调节未知样品的pH值,实现CEC的准确测定。在原有的方法基础上调节样品pH至碱性,优化后的方法精密度范围为1.02%~3.82%(n=6)。
Abstract:Compared with the traditional ammonium acetate exchange method and calcium acetate exchange method to determine cation exchange capacity (CEC), hexamminecobalt trichloride method has obvious advantages in the analysis of large quantities of samples. However, the application scope of this method is limited, and the detection results of neutral and alkaline samples are good, but the detection results of acidic samples are as low as 50%. In order to solve these problems, the pH was adjusted to alkaline with 2mol/L sodium hydroxide solution, the CEC value of the sample was significantly improved, and the determination results of both acidic and alkaline samples reached the range of standard values. By drawing the pH adjustment curve, the volume of 2mol/L sodium hydroxide solution was obtained in soil samples with different pH ranges, so as to adjust the pH value of unknown samples and realize the accurate determination of CEC. On the basis of the original method, the pH of the sample was adjusted to alkalinity, and the precision of the optimized method ranged from 1.02% to 3.82% (n=6). After optimization, the application scope of the method is expanded, the precision and accuracy are improved, and the detection efficiency of a large number of samples is effectively improved.
-

-
表 1 标准物质和实际样品详细信息
Table 1. pH and CEC in reference materials and samples
标准物质 pH值 CEC标准值
(cmol+/kg)标准物质和实际样品 pH值 CEC标准值
(cmol+/kg)GBW07412 6.8 16.0±2.1 GBW07414a 8.18 17.0±1.0 GBW07413 8.15 13.0±1.1 GBW07460 8.5 9.6±1.3 GBW07414 8.18 22.4±1.7 样品1 6.23 — GBW07415 6.08 19.6±2.2 样品2 7.80 — GBW07416 4.71 11.2±1.5 样品3 5.51 — GBW07417 6.8 6.0±0.5 表 2 标准物质的pH值、标准值及不同pH条件下CEC的测定结果
Table 2. The pH, standard values of national reference materials and the determination results of CEC at different pH.
标准物质
编号调节pH前
CEC测定值
(cmol+/kg)调节pH后
CEC测定值
(cmol+/kg)CEC
标准值
(cmol+/kg)pH
标准值GBW07412 8.6 18.4 16.0±2.1 6.80 GBW07413 5.5 8.2 13.0±1.1 8.15 GBW07414 19.1 23.4 22.4±1.7 8.18 GBW07415 9.8 16.0 19.6±2.2 6.08 GBW07460 6.9 7.7 9.6±1.3 8.50 表 3 不同土壤pH值范围下,2mol/L氢氧化钠溶液用量
Table 3. Dosage of 2mol/L NaOH solution under different soil pH ranges
土壤样品pH值范围 取用2mol/L氢氧化钠溶液
体积(mL)4~5 0.35 5~6 0.25 6~7 0.20 >7 0.15 表 4 方法准确度和精密度实验结果
Table 4. Precision and accuracy tests of the method
标准物质编号 CEC标准值
(cmol+/kg)CEC单次测定值
(cmol+/kg)CEC测定平均值
(cmol+/kg)RSD
(%)GBW07412 16.0±2.1 16.3 16.6 15.7 16.2 2.09 16.5 16.1 15.9 GBW07413 13.0±1.1 10.7 11.0 10.6 10.9 2.81 11.0 11.4 10.7 GBW07414 22.4±1.7 21.1 21.2 21.1 21.3 1.02 21.5 21.4 21.6 GBW07415 19.6±2.2 17.0 17.3 17.3 17.3 1.06 17.2 17.5 17.4 GBW07416 11.2±1.5 11.4 10.6 11.4 11.3 3.82 11.9 11.4 11.2 GBW07417 6.0±0.5 6.5 6.5 6.5 6.4 1.61 6.4 6.2 6.5 GBW07414a 17.0±1.0 17.0 15.2 16.0 16.1 3.82 16.2 15.7 16.3 GBW07460 9.6±1.3 7.6 7.7 7.6 7.6 1.32 7.5 7.4 7.5 样品1 — 11.9 11.6 11.7 11.7 1.93 11.6 11.9 11.3 样品2 — 22.6 23.1 22.5 22.5 1.50 22.1 22.6 22.3 样品3 — 8.8 8.4 8.2 8.4 3.01 8.6 8.2 8.2 -
[1] 赵莉. 乙酸铵交换法测定土壤阳离子交换量的不确定度评定研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2015, 40(10): 146−149.
Zhao L. Uncertainty in determining of cation exchange capacity in soil samples by ammonium acetate exchange method[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 40(10): 146−149.
[2] 康婷, 周春火, 魏宗强, 等. 江西省土壤阳离子交换量区域分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(14): 66−71.
Kang T, Zhou C H, Wei Z Q, et al. Regional distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil cation exchange capacity in Jiangxi[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(14): 66−71.
[3] Ngo D N G, Chuang X Y, Huang C P, et al. Compositional characterization of nine agricultural waste biochars: The relations between alkaline metals and cation exchange capacity with ammonium adsorption capability[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023(11): 110003.
[4] Jiang J, Wang Y P, Yu M X, et al. Soil organic matter in important for acid buffering and reducing aluminum leaching from acidic forest soils[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018(501): 86−94.
[5] Shekofteh H, Ramazani F, Shirani H. Optimal feature selection for predicting soil CEC: Comparing the hybrid of ant colony organization algorithm and adaptive network-based fuzzy system with multiple linear regression[J]. Geoderma, 2017(298): 27−34.
[6] Zhao X Z T, Arshad M, Li N, et al. Determination of the optimal mathematical model, sample size, digital data and transect spacing to map CEC (cation exchange capacity) in a sugarcane field[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020(173): 105436.
[7] Emamgholizadeh S, Bazoobandi A, Mohammadi B, et al. Prediction of soil cation exchange capacity using enhanced machine learning approaches in the southern region of the Caspian Sea[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2023(14): 101876.
[8] Aihemaiti A, Jiang J G, Li D A, et al. The interaction of metal concentrations and soil properties on toxic metal accumulation of native plants in vanadium mining area[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018(222): 216−226.
[9] Cui X Y, Mao P, Sun S, et al. Phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated soils by Amaranthus hypochondriacus L: The effects of soil properties highlighting cation exchange capacity[J]. Chemosphere, 2021(283): 131067.
[10] Liddicoat C, Bi P, Waycott M, et al. Ambient soil cation exchange capacity inversely associates with infectious and parasitic disease risk in regional Australia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018(626): 117−125.
[11] 白志强, 张世熔, 钟钦梅, 等. 四环盆地西缘土壤阳离子交换量的特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(3): 581−587.
Bai Z Q, Zhang S R, Zhong Q M, et al. Characteristics and impact factors of soil cation exchange capacity in western margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(3): 581−587.
[12] Chen Y T, Gao S B, Jones E J, et al. Prediction of soil cay content and cation exchange capacity using visible near-infrared spectroscopy, portable X-ray fluorescence, and X-ray diffraction techniques[J]. Environment Science and Technology, 2021, 55(8): 4629−4637. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04130
[13] Wan M X, Hu M Y, Qu M K, et al. Rapid estimation of soil cation exchange capacity through sensor data fusion of portable XRF spectrometry and vis-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Geoderma, 2020(363): 114163.
[14] Renault P, Cazevieille P, Verdier J, et al. Variations in the cation exchange capacity of a ferralsol supplied with vinasse, under changing aeration conditions comparison between CEC measuring methods[J]. Geoderma, 2009(154): 101−110.
[15] 黄英, 白冰, 李洋冰, 等. 三氯化六氨合钴浸提-分光光度法测定泥质砂岩黏土阳离子交换量[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2023, 59(2): 232−234.
Huang Y, Bai B, Li Y B, et al. Determination of cation exchange capacity of argillaceous sandstone clay by cobalt trichloride leaching-spectrophotometry[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis: Part B (Chemical Analysis), 2023, 59(2): 232−234.
[16] 胡梦颖, 张鹏鹏, 徐进力, 等. CEC前处理系统-凯氏定氮仪快速测定土壤中的阳离子交换量[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(2): 458−463.
Hu M Y, Zhang P P, Xu J L, et al. Rapid determination of soil cation exchange capacity using a cation exchange capacity pretreatment system and a Kjeldahl apparatus[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 458−463.
[17] Enang R K, Kips P A, Yerima B P K, et al. Pedotransfer functions for cation exchange capacity estimation in highly weathered soils of the tropical highlands of NW Cameroon[J]. Geoderma Regional, 2022(29): e00514.
[18] 杨利利, 李菲, 陈渝, 等. 分光光度法测定土壤中阳离子交换量的优化改进[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(35): 119−122.
Yang L L, Li F, Chen Y, et al. Optimization and improvement of spectrophotometry method to determine cation exchange capacity in soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(35): 119−122.
[19] 侯玉兰, 吴银菊, 胡芳, 等. 全自动淋洗-凯氏定氮法快速测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2022, 58(8): 966−969.
Hou Y L, Wu Y J, Hu F, et al. Rapid determination of soil cation exchange capacity by automatic leaching—Kjeldahl nitrogen determination method[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis: Part B (Chemical Analysis), 2022, 58(8): 966−969.
[20] 拉毛吉, 王玉功, 张榕. 乙酸铵离心交换法和乙酸钙离心交换法测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(3): 38−41.
La M J, Wang Y G, Zhang R. Determination of cation exchange capacity of soil by centrifugal exchange of ammonium and calcium acetates[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 7(3): 38−41.
[21] 陈桂华, 范芳, 林芷君. 三氯化六氨合钴浸提-分光光度法测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2019, 55(12): 1448−1451.
Chen G H, Fan F, Lin Z J. Determination of soil cation exchange capacity by cobalt hexamine trichloride extraction-spectrophotometry[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis: Part B (Chemical Analysis), 2019, 55(12): 1448−1451.
[22] Purnamasari L, Rostaman T, Widowati L R, et al. Comparison of appropriate cation exchange capacity (CEC) extraction methods for soils from several regions of Indonesia[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 648: 012209. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/648/1/012209
[23] 林清火, 刘海林, 王莉, 等. 碳基土壤调理剂对橡胶园土壤pH和阳离子交换量的影响[J]. 热带农业科学, 2018, 38(12): 1−9.
Lin Q H, Liu H L, Wang L, et al. Effect of biochar-based soil conditioner on the soil pH and CEC in rubber plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2018, 38(12): 1−9.
[24] 岳中慧, 岳启建, 龙寿坤, 等. 三氯化六氨合钴法浸提-分光光度法测定土壤中阳离子交换量[J]. 化学分析计量, 2022, 31(4): 55−59.
Yue Z H, Yue Q J, Long S K, et al. Determination of cation exchange capacity in soil by spectrophotometry after extraction of hexammonium cobalt trichloride[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2022, 31(4): 55−59.
[25] Kazak E S, Kazak A V. Experimental features of cation exchange capacity determination in organic-rich mudstones[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020(83): 103456.
[26] Aran D, Maul A, Masfaraud J F. A spectrophotometric measurement of soil cation exchange capacity based on cobaltihexamine chloride absorbance[J]. C. R. Geoscience, 2008(340): 865−871.
[27] 王丽敏, 吴慧, 申立, 等. 分光光度法测定土壤阳离子交换量的方法优化[J]. 环境监控与预警, 2022, 14(2): 49−52, 69.
Wang L M, Wu H, Shen L, et al. Method optimization of spectrophotometric determination of cation exchange capacity in soil[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2022, 14(2): 49−52, 69.
[28] 王俊杰, 辛文涛, 王巧环. 超声浸提-分光光度法测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2023, 13(6): 562−567.
Wang J J, Xin W T, Wang Q H. Determination of soil cation exchange capacity by ultrasonic extraction-spectrophotometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 13(6): 562−567.
[29] 刘蓉, 邓茂, 李莹莹, 等. 不同酸碱度土壤阳离子交换量的测定研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 2019, 35(1): 125−130.
Liu R, Deng M, Li Y Y, et al. Optimization for the determination of cation exchange capacity in soils with different acidity and alkalinity[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2019, 35(1): 125−130.
[30] 段小燕, 施玉格. 三氯化六氨合钴浸提-分光光度法测定新疆土壤中阳离子交换量[J]. 干旱环境监测, 2019, 33(3): 113−116.
Duan X Y, Shi Y G. Determination of the cation exchange capacity in Xinjiang soils using a hexamminecobalt trichloride solution by spectrophotography[J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 2019, 33(3): 113−116.
[31] 李媛, 段小燕, 施玉格, 等. 振荡提取-荧光分光光度法分析土壤样品中石油类物质[J]. 岩矿测试, 2023, 42(6): 1240−1247.
Li Y, Duan X Y, Shi Y G, et al. Determination of the petroleum oil in soil by fluorescence spectrophotometry with oscillatory extraction[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2023, 42(6): 1240−1247.
-



 下载:
下载: