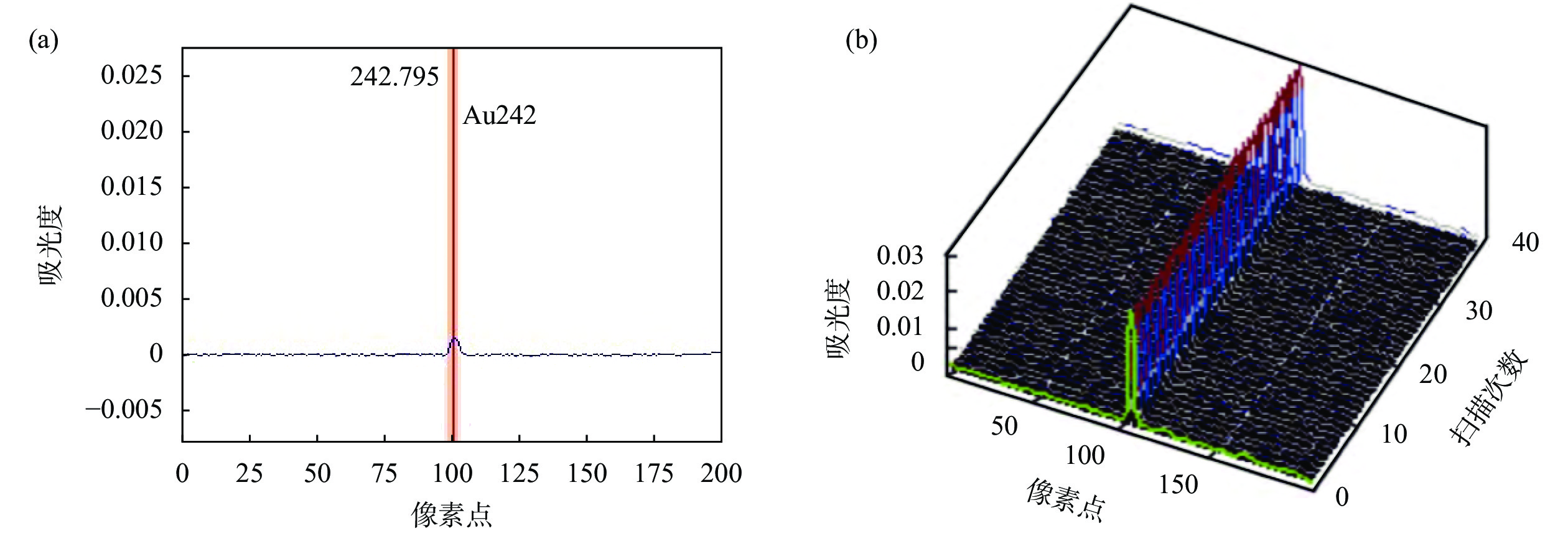
Ultratrace Gold in High-Purity Graphite by High-Resolution Continuous Light Source Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry with Hanging Droplet Microextraction
-
摘要:
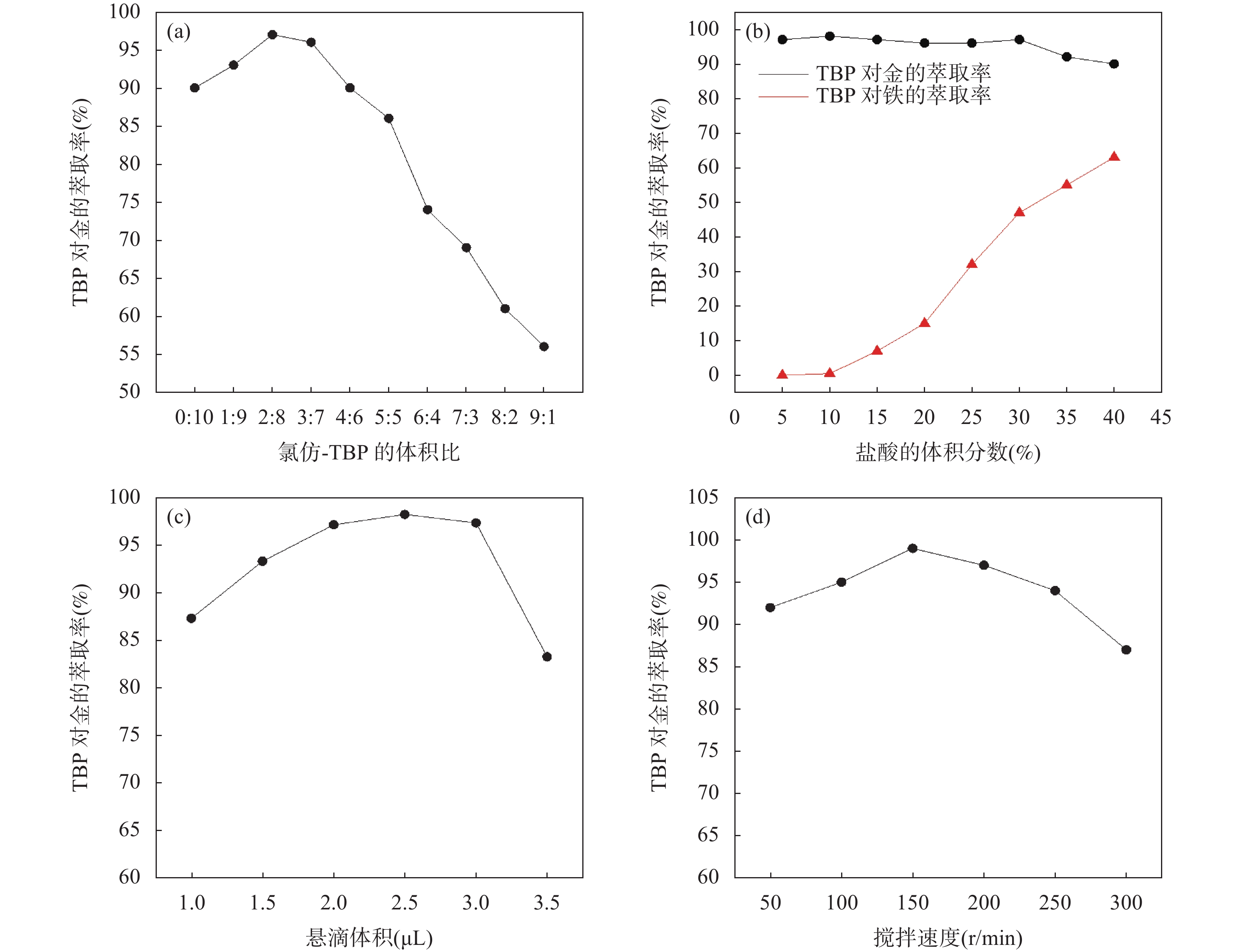
准确测定高纯石墨中的超痕量金,难点是如何在最大程度地减少样品前处理过程中器皿、试剂、材料、环境及设备所引入的二次污染的前提下,实现对样品溶液中超痕量金(0.1 ~1ng/mL)的有效分离和高倍富集。本文建立了铂皿中灰化、酸解、磷酸三丁酯悬滴微萃取的方法用于高纯石墨中超痕量金分析。首先于铂皿中高温灼烧除去样品中的固定碳,然后采用氢氟酸-王水-高氯酸将灰分消解完全制备成样品溶液,再以微升级磷酸三丁酯悬滴作为萃取剂,分离富集样品溶液中的金,最后采用高分辨连续光源石墨炉原子吸收光谱法(GFAAS)对悬滴中的金进行测定。实验结果表明,使用2.5μL磷酸三丁酯悬滴(氯仿体积为20%)作为萃取剂,在10%盐酸介质的样品溶液中萃取金2min,对金的富集倍数可达283倍。在实验条件下,金的质量浓度在0.1~2.0ng/mL范围内与其吸光度呈良好的线性关系,相关系数r为0.999,检出限为0.11ng/g,样品溶液中一定量的共存元素(如钠、镁、铝)对金的测定无干扰。按照实验方法测定5个高纯石墨实际样品中的金含量,测定结果的相对标准偏差(RSD,n=6)为1.5%~4.9%,加标回收率为94.9%~105.3%。
Abstract:The major challenge in accurately determining ultratrace gold in high-purity graphite is how to achieve effective separation and high enrichment of it (0.1−1ng/mL) in the sample solution, while minimizing the secondary pollution introduced by vessels, reagents, materials, environment, and equipment during the sample pretreatment process. A new method for the analysis of ultratrace gold in high-purity graphite is established by ashing and acid dissolution in a platinum dish, followed by microextraction with a hanging droplet of tributyl phosphate. Firstly, the fixed carbon in the sample was removed by high-temperature burning in a platinum vessel; then, the ash was completely dissolved into a sample solution using hydrofluoric acid-aqua regia-perchloric acid; next, micro-upgraded tributyl phosphate droplets were used as an extractant to separate and enrich gold from the sample solution; finally, gold in the droplets was determined using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. The experimental results showed that by using 2.5μL of tributyl phosphate (chloroform volume fraction 20%) as the extractant, gold can be extracted from a sample solution in 10% hydrochloric acid medium for 2min, and the enrichment factor for gold can reach up to 283 times. Under the selected experimental conditions, the mass concentration of gold showed a good linear relationship with its absorbance values in the range of 0.1 to 2.0ng/mL. The correlation coefficient (r) was 0.999, and the detection limit of the method was 0.11ng/g. Interference tests showed that the presence of certain coexisting elements such as sodium, magnesium, and aluminum in the sample solution had no effect on the determination of gold. According to the experimental method, the gold content in five high-purity graphite samples was measured. The relative standard deviation (RSD, n=6) of the results was 1.5%−4.9%, and the recovery rate was 94.9%−105.3%.
-

-
表 1 金的石墨炉升温程序
Table 1. The heating program for graphite furnace of Au
步骤编号 升温程序 温度
(℃)斜坡
(℃/s)保持时间
(s)载气流速
(L/min)1 干燥 90 6 10 2 2 干燥 100 3 20 2 3 干燥 150 5 10 2 4 灰化 300 100 20 2 5 灰化 500 250 10 2 6 调零 950 0 5 0 7 原子化 2000 1500 5 0 8 清洗 2450 500 5 2 表 2 CCD检测器有效像素点的优化
Table 2. Effective pixel optimization of CCD detector
有效像素点 校准曲线斜率 检出限
(ng/g)方法标准偏差
(ng/mL)1 0.1134 0.153 0.03899 3 0.1653 0.121 0.02793 5 0.1758 0.109 0.02375 7 0.1801 0.093 0.02287 9 0.1865 0.097 0.02203 表 3 方法精密度和加标回收实验
Table 3. The precision and recovery tests of the method
样品编号 6次分次测定值
(ng/g)平均值
(ng/g)RSD
(%)加标量
(ng/g)测定总量
(ng/g)回收率
(%)GC-1 3.10 3.16 3.02 3.13 3.18 3.31 3.15 1.5 2.00 5.03 94.9 GC-2 5.89 5.80 5.90 5.93 5.83 5.92 5.88 4.3 5.00 11.06 102.6 GC-3 9.34 9.57 9.21 9.51 9.45 9.37 9.41 4.9 10.00 19.88 103.7 GC-4 12.07 11.91 12.33 12.23 11.88 12.32 12.12 4.5 10.00 22.02 97.9 GC-5 15.03 15.21 14.85 14.79 14.89 15.10 14.98 4.9 15.00 30.58 105.3 表 4 不同分离富集和检测方法性能的对比
Table 4. Comparison of performance of different seperation, enrichment and measurement methods
分离富集方法 时间
(min)方法检出限
(ng/g)RSD
(%)检测方法 参考文献 悬滴微萃取 2 0.11 1.5~4.9 (n=6) 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法(GFAAS) 本文方法 泡塑吸附法 60 0.08 ≤23.2 (n=9) 火焰原子荧光光谱法(FAFS) [1] 泡塑吸附法 20 6.6 0.81~2.11 (n=10) 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) [2] 泡塑吸附法 60 0.15 / 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) [19] 介孔吸附法 180 2.0 / 火焰原子吸收光谱法(AAS) [26] 火试金法 60 / 1.5~2.1 (n=7) 火焰原子吸收光谱法(AAS) [9] 铅试金法 60 5.3 2.3~3.7 (n=6) 火焰原子吸收光谱法(AAS) [10] 铋试金法 70 / 3.6~6.1 (n=5) 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法(GFAAS) [11] 离子树脂交换法 >60 / <3.5 (n=5) 火焰原子吸收光谱法(AAS) [27] 共沉淀法 180 20.6 / 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) [18] -
[1] 申玉民, 罗治定, 郭小彪, 等. 泡塑分离富集-火焰原子荧光光谱法测定地球化学样品中的痕量金[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(1): 127−134. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201809260108
Shen Y M, Luo Z D, Guo X B, et al. Determination of trace gold in geochemical samples by flame atomic fluorescence spectrometry with PUFP separation and enrichment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(1): 127−134. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201809260108
[2] 马怡飞, 汪广恒, 张尼, 等. 乙醇介质制备载炭泡塑及其在地质样品金测定中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(5): 533−540. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801150005
Ma Y F, Wang G H, Zhang N, et al. Determination of gold in geological samples[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(5): 533−540. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801150005
[3] Liu Y H, Wang Z C, Xue D S, et al. An improved analytical protocol for the determination of sub-nanogramgold in 1-2g rock samples using GFAAS after polyurethane foam pretreatment[J]. Atomic Spectro-scopy, 2020, 41(3): 131−140. doi: 10.46770/AS.2020.03.006
[4] 王明双, 荀维超. 717阴离子交换树脂吸附高盐废水中金的性能研究[J]. 贵金属, 2022, 43(2): 47−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0676.2022.02.008
Wang M S, Xun W C. Study on the adsorption performance of 717 anion resin for gold in high-salt waste water[J]. Preciousmetals, 2022, 43(2): 47−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0676.2022.02.008
[5] Fischer L, Moser B, Hann S. Determination of background concentrations of Ag, Pd, Pt and Au in highly mineralized ground waters at sub-ng·L−1 concentrations by online matrix separation/pre-concentration coupled to ICP-SFMS[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(23): 1−21.
[6] 齐白羽, 王丁, 王卓, 等. 低温乙醇分离-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定粗铅中金[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2021, 57(11): 977−979. doi: 10.11973/lhjy-hx202111003
Qi B Y, Wang D, Wang Z, et al. Determination of gold in crude lead by ICP-AES after separation with low temperature ethano[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2021, 57(11): 977−979. doi: 10.11973/lhjy-hx202111003
[7] Liu Y H, Wan B , Xue D S. Sample digestion and combined preconcentration methods for the determination of ultra-low gold levels in rocks[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(9): 1778: 1−20.
[8] 吴俊, 傅昊, 李冰健, 等. 疏水性离子液体萃取-原子吸收光谱法分离分析微量金[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(1): 260−262. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2011)01-0260-03
Wu J, Fu H, Li B J, et al. Hydrophobic ionic liquid extraction-flam atomic absorption spectrometry for separation/analysis trace gold[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2011, 31(1): 260−262. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2011)01-0260-03
[9] 巫贞祥, 赖秋祥, 衷水平, 等. 火试金预富集-原子吸收光谱法测定文丘里泥中的金[J]. 黄金, 2021, 42(1): 88−90. doi: 10.11792/hj20210119
Wu Z X, Lai Q X, Zhong S P, et al. Determination of gold in Venturi mud by fire assay preconcentration-atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Gold, 2021, 42(1): 88−90. doi: 10.11792/hj20210119
[10] 姚明星, 毛香菊, 郭晓瑞, 等. 银保护灰吹铅试金-高分辨率连续光源火焰原子吸收光谱法测定铁粉中痕量金[J]. 冶金分析, 2022, 42(8): 48−54. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011813
Yao M X, Mao X J, Guo X R, et al. Determination of trace gold in iron powder by high resolution continuous light source flame atomic absorption spectrometry with silver protection cupellation lead fire assay enrich-ment[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2022, 42(8): 48−54. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011813
[11] 姚明星, 王威, 毛香菊, 等. 铋试金-石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定地球化学样品中痕量金铂钯钌铑铱[J]. 冶金分析, 2022, 42(9): 42−47. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011827
Yao M X, Wang W, Mao X J, et al. Determination of trace gold, platinum, palladium, ruthenium, rhodium and iridium in geochemical samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry with bismuth fire assay[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2022, 42(9): 42−47. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011827
[12] 刘娜, 刘芳美, 赖秋祥, 等. 火试金重量法测定碲化铜中的金和银[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2022, 51(6): 65−70. doi: 10.19612/j.cnki.cn11-5066/tf.2022.06.010
Liu N, Liu F M, Lai Q X, et al. Determination of gold and silver in copper telluride by fire assay gravimetric method[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2022, 51(6): 65−70. doi: 10.19612/j.cnki.cn11-5066/tf.2022.06.010
[13] 崔行宪, 石奇超. 火试金重量法与原子吸收光谱(AAS)法测定砂金矿中金的含量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2021, 4(11): 45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2021.04.009
Cui X X, Shi Q C. Determination of gold in placer golder by fire assay gravimetry method combined with AAS wet method and atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS)[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 4(11): 45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2021.04.009
[14] 邵敏, 宋虎跃, 沈芳存, 等. 液滴微萃取-石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定环境水样中痕量镉[J]. 冶金分析, 2011, 31(2): 52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2011.02.009
Shao M, Song H Y, Shen F C, et al. Determination of trace cadmium in environmental watersamples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry combined with droplet microextraction[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2011, 31(2): 52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2011.02.009
[15] Jiang H M, Hu B. Determination of trace Cd and Pb in natural waters by direct single drop microextraction combined with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Microchim Acta, 2008, 161: 101−107.
[16] Zhao L C, Li W, Hu Y Q, et, al. Optimization of lithium metaboratefusion and post-ultrasonic extraction for multi-element determination in graphite by ICP-AES[J]. Analytics Sciences December, 2021, 37: 1735−1740.
[17] 杨倩倩, 何石, 胡月, 等. 电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定高纯石墨中9种元素[J]. 冶金分析, 2016, 36(3): 49−53. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.009712
Yang Q Q, He S, Hu Y, et al. Determination of nine elements in high purity graphite by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2016, 36(3): 49−53. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.009712
[18] 王琳, 唐志中, 来新泽, 等. 混合吸附剂分离富集-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中铂钯金[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(3): 420−426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.03.011
Wang L, Tang Z Z, Lai X Z, et al. Determination of platinum, palladium and gold in geological samples by bomb-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry with concentrate and extraction by mixed adsorbent[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(3): 420−426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.03.011
[19] 于立华. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定地球化学样品中金时样品前处理条件的优化[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2019, 9(2): 46−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2019.02.010
Yu L H. Optimization of pretreatment conditions for determination of gold in geochemical samples by ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Journal Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 9(2): 46−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2019.02.010
[20] Yu H, Jia Y L, Hong M, et al. Hybrid monolith assisted magnetic ion-imprinted polymer extraction coupled with ICP-MS for determination of trace Au(Ⅲ) in environmental and mineral samples[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2020, 158(1): 1−8.
[21] Xia L, Li X, Wu Y, et al. Ionic liquids based single drop microextraction combined with electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for determination of Co, Hg and Pb in biological and environmental samples[J]. Spectrochim Acta Part B, 2008, 63: 1290−1296. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.09.018
[22] 张爱滨, 魏进武, 王燕, 等. 顺序扫描ICP-AES法测定高纯石墨灰分中14种杂质金属元素的方法研究[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2003, 33(4): 609−614. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2003.04.019
Zhang A B, Wei J W, Wang Y, et al. Determination of impurity elements in high purity graphite ash by equential scan inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2003, 33(4): 609−614. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2003.04.019
[23] Oshima T, Koyama T, Otsuki A N. A comparative study on the extraction of Au(III) using cyclopentylmethyl ether, dibutylcarbitol, and methyl isobutyl ketone in acidic chloride media[J]. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2021, 39: 477−490. doi: 10.1080/07366299.2021.1874108
[24] 王小强, 赵亚男, 梁倩, 等. 泡沫塑料富集-火焰原子吸收光谱法测定金矿石中金[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2022, 12(3): 110−114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2022.03.016
Wang X Q, Zhao Y N, Liang Q. Determination of gold in gold ores by flame atomic absorption spectrometry with foam plastics enrichment[J]. China Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 12(3): 110−114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2022.03.016
[25] 单兴刚, 林云芬. 乙酸丁酯萃取-火焰原子吸收光谱法测定矿石中痕量金[J]. 冶金分析, 2011, 31(3): 64−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2011.03.013
Shan X G, Lin Y F. Determination of trace gold in ore by butyl acetate extraction and flame atomic absorption spectro-metry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2011, 31(3): 64−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2011.03.013
[26] Joanna D, Marzena D, Rafał O, et al. An ion-imprinted thiocyanato-functionalized mesoporous silica for preconcentration of gold(Ⅲ) prior to its quantitation by slurry sampling graphite furnace AAS[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2018, 185(12): 564. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-3106-x
[27] 周陶鸿, 黄健, 田琼, 等. 阴离子交换固相萃取在测定铜矿和粗铜中金的应用[J]. 冶金分析, 2010, 30(8): 66−69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2010.08.014
Zhou T H, Huang J, Tian Q, et al. Application of anion exchange solid phase extraction in determination of gold in copper concentrate and blister copper[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2010, 30(8): 66−69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2010.08.014
-



 下载:
下载: