Determination of Organic Carbon in Soil and Sediment by the Elemental Analyzer with Silver Cup Digestion Method
-
摘要:
土壤有机碳是衡量土壤健康和生态系统功能的重要指标,对农业生产和环境保护具有重要意义。准确测定土壤有机碳含量有助于评估土壤质量、优化施肥管理、提高作物产量,并在应对气候变化、碳循环研究中发挥关键作用。本文旨在建立一种快速准确测定土壤和沉积物中有机碳含量的方法,以支持科学研究和农业生产。实验采用银杯消解-元素分析仪法,通过优化样品前处理过程,包括加酸浓度、加酸量、称样量和消解温度,使用81孔位铜板和银杯处理土壤样品。具体操作为使用Φ5mm×9mm规格银杯称取25mg样品,加入80µL的2mol/L盐酸去除无机碳,70℃电热板干燥,对高无机碳样品进行反复加酸加热处理,并利用低含量和高含量标准物质绘制混合标准曲线,通过日校准方法定量有机碳。该方法在21.2~6704.3μg有机碳含量范围内显示出良好的线性关系,线性相关系数为0.9998。样品称样量为25mg时,方法检出限和定量限分别为0.07%和0.23%,6种标准物质(GBW07406、GBW07385、GBW07391、GBW07544、GBW07546和GBW07365)中有机碳测定值的相对标准偏差(RSD)在0.67%~5.14%之间,测定值均在标准值范围内。该方法具有高精密度和准确度,能够满足常规土壤和沉积物有机碳测定要求,适用于大批量样品的检测分析。
Abstract:Soil organic carbon (SOC) is an important indicator of soil health and ecosystem functioning and is of great significance for agricultural production and environmental protection. Accurate determination of SOC content is essential for assessing soil quality, optimizing fertilizer management, improving crop yields, and contributing greatly in the research of tackling climate change as well as the carbon cycle. A rapid and accurate method for the determination of organic carbon in soil and sediment was established to support scientific research and agricultural production. The silver cup digestion-elemental analyzer method was used to process soil samples using 81-porosity copper plates and silver cups by optimizing sample pretreatment, including acid concentration and volume, sample weight as well as digestion temperature. The specific procedure was initially weighing 25mg of sample using Φ5mm×9mm silver cups, then adding 80L of 2mol/L hydrochloric acid to remove inorganic carbon, followed by drying the sample on an electric hot plate at 70℃. Samples with high inorganic carbon were treated by repeated acid addition. Low and high content standards were used to form a mixed standard curve to quantify the organic carbon with a daily calibration method. The method demonstrated excellent linearity in the range of 21.2−6704.3μg of organic carbon content with a linear correlation coefficient of 0.9998. The limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) of the method were 0.07% and 0.23%, respectively, based on a sample weight of 25mg. The precision of organic carbon determined for six standard substances (GBW07406, GBW07385, GBW07391, GBW07544, GBW07544, GBW07546 and GBW07365) ranged from 0.67% to 5.14%, with all measured values falling within the range of the standard values. The method demonstrates high precision and accuracy, which meets the requirements for the determination of organic carbon in soil and sediment and is suitable for the analysis of large quantities of samples.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- sediments /
- organic carbon /
- silver cup digestion /
- element analyzer
-

-
表 1 标准物质有机碳含量的标准值
Table 1. Reference values of organic carbon content in the reference materials
标准物质类型 编号 有机碳标准值
(%)无机碳标准值
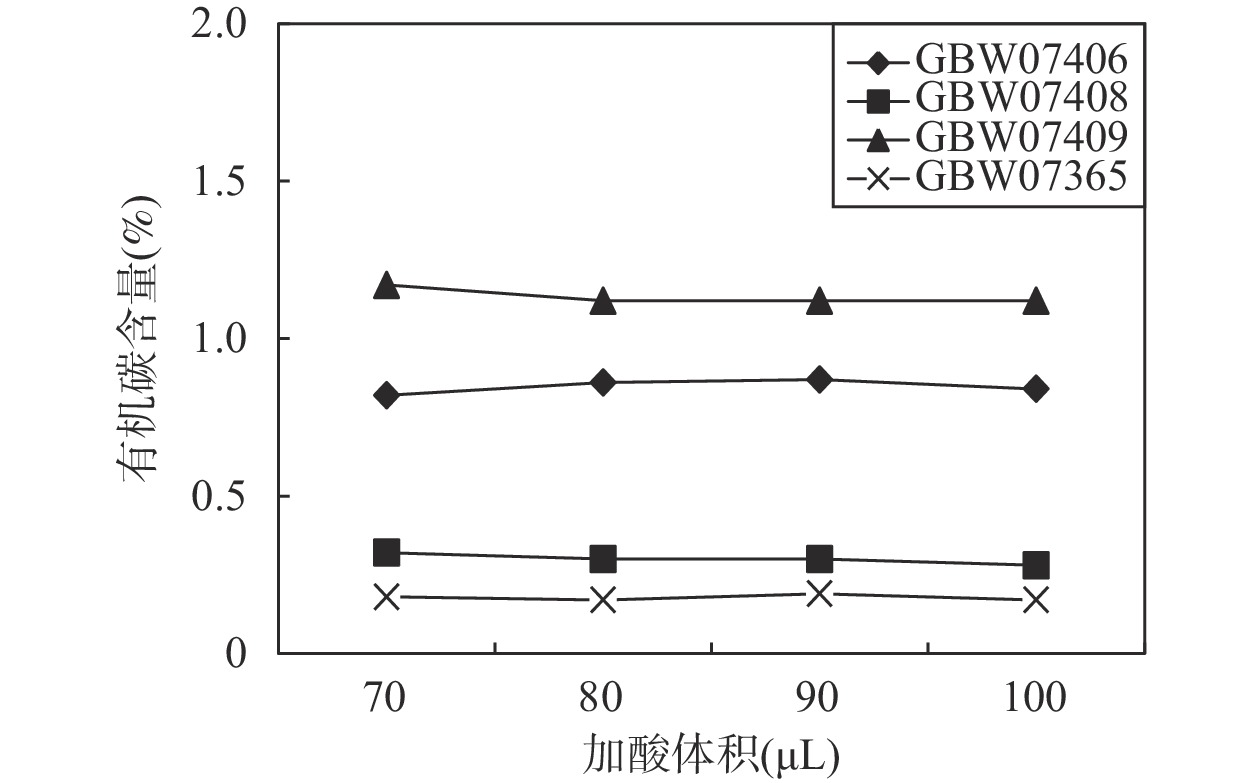
(%)土壤 GBW07406 0.81±0.09 0.02 土壤 GBW07408 (0.30) 1.63 土壤 GBW07544 0.48±0.04 1.96 土壤 GBW07546 0.44±0.03 3.37 土壤 CatNo.2181 (1.89) 0.30 土壤 GBW07409 1.1±0.1 0.8 泛滥平原沉积物 GBW07385 1.12±0.09 0.56 泛滥平原沉积物 GBW07390 0.79±0.09 1.08 泛滥平原沉积物 GBW07391 2.00±0.17 1.03 水系沉积物 GBW07365 0.18±0.02 2.42 表 2 三种消解温度下标准物质有机碳的测定结果
Table 2. Analytical results of organic carbon content in standard substances at three digestion temperatures
消解温度
(℃)有机碳含量测定值(%) GBW07406 GBW07408 GBW07409 GBW07385 60 0.85 0.31 1.08 1.14 70 0.87 0.30 1.13 1.13 80 0.84 0.30 1.12 1.13 标准值 0.81±0.09 (0.30) 1.10±0.10 1.12±0.09 表 3 称样量对有机碳测定结果的影响
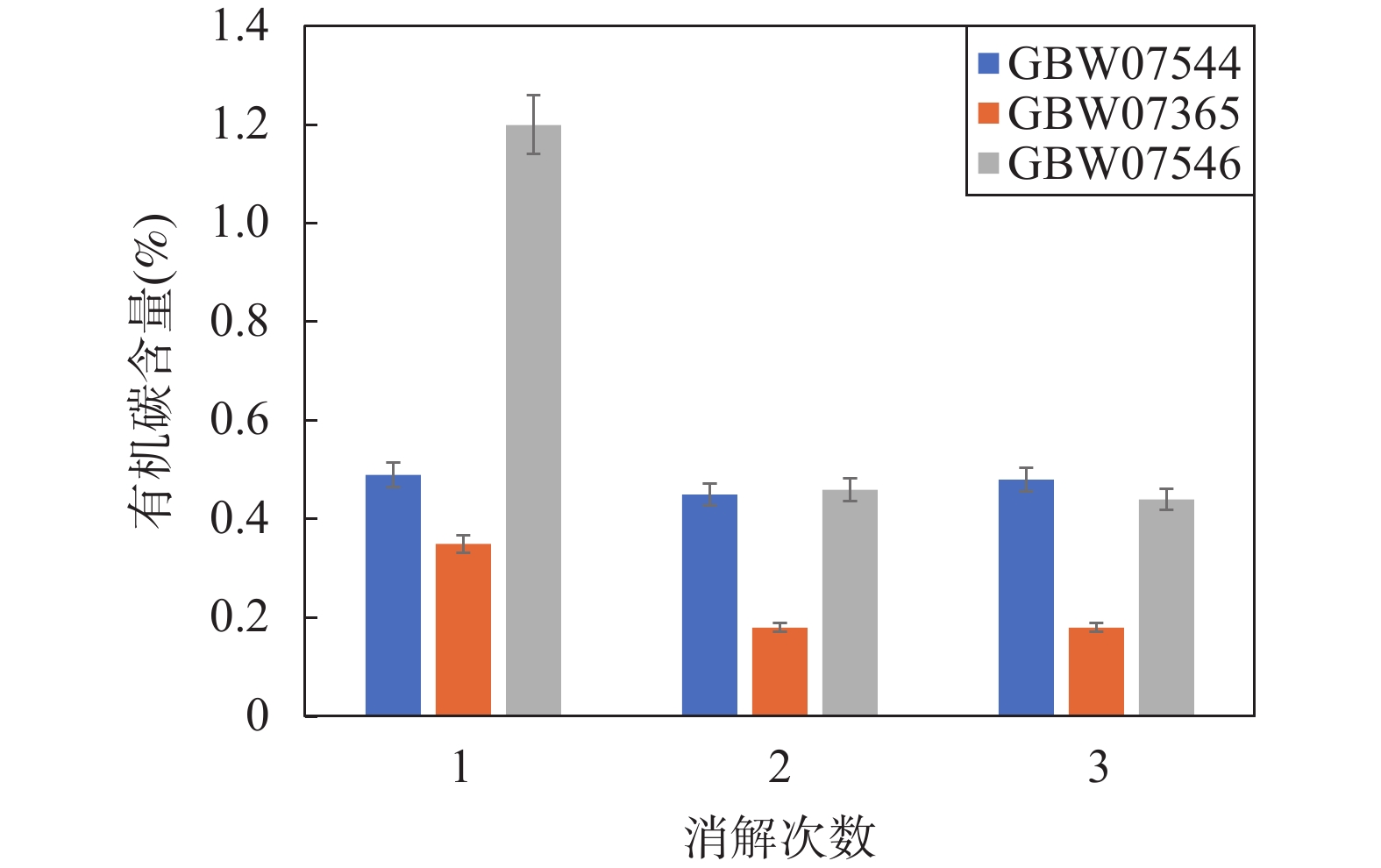
Table 3. Effect of sample weight on determination of organic carbon
称样量
(mg)一次消解有机碳测定值(%) 二次消解有机碳测定值(%) 三次消解有机碳
测定值(%)GBW07406 GBW07390 GBW07391 GBW07408 GBW07544 GBW07544 GBW07546 GBW07365 GBW07546 20 0.79 0.84 2.09 0.31 0.5 0.5 0.49 0.19 0.45 25 0.8 0.79 2.04 0.31 0.46 0.46 0.45 0.20 0.44 30 0.78 0.82 2.07 0.28 0.68 0.47 0.45 0.17 0.42 35 0.77 0.82 2.07 0.3 0.88 0.43 0.44 0.16 0.44 40 0.79 0.8 2.08 0.33 1.09 0.45 0.59 0.16 0.42 标准值 0.81±0.09 0.79±0.09 2.00±0.17 (0.3) 0.48±0.04 0.48±0.04 0.44±0.03 0.18±0.02 0.44±0.03 表 4 方法精密度
Table 4. Precision tests of the method
标准物质编号 有机碳含量
标准值(%)有机碳含量测定值(%) 有机碳含量
测定平均值
(%)RSD
(%)相对误差
(%)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 GBW07406 0.81±0.09 0.79 0.80 0.78 0.77 0.79 0.79 0.79 0.79 1.01 −2.5 GBW07385 1.12±0.09 1.14 1.13 1.13 1.12 1.14 1.13 1.10 1.13 1.22 0.9 GBW07391 2.00±0.17 2.09 2.09 2.07 2.07 2.08 2.08 2.05 2.08 0.67 4.0 GBW07544 0.48±0.04 0.46 0.44 0.45 0.47 0.44 0.48 0.45 0.46 3.27 −4.2 GBW07546 0.44±0.03 0.47 0.45 0.45 0.47 0.45 0.45 0.41 0.45 4.78 2.3 GBW07365 0.18±0.02 0.17 0.18 0.17 0.18 0.20 0.18 0.18 0.18 5.14 0 表 5 实际样品有机碳含量分析结果
Table 5. Analytical results of organic carbon content in the practical samples
实际样品
编号有机碳含量测定值%) 两种分析方法的
相对偏差(%)银杯消解-
元素分析仪法重铬酸钾
容量法1-1 0.64 0.65 1.1 1-2 0.84 0.80 3.4 1-3 0.50 0.48 2.9 1-4 3.22 3.40 3.8 1-5 1.00 0.94 4.4 表 6 银杯消解-元素分析仪法与重铬酸钾容量法的比较
Table 6. Comparison between silver cup digestion-elemental analyzer method and potassium dichromate volumetric method
参数 重铬酸钾容量法 银杯消解-元素分析仪法 仪器及耗材 酸式滴定管、锥形瓶若干、电子天平、研钵、水浴锅、移液管 银杯、电子天平、电热板、元素分析仪 试剂 重铬酸钾溶液、邻菲罗啉指示剂、浓硫酸、蒸馏水、硫酸亚铁溶液 盐酸 土壤称样量 0.1g 25mg 前处理时间及效率 1h处理30件样品 1h处理81件样品 测定方式 人工滴定反应 元素分析仪自动进样 -
[1] 查同刚. 土壤理化分析[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2017: 79−87.
Zha T G. Soil physicochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2017: 79−87
[2] Hicks P C E, Ryals R, Zhu B, et al. The deep soil organic carbon response to global change[J]. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2023, 54(1): 375−401. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-102320-085332
[3] Ferraz M A, Choueri R B, Castro Í B, et al. Influence of sediment organic carbon on toxicity depends on organism’s trophic ecology[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 261: 114134.1−114134.10. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114134
[4] 李源, 尹肖尧, 常钟元. 高频红外碳硫仪测定土壤和沉积物中有机质[J]. 化学分析计量, 2020, 29(6): 75−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2020.06.017
Li Y, Yin X Y, Chang Z Y. Determination of organic matter in soil and sediment by high frequency infrared carbon sulphur instrument[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2020, 29(6): 75−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2020.06.017
[5] 吴才武, 夏建新, 段峥嵘. 土壤有机质测定方法述评与展望[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(3): 453−460. doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2015.03.004
Wu C W, Xia J X, Duan Z R. Review on detection methods of soil organic matter (SOM)[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(3): 453−460. doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2015.03.004
[6] 李国傲, 何咏, 陈雪, 等. 全自动消解测定土壤/沉积物中的有机碳[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(5): 152−155. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201605033
Li G A, He Y, Chen X, et al. Determina of organic carbon in soil/sediments by automatic digestion[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(5): 152−155. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201605033
[7] 李朝英, 郑路, 郑之卓, 等. 自动滴定仪测定土壤有机碳及其组分的方法优化[J]. 岩矿测试, 2024, 43(4): 632−640. doi: 10.15898/j.ykcs.202404210092
Li Z Y, Zheng L, Zheng Z Z, et al. Method optimization for the determination of soil organic carbon and its components by automatic titrator[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2024, 43(4): 632−640. doi: 10.15898/j.ykcs.202404210092
[8] 杨林婧, 杨莎, 张圣杨, 等. 农田土壤有机碳高光谱特征及定量监测研究[J]. 激光生物学报, 2024, 33(4): 316−325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2024.04.004
Yang L J, Yang S, Zhang S Y, et al. Hyperspectral characteristics and quantitative monitoring of soil organic carbon in farmland[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 316−325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2024.04.004
[9] 于雯泉, 钟少军. 海洋沉积物有机碳分析方法中干燥预处理过程人为误差的发现及其意义[J]. 环境科学学报, 2007, 27(5): 861−867. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2007.05.025
Yu W Q, Zhong S J. Freeze-drying pretreatment improves organic carbon determinations of marine sediments[J]. Acta Scientiac Circumstantiac, 2007, 27(5): 861−867. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2007.05.025
[10] 高少鹏, 徐柏青, 王君波, 等. 总有机碳分析仪准确测定湖泊沉积物中的TOC[J]. 分析试验室, 2019, 38(4): 413−416. doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2018.072501
Gao S P, Xu B Q, Wang J B, et al. Measuring total organic carbon precisely in lake sediment in Xizang Plateau by TOC analyzer[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2019, 38(4): 413−416. doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2018.072501
[11] 秦超, 李飞, 李贺, 等. 高频红外碳硫仪测定土壤中低含量的碳, 硫, 有机碳[J]. 当代化工研究, 2022(8): 47−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2022.08.015
Qin C, Li F, Li H, et al. Determination of low content of carbon, sulfur and organic carbon in soil by high frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2022(8): 47−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2022.08.015
[12] Avramidis P, Bekiari V. Application of a catalytic oxidation method for the simultaneous determination of total organic carbon and total nitrogen in marine sediments and soils[J]. PLos One, 2021, 16(6): e0252308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252308
[13] Hu J, Loh P S, Chen Z, et al. Storage and dynamics of soil organic carbon in allochthonous-dominated and nitrogen-limited natural and planted mangrove forests in Southern Thailand[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2024, 200: 1.1−1.14. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116064
[14] Ma H, Peng M, Yang Z, et al. Spatial distribution and driving factors of soil organic carbon in the Northeast China Plain: Insights from latest monitoring data[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 911: 168602. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168602
[15] Hernández T D B, Slater B K, Shaffer J M, et al. Comparison of methods for determining organic carbon content of urban soils in Central Ohio[J]. Geoderma Regional, 2023, 34: e00680. doi: 10.1016/j.geodrs.2023.e00680
[16] 王巧环, 任玉芬, 孟龄, 等. 元素分析仪同时测定土壤中全氮和有机碳[J]. 分析试验室, 2013, 32(10): 41−45.
Wang Q H, Ran Y F, Meng L, et al. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and organic carbon in soil with an elemental analyzer[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2013, 32(10): 41−45.
[17] 谭扬, 吴学丽, 侯立杰. 样品处理方法对海洋沉积物有机碳稳定同位素测定的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(5): 780−784. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2018.05.023
Tan Y, Wu X L, Hou L J. The effects of sample treatment methods on marine sediment organic carbon stable isotope[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(5): 780−784. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2018.05.023
[18] 祝孟博, 宋建中, 彭平安. 预处理过程对不同类型样品中有机碳含量和稳定碳同位素测定的影响[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(4): 476−482. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2015.04.015
Zhu M B, Song J Z, Peng P A. Influences of pretreatment procedures on determination of total organic carbon and stable carbon isotope in different samples[J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(4): 476−482. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2015.04.015
[19] 闵秀云, 武君, 高春亮, 等. 基于元素分析仪测定土壤有机碳的不同前处理方法对比研究[J]. 盐湖研究, 2020, 28(4): 64−70. doi: 10.12119/j.yhyj.202004008
Min X Y, Wu J, Gao C L, et al. The comparative study on different pretreatment methods of soil organic carbon determined by elemental analyzer[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2020, 28(4): 64−70. doi: 10.12119/j.yhyj.202004008
[20] 孙萱, 宋金明, 于颖, 等. 元素分析仪快速测定海洋沉积物TOC和TN的条件优化[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(7): 14−19. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130801001
Sun X, Song J M, Yu Y, et al. A rapid method for determing the total organic carbon and total nitrogen in marine sediments with an elemental analyzer[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(7): 14−19. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130801001
[21] Apesteguia M, Plante A F, Virto I. Methods assessment for organic and inorganic carbon quantification in calcareous soils of the Mediterranean region[J]. Geoderma Regional, 2018, 12: 39−48. doi: 10.1016/j.geodrs.2017.12.001
[22] Matsui Y, Fujisaki W, Torimoto J, et al. Gold-coated silver capsule for elemental analyzer-isotope ratio mass spectrometer: Robust against pretreatment of rock material for organic carbon and δ13C analyses[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2021, 55(3): e1−e8. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0626
[23] 孙辞, 崔杰华, 林桂凤, 等. 元素分析仪测定低含碳量土壤样品方法的改进[J]. 辽宁大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 44(4): 337−341. doi: 10.16197/j.cnki.lnunse.2017.04.010
Sun C, Cui J H, Lin G F, et al. Improvement of methodology for determining low carbon soil samples by elemental analyzer[J]. Journal of Liaoning University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2017, 44(4): 337−341. doi: 10.16197/j.cnki.lnunse.2017.04.010
-




 下载:
下载: