PALEOGENE VALLEY SYSTEM AND ITS CONTROL ON PROXIMAL CLASTIC DEPOSITS IN THE SOUTHERN SUB-SAG OF MIAOXI SAG, BOHAI BAY BASIN
-
摘要:
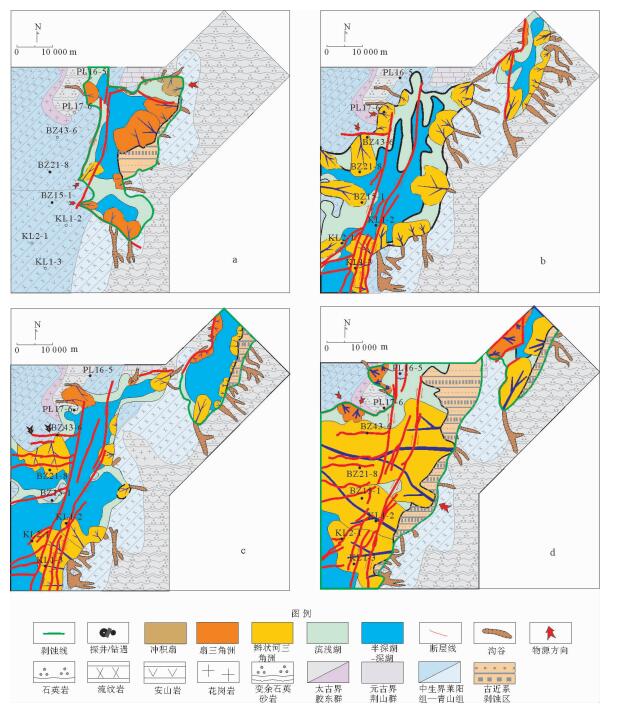
为了更好地预测低勘探区有利砂体的展布,在综合利用测井、钻井、地震等资料的基础上,对渤海湾盆地庙西南洼古近系的沟谷特征及其对近源碎屑沉积的控制作用进行了研究。结果表明:与郯庐断裂近EW向垂直相交的大型基底断裂在古近纪表现为长期拉张沉降特征,形成区域性的大型沟谷,多控制着次级洼陷的发育;而与郯庐断裂NW向、NNW向相交的派生断层一般处于挤压应力状态,多发育小型挤压断裂型沟谷。这些小型沟谷在缓坡带和陡坡带的表现特征具有明显差异。通过地震反射、地震相、属性分析和钻井资料相结合的手段,识别并确定不同层段的近源碎屑沉积体的展布,对比发现:NE向或近EW向的区域性大型沟谷往往成为陆源碎屑物质的宏观进积方向,规模相对偏小的大型沟谷,对碎屑物质进积方向的控制作用更为明显;而NW向的小型挤压性断沟,只能控制局部陆源碎屑物质的进积,沿着这些小型沟谷进入盆地的方向,往往能够准确寻找到各类近源碎屑沉积体的位置,这将有利于指导庙西南洼古近系的勘探部署。
Abstract:In order to seek for subtle reservoirs and favorable sand bodies in low exploration blocks, this paper is devoted to the study of valley system and its controls over the proximal clastic deposits based on logging, drilling, seismic data, taking the Paleogene southern sub-sag of the Miaoxi Sag, Bohai Bay Basin as a case. It is observed that the basement faults roughly in east-west direction perpendicular to the Tan-Lu fault are characterized by long-term tensile subsidence in Paleogene. These faults always form regional valleys and control the secondary subsidence in the period. However, the northwestern or north-northwestern faults, which intersect the Tan-Lu fault at an acute angle, are general under extrusion stress. Mostly, they form small compressive faulting valleys. According to the geometry of the small valleys, they can be divided into subvalleys in various shapes, such as V-type, U-type, W-type subvalleys. The performance of these small valleys on the gentle slope are rather different to those on the steep slope. On the side of steep slope, small valleys control the development of compact fan delta. On the side of gentle slope, however, small valleys control the development of large-scale braided delta. It is useful and profitable to identify and determine the distribution of terrigenous clastic deposits at different layers using seismic reflection, seismic facies, attribute analysis, drilling data and so on as tools. The northeastern or near east-west regional valleys tend to form the macroscopic progradational direction of terrigenous clastic deposits. The smaller of the regional valleys, the more can control the direction of the main terrigenous clastic material into the basin. The small northwestern valleys, belonging to the compressive broken trench, can only control partial progradation of terrigenous clastic materials. Along the direction of these small valleys into the basin, it is often able to accurately find the location for proximal clastic deposition. To clarify the location of these small valleys is conducive to the following exploration and deployment.
-
Key words:
- valley /
- proximal clastic deposits /
- Tan-Lu fault /
- southern sub-sag /
- Bohai Bay Basin
-

-
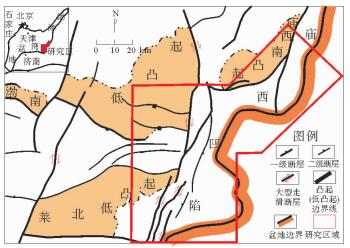
图 1 渤海湾盆地庙西南洼研究区位置(据文献[11]修改)
Figure 1.
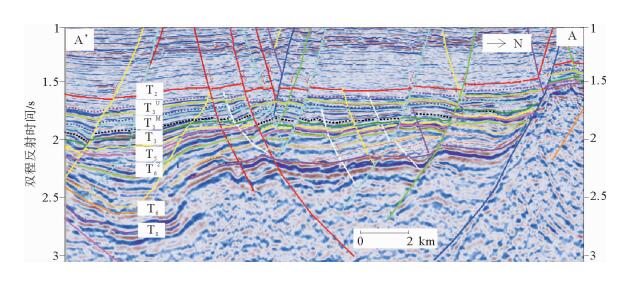
图 7 庙西南洼典型的前积反射剖面(剖面位置见图 6)
Figure 7.
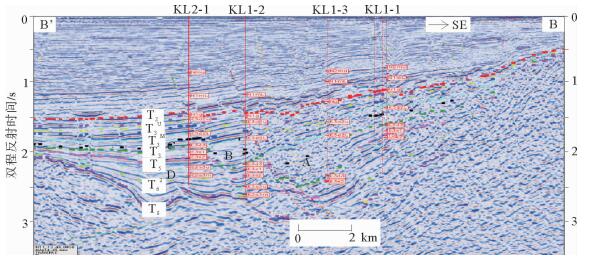
图 8 KL1-1—KL1-3—KL1-2—KL2-1井井震结合剖面图(剖面位置见图 6)
Figure 8.
-
[1] Allen P A.From Landscapes into Geological History[J].Nature, 2008, 451:274-276. doi: 10.1038/nature06586
[2] Smme T O, Helland-hansen W, Martinsen O J, et al.Relationships between morphological and sedimentological parameters in source-to-sink systems:a basis for predicting semi-quantitative characteristics in subsurface systems[J]. Basin Research, 2009, 21(4):361-387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2009.00397.x
[3] Smme T O, Jackson C A-L, Vaksdal M.Source-to-Sink Analysis of Ancient Sedimentary Systems Using a Subsurface Case Study from the More-Trndelag area of southern Norway:Part 1-depositional setting and fan evolution[J].Basin Research, 2013, 25(5):489-511. doi: 10.1111/bre.12013
[4] Walsh J P, Wiberg P L, Aalto R, et al.Source-to-sink research:economy of the Earth's surface and its strata[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 153:1-6. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ef58c984eeb5d9dd7b5a987a2b1e605f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] 庞雄, 彭大钧, 陈长民, 等.三级"源-渠-汇"耦合研究珠江深水扇系统[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(6):857-864. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.06.016
[6] 林畅松, 夏庆龙, 施和生, 等.地貌演化、源-汇过程与盆地分析[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):9-20. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.002
[7] 施和生.油气勘探"源-汇-聚"评价体系及其应用--以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[J].中国海上油气, 2015, 27(5):1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201505001
[8] 吴冬, 朱筱敏, 刘常妮, 等."源-汇"体系主导下的断陷湖盆陡坡带扇三角洲发育模式探讨:以苏丹Muglad盆地Fula凹陷为例[J].高校地质学报, 2015, 21(4):653-663.
[9] 祝彦贺, 朱伟林, 徐强, 等.珠江口盆地13.8 Ma陆架边缘三角洲与陆坡深水扇的"源-汇"关系[J].中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 42(12):3827-3834. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201112037
[10] 徐长贵, 赖维成, 薛永安, 等.古地貌分析在渤海古近系储集层预测中的应用[J].石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(5):53-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2004.05.012
[11] 徐长贵.渤海古近系坡折带成因类型及其对沉积体系的控制作用[J].中国海上油气, 2006, 18(6):365-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.06.002
[12] 徐长贵.陆相断陷盆地源-汇时空耦合控砂原理:基本思想、概念体系及控砂模式[J].中国海上油气, 2013, 25(4):1-11.
[13] 冯有良.断陷盆地层序格架中岩性地层油气藏分布特征[J].石油学报, 2005, 26(4):17-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2005.04.004
[14] 冯有良.断陷湖盆沟谷及构造坡折对砂体的控制作用[J].石油学报, 2006, 27(1):13-16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.003
[15] 冯有良, 周海民, 任建业, 等.渤海湾盆地东部古近系层序地层及其对构造活动的响应[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 40(10):1356-1376. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201010006
[16] 加东辉, 徐长贵, 杨波, 等.辽东湾辽东带中南部古近纪古地貌恢复和演化及其对沉积相的控制[J].古地理学报, 2007, 9(2):155-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.02.004
[17] 朱红涛, 杨香华, 周心怀, 等.基于层序地层学和地震沉积学的高精度三维沉积相:以渤中凹陷西斜坡BZ3-1区块东营组为例[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(6):1073-1084. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2011.113
[18] 朱红涛, 杨香华, 周心怀, 等.基于地震资料的陆相湖盆物源通道特征分析:以渤中凹陷西斜坡东营组为例[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(1):121-129. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.012
[19] 姜楠.黄河口凹陷古近系沟谷发育特征初探[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2014.
[20] 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 李德江, 等.渤海湾盆地辽东湾地区古近系地震相研究[J].沉积学报, 2007, 25(4):554-563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.04.009
[21] 朱强.等时地层格架下的地震相分析方法与应用研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2010.
[22] 韩文功, 季建清, 王金铎, 等.郯庐断裂带古新世-早始新世左旋走滑活动的反射地震证据[J].自然科学进展, 2005, 15(11):1383-1388. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2005.11.016
[23] 贾红义, 杨长春, 于建国, 等.济阳坳陷东营凹陷早始新世构造体制转换与油气成藏[J].地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(4):1312-1319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.04.042
[24] 李理, 谭明友, 张明振, 等.潍北-莱州湾凹陷郯庐断裂带新生代走滑特征[J].地质科学, 2009, 44(3):855-864. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.03.006
[25] 黄雷, 王应斌, 武强, 等.渤海湾盆地莱州湾凹陷新生代盆地演化[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(6):867-876. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.06.002
[26] 吴智平, 薛雁, 颜世永, 等.渤海海域渤东地区断裂体系与盆地结构[J].高校地质学报, 2013, 19(3):463-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.03.008
[27] 张晓庆, 吴智平, 周心怀, 等.渤海南部新生代构造发育与演化特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(1):50-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201701004
[28] 张世奇, 纪友亮.东营凹陷早第三纪古气候变化对层序发育的控制[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 1997, 22(6):26-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800557053
-



 下载:
下载: