THERMO-COMPRESSION SIMULATION EXPERIMENT AND GAS GENERATION POTENTIAL ANALYSIS OF HUIZHOU 26-6 SOURCE ROCKS IN THE PEARL RIVER MOUTH BASIN
-
摘要:
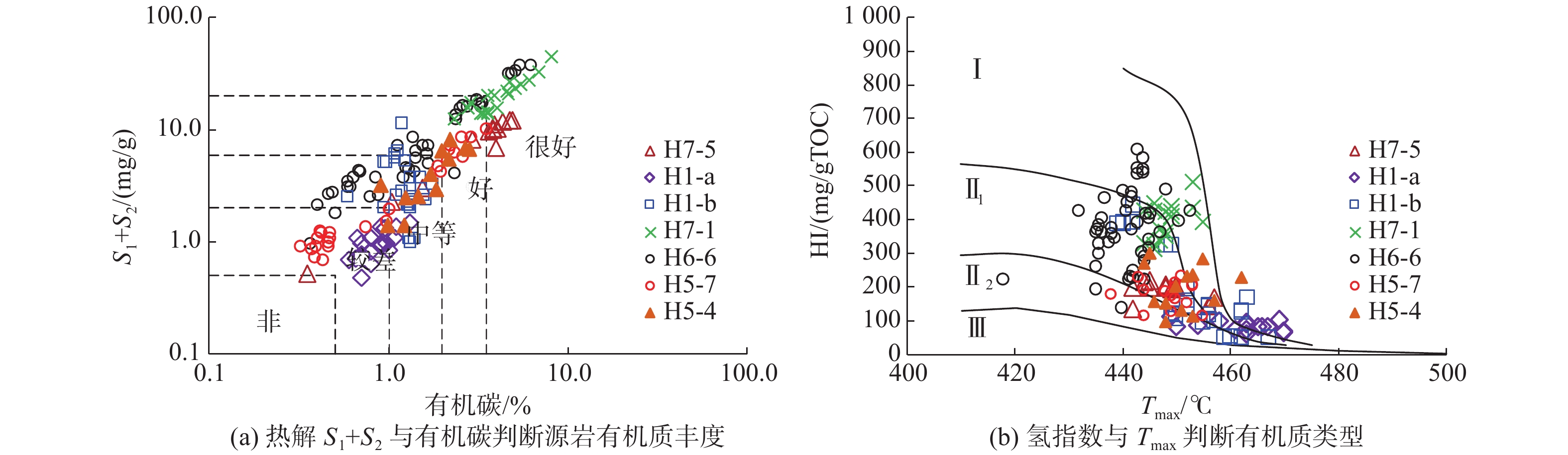
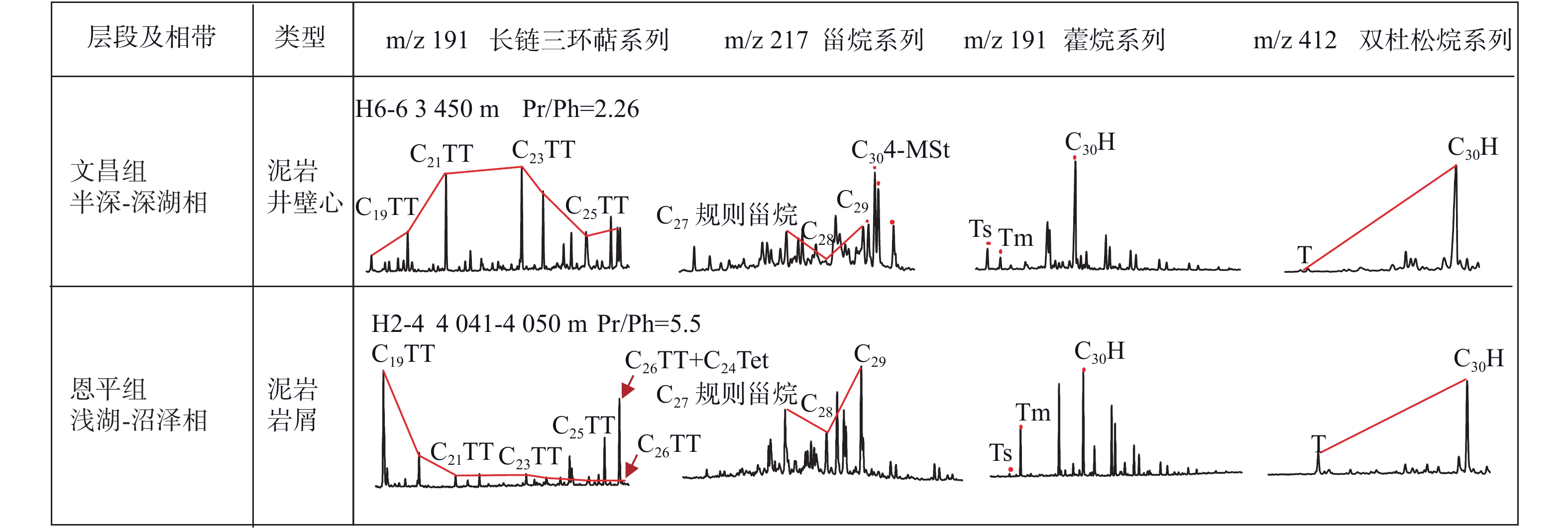
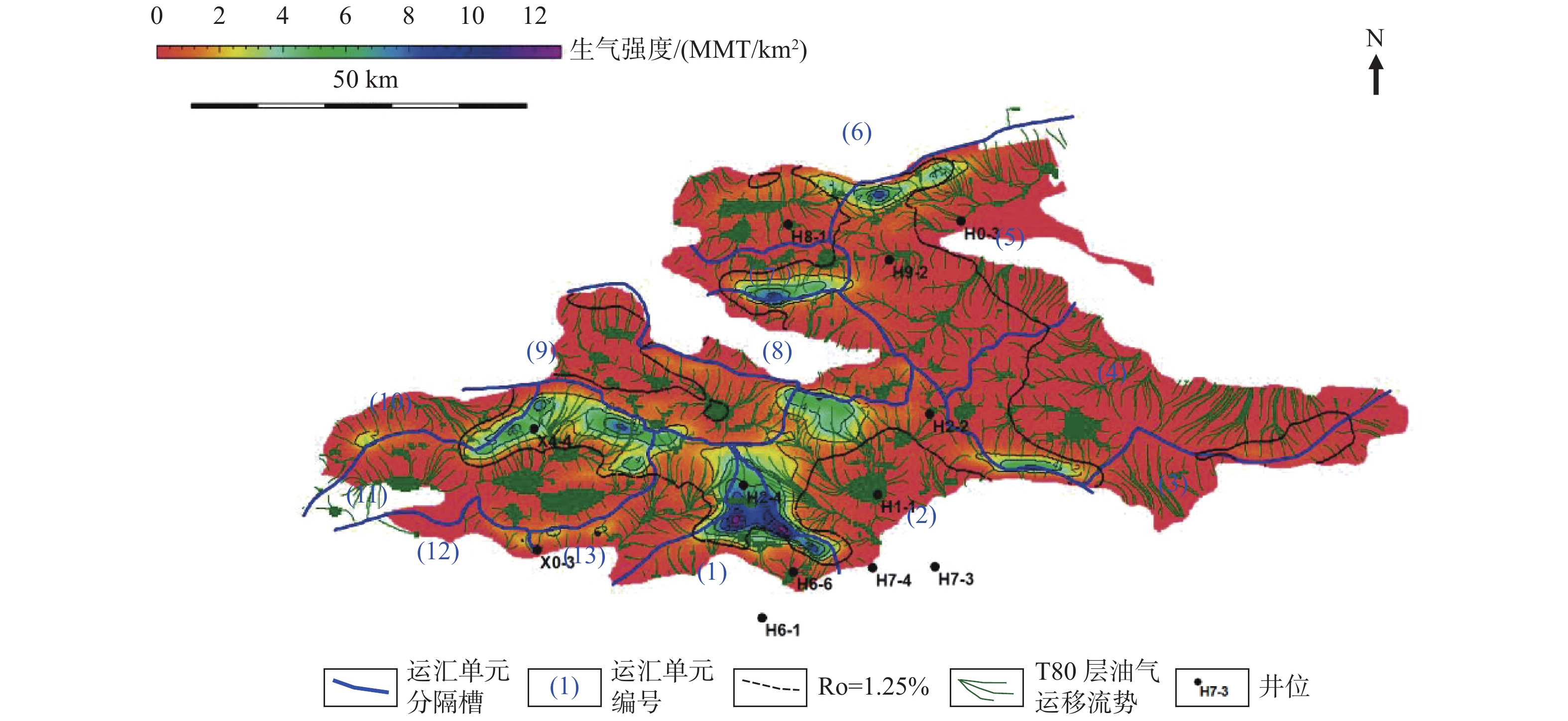
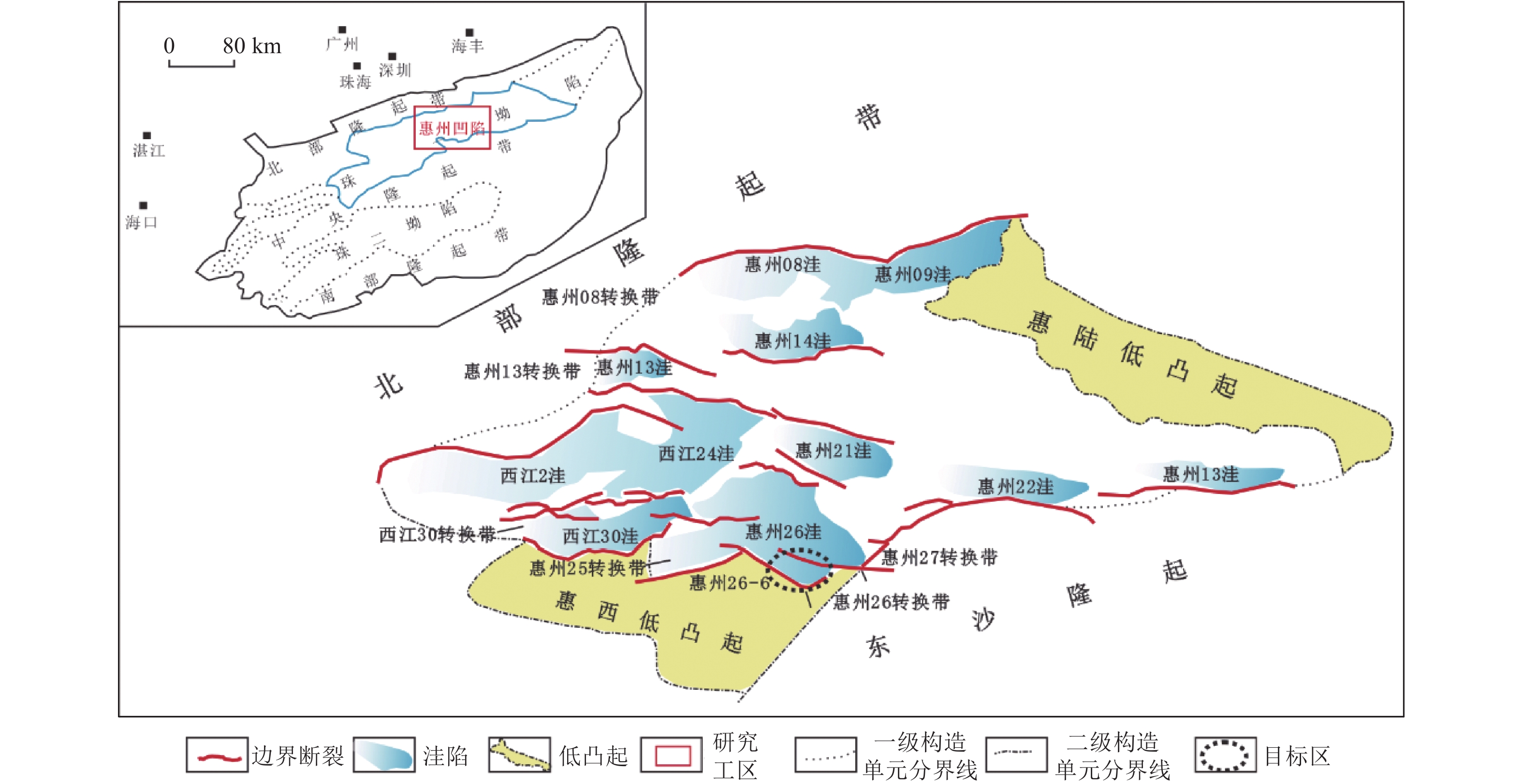
数十年勘探实践表明,珠江口盆地浅水区和深水区商业油气发现呈现“北油南气”的分布格局;随着浅水区中深层勘探不断深入,珠江口盆地珠一坳陷惠州凹陷惠州26-6构造在中生界潜山和古近系获得首个凝析气规模商业发现,引起了大家对珠江口盆地浅水区天然气资源潜力的关注。为客观有效评价珠江口盆地浅水区油型烃源岩生气潜力,选取了惠州26-6文昌组半深湖相暗色泥岩样品(Ⅱ1型)进行了半开放体系下热压模拟实验,研究了珠一坳陷惠州凹陷惠州26洼油型烃源岩在生油气高峰阶段和在不同演化阶段的产油气率,综合分析了惠州26洼油型烃源岩的生排烃模式及生烃潜力;并从烃源岩热演化程度、烃源岩生气潜力及优势汇聚方向等方面分析了惠州26-6油气田的成藏条件。
Abstract:Exploration practice in the Pearl River Mouth Basin suggests that the distribution of commercial oil and gas discoveries follow a pattern of “oil in north and gas in south”. With the progress in middle and deep exploration in the shallow water area, the first large-scale condensate gas reservoir was discovered in Mesozoic buried hills and Paleogene system of the Huizhou 26-6 structure in the Zhuyi Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, which has raised people's attention to the natural gas resource potential in the shallow water area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin. In order to objectively and effectively evaluate the hydrocarbon potential of oil-type source rocks in shallow water area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, the semi-deep lacustrine dark mudstone sample (Type Ⅱ1) of the Wenchang Formation in the Huizhou 26-6 was selected to conduct the thermo-compression simulation experiment under a semi-open system. The model of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion are analyzed synthetically with the hydrocarbon potential of the oil-type source rocks, based on the analysis of the peak stages of hydrocarbon generation and the study of oil and gas production rates at different evolutionary stages for the oil type source rocks in the Huizhou 26 sag. In addition, the forming conditions of Huizhou 26-6 oil and gas field are investigated from the aspects of thermal evolution of source rocks, gas potential of source rocks and dominant convergence direction.
-

-
表 1 样品基本参数
Table 1. Basic sample parameters
样品 层段 深度/m 沉积相 岩性 样品量/g TOC
/%Tmax
/℃S1
/(mg/g)S2
/(mg/g)S1+S2
/(mg/g)HI
/(mg/gTOC)Ro/% H6-6原样 文四段 3450 半深-深湖相 深褐色泥岩井壁心 10 5.51 443 3.53 33.17 36.70 601 0.62 H6-6混合样 文四段 3456~3468 半深-深湖相 深褐色泥岩岩屑 10 4.78 443 5.01 26.20 31.21 548 0.59 表 2 珠一坳陷文昌组水分析数据
Table 2. Water analysis data of Wenchang Formation in Zhu I Depression
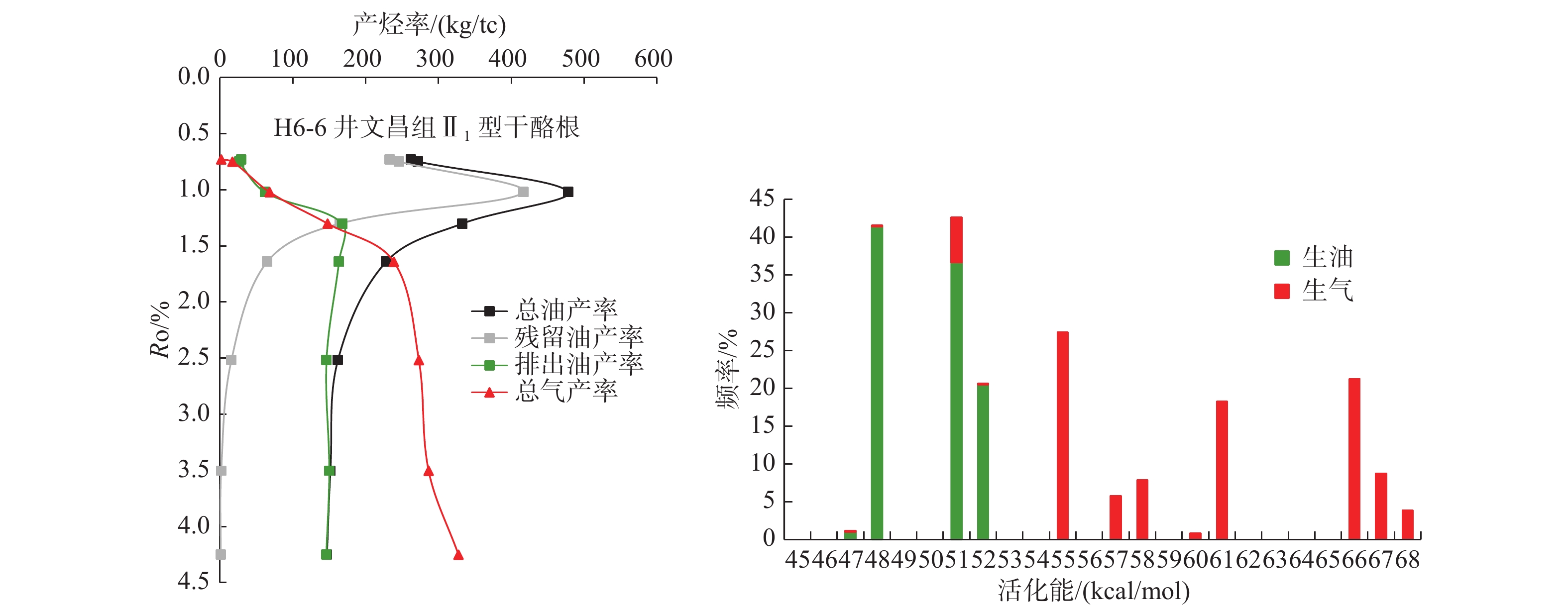
层位 文昌组 层位 文昌组 PH 6.97 Sulfate,SO42− 221.748 4 Specific Gravity @ 60 ℉ 1.0237 Bicarbonate,HCO3− 844.479 4 Conductivity@25 ℃ 54.2 Carbonate,CO32− 0 Calcium,Ca2+ 1120.2 Hydroxide,OH− 0 Magnesium,Mg2+ 190.8 Salinity 31.544 35 Iron,Fe 4.856 Total Solids(calculated) 33 899.93 Barium,Ba2+ 0 Ionic Strength 0.593 952 Sodium,Na+ 10 756.46 Total Alkalinity 692.196 3 Potassium,K+ 1 149.8 Viscosity at 20 ℃ 0.984 721 Chloride,Cl− 19 611.58 表 3 惠州26-6典型半深湖-深湖相烃源岩半开放体系下热压模拟实验产烃率数据
Table 3. Hydrocarbon production rate data from thermocompression simulation experiment of typical semi-deep lacustrine and deep lacustrine source rocks for Huizhou 26-6 in semi-open system
井号 深度/m 岩性 编号 重量/g 温度/℃ 总油产率kg/tc 残留油产率/
(kg/tc)排出油产率/
(kg/tc)烃气体积产率/
(m3/tc)烃气质量产率/(kg/tc) 总产烃率/
(kg/tc)H6-6井 3456
~
3468文昌组Ⅱ1型
深褐色泥岩
岩屑1 125 250 262.04 233.01 29.04 0.97 1.63 263.67 2 125 300 271.97 245.69 26.29 10.28 17.02 289.00 3 125 350 477.86 416.27 61.59 47.69 68.02 545.88 4 125 375 332.74 164.68 168.06 105.43 147.65 480.40 5 125 400 228.12 64.84 163.28 172.82 238.57 466.69 6 125 450 161.86 15.66 146.20 261.83 272.93 434.78 7 125 500 151.52 1.59 149.93 345.20 286.31 437.83 8 125 550 146.76 0.88 145.88 425.33 327.32 474.08 注:kg/tc表示kg/t有机碳 -
[1] 陈长民, 施和生, 许仕策, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
[2] 施和生,朱俊章,姜正龙,等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气资源再评价[J]. 中国海上油气,2009,21(1):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.01.002
[3] 施和生, 代一丁, 刘丽华, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气藏地质特征与分布发育基本模式[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(2): 120-133.
[4] 何家雄,吴文海,祝有海,等. 南海北部边缘盆地油气成因及运聚规律与勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学,2010,21(1):7-17.
[5] 张贺,李雅君,徐康宁,等. 珠江口盆地恩平组烃源岩热压模拟实验及生烃条件[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2018,37(5):36-42.
[6] 张功成,陈国俊,张厚和,等. “源热共控”中国近海盆地油气田“内油外气”有序分布[J]. 沉积学报,2012,30(1):1-19.
[7] 张功成,李友川,刘世翔,等. “源热共控”中国海油气田“近岸油、远岸气”有序分布[J]. 中国石油勘探,2014,19(5):1-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.05.001
[8] 史玉玲,侯读杰,马宁. 惠州凹陷生烃潜力及油源对比[J]. 石油天然气学报,2011,33(10):15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2011.10.004
[9] 朱俊章, 施和生, 邓宏文, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷古近系烃源岩层序地层学和地球化学研究[J]. 天然气地球科学. 2007, 18(5): 709-714.
[10] 米敬奎, 张水昌, 王晓梅, 等. 不同类型生烃模拟实验方法对比与关键技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(4): 409-414.
[11] 王治朝,米敬奎,李贤庆,等. 生烃模拟实验方法现状与存在问题[J]. 天然气地球科学,2009,20(4):592-597.
[12] 朱俊章, 施和生, 舒誉, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷典型烃源岩热压模拟实验: 生排烃模式及TOC恢复系数探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(4): 573-578.
[13] 田立新, 刘杰, 张向涛, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州26-6大中型泛潜山油气田勘探发现与成藏模式[J].中国石油勘探, 2020, 32(4): 1-11.
[14] 郑伦举,秦建中,何生,等. 地层孔隙热压生排烃模拟实验初步研究[J]. 石油实验地质,2009,31(3):296-302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.03.017
[15] 程克明,熊英,刘新月. 煤系源岩倾油倾气性研究[J]. 沉积学报,2004,22(S1):56-60.
[16] BURNHAM A K. Global chemical kinetics of fossil fuels[M]. Switzerland: Springer, 2017: 312.
[17] 施和生, 舒誉, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地古近系石油地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
[18] 施和生. 论油气资源不均匀分布与分带差异富集:以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(5):1-8.
[19] 胡朝元. "源控论"适用范围量化分析[J]. 天然气工业,2005,25(10):25-27.
[20] 施和生. 油气勘探"源—汇—聚"评价体系及其应用:以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2015,27(5):1-12.
-



 下载:
下载: