Reservoir characteristics and densification process of Pinghu Formation in western slope of Xihu Sag
-
摘要:
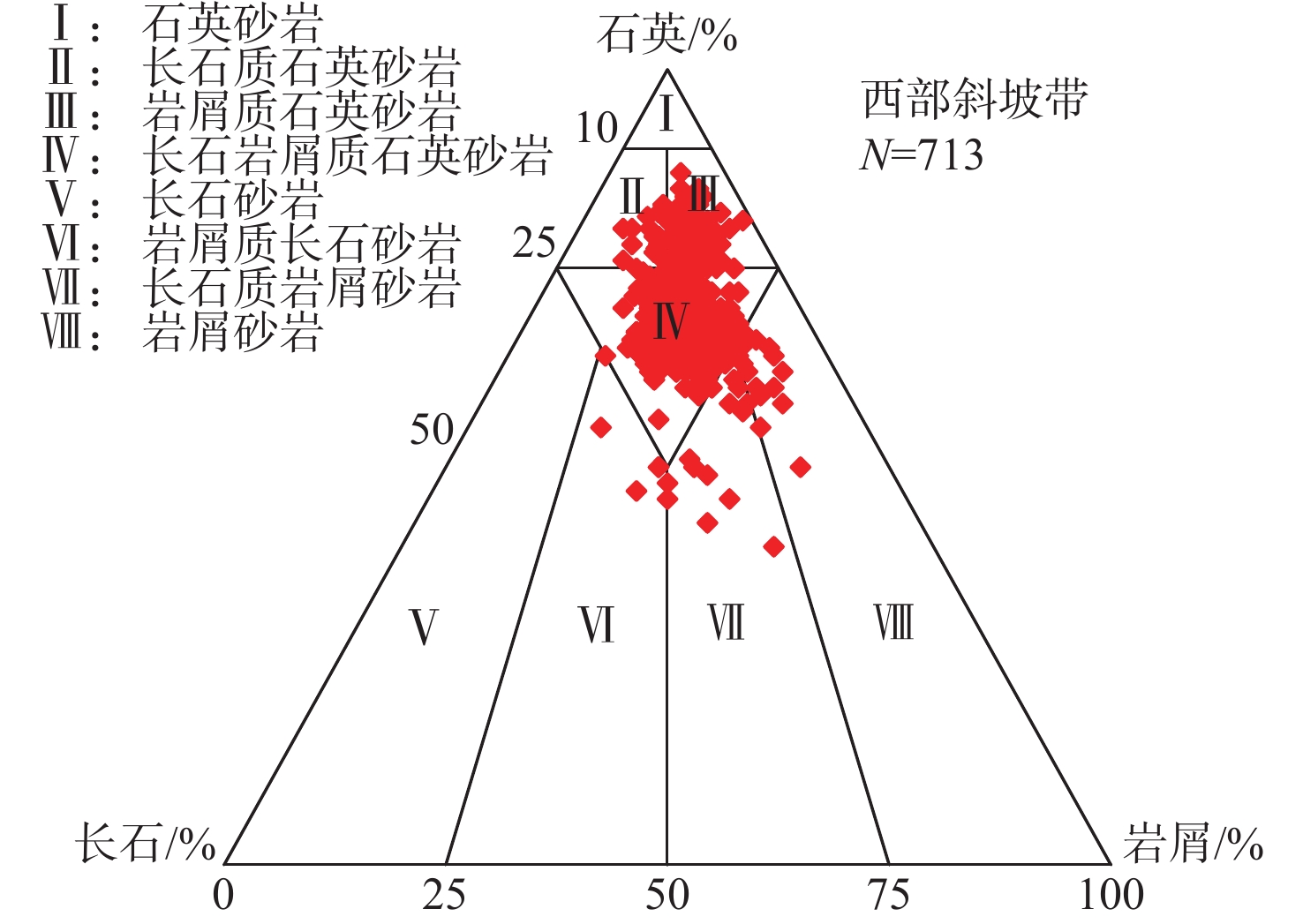
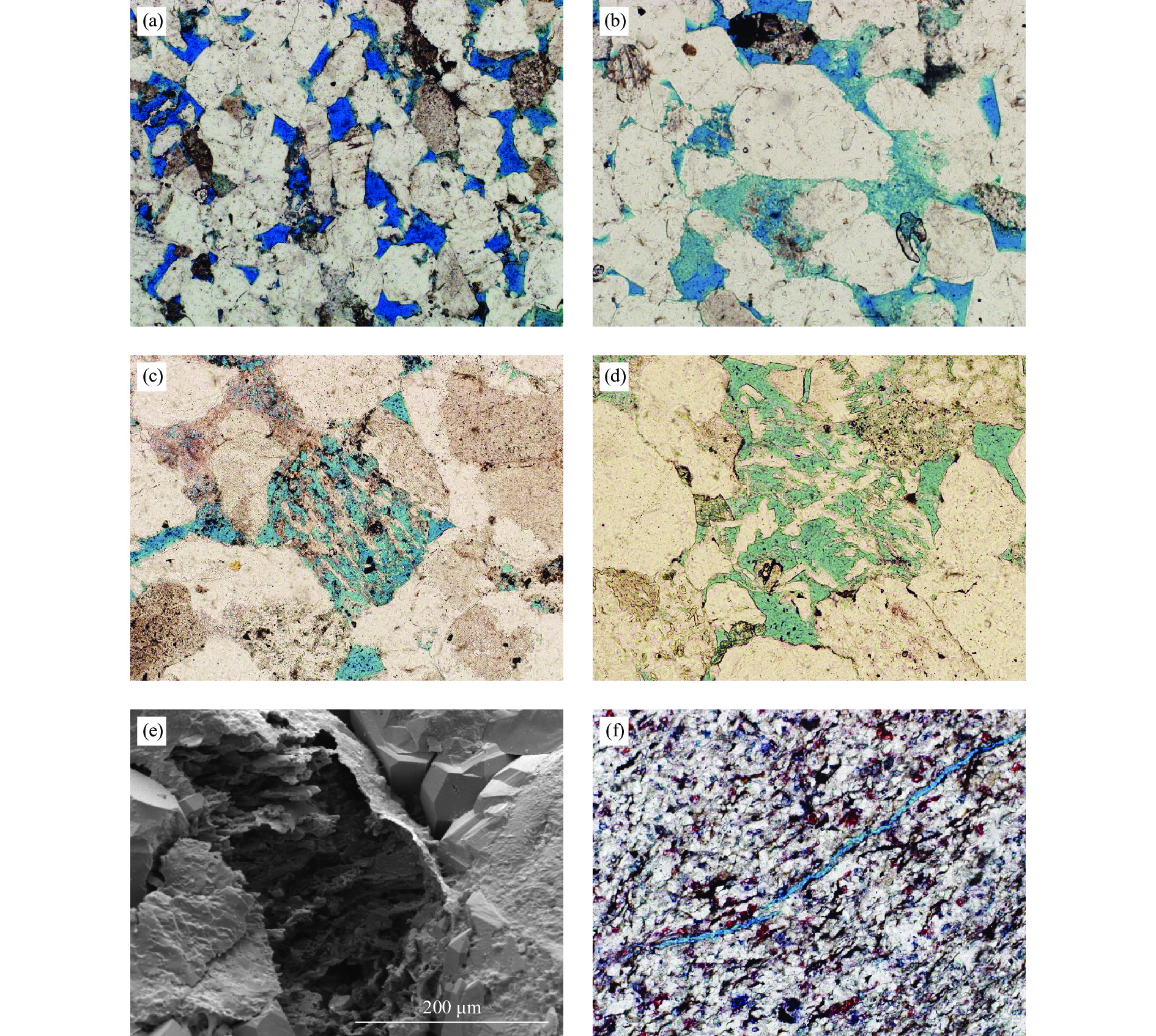
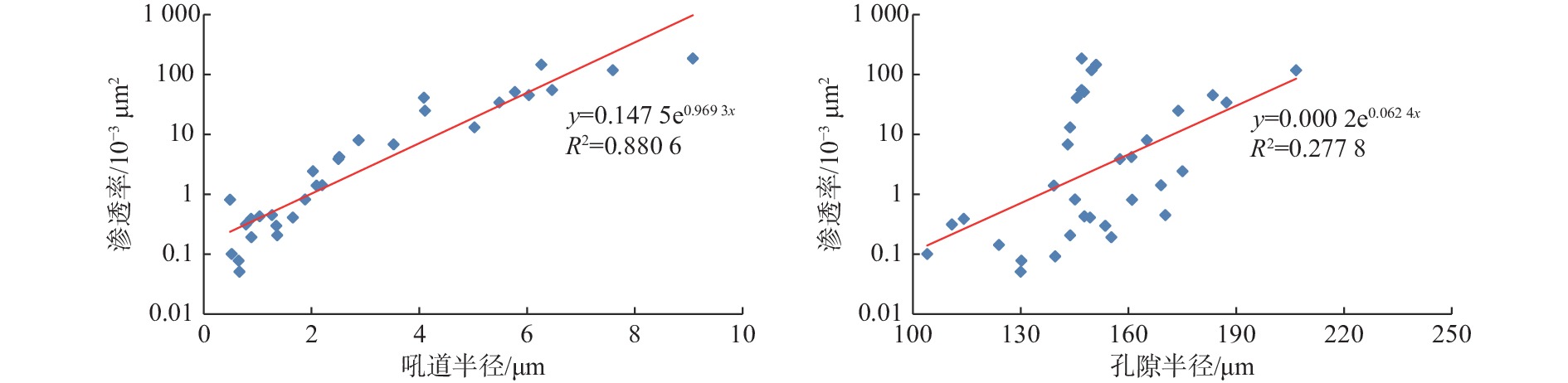
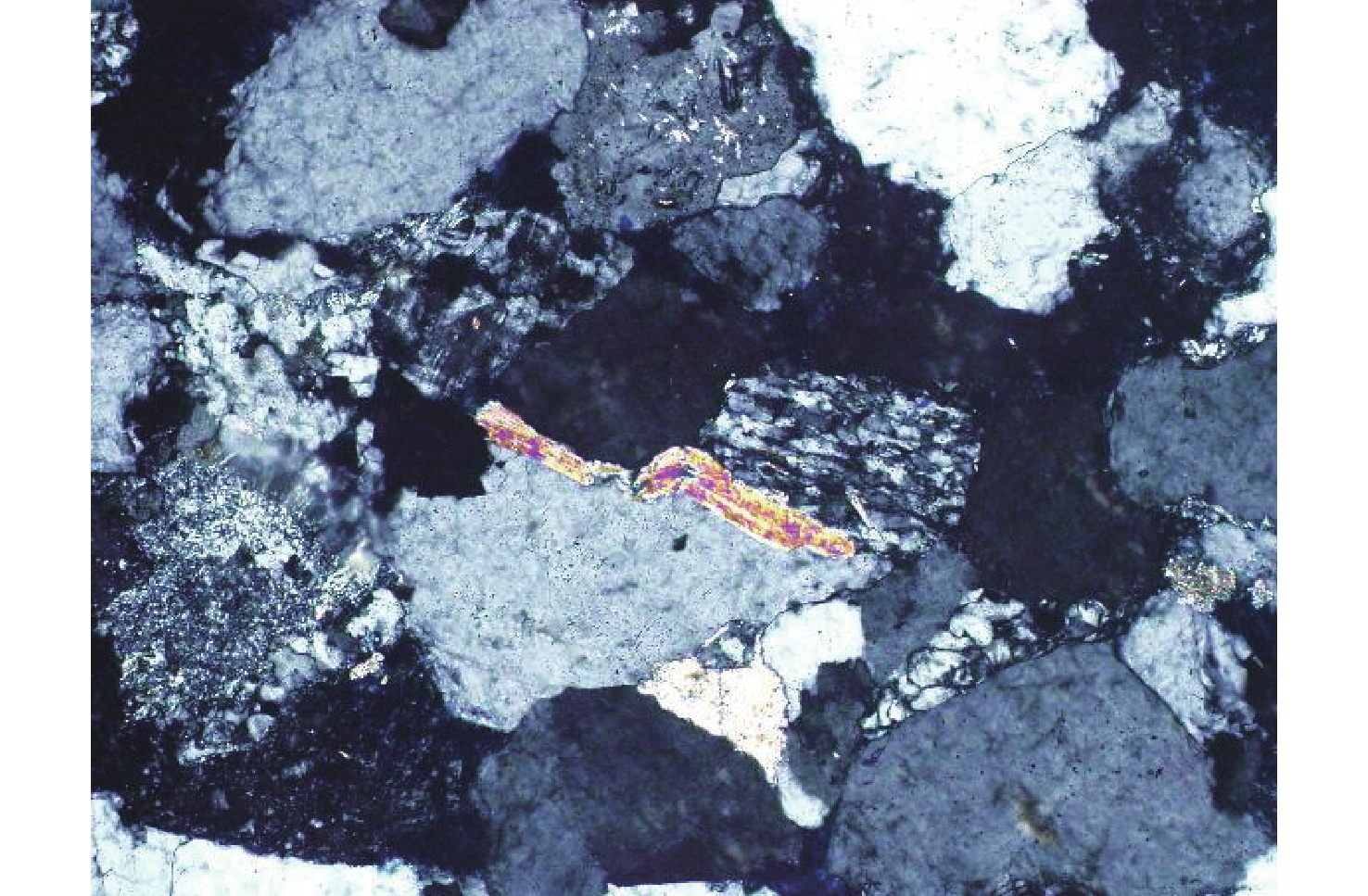
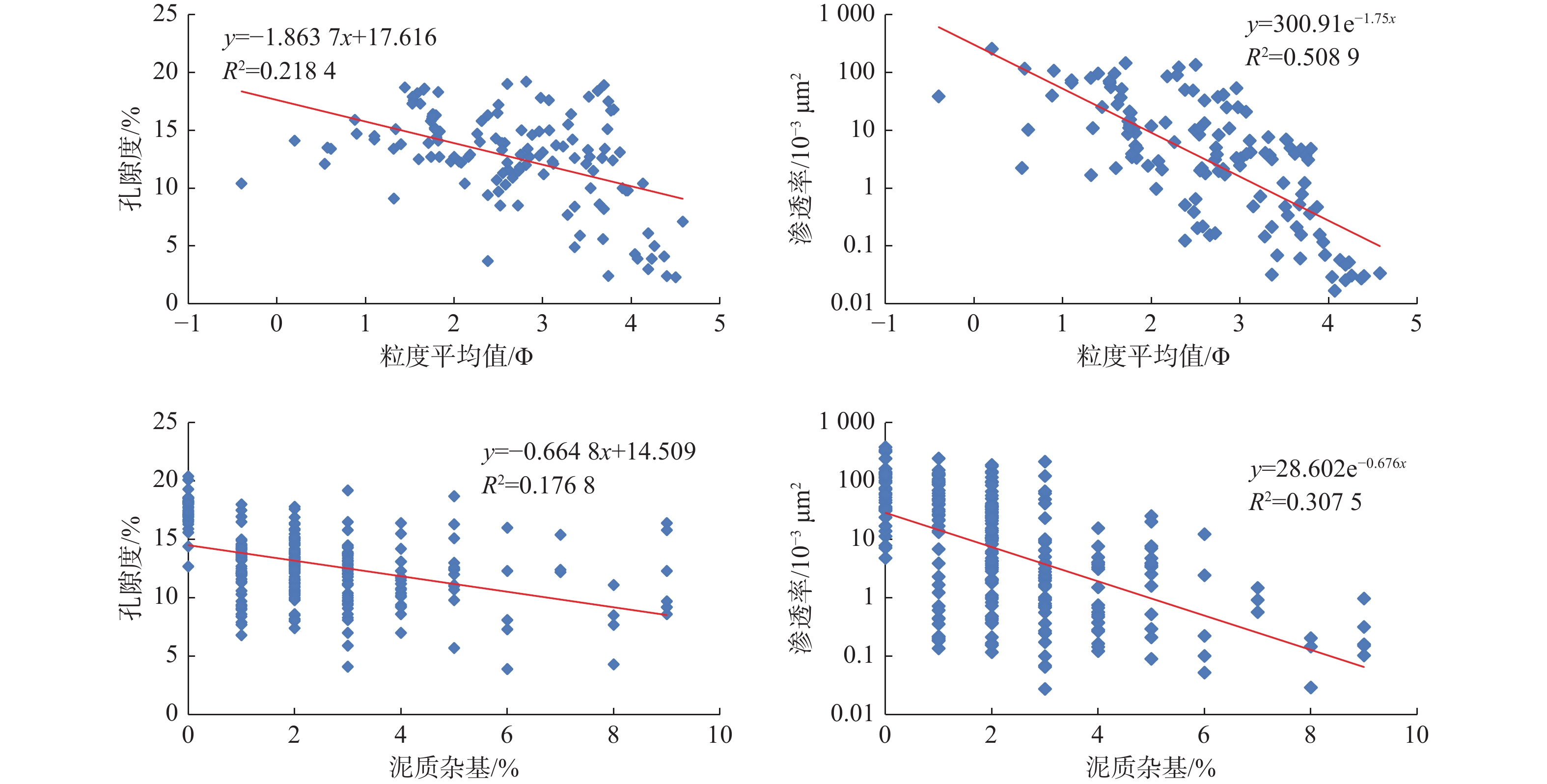
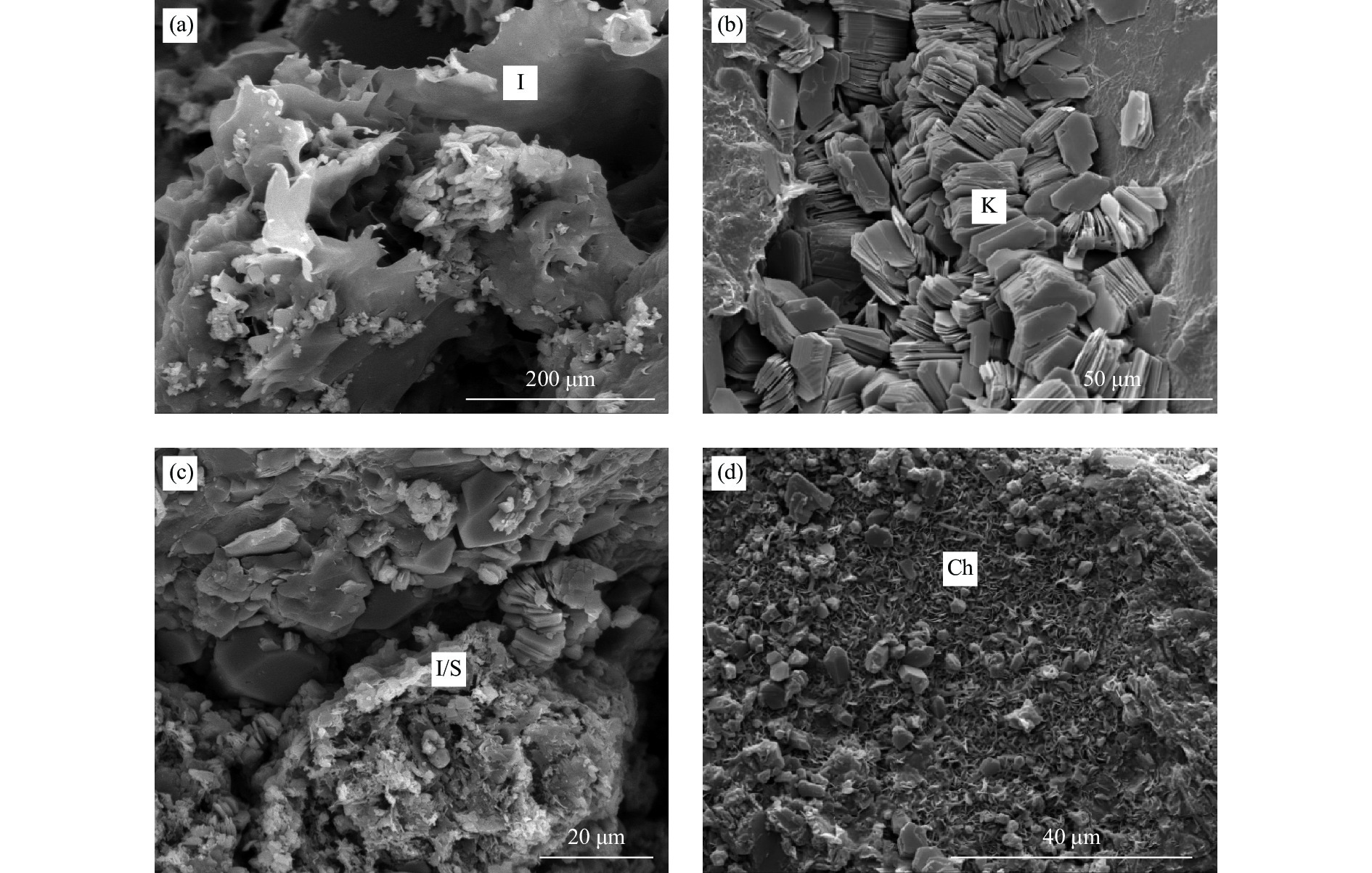
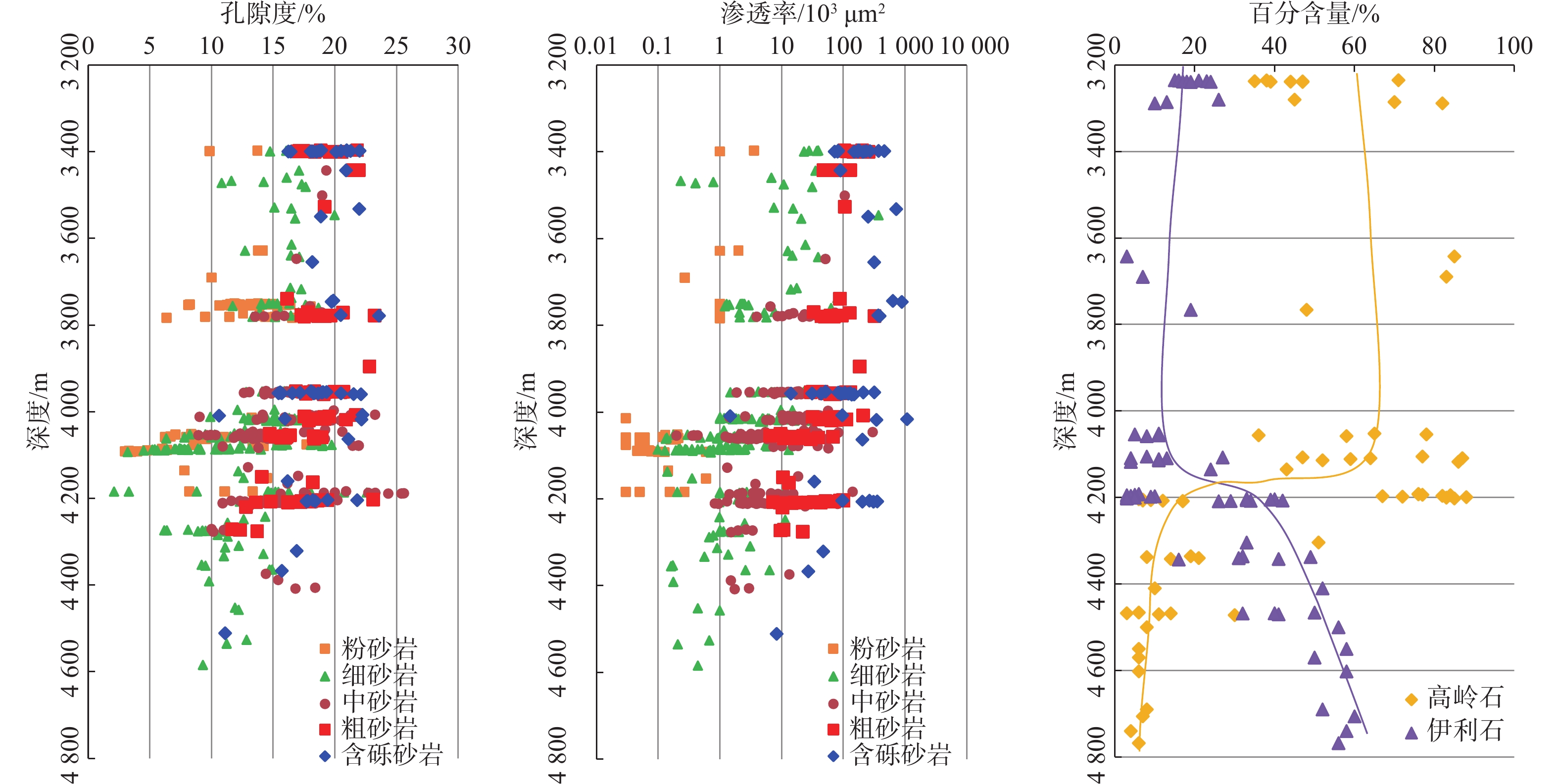
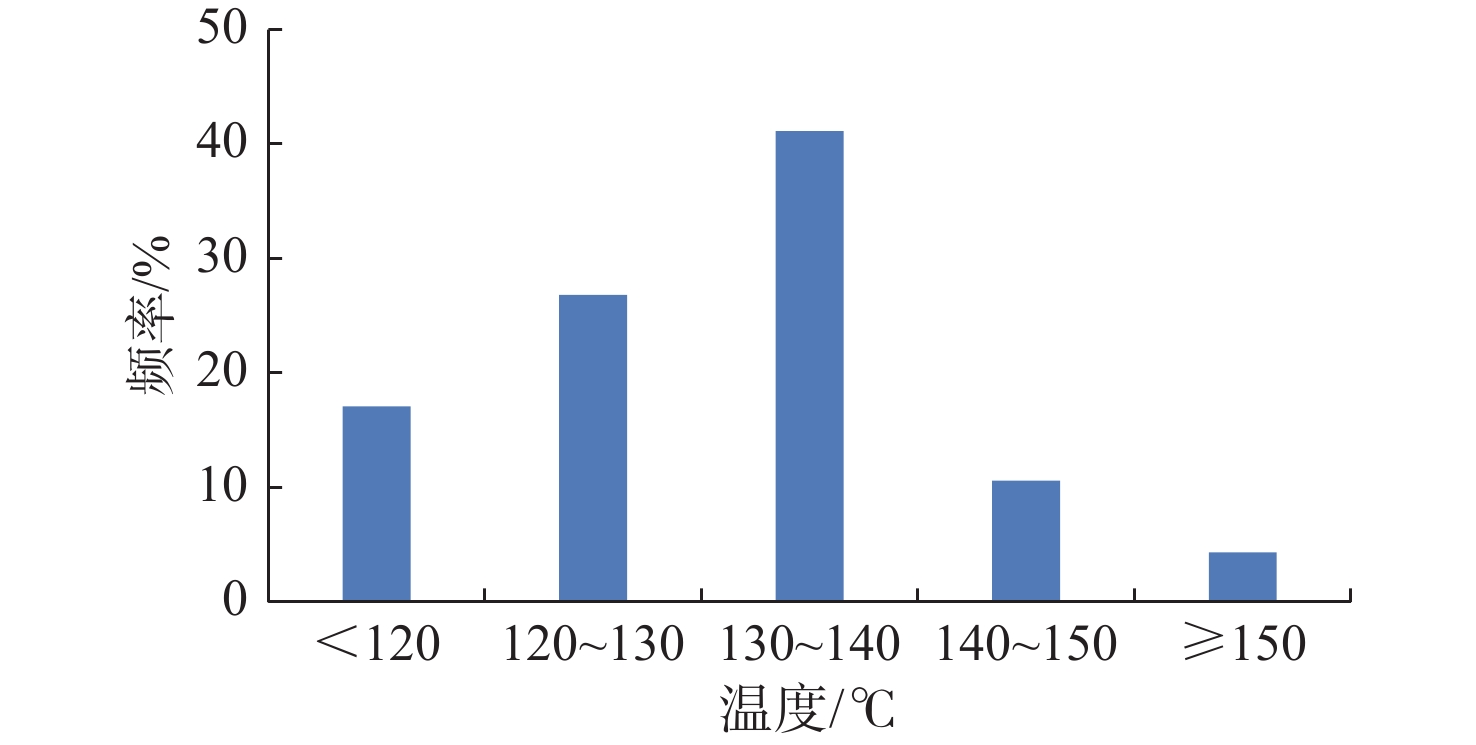
综合应用铸体薄片、扫描电镜、阴极发光、恒速压汞、流体包裹体和X衍射等分析技术,对储层岩石学、孔喉结构和成岩作用类型及特征进行深入研究,探讨储层致密化过程和物性演化。结果表明:平湖组储层砂岩类型主要为长石岩屑质石英砂岩,以细—中粒结构为主,分选性中到好;孔隙类型以溶蚀粒间孔为主,孔隙半径主要集中于130~190 μm,喉道半径主要集中于0.2~10 μm;埋藏压实是导致平湖组储层低渗-特低渗的主因,埋深、粒度及泥质决定了压实作用的强弱,而后期次生溶蚀及胶结作用的差异加剧了储层的非均值性。中成岩A期平湖组储层次生溶蚀规模受限于流体环境,细粒沉积不利于后期溶蚀是造成储层致密化的主因;进入中成岩B期,成岩环境呈碱性且逐渐封闭,大量含铁碳酸盐、呈丝状或弯曲片状伊利石等富集堵塞喉道,致使储层大规模致密。
Abstract:By means of casting thin section, scanning electron microscope, cathodoluminescence, constant-rate mercury injection, fluid inclusions, X-ray diffraction, we studied the reservoir petrology, pore throat structure, types, and characteristics of diagenesis, and discussed the densification process and physical evolution of the reservoir of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Basin. Results show that the reservoir sandstone of the Pinghu Formation is mainly feldspar lithic quartz sandstone, the structure is mainly fine-medium grain with medium to good sorting. Intergranular pores formed the main reservoir space, and the pore radius ranged 130~190 μm, with throat radius of 0.2~10 μm. Burial compaction is the main cause of low permeability and density of PF reservoir. Depth, grain size, and argillaceous content determined the strength of compaction. In addition, the difference of secondary corrosion and cementation in later stage intensified the heterogeneity of reservoirs. In diagenetic stage, the scale of bio-dissolution in the Pinghu Formation reservoir was limited by fluid environment, and fine-grain particle deposition was not conducive to late dissolution, which are the two main reasons for reservoir densification. In diagenetic stage, the diagenetic environment was alkaline and gradually closed, after which a large number of iron-bearing carbonates, filamentous, and curved illite were built up and block the throat, resulting in the large-scale compaction of the reservoir.
-
Key words:
- Xihu Sag /
- Pinghu Formation /
- differential compaction /
- densification /
- heterogeneous reservoir
-

-
表 1 研究区X3井油田水测试结果
Table 1. Water test results of some wells in the Pinghu Formation
井号 井深/m 层位 离子类型 离子含量/(mg/L) pH值 酸碱程度 X3 4 186.7~4 202.5 平湖组 钾+钠 6 423.31 6.85 弱酸性 钙 187.33 镁 38.87 碳酸氢根 1 660.72 4 231.7~4 286.6 平湖组 钾+钠 3 354.51 7.55 弱碱性 钙 39.44 镁 0 碳酸氢根 4 092.49 表 2 平湖组储层孔隙恢复定量计算公式及选取参数
Table 2. Quantified calculation formula of reservoir porosity recovery and involved parameters of Pinghu Formation
孔隙演化参数 定量表征公式 压实作用 压实后的剩余孔隙度(Φ2)/% Φ2= w+(ΦC×ΦM/ΦT) 胶结作用 胶结后的剩余孔隙度(Φ3)/% Φ3=ΦC×ΦM/ΦT 溶解作用 溶蚀增孔(Φ4)/% Φ4=ΦS×ΦM/ΦT 现今孔隙度 最终平均孔隙度(Φ5)/% Φ5=Φ3+Φ4 注:w为胶结物的质量分数,%;ΦC为残余原生粒间孔面孔率,%;ΦM为实测平均孔隙度,%;ΦT为总面孔率,%;ΦS为溶蚀孔面孔率,%。 -
[1] 李建忠,郭彬程,郑民,等. 中国致密砂岩气主要类型、地质特征与资源潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学,2012,23(4):607-615.
[2] 张春林,李剑,刘锐娥. 鄂尔多斯盆地盒8段致密砂岩气储层微观特征及形成机理[J]. 中国石油勘探,2019,24(4):476-484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.04.008
[3] 朱筱敏,潘荣,朱世发,等. 致密储层研究进展和热点问题分析[J]. 地学前缘,2018,25(2):141-146. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2018.02.015
[4] 国家能源局. SY/T6832—2011致密砂岩气地质评价方法[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.
[5] 徐昉昊,袁海峰,黄素,等. 川中地区须家河组致密砂岩气成藏机理[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2012,39(2):158-163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2012.02.007
[6] 朱瑞静,李荣西,刘新社,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部上古生界致密砂岩气储层成岩演化特征及物性演化[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(5):637-650.
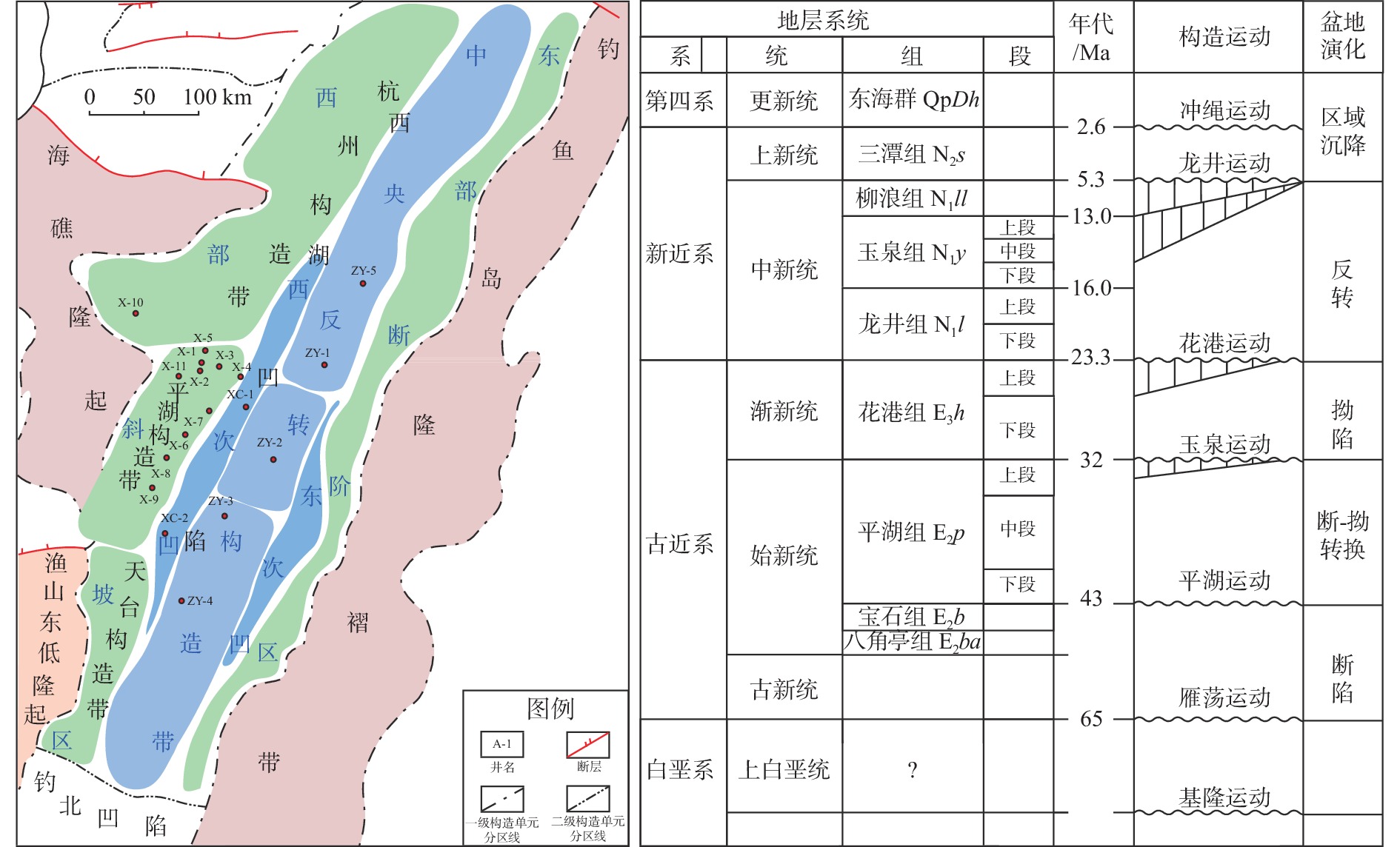
[7] 黄导武, 段东平, 刘彬彬, 等. 西湖凹陷低渗-致密砂岩气藏储层特征及差异成因[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 31(3): 99-107.
[8] 周心怀,蒋一鸣,唐贤君. 西湖凹陷成盆背景、原型盆地演化及勘探启示[J]. 中国海上油气,2019,31(3):1-10.
[9] 华东石油学院岩矿教研室. 沉积岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1982: 112-114.
[10] 刘金水,曹冰,徐志星,等. 西湖凹陷某构造花港组沉积相及致密砂岩储层特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2012,39(2):130-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2012.02.003
[11] 肖晓光,侯国伟,张武,等. 西湖凹陷平湖组低渗储层成岩环境及孔隙演化[J]. 海相油气地质,2021,26(1):60-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2021.01.007
[12] 武文慧. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界储层砂岩特征及成岩作用研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010.
[13] 梁建设,王琪,郝乐伟,等. 西湖凹陷渐新统花港组储层砂岩成岩环境演化探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学,2012,23(4):673-680.
[14] 苏奥,陈红汉,吴悠,等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中西部低渗近致密:致密砂岩气成因、来源及运聚成藏[J]. 地质学报,2018,92(1):184-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.01.013
[15] 黄鑫,林承焰,黄导武,等. 西湖凹陷中央反转带中北部花港组砂岩储层成岩差异演化特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2022,29(2):1-12.
[16] BEARD D C,WEYL P K. Influencing of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1973,57(2):349-369.
[17] SURDAM R C,CROSSEY L J,HAGEN E S,et al. Organic-inorganic and sandstone diagenesis[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1989,73:1-23.
[18] SCHERER M. Parameters influencing porosity in sandstones:a model for sandstones porosity prediction[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1987,71(5):485-491.
[19] TAYLOR H P,FRECHEN J,DEGENS E T. Oxygen and carbon isotope studies of carbonatites from the Laacher See District,West Germany and the Alnö District,Sweden[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1967,31(3):407-430. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(67)90051-8
[20] 黄思静,黄可可,冯文立,等. 成岩过程中长石、高岭石、伊利石之间的物质交换与次生孔隙的形成:来自鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界和川西凹陷三叠系须家河组的研究[J]. 地球化学,2009,38(5):498-506. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.05.009
[21] 徐国盛,徐芳艮,袁海锋,等. 西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组致密砂岩储层成岩环境演变与孔隙演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,43(4):385-395. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2016.04.01
[22] 张建培,葛和平,张涛,等. 西湖凹陷古近系及新近系储层砂岩自生高岭石分布特征及形成机制[J]. 中国海上油气,2008,20(6):362-366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.06.002
[23] 石广仁. 蒙皂石向伊利石转化的溶解沉淀模型[J]. 石油学报,2006,27(6):47-50. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.06.010
[24] 公繁浩,鲍志东,范正平,等. 自生绿泥石对砂岩储集层影响的新认识[J]. 新疆石油地质,2011,32(4):338-341.
[25] 邹明亮,黄思静,胡作维,等. 西湖凹陷平湖组砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物形成机制及其对储层质量的影响[J]. 岩性油气藏,2008,20(1):47-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.01.008
[26] KEITH M L,WEBER J N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1964,28(10/11):1787-1816.
[27] LAN Y F,HUANG S J,MA Y K,et al. Genesis of negative carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of carbonate rocks in lower Miocene Zhujiang Formation,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Geological Review,2016,62(4):915-928.
[28] 吴素娟,黄思静,孙治雷,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组砂岩中的白云石胶结物及形成机制[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2005,32(6):570-575.
[29] 武文慧,黄思静,陈洪德,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界碎屑岩硅质胶结物形成机制及其对储集层的影响[J]. 古地理学报,2011,13(2):193-200. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2011.02.007
[30] 刘德汉, 卢焕章, 肖贤明. 油气包裹体及其在石油勘探和开发中的应用[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2007.
[31] 刘勇,徐国盛,曾兵,等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷花港组储层孔隙演化与油气充注关系[J]. 石油实验地质,2018,40(2):168-176. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802168
-



 下载:
下载: