Paleoenvironmental reconstruction of organic-rich shale in the Hetang Formation of the Lower Yangtze Block: a case study of Well XY1
-
摘要:
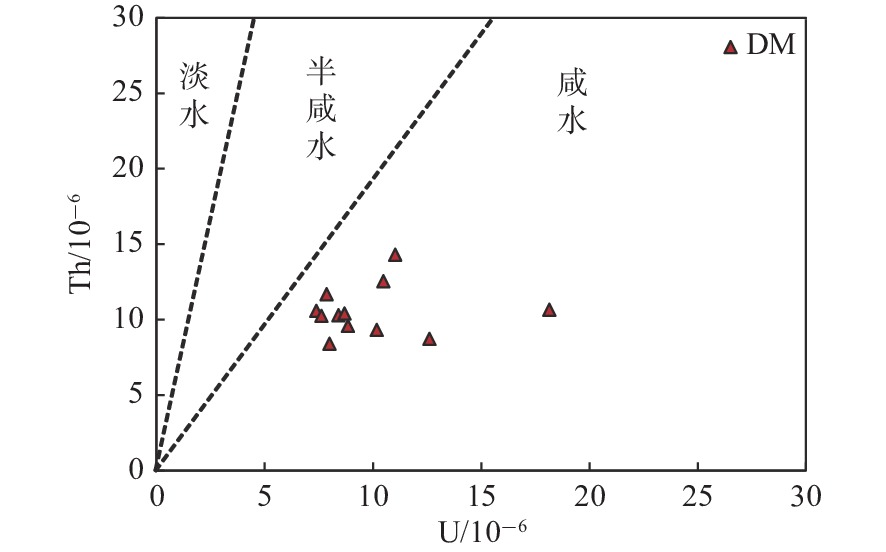
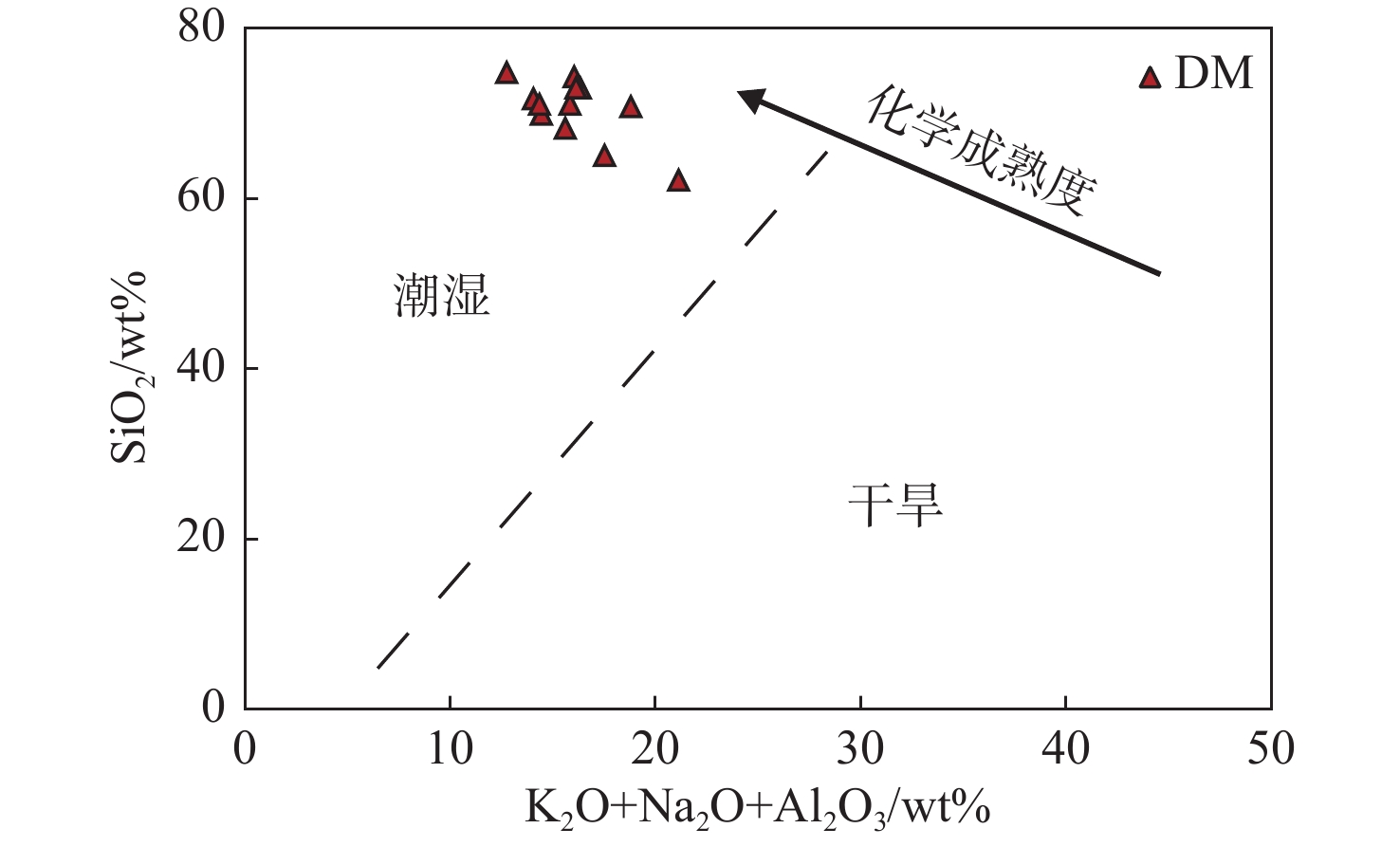
元素地球化学特征可以有效地反映沉积物沉积背景与沉积环境。以宣城地区宣页1井(下称XY1井)下寒武统荷塘组富有机质页岩为例,利用元素地球化学指标,对下扬子地块宣城地区荷塘组富有机质页岩的构造背景与沉积环境进行了分析。结果显示,荷塘组富有机质页岩属于温暖潮湿气候背景下的稳定大陆边缘沉积,为缺氧-贫氧的海相环境,水体具有较高生产力。综合古环境参数恢复结果认为,荷塘组富有机质页岩为深水滞留沉积的产物,水体深度先加深后变浅。
Abstract:The sedimentary background and environment can be studied effectively through the element geochemical characteristics. Taking the organic-rich shale of the Lower Cambrian Hetang Formation in XY1 in Xuancheng Area as an example, the structural background and sedimentary environment of the organic-rich shale of the Hetang Formation in Xuancheng area of the Lower Yangtze block were analyzed by using the element geochemical indexes. The results show that: the organic-rich shales were deposited in a stable continental margin under warm and humid climate, and the marine environment was anoxic to oxygen poor. The water body was highly productive. The paleoenvironmental parameters indicate that organic-rich shale of Hetang Formation is of continental slope facies deposited in deep water, and the water depth deepened first and then shallowed.
-
Key words:
- element geochemistry /
- Lower Yangtze Block /
- Hetang Formation /
- organic-rich shale /
- paleoenvironment
-

-
表 1 荷塘组富有机质页岩主量、微量元素分析结果
Table 1. Results of analyses of major and trace elements in organic-rich shale of Hetang Formation
编号 X-1 X-2 X-3 X-4 X-5 X-6 X-7 X-8 X-9 X-10 X-11 X-12 主量元素 K2O 5.23 4.96 5.00 6.17 5.50 5.46 4.47 5.44 5.44 6.28 6.42 5.26 Na2O 0.08 0.075 0.069 0.084 0.063 0.06 0.048 0.057 0.055 0.067 0.18 0.061 SiO2 69.84 71.64 70.98 64.97 71.00 68.16 74.74 72.9 74.21 70.72 62.07 72.9 Al2O3 9.12 9.00 9.26 11.25 10.25 10.06 8.21 10.83 10.53 12.44 14.51 10.8 微量元素 Sr 21.1 16.4 22.8 19.8 31.1 40.9 32.9 30.3 25.8 24.5 43.0 19.2 Cu 83.1 52.8 37.5 610 40.3 66.7 21.9 28.4 36.3 29.9 144 30.4 Ni 90.4 81.7 61.0 104 41.6 68.4 44.4 77.7 81.3 71.4 102 68.1 V 208 162 146 280 77.1 91.5 192 368 277 287 372 424 Cr 51.4 45.1 45.1 62.4 47.3 47.2 42.7 59.5 57.4 66.8 73.6 66.4 Th 9.58 10.6 8.71 12.5 10.27 10.6 8.39 10.39 10.24 11.7 14.3 9.31 U 8.84 18.1 12.6 10.5 8.41 7.38 7.99 8.69 7.62 7.86 11.0 10.2 Mo 31.1 62.2 36.9 40.7 21.2 20.6 33.9 27.8 29.2 32.8 50.9 51.1 Ba 17825 5550 6722 19957 4679 4745 3561 3942 4042 4689 15573 6639 Co 50.95 111.14 25.48 69.64 27.31 38.15 44.66 25.25 29.45 20.43 50.03 29.24 La 25.10 31.69 20.16 50.85 26.87 27.30 15.36 13.16 21.02 22.31 22.94 26.55 数据处理 V/Cr 0.28 0.29 0.34 0.26 0.40 0.36 0.24 0.31 0.26 0.24 0.22 0.20 MoEF 20.70 41.50 24.62 27.15 14.15 13.70 22.60 18.54 19.45 21.85 33.93 34.04 UEF 0.10 0.10 0.12 0.09 0.14 0.13 0.08 0.11 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.07 V/(V+Ni) 0.22 0.23 0.25 0.20 0.28 0.26 0.19 0.24 0.21 0.19 0.18 0.17 K2O/Na2O 65.38 66.1 72.5 73.5 87.30 91.00 93.13 95.44 98.91 93.73 35.7 86.2 SIO2/Al2O3 7.66 7.96 7.67 5.78 6.93 6.78 9.10 6.73 7.05 5.68 4.28 6.75 Th/U 1.08 0.59 0.69 1.20 1.22 1.43 1.05 1.20 1.34 1.49 1.30 0.91 Ba生物 16087 3835 4957 17813 2726 2828 1997 1878 2035 2318 12808 4581 t 0.64 0.81 0.52 1.30 0.69 0.70 0.39 0.34 0.54 0.57 0.59 0.68 H 125.18 55.90 260.14 94.44 249.18 172.04 140.12 253.46 222.80 337.99 126.91 230.30 注:主量元素单位为%;微量元素单位为10−6;H单位为m。 -
[1] WANG Q,CHEN X,JHA A N,et al. Natural gas from shale formation:the evolution,evidences and challenges of shale gas revolution in United States[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2014,30:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.08.065
[2] 崇璇. 渝东南地区五峰—龙马溪组高频层序地层及对页岩储层的控制研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2020.
[3] 詹容若. 张家滩页岩沉积作用和层序发展过程[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2021.
[4] 张记刚,杜猛,陈超,等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组页岩储层孔隙结构定量表征[J]. 岩性油气藏,2022,34(4):89-102. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220409
[5] 姜振学,梁志凯,申颍浩,等. 川南泸州地区页岩气甜点地质工程一体化关键要素耦合关系及攻关方向[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(1):110-129.
[6] 徐银波, 毕彩芹, 李锋, 等. 三塘湖盆地石头梅地区巴油页1井二叠系芦草沟组有机相分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(11): 4094-4104.
[7] BRUMSACK H J. The trace metal content of recent organic carbon-rich sediments:implications for Cretaceous black shale formation[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2006,232(2):344-361.
[8] CAINENG Z,ZHI Y,JINGWEI C,et al. Formation mechanism,geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2013,40(1):15-27. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(13)60002-6
[9] 王昌勇, 常玖, 李楠, 等. 四川盆地东部地区早侏罗世湖泊古水深恢复[J/OL]. 沉积学报, 2022: 1-16. DOI: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.036
[10] 张俊鹏,李超,张元动. 早古生代海洋缺氧事件的地质记录与背景机制[J]. 科学通报,2022,67(15):1644-1659.
[11] 姚红生,何希鹏,汪凯明. 下扬子皖南地区下寒武统荷塘组页岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(4):32-41. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.123
[12] 曾子轩,刘晓峰,楼章华,等. 古代深海硅质岩-粘土岩-碳酸盐岩系列(SAC)的岩石学分类[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(2):475-488.
[13] 朱文博,张训华,曲中党,等. 赣东–浙西下寒武统荷塘组稀土元素特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(2):88-99. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020031201
[14] 樊佳莉. 下扬子地区下寒武统富有机质页岩的岩相与沉积环境[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(5):156-163. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2017.0521
[15] 胡杰,陈哲,薛耀松,等. 皖南早寒武世荷塘组海绵骨针化石[J]. 微体古生物学报,2002,19(1):55-64.
[16] LIU B,SONG Y,ZHU K,et al. Mineralogy and element geochemistry of salinized lacustrine organic-rich shale in the Middle Permian Santanghu Basin:implications for paleoenvironment,provenance,tectonic setting and shale oil potential[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,120:104569. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104569
[17] DO NASCIMENTO C A,DE SOUZA E S,MARTINS L L,et al. Changes in depositional paleoenvironment of black shales in the Permian Irati Formation (Paraná Basin,Brazil):geochemical evidence and aromatic biomarkers[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2021,126:104917. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.104917
[18] WANG S,SONG D,WANG Y,et al. Sedimentary geochemical proxies for paleoenvironment interpretation of organic-rich shale:a case study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation,southern Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2016,28:691-699. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.11.045
[19] 印峰,杨风丽,叶芳,等. 晚震旦至中奥陶世下扬子被动大陆边缘原型盆地特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2013,38(5):1053-1064.
[20] 郭念发. 下扬子盆地与区域地质构造演化特征及油气成藏分析[J]. 浙江地质,1996,12(2):19-27.
[21] 吴浩,姚素平,焦堃,等. 下扬子区上二叠统龙潭组页岩气勘探前景[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(5):870-876. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.05.026
[22] 骆学全,孙建东,班宜忠,等. 华东片区Ⅳ级成矿单元划分及成矿地质特征[J]. 华东地质,2015,36(3):157-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2015.03.001
[23] 肖万峰,洪大军,雷丁尔,等. 安徽宁国石口金矿地质特征及控矿因素[J]. 华东地质,2020,41(3):265-270.
[24] 谢忱, 曾庆, 刘志坚, 等. 四川盆地基底断裂特征及对下二叠统沉积的控制作用初探[C]//2017全国沉积学与油气资源勘探开发利用技术研讨会论文集. 2017: 178-185.
[25] BHATIA M R. Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones[J]. The Journal of Geology,1983,91(6):611-627. doi: 10.1086/628815
[26] IBAD S M,PADMANABHAN E. Inorganic geochemical,mineralogical and methane sorption capacities of Paleozoic shale formations from Western Peninsular Malaysia:implication of shale gas potential[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2022,140:105269. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105269
[27] ZHOU Y,LIU Z,MAND K,et al. Analysis of geochemical characteristics of Jurassic sandstones in southern margin of Junggar Basin:provenance and paleosedimentary environment recovery[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2022,146:104922. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104922
[28] ROSER B P,KORSCH R J. Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio[J]. The Journal of Geology,1986,94(5):635-650. doi: 10.1086/629071
[29] ADAMS J A S,WEAVER C E. Thorium-to-uranium ratios as indicators of sedimentary processes:example of concept of geochemical facies[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1958,42(2):387-430.
[30] 王峰,刘玄春,邓秀芹,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地纸坊组微量元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 沉积学报,2017,35(6):1265-1273. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2017.06.017
[31] 张天福,孙立新,张云,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组、直罗组泥岩微量、稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J]. 地质学报,2016,90(12):3454-3472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.12.013
[32] LERMAN A. 湖泊的化学地质学和物理学[M]. 王苏民, 等, 译.北京: 地质出版社, 1989.
[33] 李乐,姚光庆,刘永河,等. 塘沽地区沙河街组下部含云质泥岩主微量元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(9):1480-1496.
[34] SUTTNER L J,DUTTA P K. Alluvial sandstone composition and paleoclimate; I,Framework mineralogy[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1986,56(3):329-345.
[35] 樊秋爽,夏国清,李高杰,等. 古海洋氧化还原条件分析方法与研究进展[J]. 沉积学报,2022,40(5):1151-1171. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2021.023
[36] 付金华,李士祥,徐黎明,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段古沉积环境恢复及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(6):936-946. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.06.02
[37] JONES B,MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology,1994,111(1):111-129.
[38] ALGEO T J,MAYNARD J B. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems[J]. Chemical geology,2004,206(3/4):289-318.
[39] ALGEO T J,TRIBOVILARD N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum–uranium covariation[J]. Chemical Geology,2009,268(3/4):211-225.
[40] 张晓潼,袁华茂,宋金明,等. 海洋Re、Mo和U对氧化还原环境的指示作用[J]. 地球科学进展,2022,37(4):358-369. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.4.dqkxjz202204003
[41] TRIBOVILARD N,ALGEOT J,BAUDIN F,et al. Analysis of marine environmental conditions based on molybdenum–uranium covariation:applications to Mesozoic paleoceanography[J]. Chemical Geology,2012,324:46-58.
[42] SCHOEPFER S D,SHEN J,WEI H,et al. Total organic carbon,organic phosphorus,and biogenic barium fluxes as proxies for paleomarine productivity[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2015,149:23-52. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.08.017
[43] BISHOP J K B. The barite-opal-organic carbon association in oceanic particulate matter[J]. Nature,1988,332(6162):341-343. doi: 10.1038/332341a0
[44] DEHAIRS F,CHESSELET R,JEDWAB J. Discrete suspended particles of barite and the barium cycle in the open ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1980,49(2):528-550. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90094-1
[45] DYMOND J,COLLIER R. Particulate barium fluxes and their relationships to biological productivity[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,1996,43(4/6):1283-1308.
[46] GINGELE F X, ZABEL M, KASTEN S, et al. Biogenic barium as a proxy for paleoproductivity: methods and limitations of application[M]//Use of Proxies in Paleoceanography. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1999: 345-364.
[47] STEDMAN N J,MORRIS G M,ATKINSON P J. Bibliography of theoretical calculations in molecular pharmacology[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics,1987,5(4):211-222. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(87)80031-0
[48] 万锦峰,鲜本忠,佘源琦,等. 基于伽马能谱测井信息的古水深恢复方法:以塔河油田4区巴楚组为例[J]. 石油天然气学报,2011,33(6):98-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2011.06.021
[49] 陆雨诗,胡勇,侯云东,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘羊虎沟组微量元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(28):11999-12009. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.28.013
-




 下载:
下载: