Variation of deposition rate and evolution of depositional environment in the Modaomen estuary of Pearl River in the past 100 years indicated by grain size and 210Pbex
-
摘要:
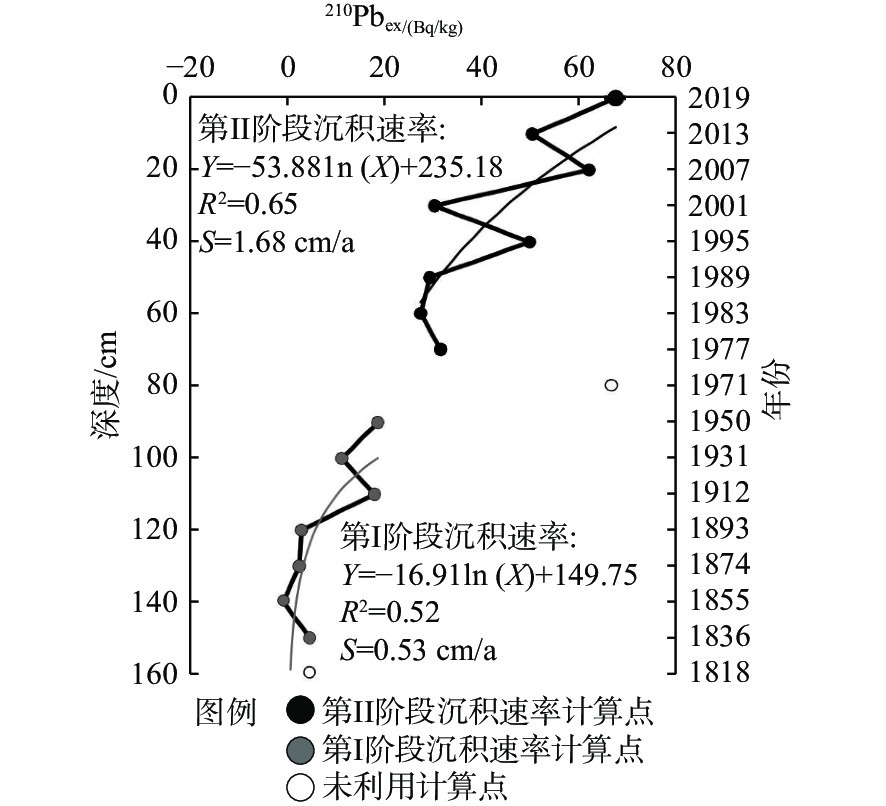
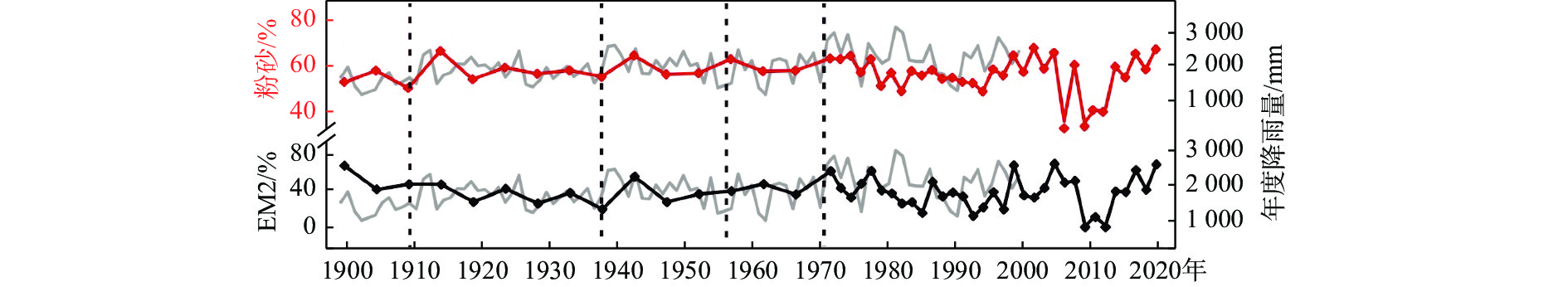
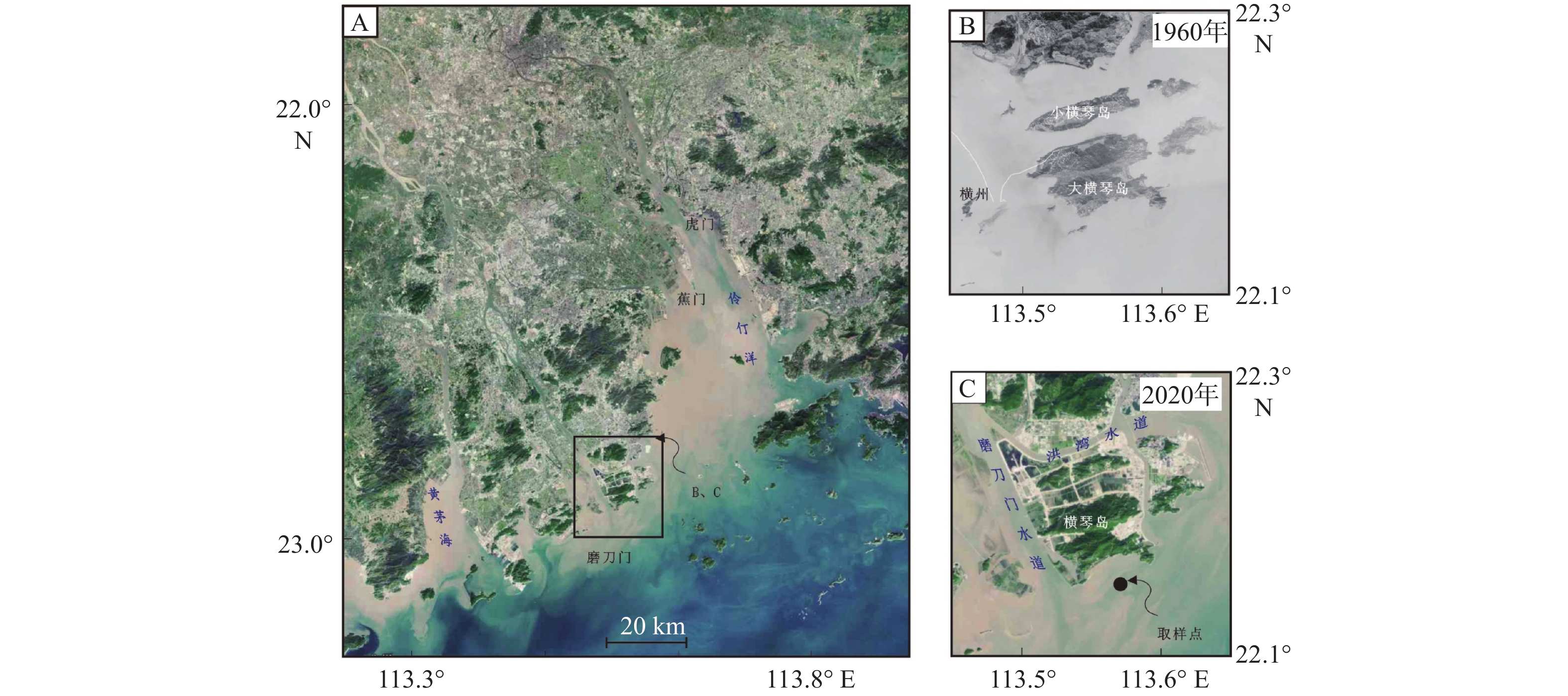
磨刀门作为珠江三角洲河流水系重要的入海口之一,是研究人类活动对河口岸沉积环境影响的理想区域。然而,由于沉积物年龄难以确定,使得相关研究十分匮乏。因此,本文通过210Pb同位素重建了磨刀门河口浅滩沉积柱的年龄框架,并结合粒度特征和粒度端元分析,讨论了百年来的沉积环境演变及控制机制。结果表明,区域的沉积主要源自西江径流来砂和外海潮流再输入泥沙,受近岸颗粒输入影响。在20世纪70年代前后,该区域沉积环境发生了显著的变化,磨刀门河口沉积速率由0.53 cm/a(70年代前)突然增加到1.68 cm/a(70年代后),且伴随沉积物粒度各组分及参数变异系数增大,粗粒物质增加,潮流物源输入减少,径流及近岸物源输入增加。这可能与西江输沙量变化和磨刀门区域1970年以来发生的围填海等人类活动增强有关。
Abstract:As one of the important estuaries of the Pearl River system, Modaomen estuary is an ideal area to study the impact of human activities on the depositional environment of river estuaries. However, due to the difficulty in determining the sedimentary age, the relevant studies are scarce. Therefore, we studied the evolution and control mechanism of depositional environment in the last hundred years and determined the age and deposition rate of a core in Modaomen estuary shoal thru 210Pb dating technique in combination of grain size characteristics and grain size end element analysis. Results show that the sediments of the core are mainly from the Xijiang River runoff and the reinput sediment by offshore tidal current, and influenced by the inshore particle input. Besides, the depositional environment in this area have been changed significantly in the 1970s. The deposition rate in Modaomen increased from 0.53 cm/a (before 1970s) to 1.68 cm/a (after 1970s) with increases in the variation coefficient of every grain-size component, coarse grain fraction, and material input from runoff and inshore supply, and with decrease of tidal material input, which is probably related to the change in sediment discharge from Xijiang River and intensified human activities including reclamation in Modaomen since 1970s.
-
Key words:
- Pearl River Delta /
- offshore deposit /
- grain size /
- 210Pbex /
- modern depositional environment /
- deposition rate
-

-
表 1 粒度组分及粒度参数计算值
Table 1. Statistical results of grain size compositions and parameters
深度/cm 参数 组分含量/% 中值粒径/Ф 平均粒径
/Ф分选系数 偏态值 峰态值 砂 粉砂 黏土 0~80 最大值 37.88 72.96 58.13 8.26 8.35 3.05 0.40 1.12 最小值 0.00 41.37 17.00 4.81 5.36 1.47 −0.08 0.73 平均值 6.34 61.78 31.88 6.89 7.03 1.90 0.13 0.97 标准偏差 9.12 7.75 8.79 0.73 0.67 0.31 0.10 0.09 变异系数 1.44 0.13 0.28 0.11 0.10 0.17 0.80 0.09 80~170 最大值 37.88 79.01 58.13 8.26 8.35 3.05 0.80 1.13 最小值 0.00 0.13 0.28 0.11 0.10 0.17 −0.09 0.09 平均值 2.81 64.91 32.28 7.06 7.19 1.78 0.13 1.01 标准偏差 3.05 6.69 7.08 0.46 0.41 0.19 0.09 0.06 变异系数 1.08 0.10 0.22 0.07 0.06 0.11 0.68 0.06 0~170 最大值 37.88 79.01 58.13 8.26 8.35 3.05 0.40 1.13 最小值 0.00 41.37 17.00 4.81 5.36 1.47 −0.09 0.73 平均值 4.47 63.44 32.09 6.98 7.11 1.84 0.13 0.99 标准偏差 6.82 7.32 7.87 0.60 0.55 0.26 0.09 0.08 变异系数 1.52 0.12 0.25 0.09 0.08 0.14 0.73 0.08 表 2 端元相对含量及平均粒径统计结果
Table 2. Statistical results of end-members abundance and mean size
EM1 EM2 EM3 EM4 黏土/% 58.81 17.86 19.50 19.58 粉砂/% 41.19 82.11 43.36 69.12 砂/% 0.00 0.03 37.14 11.30 平均值/% 36.91 39.33 6.45 17.30 端元平均粒级/μm 3.59 11.20 — 40.80 -
[1] 贾建军,高抒,高建华,等. 珠江口河流输沙、河口沉积与粒度信息之间的联系[J]. 海洋科学进展,2005,23(3):298-304.
[2] 陈吉余,陈沈良. 中国河口研究五十年:回顾与展望[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2007,38(6):81-486.
[3] 黄镇国,张伟强. 珠江河口磨刀门的整治与地貌演变[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2005,21(6):61-65,73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2005.06.014
[4] 贾良文,吕晓莹,程聪,等. 珠江口磨刀门月际尺度地貌演变研究[J]. 海洋学报,2018,40(9):65-77.
[5] 刘志勇,潘少明,程功弼,等. 珠江口沉积物210Pb分布特征及环境意义[J]. 沉积学报,2010,28(1):166-175.
[6] 蒋陈娟,周佳楠,杨清书. 珠江磨刀门河口潮汐动力变化对人类活动的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报,2020,39(6):66-76.
[7] 张虎男,郭钦华,陈伟光,等. 西江断裂磨刀门段地质近期活动性研究[J]. 华南地震,1990,10(1):15-26. doi: 10.13512/j.hndz.1990.01.002
[8] 陈耀泰,罗章仁. 珠江口现代沉积速率及其反映的沉积特征[J]. 热带海洋,1991(2):57-64.
[9] APPLEBY P,OLDFIELD F,THOMPSON R,et al. 210Pb dating of annually laminated lake sediments from Finland[J]. Nature,1979,280(5):53-55.
[10] SMITH J N,WALTON A. Sediment accumulation rates and geochronologiesmeasured in the Saguenay Fjord using the 210Pb dating method[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1980,44(2):225-240. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90134-9
[11] CARPENTER R,BENNETT J T,PETERSON M L. 210 Pb activities in and fluxesto sediments of the Washington continental slope and shelf[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1981,45(7):1155-1172. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90139-3
[12] 康兴伦. 沉积物中210Pb的分析方法研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1988(2): 49-53
[13] 万国江. 现代沉积的210Pb计年[J]. 第四纪研究,1997,17(3):230-239. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.03.005
[14] 林瑞芬,闵育顺,卫克勤,等. 珠江口沉积柱样210Pb法年龄测定结果及其环境地球化学意义[J]. 地球化学,1998,27(5):401-411. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1998.05.001
[15] CORCORAN M,SHERIF M I,SMALLEY C,et al. Accumulation rates,focusing factors,and chronologies from depth profiles of 210Pb and 137Cs in sediments of the Laurentian Great Lakes[J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research,2018,44(4):693-704. doi: 10.1016/j.jglr.2018.05.013
[16] FLEMMING B W. A revised textural classification of gravel-free muddy sediments on the basis of ternary diagrams[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2000,20(10):1125-1137.
[17] 贾建军,高抒,高建华,等. 珠江口河流输沙、河口沉积与粒度信息之间的联系[J]. 海洋科学进展,2005,23(3):297-304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.03.007
[18] 彭晓彤,周怀阳,叶瑛,等. 珠江河口沉积物粒度特征及其对底层水动力环境的指示[J]. 沉积学报,2012,22(3):487-493.
[19] 王祥东,刘勇,李广雪. 黄河口百米地质钻孔粒度特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(4):1-6.
[20] 田庆春,石小静,石培宏. 青藏高原腹地湖泊沉积粒度特征及其古环境意义[J]. 盐湖研究,2021,29(1):25-32.
[21] 王伟,汤世凯,胡艳萍,等. 山东半岛南部丁字湾口外海底沉积物粒度时空变化及影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(2):70-80. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021050601
[22] 马玉婷,蔡华阳,杨昊,等. 珠江磨刀门河口水位分布演变特征及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报,2022,41(2):52-64. doi: 10.11978/2021072
[23] 吕海滨,吴超羽,任杰,等. 四十年来磨刀门河口水动力对地形的响应[J]. 海洋通报,2007,26(1):20-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.01.003
[24] 吕海滨,吴超羽,刘斌. 珠江口磨刀门整治前后水动力数值模拟[J]. 海洋科学,2006,30(11):58-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2006.11.013
[25] FOLK R L,ANDREWS P B. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,1970,13(4):937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[26] 王福,杨彪,田立柱,等. 开放潮坪地区210Pbexc测年CIC和CRS计算模式的选择[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(6):971-981.
[27] ASHLEY G M. Interpretation of polymodal sediments[J]. Journal of Geology,1978,86(4):411-421. doi: 10.1086/649710
[28] 安福元,马海州,樊启顺,等. 粒度在沉积物物源判别中的运用[J]. 盐湖研究,2012,20(1):49-56.
[29] WELTJE G J. End-member modeling of compositional data:numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem[J]. Mathematical Geology,1997,29(4):503-549. doi: 10.1007/BF02775085
[30] PATERSON G A,HESLOP D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2015,16(12):4494-4506.
[31] 张晓东,翟世奎,许淑梅. 端元分析模型在长江口邻近海域沉积物粒度数据反演方面的应用[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2006,28(4):159-166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2006.04.021
[32] 赵庆, 郑祥民, 周立旻, 等. 末次冰期东海嵊山岛黄土粒度端元分析及其环境意义[J/OL]. 沉积学报: 1-18. [2023-06-08]. https://doi.org/10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.085.(网络首发)
[33] 方海超,黄朋,孙家文,等. 鸭绿江端元粒度分级样品常量元素控制因素分析及物源识别[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,39(3):72-83.
[34] 林镇坤,王爱军,叶翔. 南流江河口水下三角洲表层沉积物端元分析及其沉积动力环境意义[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(1):124-134.
[35] 王珊珊,曹志敏,兰东兆,等. 珠江口沉积地球化学特征与古环境演化过程[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2010,35(2):261-267.
[36] 何志刚,莫文渊,刘春莲,等. 从沉积速率和沉积物粒度看冰后期海侵以来珠江三角洲西江大鳌沙的形成[J]. 古地理学报,2007,9(3):331-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.03.011
[37] 李春初, 田向平, 罗宪林, 等. 西江磨刀门拦门沙的形成演变及口门整治问题[C]//第七界全国海岸工程学术讨论会文集(上), 珠海: 中国水利学会, 1993: 172-181.
[38] 朱颖洁,郭纯青,黄夏坤. 气候变化和人类活动影响下西江梧州站降水径流演变研究[J]. 水文,2010,30(3):50-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2010.03.011
[39] 杨蕾. 珠江磨刀门河口的沉积化学环境研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2006.
[40] 刘成,何耘,刘桉. 河流输沙量变化的主要驱动因素[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2017,37(1):1-7.
[41] 曾昭璇. 从磨刀门历史地貌学研究看口门整治问题(上)[J]. 人民珠江, 1982(5): 11-15
[42] 刘斌,吕海滨,吴超羽,等. 磨刀门河口在20世纪60至70年代的演变模拟与动力地貌过程分析[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2014,36(2):75-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.02.008
[43] 赵荻能. 珠江河口三角洲近165年演变及对人类活动响应研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017: 1-216.
[44] 陈晖,谭超,黄本胜,等. 大规模围垦后磨刀门河口沉积环境演变分析[J]. 泥沙研究,2021,46(3):64-71. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2021.03.010
[45] 张子昊,李嘉怡,刘锋,等. 西江网河河床演变对人类活动的响应[J]. 泥沙研究,2020,45(3):61-66. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2020.03.009
[46] 杜以超,罗孝文,王峻,等. 近70年珠江水沙变化特征及人类活动影响因素分析[J]. 海洋学研究,2022,40(4):52-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2022.04.005
-



 下载:
下载: