Pollutant dispersion from the Xiaoqing River into the sea and its response to the nearshore construction
-
摘要:
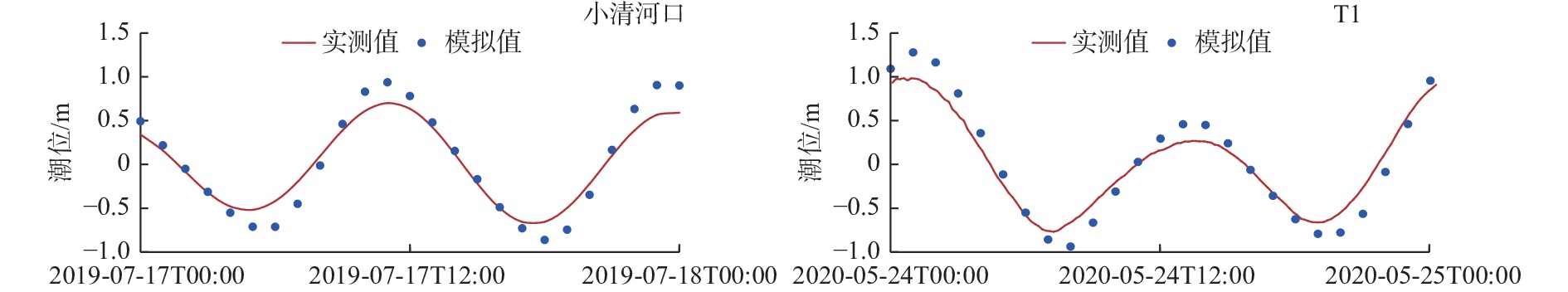
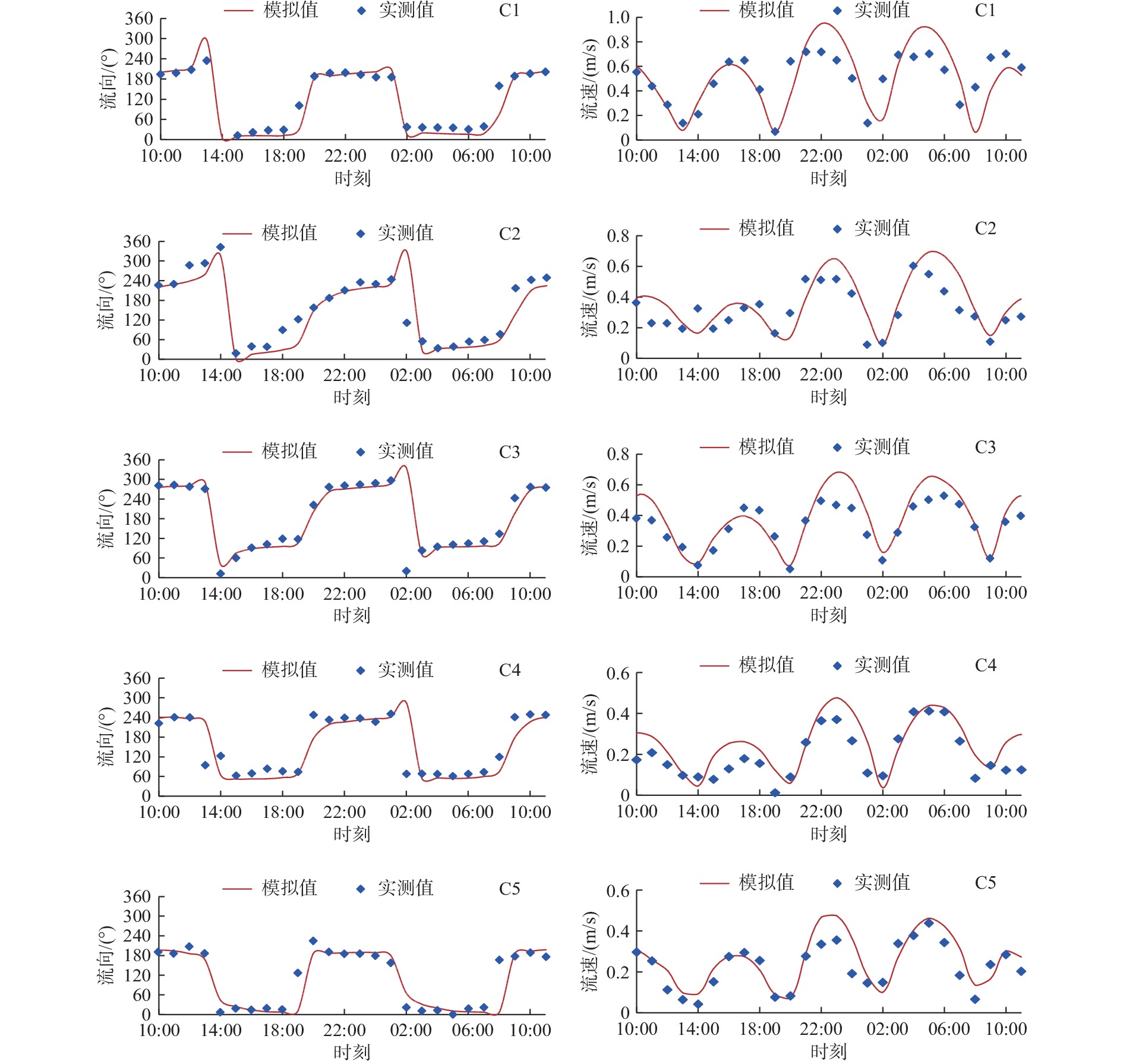
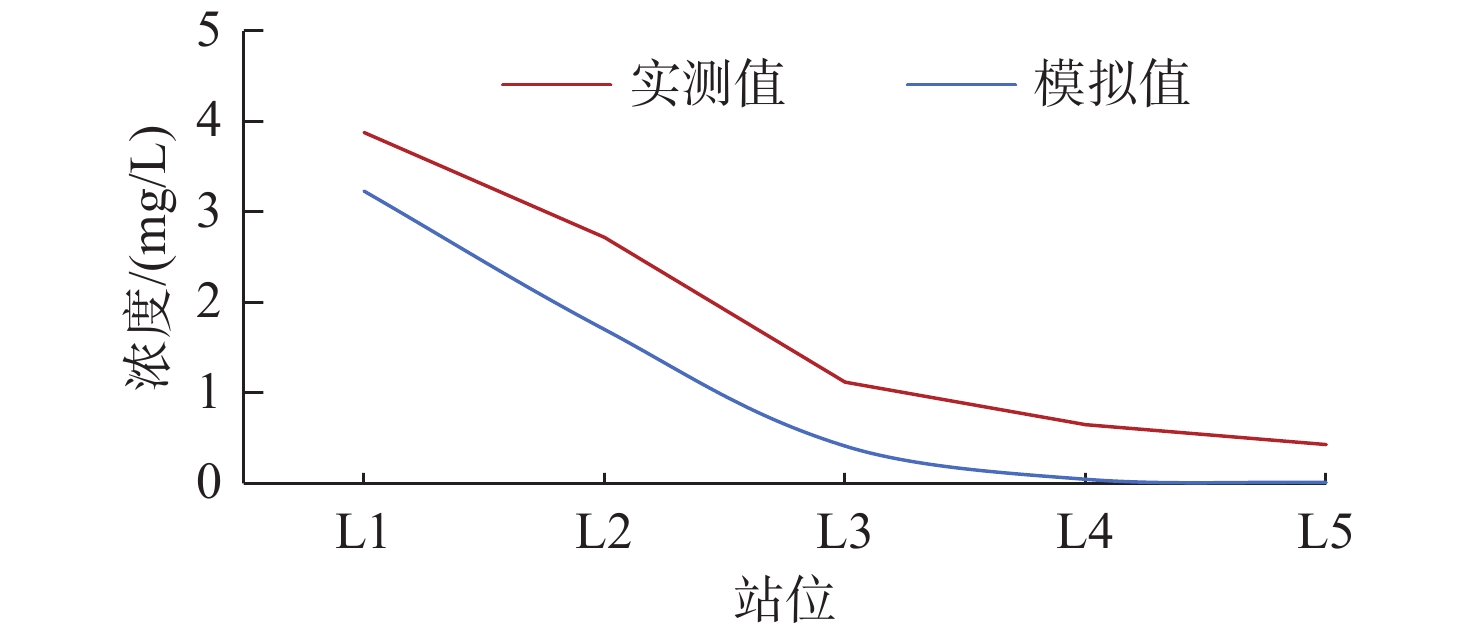
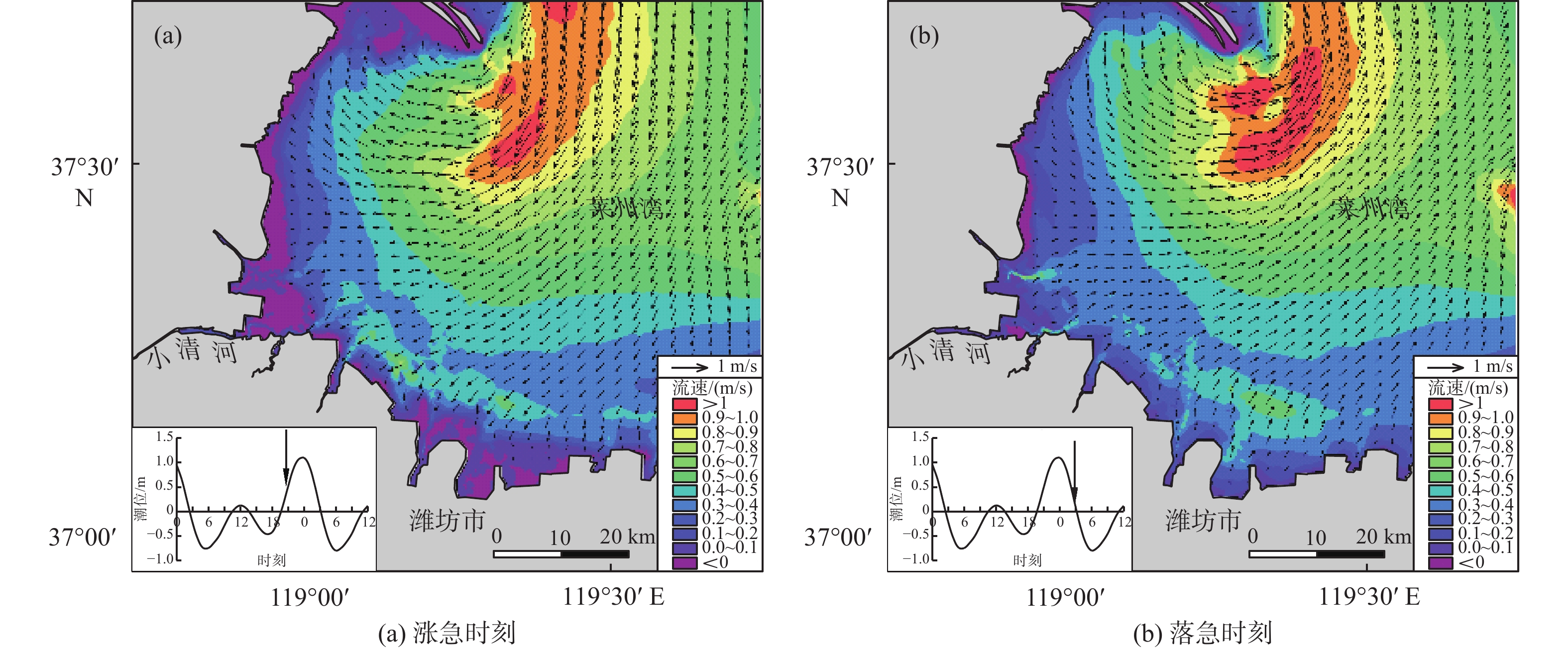
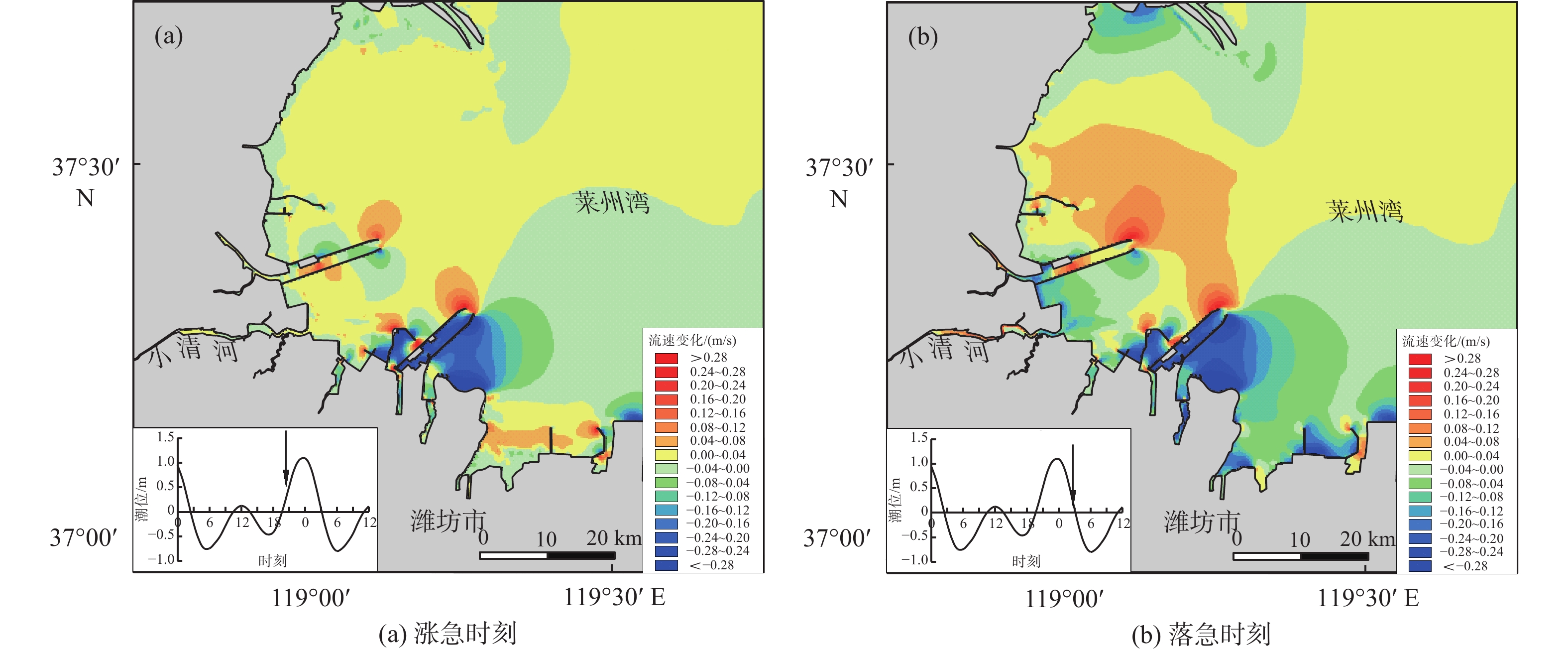
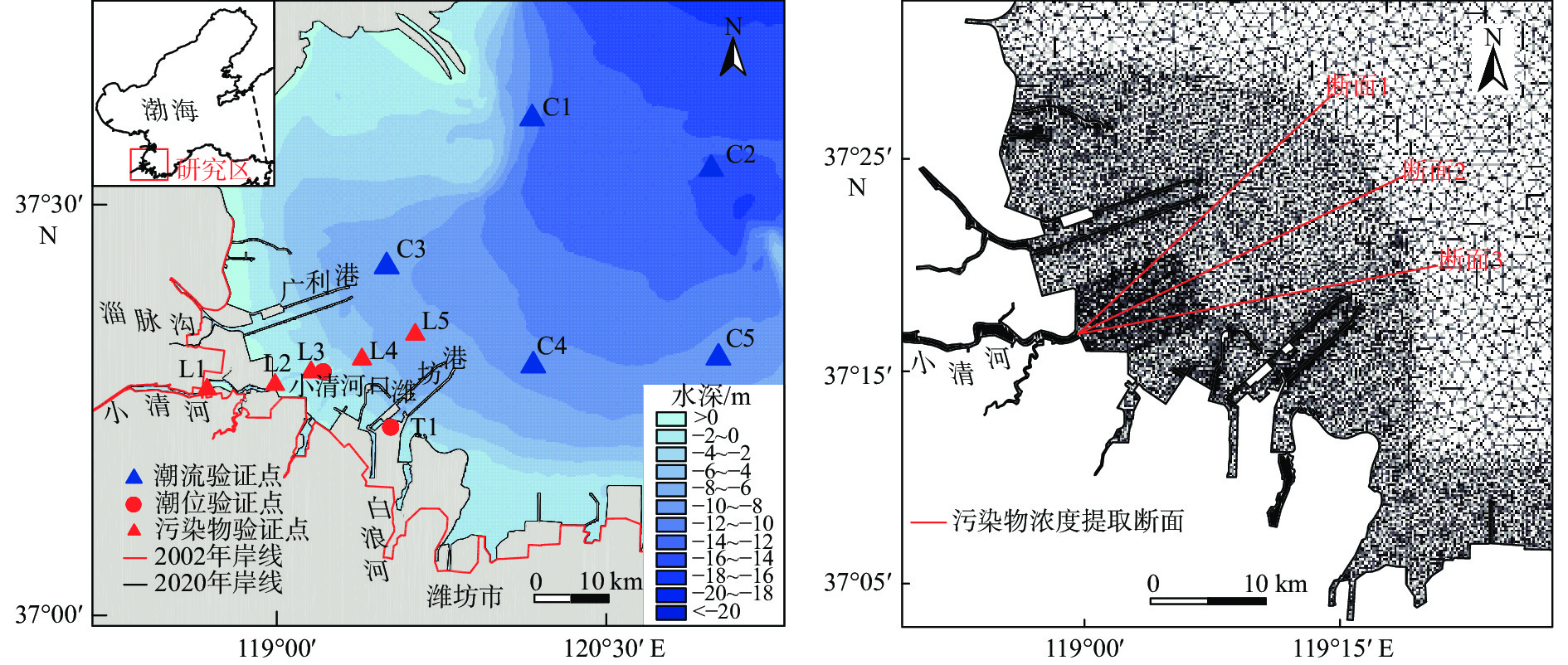
河流入海污染物是近海污染物的主要来源之一。小清河是莱州湾西南部主要入海河流和污染物来源,近年来小清河口两侧近岸工程建设规模不断扩大,其对小清河入海污染物扩散的影响如何有待深入研究。采用MIKE21数值模型模拟了近岸工程建设对潮流场的影响及小清河入海污染物(无机氮、活性磷酸盐)的扩散特征,探讨了入海污染物扩散对近岸工程建设的响应。研究结果表明:小清河口两侧近岸工程的建设,导致小清河河口附近海域流速有所减小,减小值介于2~21 cm/s。河口两侧的堤坝、防波堤等工程阻挡了污染物向东南、西北方向扩散,使小清河入海污染物扩散范围有所减小,不利于污染物扩散,导致河口附近海域污染物浓度有所增加,从而加剧了小清河河口附近海域的水质污染。因此,近岸工程建设会造成工程附近海域的潮流减弱,削弱近海海域的污染物扩散能力。
Abstract:Pollutants from rivers are the main source of offshore pollution. Xiaoqing River is the main inlet river and pollutant source in the southwestern part of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea. In recent years, the scale of nearshore constructions on both sides of Xiaoqing River estuary is constantly expanding. The response of the inlet pollutant dispersion to the nearshore construction region need to be studied deeply. The influence of nearshore construction on the tidal field and the dispersion characteristics of the inlet pollutants (dissolved inorganic nitrogen and active phosphate) from Xiaoqing River were numerically simulated in MIKE21 model, and the response of the inlet pollutant dispersion to the nearshore construction was discussed. Results show that the construction of nearshore projects on both sides of the Xiaoqing River estuary has led to a decrease of 2-21 cm/s in flow velocity in the nearshore of the estuary. Dikes and breakwaters on both sides of the estuary blocked the dispersion of pollutants to the southeast and northwest, which reduced the dispersion range of pollutants into the estuary, increased the concentration of pollutants in the estuary, and aggravated the water pollution in local areas. Therefore, the construction of nearshore projects could weaken the tidal currents around the concentration and the pollutant dispersion capacity in the offshore marine areas.
-

-
表 1 研究区遥感影像数据源信息表
Table 1. Specificatrions of remote sensing data in the study area
成像日期 卫星类型 成像类型 轨道行列号 波段数 空间分辨率/m 2002-02-01 Landsat7 ETM 121/34 8 30 2020-02-24 Landsat8 ETM 121/34 11 15 表 2 计算工况参数信息表
Table 2. Information of the working conditions and parameters for calculation
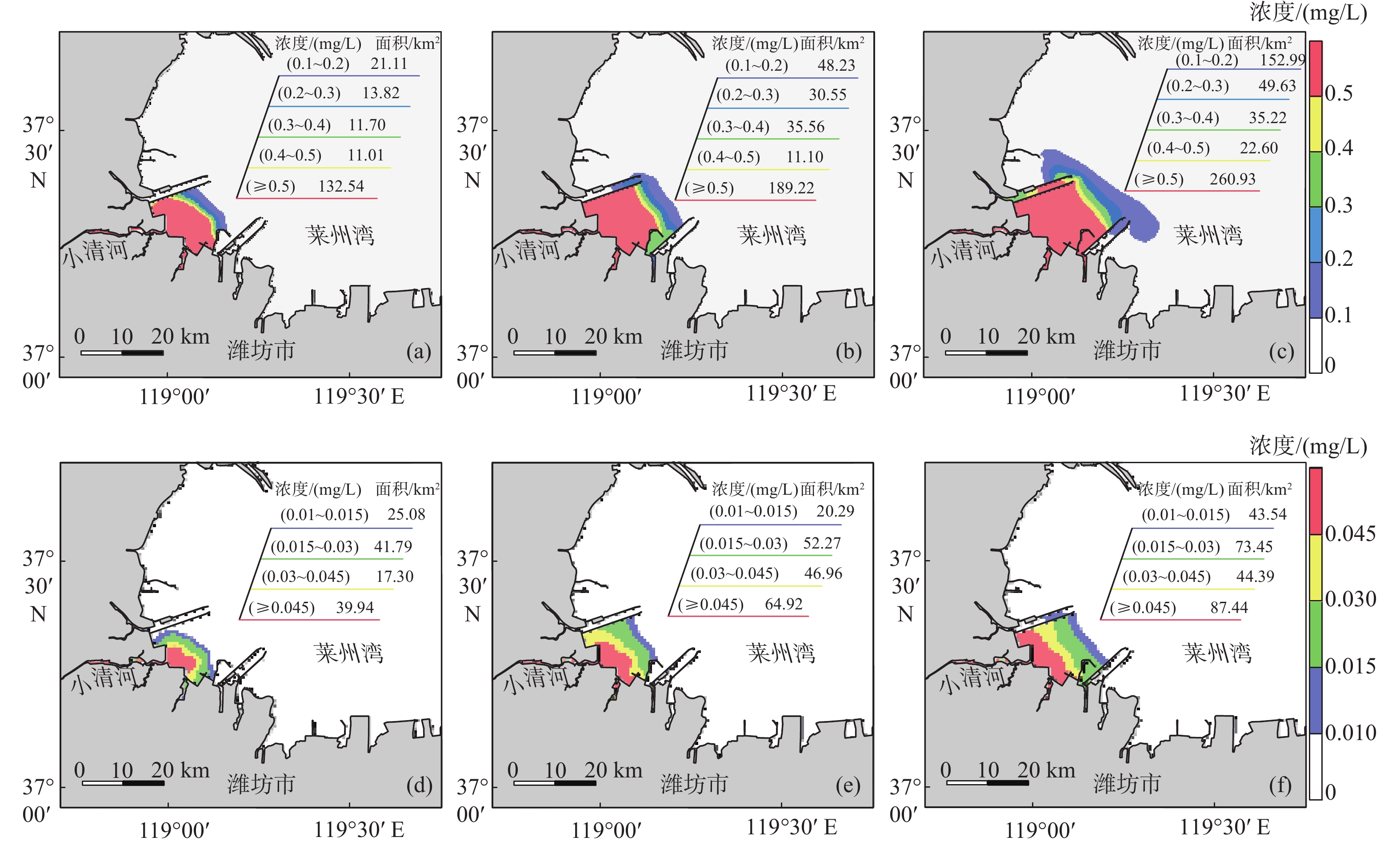
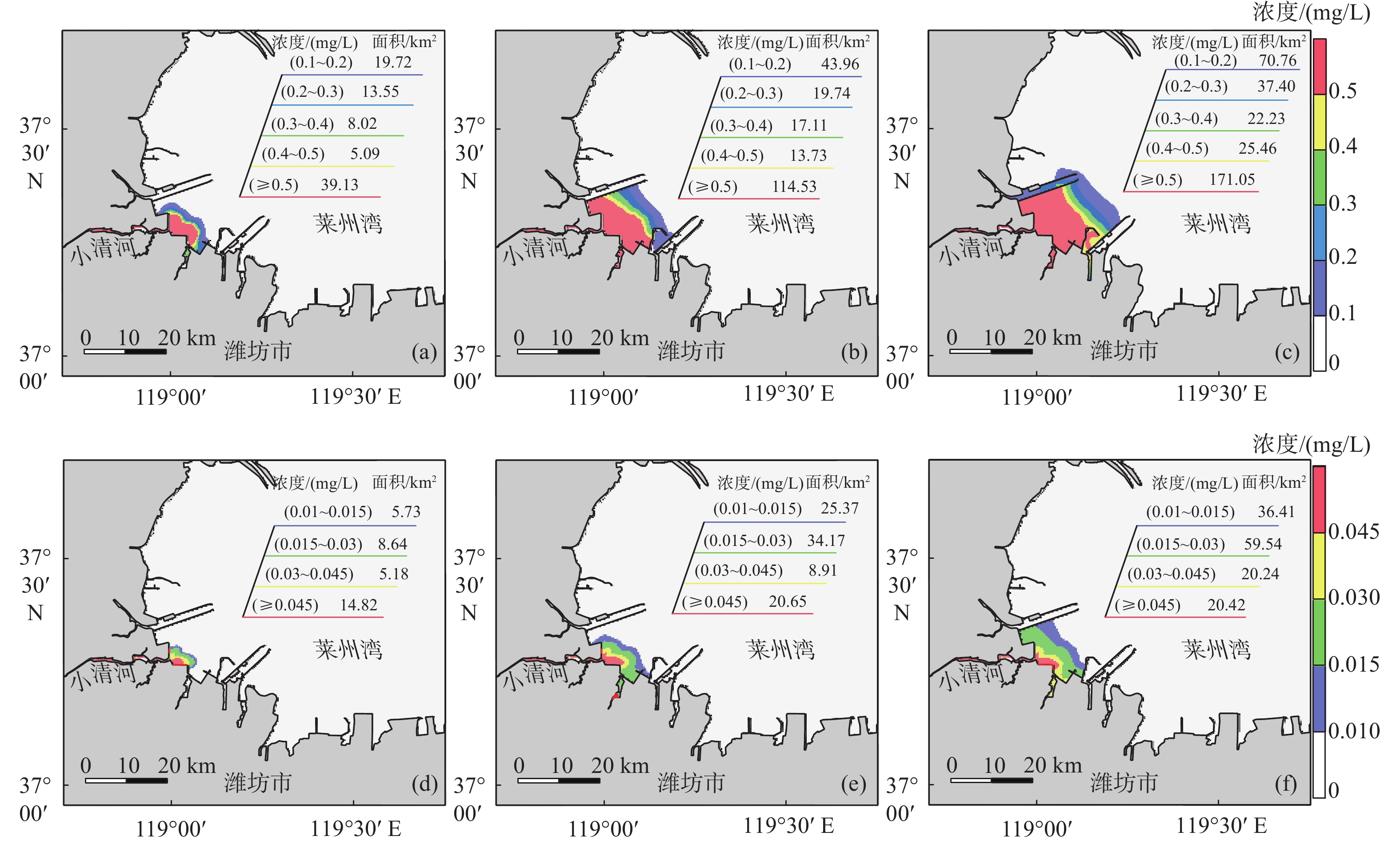
季节 入海径流量/(m3/s) 无机氮/(mg/L) 活性磷酸盐/(mg/L) 丰水期 81.3 5.782 0.105 枯水期 26.93 9.503 0.120 表 3 近岸工程建设前后小清河入海污染物扩散面积计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of the dispersion area of pollutants from Xiaoqing River into the sea before and after nearshore construction
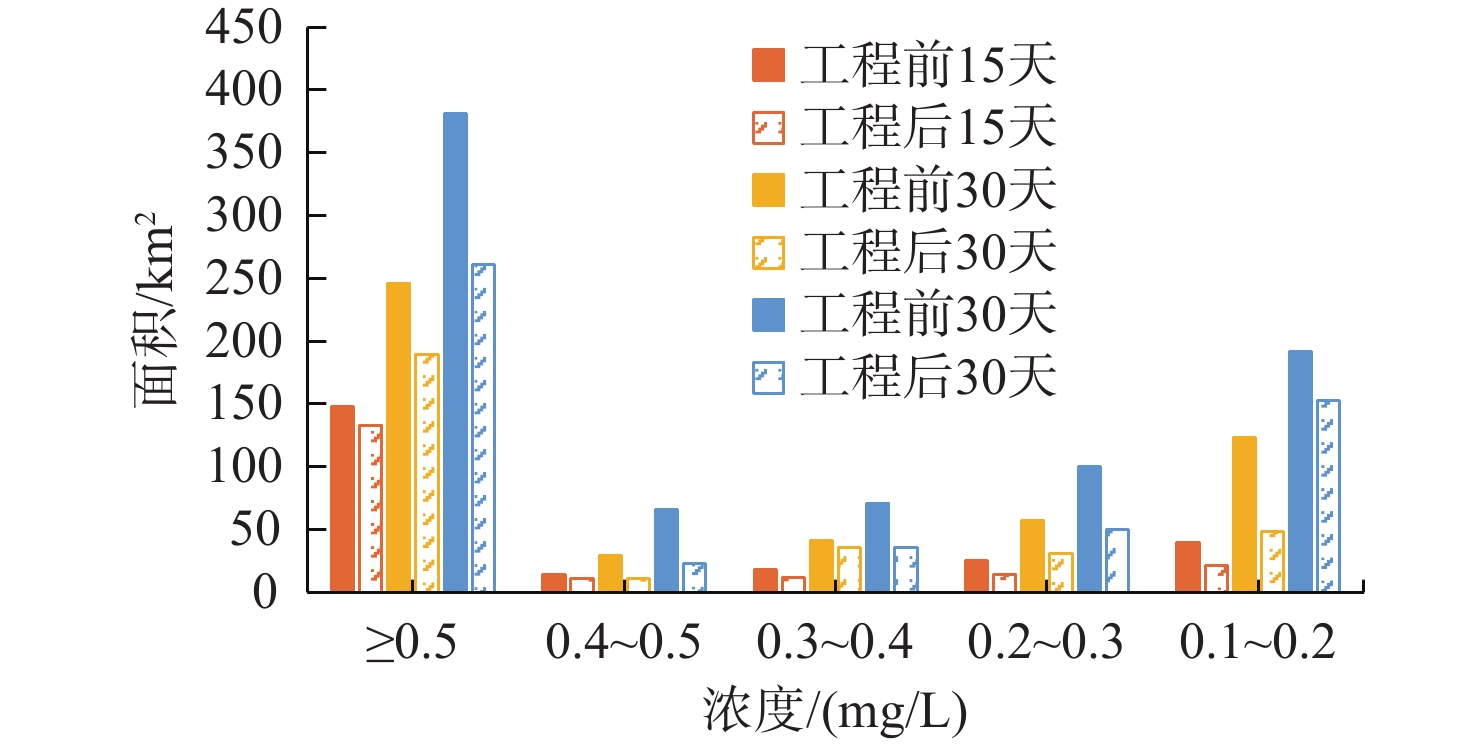
km2 季节 污染物 时期 15 d扩散面积 30 d扩散面积 60 d扩散面积 丰水期 无机氮 近岸工程建设前 245.34 496.00 809.53 近岸工程建设后 190.19 314.65 521.37 面积差(后−前) −55.15 −181.35 −288.16 活性磷酸盐 近岸工程建设前 141.22 234.24 355.63 近岸工程建设后 124.11 184.45 248.82 面积差(后−前) −17.11 −49.79 −106.81 枯水期 无机氮 近岸工程建设前 108.61 277.52 543.91 近岸工程建设后 85.52 209.07 326.90 面积差(后−前) −23.09 −68.45 −217.00 活性磷酸盐 近岸工程建设前 43.87 100.68 141.63 近岸工程建设后 34.37 89.10 136.62 面积差(后−前) −9.50 −11.58 −5.01 -
[1] SHAN J Z,LI J M. Valuing marine ecosystem service damage caused by land reclamation:insights from a deliberative choice experiment in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Marine Policy,2020,122(12):104249.
[2] LI F X,DING D D,CHEN Z J,et al. Change of sea reclamation and the sea-use management policy system in China[J]. Marine Policy,2020,115(5):103861.
[3] 梁晓倩. 入海河流水体和沉积物氮磷迁移转化机制研究[D]. 北京:华北电力大学(北京),2019.
[4] YU J,ZHANG W,TAN Y,et al. Dual-isotope-based source apportionment of nitrate in 30 rivers draining into the Bohai Sea,north China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2021,283:117112. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117112
[5] GRANIT J J,LYMER B L,OLSEN S,et al. A conceptual framework for governing and managing key flows in a source-to-sea continuum[J]. Water Policy,2017,19(4):2017126.
[6] YANG F X,YU Z G,BOUWMAN A F,et al. Human-driven long-term disconnect of nutrient inputs to the Yellow River Basin and river export to the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2023,618:129279. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129279
[7] GAO G D,WANG X H,BAO X W. Land reclamation and its impact on tidal dynamics in Jiaozhou Bay,Qingdao,China[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2014,151:285-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.07.017
[8] 张威,唐军,梁丙臣. 胶州湾前湾围填海工程对其污染物输运影响的模拟研究[J]. 海洋环境科学,2017,36(1):29-36.
[9] LATAPY A, HÉQUETTE A, NICOLLE A, et al . Influence of shoreface morphological changes since the 19th century on nearshore hydrodynamics and shoreline evolution in Wissant Bay (northern France)[J]. Marine Geology,2020 ,422 :106095 .LATAPY A,HÉQUETTE A,NICOLLE A,et al. Influence of shoreface morphological changes since the 19th century on nearshore hydrodynamics and shoreline evolution in Wissant Bay (northern France)[J]. Marine Geology,2020,422:106095.
[10] 聂超辉,吴园园,朱金龙,等. 莱州湾西南部岸线变迁对海域水动力影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋环境科学,2023,42(2):228-236.
[11] 陈则实,王文海,吴桑云. 中国海湾引论[M]. 北京:海洋出版社,2007.
[12] SHEN C C,ZHANG W,SHI H H,et al. Assessment and regulation of ocean health based on ecosystem services:case study in the Laizhou Bay,China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2015,34(12):61-66. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0777-6
[13] WANG X,CHEN W Q,ZHANG L P,et al. Estimating the ecosystem service losses from proposed land reclamation projects:a case study in Xiamen[J]. Ecological Economics,2010,69(12):2549-2556. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2010.07.031
[14] 张传鑫,陈静,纪莹璐,等. 基于碳氮稳定同位素技术的小清河口邻近海域底栖食物网结构研究[J]. 海洋学报,2022,44(1):89-100.
[15] WEI Y Q,CUI H W,HU Q J,et al. Eutrophication status assessment in the Laizhou Bay,Bohai Sea:further evidence for the ecosystem degradation[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2022,181:113867. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113867
[16] 赵鹏,江文胜,毛新燕,等. 2000—2005年莱州湾盐度的变化及其主要影响因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2010,41(1):12-23.
[17] JI G C,ZOU L,GUAN W C,et al. Partition,transportation and ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) under heavy anthropogenic estuary:a case study in the Xiaoqing River Estuary,North China[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science,2021,43:101664. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101664
[18] LI Q F,ZHANG Y Q,LU Y L,et al. Risk ranking of environmental contaminants in Xiaoqing River,a heavily polluted river along urbanizing Bohai Rim[J]. Chemosphere,2018,204:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.030
[19] JIANG T J,SKYLLBERG U,BJÖRN E,et al. Characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and relationship with dissolved mercury in Xiaoqing River-Laizhou Bay estuary,Bohai Sea,China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2017,223:19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.006
[20] ZHEN X M,TANG J H,LIU L,et al. From headwaters to estuary:distribution and fate of halogenated flame retardants (HFRs) in a river basin near the largest HFR manufacturing base in China[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2018,621:1370-1377. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.091
[21] 崔燕,张龙军,罗先香,等. 小清河口水质污染现状及富营养化评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(2):60-66.
[22] HE X Q,CHEN G J,FANG Z Y,et al. Source identification of chromium in the sediments of the Xiaoqing River and Laizhou Bay:a chromium stable isotope perspective[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,264:114686. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114686
[23] 沈佳裕,罗先香,郑浩,等. 小清河口及邻近海域表层沉积物重金属污染及生态风险特征[J]. 环境化学,2017,36(7):1516-1524.
[24] 蔡永兵,孟凡德,李飞跃,等. 小清河口闸控感潮河段As、Sb的时空分布特征及入海通量估算[J]. 海洋环境科学,2020,39(6):895-901.
[25] 刘潇,冯秀丽,刘杰. 港口工程影响下莱州湾西南侧海域水动力演化特征[J]. 海洋科学,2016,40(3):138-145.
[26] 王志伟. 基于Landsat影像的天津市滨海新区海岸线提取及变化分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2021.
[27] 许婷. 丹麦MIKE21模型概述及应用实例[J]. 水利科技与经济,2010,16(8):867-869.
[28] 黄磊,黄祖珂. 潮汐原理与计算[M]. 青岛:中国海洋大学出版社,2005.
[29] 朱雅琴,张法星,许唯临. 舌形挑流鼻坎水力特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2004,4(5):397-402.
[30] 岳青华,丁聪. 围填海工程对半封闭海湾水动力环境影响分析:以大鹏湾内围填海工程为例[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2019(11):129-132.
[31] 刘建强. 莱州湾海洋工程建设对小清河口环境影响数值研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学,2012.
[32] 田艳,于定勇,李云路. 莱州湾围填海工程对海洋环境的累积影响研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(1):117-124.
[33] 吕婷,苏博,王佳莹,等. 海洋工程影响下莱州湾海域水动力环境变化特征[J]. 海洋环境科学,2017,36(4):571-577.
[34] FAN X Z,DAI X Y,YANG G J,et al. Detecting artificialization process and corresponding state changes of estuarine ecosystems based on naturalness assessment[J]. Ocean and Coastal Management,2017,146:178-186. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2017.07.007
[35] DAFFORN K A,MAYER-PINTO M,MORRIS R L,et al. Application of management tools to integrate ecological principles with the design of marine infrastructure[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2015,158:61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.05.001
[36] 龚旭东,俞缙,蓝尹余. 半封闭海湾围填海对水动力环境的影响分析[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版),2019,40(1):72-78.
[37] TETSUO Y,KAZUNORI O. Change of tide,tidal current,and sediment due to reclamation in Tokyo Bay[J]. Oceanography in Japan,1999,6(8):411-415.
[38] LIN L,LIU Z,XIE L,et al. Dynamics governing the response of tidal current along the mouth of Jiaozhou Bay to land reclamation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2015,120(4):2958-2972.
[39] MENG W Q,HU B B,HE M X,et al. Temporal-spatial variations and driving factors analysis of coastal reclamation in China[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2017,191:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.04.008
[40] ZHANG P,SU Y,LIANG S K,et al. Assessment of long-term water quality variation affected by high-intensity land-based inputs and land reclamation in Jiaozhou Bay,China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2017,75:210-219. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.035
[41] HUNG J J,HUNG P Y. Carbon and nutrient dynamics in a hypertrophic lagoon in southwestern Taiwan[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2003,42(3):97-114.
[42] LI L J,LI G S,DU J Q,et al. Effects of tidal flat reclamation on the stability of coastal wetland ecosystem services:a case study in Jiangsu Coast,China[J]. Ecological Indicators,2022,145:109697. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109697
[43] HUNG J J,HUANG W C,YU C S. Environmental and biogeochemical changes following a decade's reclamation in the Dapeng (Tapong) Bay,southwestern Taiwan[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2013,130:9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.03.018
-



 下载:
下载: