Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of surface sediments in Jiaozhou Bay
-
摘要:
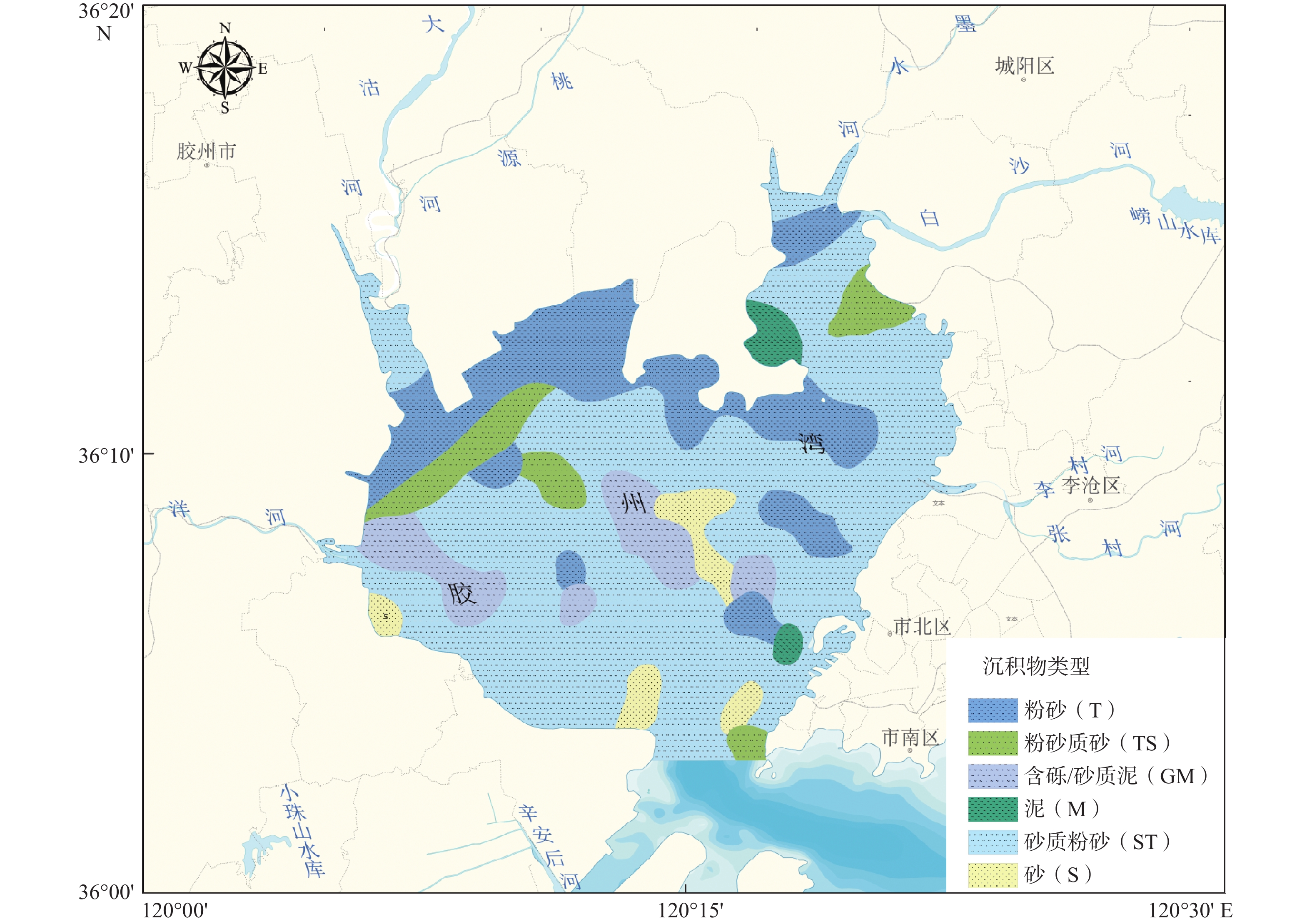
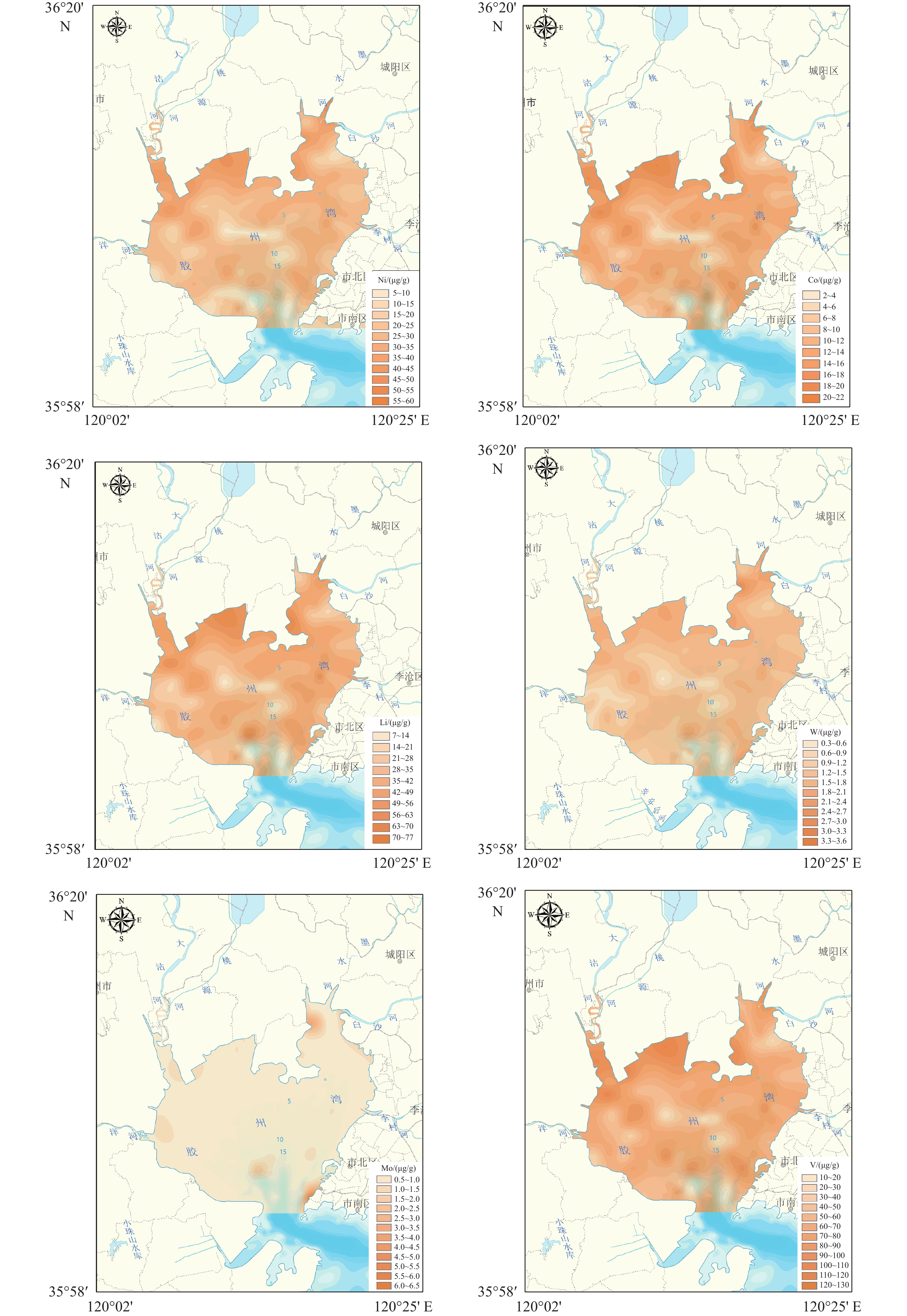
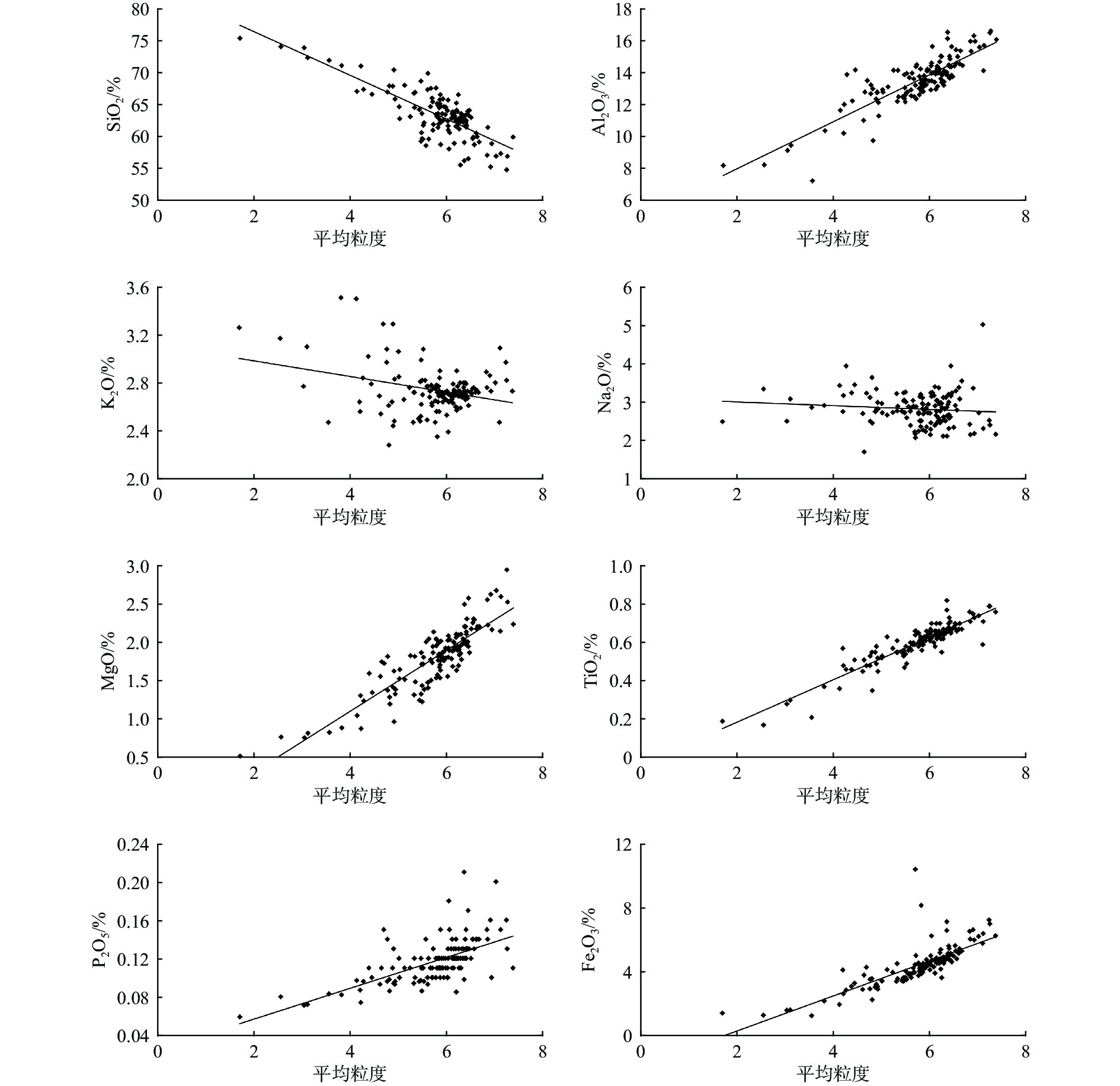
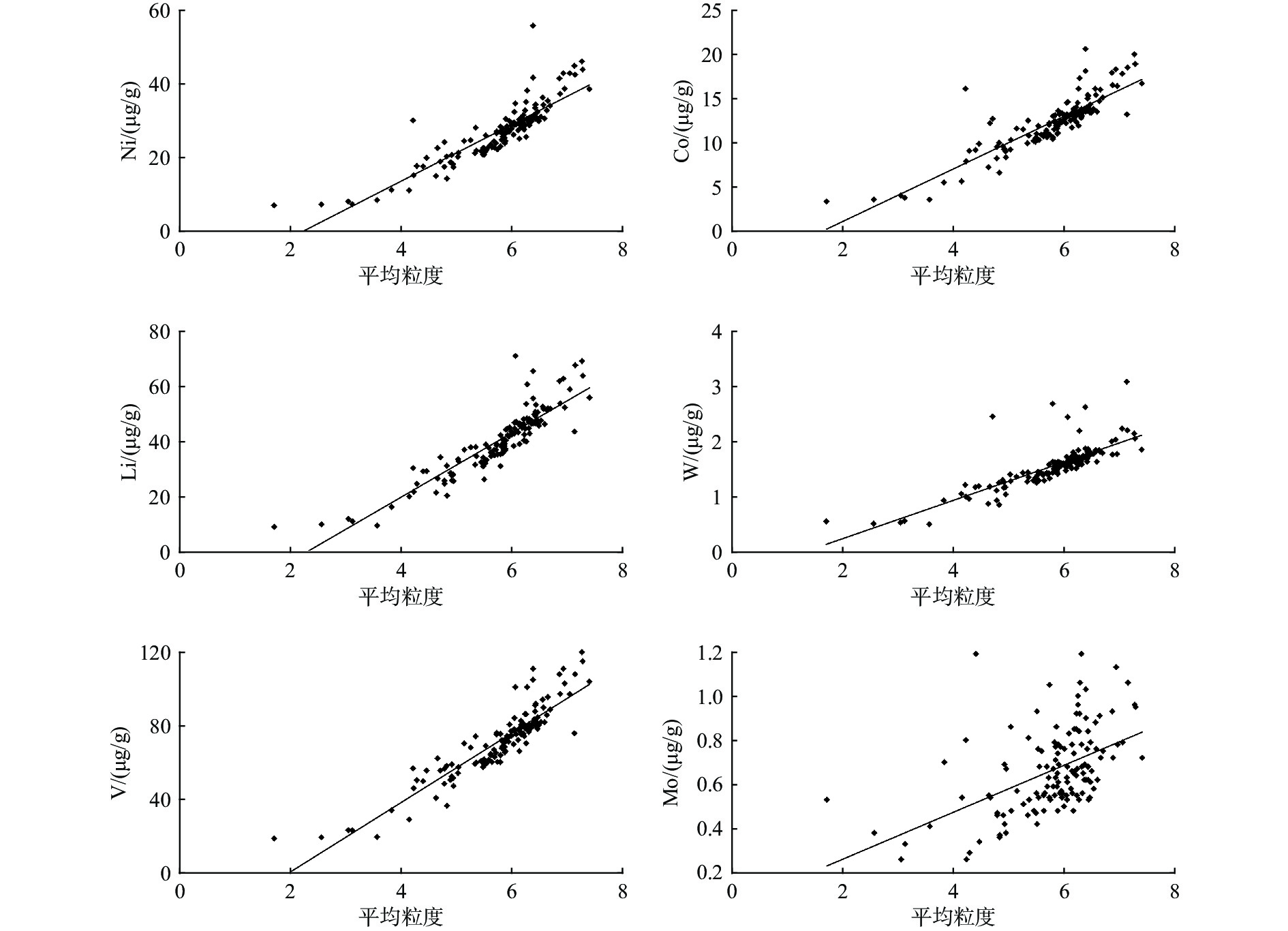
通过对胶州湾150个站位表层沉积物的粒度和地球化学组成进行特征分析、相关性分析和因子分析,探讨了其空间分布特征、元素相关性和元素组合特征,充分挖掘沉积物的地球化学特征及其控制因素。结果表明,胶州湾表层沉积物类型丰富,主要以砂质粉砂为主。沉积物常量元素以SiO2、Al2O3为主,SiO2高值区主要分布于调查区东北部以及中部偏西等区域,Al2O3在调查区北部、东北部河口及其近岸含量较高,表明沉积物主要为陆源碎屑沉积物。微量元素含量最高的为V,其次为Li和Ni,其含量分布与Al2O3相近。除CaO外,研究区常微量元素的空间变异系数均较小,表明各元素在研究区分布相对均匀。元素的相关性和因子分析结果显示,研究区大部分常微量元素(Al2O3、MgO、CaO、TiO2、MnO、Fe2O3、Ni、Co、Li、W、V等)含量的变化遵循粒度控制规律,而CaO、P2O5的含量主要受风化作用和人类活动的共同影响。
Abstract:Based on the correlation analysis and factor analysis of grain size and geochemical compositions of 150 surface sediments from Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, East China, the spatial distribution, element correlation, and element combination were studied, and the sedimentary environmental implication of geochemical characteristics of the in-bay sediments was revealed. The results show that the surface sediments are rich in types, mainly sandy silts in Jiaozhou Bay. The major elements of the sediments are predominated by SiO2 and Al2O3, and the high value area of SiO2 is mainly distributed in the northeast and west-central areas, and the content of Al2O3 is higher in the estuaries of the north and northeast of the bay and near the coast, indicating that the sediments are mainly terrigenous detrital sediments. The highest trace elements is V, followed by Li and Ni, and the content distribution is similar to that of Al2O3. Except for CaO, the spatial variation coefficients of the elements in the bay are small, indicating that the distribution of the elements was relatively uniform. The results of the correlation analysis and factor analysis suggest that the grain size is the main factor controlling the distribution of most major and trace elements (Al2O3, MgO, CaO, TiO2, MnO, Fe2O3, Ni, Co, Li, W, V, etc.) in the bay. The contents of CaO and P2O5 are mainly affected by weathering and human activities.
-
Key words:
- Jiaozhou Bay /
- surface sediment /
- grain size /
- geochemistry /
- major element /
- trace element
-

-
表 1 表层沉积物常量元素含量
Table 1. Content of major elements in the surface sediments
主量元素 全国海域平均值/% 平均值/% 最大值/% 最小值/% 标准偏差 变异系数/% SiO2 62.51 61.87 74.70 53.07 4.24 0.07 Al2O3 11.09 13.36 16.60 7.22 1.66 0.12 CaO 5.30 2.47 13.96 0.63 2.27 0.92 MgO 1.82 1.76 2.94 0.51 0.43 0.25 K2O 2.32 2.74 3.51 2.28 0.19 0.07 Na2O 1.99 2.83 5.03 1.71 0.43 0.15 TiO2 0.58 0.59 0.82 0.17 0.12 0.20 P2O5 0.11 0.12 0.39 0.06 0.03 0.28 MnO 0.07 0.10 0.31 0.05 0.04 0.38 Fe2O3 4.43 4.31 10.42 1.26 1.31 0.30 表 2 表层沉积物微量元素含量统计
Table 2. Content of trace elements in the surface sediments
微量元素 全国海域平均值/10−6 平均值/10−6 极大值/10−6 极小值/10−6 标偏偏差 变异系数/% Ni 24.00 26.98 56.30 7.52 8.27 0.31 Co 12.00 12.02 20.60 3.34 3.27 0.27 Li 38.00 39.28 70.90 8.98 12.21 0.31 W 1.50 1.52 3.09 0.51 0.41 0.27 Mo 0.50 0.66 1.46 0.26 0.20 0.31 V 70.00 70.05 120.00 18.80 19.64 0.28 表 3 研究区表层沉积物元素相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficient of elements in surface sediments of the study area
SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO TFe2O3 Ni Co Li W Mo V 砂 粉砂 黏土 SiO2 1 Al2O3 −0.02 1 CaO −0.58 −0.76 1 MgO −0.30 0.87 −0.52 1 K2O −0.07 −0.11 0.04 −0.09 1 Na2O −0.15 −0.06 0.05 −0.12 0.08 1 TiO2 0.05 0.91 −0.73 0.86 −0.31 −0.19 1 P2O5 −0.42 0.13 0.05 0.19 −0.13 0.43 0.09 1 MnO −0.29 0.54 −0.28 0.65 0.07 −0.15 0.51 0.20 1 Fe2O3 −0.18 0.76 −0.56 0.81 −0.19 −0.20 0.83 0.18 0.58 1 Ni −0.24 0.86 −0.54 0.88 −0.20 −0.10 0.89 0.29 0.69 0.84 1 Co −0.15 0.87 −0.59 0.88 −0.18 −0.16 0.91 0.12 0.66 0.83 0.97 1 Li −0.14 0.88 −0.61 0.89 −0.16 −0.10 0.90 0.12 0.58 0.82 0.94 0.95 1 W −0.27 0.76 −0.50 0.79 −0.18 0.06 0.78 0.47 0.56 0.75 0.86 0.82 0.84 1 Mo −0.40 0.13 0.04 0.19 0.07 0.13 0.07 0.46 0.14 0.20 0.17 0.15 0.13 0.57 1 V −0.10 0.91 −0.65 0.88 −0.21 −0.18 0.93 0.11 0.59 0.85 0.96 0.97 0.97 0.81 0.10 1 砂 0.20 −0.80 0.61 −0.83 0.33 0.09 −0.90 −0.19 −0.44 −0.75 −0.84 −0.83 −0.87 −0.79 −0.10 −0.87 1 粉砂 −0.12 0.73 −0.64 0.72 −0.41 −0.04 0.85 0.14 0.32 0.66 0.73 0.73 0.77 0.72 0.07 0.77 −0.96 1 黏土 −0.40 0.81 −0.50 0.85 −0.12 −0.17 0.81 0.24 0.53 0.74 0.85 0.84 0.86 0.75 0.14 0.86 −0.85 0.68 1 注:样本数为150。 表 4 胶州湾表层沉积物元素因子分析
Table 4. Analysis of elements factors in the surface sediments from Jiaozhou Bay
元素 F1 F2 F3 SiO2 −0.154 −0.807 0.456 Al2O3 0.924 −0.136 0.120 CaO −0.653 0.509 −0.438 MgO 0.927 0.067 −0.136 K2O −0.191 0.089 −0.273 Na2O −0.124 0.458 0.641 TiO2 0.942 −0.223 0.091 P2O5 0.228 0.741 0.388 MnO 0.671 0.157 −0.369 Fe2O3 0.885 −0.006 −0.084 Ni 0.970 0.070 −0.054 Co 0.966 −0.054 −0.088 Li 0.958 −0.056 −0.025 W 0.886 0.325 0.165 Mo 0.222 0.675 0.115 V 0.972 −0.117 −0.037 方差/% 56.01 14.74 7.96 累积方差/% 56.01 70.75 78.71 -
[1] 崔振昂,甘华阳,刘文涛,等. 北部湾东部海域表层沉积物常量元素地球化学特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 物探化探计算技术,2015,37(4):522-531. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2015.04.18
[2] AHMAD I,CHANDRA R. Geochemistry of loess-paleosol sediments of Kashmir Valley,India:provenance and weathering[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2013,66:73-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.029
[3] 雷志宇,刘荣波,胡日军,等. 黄河三角洲周边海域表层沉积物地球化学特征分布及影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(6):104-118. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022041301
[4] GAO G D,WANG X H,BAO X W. Land reclamation and its impact on tidal dynamics in Jiaozhou Bay,Qingdao,China[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2014,151:285-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.07.017
[5] XU F J,QIU L W,CAO Y C,et al. Trace metals in the surface sediments of the intertidal Jiaozhou Bay,China:sources and contamination assessment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,104:371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.01.019
[6] YANG Y L,GAI N,GENG C Z,et al. East Asia monsoon's influence on seasonal changes of beryllium-7 and typical POPs in near-surface atmospheric aerosols in mid-latitude city Qingdao,China[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2013,79:802-810. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.07.021
[7] DENG B, ZHANG J, ZHANG G R, et al. Enhanced anthropogenic heavy metal dispersal from tidal disturbance in the Jiaozhou Bay, North China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2010, 161(1/4): 349-358.
[8] LIU S M,ZHANG J,CHEN H T,et al. Factors influencing nutrient dynamics in the eutrophic Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Progress in Oceanography,2005,66(1):66-85.
[9] YE S Y,EDWARDS L A,DING X G,et al. Trace metals in porewater of surface sediments and their bioavailability in Jiaozhou Bay,Qingdao,China[J]. Environmental Geology,2011,64(6):1641-1646. doi: 10.1007/s12665-010-0719-8
[10] 庄海海,徐绍辉,高茂生,等. 胶州湾表层沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(9):24-31. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.09004
[11] 张珂,王朝晖,冯杰,等. 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 分析测试学报,2011,30(12):1406-1411. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2011.12.015
[12] 郭军辉,殷月芬,陈发荣,等. 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属污染分布特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 环境污染与防治,2012,34(3):13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2012.03.004
[13] 何书锋,李广雪,史经昊. 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属元素分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(4):41-48. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2013.04.005
[14] 刘兆庆,徐方建,田旭,等. 胶州湾潮间带表层沉积物重金属污染评价[J]. 中国环境科学,2017,37(6):2239-2247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.06.031
[15] 胡睿,窦衍光,邹亮,等. 胶州湾海域表层沉积物重金属元素分布特征与风险评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(11):11-21. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.104
[16] FOLK R L,WARD W C. Brazos River bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1957,27(1):3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[17] WENTWORTH C K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments[J]. The Journal of Geology,1922,30(5):377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910
[18] MCMANUS J. Grain size determination and interpretation[M]. //Tucker M. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Public, 1988: 63-85.
[19] 郭飞,高茂生,侯国华,等. 莱州湾07钻孔沉积物晚更新世以来的元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2016,38(3):145-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.03.014
[20] 石学法,刘升发,乔淑卿,等. 中国东部近海沉积物地球化学:分布特征、控制因素与古气候记录[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2015,34(5):883-894. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.001
[21] KANG X M,SONG J M,YUAN H M,et al. Speciation of heavy metals in different grain sizes of Jiaozhou Bay sediments:bioavailability,ecological risk assessment and source analysis on a centennial timescale[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2017,143:296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.036
[22] GAO X L,SONG J M,LI X G,et al. Sediment quality of the Bohai Sea and the northern Yellow Sea indicated by the results of acid-volatile sulfide and simultaneously extracted metals determinations[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,155:111-147.
[23] KUMAR A,SINGHAL R K,ROUT S,et al. Spatial geochemical variation of major and trace elements in the marine sediments of Mumbai Harbor Bay[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2013,70(7):3057-3066. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2366-3
[24] 方海超,黄朋,周宇,等. 北黄海表层沉积物常量元素分布特征及其控制因素分析[J]. 海洋科学,2015,39(4):108-116. doi: 10.11759/hykx20131031001
-



 下载:
下载: