Sedimentary characteristics of a drilling core from the Zhongsha atoll lagoon: responses to sea level and provenance changes
-
摘要:
基于中沙环礁潟湖的50.5 m钻孔岩芯,采用薄片观察、测年、主微量元素和碳氧同位素分析等方法,探讨了钻孔岩芯的层序地层、沉积微相和地球化学特征。结果显示该处沉积过程对晚第四纪海平面变化和物源有明显响应。结合测年结果,将岩芯的生物礁灰岩划分为10个更新世层序,且可与MIS5—MIS23阶段间冰期海水高位时期相对应。元素Sr和U的含量变化随深度加大而呈现阶梯式下降,这是由于冰期海水低位时期碳酸盐岩台地反复暴露使得老地层接受更长时间淡水成岩作用从而导致元素累积流失更多,且数值下降处可以指示层序界面。该钻孔钻遇的珊瑚礁多发育在高位体系域的进积阶段,推测是由于晚第四纪时期海平面变化速度快,且呈现迅速上升而缓慢下降的特征引起的。物源贡献因子分析结果显示,陆源物质来源、文石和高镁方解石来源、低镁方解石来源和鸟类粪便来源等4类物源影响礁灰岩的主量元素组成。本研究还揭示出现今潟湖钻遇的珊瑚礁地层有对晚第四纪10万a短偏心率周期的海平面变化响应较好,体现潟湖和台地边缘珊瑚礁的差异生长是造成现今环礁潟湖水深较大的原因之一,对解释现代环礁由来有一定的启示意义。
Abstract:Based on thin-section observation, dating results, analysis of major and minor elements and carbon and oxygen stable isotopes, the sequence stratigraphy, sedimentary facies and geochemical characteristics of a 50.5-m drill core in the atoll lagoon were examined and its significance for paleoclimate and paleoenvironment was explored. Results show that sedimentary features well responded to the Late Quaternary sea level change and provenance. Using dating results, ten Pleistocene sequences were correlated with interglacial stages during Marine Isotope Stages 5-23. The gradual decrease in Sr and U values is due to the longer duration of exposure and meteoric diagenesis of the older sequence relative to the younger sequence in the carbonate platform, clearly indicating the existence of a sequence boundary. The reef facies were formed mainly during sea level fall, indicating progradational growth of the reef. Rapid sea level rise and slow sea level fall lead to reef facies preferring to grow in the highstand systems tracts of the sequences. Four potential sources were identified from the combined PMF (positive matrix factorization) factor profiles and factor contributions. Our results indicate the drilling reef layers in the modern lagoon can well reflect the sea level change controlled by the eccentricity cycles of 100 ka and that greater reef thickening of aggradational reef in the marginal platform than that of progradational reef in the lagoon, which enriched our understanding of the evolutional processes of the atoll with a deep lagoon.
-

-
表 1 AMS14C测年结果
Table 1. AMS14C dating results
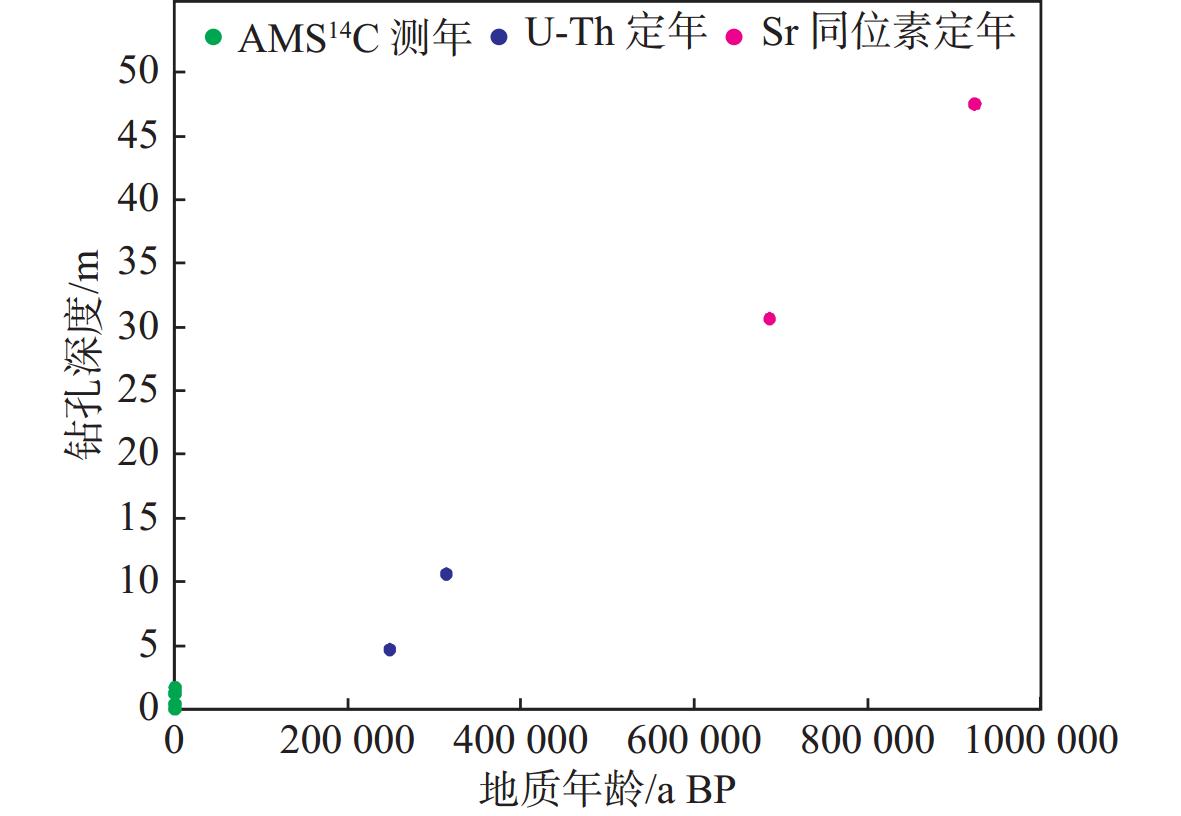
深度/mbsf 编号 样品 14C 年龄/a BP (13C/12C)/‰ 校正年龄(范围)/cal a BP 校正年龄(中值)/cal a BP 0.01 Beta-530262 有孔虫 440±30 −0.3 130~0 65 0.41 Beta-530263 有孔虫 540±30 +0.1 266~66 166 1.26 Beta-530265 有孔虫 570±30 +0.9 285~111 198 1.68 Beta-530266 有孔虫 820±30 +0.4 513~396 454.5 表 2 ZS-01钻孔所取珊瑚的230Th/234U 比值与测年结果
Table 2. 230Th/234U dating results for corals from Core ZS-01
深度/m 样品 U/(μg/g) Th /(μg/g) 234U/238U/10-6 234U 230Th/238U 230Th/232Th/10−6 年龄/a BP 误差(2σ) 4.67 珊瑚 3 472.5±5.2 4 671±94 59.104±0.097 75.2±1.8 0.983 8±0.0017 12 060±243 248 447 2 461 10.60 灰岩 1 784.1±2.3 557±12 58.718±0.104 68.2±1.9 1.028 8±0.0018 54 311±1199 313 774 4 927 22.10 珊瑚 1 149.0±1.5 276±8 56.403±0.105 26.1±1.9 1.039 3±0.0020 71 336±2 086 >600 000 \ 26.64 灰岩 2 182.8±2.9 19 175±384 56.508±0.098 28±1.8 1.0448±0.0019 1 961±39 >600 000 \ 40.95 珊瑚 1 244.1±1.8 49 541±993 57.131±0.13 39.3±2.4 1.1045±0.0021 457±9 >600 000 \ 表 3 ZS-01钻孔87Sr/86Sr比值和定年结果
Table 3. 87Sr/86Sr ratios and dating results for Core ZS-01
深度/m 编号 样品 87Sr/86Sr 2σ 最小年龄/a BP 平均年龄/a BP 最大年龄/a BP 30.63 IS-0599 灰岩 0.709 151 0.000 005 617 000 687 000 773 000 47.5 IS-0600 灰岩 0.709 142 0.000 019 826 000 924 000 1 019 000 表 4 ZS-01钻孔常量、微量元素相关性系数表(n=186, P<0.01)
Table 4. The correlations of main and minor elements in ZK-01 carbonate profile
Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 K2O CaO TiO2 MnO Fe2O3 Sr U Na2O 1.00 MgO 0.79 1.00 Al2O3 0.23 0.18 1.00 SiO2 0.29 0.14 0.50 1.00 P2O5 0.40 0.67 0.13 0.16 1.00 K2O 0.37 0.18 0.57 0.84 0.21 1.00 CaO −0.87 −0.91 −0.30 −0.25 −0.52 −0.32 1.00 TiO2 0.24 0.08 0.85 0.49 0.07 0.72 −0.23 1.00 MnO 0.31 0.47 0.21 0.45 0.70 0.53 −0.43 0.25 1.00 Fe2O3 −0.08 −0.06 0.59 0.66 0.16 0.82 −0.02 0.70 0.49 1.00 Sr 0.74 0.78 0.12 0.01 0.35 0.03 −0.79 0.00 0.07 −0.19 1.00 U 0.43 0.53 0.12 0.05 0.45 0.08 −0.46 0.02 0.12 −0.01 0.76 1.00 表 5 不同因子数量的PMF分析结果对比
Table 5. A comparison of the performance of the PMF models with varying numbers of factors
物源贡献因子个数 3 4 5 6 因子 1 SiO2,K2O,TiO2,Fe2O3,Al2O3,P2O5 ,MnO SiO2,K2O,TiO2,Fe2O3, Al2O3 SiO2 SiO2 因子 2 Na2O,MgO Na2O,MgO Na2O,MgO Na2O,MgO 因子 3 CaO,LOI CaO,LOI CaO,LOI CaO,LOI 因子 4 P2O5,MnO P2O5,MnO,Al2O3 P2O5,MnO,Al2O3 因子 5 K2O,TiO2,Fe2O3 K2O,TiO2,Fe2O3 因子6 Na2O -
[1] SUN Y,YIN Q,CRUCIFIX M,et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Nature Communications,2019,10:352. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08257-9
[2] PISIAS N G,MOORE T C. The evolution of Pleistocene climate:a time series approach[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 1981,52:450-458.
[3] RAYMO M E,OPPO D W,CURRY W. The Mid-Pleistocene climate transition:a deep sea carbon isotopic perspective[J]. Paleoceanography,1997,12:546-559. doi: 10.1029/97PA01019
[4] HERBERT T D,PETERSON L C,LAWRENCE K T,et al. Tropical ocean temperatures over the past 3.5 million years[J]. Science,2010,328:1530-1534. doi: 10.1126/science.1185435
[5] LISIECKI L E,RAYMO M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records[J]. Paleoceanography,2005,20:PA1003.
[6] DROXLER A W,JORRY S J. The origin of modern atolls:challenging Darwin's deeply ingrained theory[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science,2021,13:537-573. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-122414-034137
[7] CAMOIN G F,EBREN P,EISENHAUER A,et al. A 300 000-yr coral reef record of sea level changes,Mururoa atoll (Tuamotu archipelago,French Polynesia)[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2001,175:325-341.
[8] MONTAGGIONI L F,BORGOMANO J,FOURNIER F,et al. Response of the Great Barrier Reef to sea-level and environmental changes over the past 30,000 years [J]. Nature Geoscience,2018,11:426-432.
[9] MELIM L A. Limitations on lowstand meteoric diagenesis in the Pliocene-Pleistocene of Florida and Great Bahama Bank:implications for eustatic sea-level models[J]. Geology,1996,24:893-896.
[10] RITTER A C,MAVROMATIS V,DIETZEL M,et al. Exploring the impact of diagenesis on (isotope) geochemical and microstructural alteration features in biogenic aragonite[J]. Sedimentology,2017,64:1354-1380. doi: 10.1111/sed.12356
[11] WU F,XIE X N,COLETTI G,et al. Coralline algal and foraminiferal records of the Pliocene paleoclimatic conditions and water-depth changes in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2023,153:106276.
[12] LI Y Q,YU K F,BIAN L Z,et al. Paleo-water depth variations since the Pliocene as recorded by coralline algae in the South China Sea [J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2021,562:110107.
[13] MENG M,YU K F,HALLOCK P,et al. Foraminifera indicate Neogene evolution of Yongle Atoll from Xisha Islands in the South China Sea [J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2022,602:111163.
[14] WEBSTER J M,WALLACE L,SILVER E,et al. Coralgal composition of drowned carbonate platforms in the Huon Gulf,Papua New Guinea; implications for lowstand reef development and drowning[J]. Marine Geology,2004,204:59-89. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00356-6
[15] CHEN W L,HUANG X X,WU S G,et al. Facies character and geochemical signature in the late Quaternary meteoric diagenetic carbonate succession at the Xisha Islands,South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2021,40:94-111.
[16] LI R,QIAO P J,CUI Y C,et al. Composition and diagenesis of Pleistocene aeolianites at Shidao,Xisha Islands:implications for palaeoceanography and palaeoclimate during the last glacial period[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,2018,490:604-616.
[17] 陈万利,吴时国,黄晓霞,等. 西沙群岛晚第四纪碳酸盐岩淡水成岩作用:来自永兴岛SSZK1钻孔的地球化学响应证据[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(6):1296-1312.
[18] LIU X F,LIU X M,WANG X K,et al. Dolostone as a reliable tracer of seawater lithium isotope composition[J]. Communications Earth & Environment,2023,4(1):58.
[19] LI R,QIAO P J,CUI Y C,et al. Composition and diagenesis of Pleistocene aeolianites at Shidao,Xisha Islands:implications for palaeoceanography and palaeoclimate during the last glacial period [J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2018,490:604-616.
[20] WU F,ZHU Y H. Quaternary subsidence history of Xisha Islands (northern South China Sea):evidences from the reef-bank system [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2022,144:105843.
[21] ZHU X W,JIA G D,TIAN Y H,et al. Ancient hydrocarbon slicks recorded by a coral atoll in the South China Sea [J]. Chemical Geology,2023,619:121316.
[22] LI G,XU W H,LUO Y,et al. Strontium isotope stratigraphy and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb carbonate age constraints on the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern South China Sea [J]. GSA Bulletin. 2022,135 (1/2):271–285.
[23] SHAO L,CUI Y C,QIAO P J,et al. Sea-level changes and carbonate platform evolution of the Xisha Islands (South China Sea) since the Early Miocene[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2017,485:504-516.
[24] WANG P X,LI Q. The South China sea:paleoceanography and sedimentology[M]. Berlin:Springer Publishing,2009:0-506.
[25] SIBUET J C,YEH Y C,LEE C S. Geodynamics of the South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics,2016,692:98-119. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.022
[26] STEUER S,FRANKE D,MERESSE F,et al. Time constraints on the evolution of southern Palawan Island,Philippines from onshore and offshore correlation of Miocene limestones[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2013,76:412-427. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.007
[27] DING W W,LI J B,DONG C Z,et al. Oligocene–Miocene carbonates in the Reed Bank area,South China Sea,and their tectono-sedimentary evolution [J]. Marine Geophysical Research,2014,36:149-165.
[28] DING W W,LI J B. Conjugate margin pattern of the Southwest Sub-basin,South China Sea:insights from deformation structures in the continent‐ocean transition zone[J]. Geological Journal,2015,51:524-534.
[29] HUANG X X,BETZLER C,WU S G,et al. First documentation of seismic stratigraphy and depositional signatures of Zhongsha atoll (Macclesfield Bank),South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,117:104349.
[30] WU S G,YANG Z,WANG D W,et al. Architecture,development and geological control of the Xisha carbonate platforms,northwestern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2014,350:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.12.016
[31] YI L,JIAN Z M,LIU X Y,et al. Astronomical tuning and magnetostratigraphy of Neogene biogenic reefs in Xisha Islands,South China Sea[J]. Science Bulletin,2018,63:564-573. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.04.001
[32] SUN Z,ZHONG Z H,KEEP M,et al. 3D analogue modeling of the South China Sea:a discussion on breakup pattern[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2009,34:544-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.09.002
[33] LI C F,LI J,DING W,et al. Seismic stratigraphy of the central South China Sea basin and implications for neotectonics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2015,120:1377-1399. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011686
[34] 陈俊锦,张经纬,刘时桥,等. 南海中沙群岛海域表层沉积物粒度特征及其输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(2):15-27.
[35] CHENG H,LAWRENCE EDWARDS R,SHEN C C,et al. Improvements in 230Th dating,230Th and 234U half-life values,and U–Th isotopic measurements by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2013,371/372:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.04.006
[36] MCARTHUR J M,HOWARTH R J,BAILEY T R. Strontium isotope stratigraphy:LOWESS Version 3:best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0-509 Ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age[J]. The Journal of Geology,2001,109:155-170.
[37] WU F,XIE X,BETZLER C,et al. The impact of eustatic sea-level fluctuations,temperature variations and nutrient-level changes since the Pliocene on tropical carbonate platform (Xisha Islands,South China Sea)[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2019,514:373-385.
[38] PAATERO P,HOPKE P K. Rotational tools for factor analytic models[J]. Journal of Chemometrics,2009,23:91-100. doi: 10.1002/cem.1197
[39] HAJIKAZEMI E,AL-AASM I S,CONIGLIO M. Subaerial exposure and meteoric diagenesis of the Cenomanian-Turonian Upper Sarvak Formation,southwestern Iran[J]. Geological Society,2010,330(1):253-272.
[40] 尤丽,于亚苹,廖静,等. 西沙群岛西科1井第四纪生物礁中典型暴露面的岩石学与孔隙特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):671-676.
[41] 罗云,黎刚,徐维海,等. 南科1井第四系暴露面特征及其与海平面变化的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报,2022,41(1):143-157. doi: 10.11978/2021013
[42] WU S G,CHEN W L,HUANG X X,et al. Facies model on the modern isolated carbonate platform in the Xisha Archipelago,South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2020,425:106203.
[43] MONTAGGIONI L F,BORGOMANO J,FOURNIER F,et al. Quaternary atoll development:new insights from the two‐dimensional stratigraphic forward modelling of Mururoa Island (Central Pacific Ocean)[J]. Sedimentology,2015,62:466-500. doi: 10.1111/sed.12175
[44] 刘健,韩春瑞,吴建政,等. 西沙更新世礁灰岩大气淡水成岩的地球化学证据[J]. 沉积学报,1998,16(4):71-77.
[45] DECHNIK B,WEBSTER J M,WEBB G E,et al. The evolution of the Great Barrier Reef during the Last Interglacial Period[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2017,149:53-71. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.11.018
[46] ZHAO K,DU X,JIA J,et al. Effects of sea-level variation and sedimentary noise variation on the development of biogenic reefs since the Pliocene among the Xisha Islands,South China Sea[J]. GSA Bulletin,2021,134:1781-1792.
[47] 朱伟林,王振峰,米立军,等. 南海西沙西科1井层序地层格架与礁生长单元特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):677-687.
[48] LIU J,WEBSTER J M,SALLES T,et al. The Formation of Atolls:new insights from numerical simulations.[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2022,127:e2022JF006812.
[49] LI T,LI X J,LUO W D,et al. Combined classification and source apportionment analysis for trace elements in western Philippine Sea sediments[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2019,675:408-419.
[50] LI T,SUN G,YANG C,et al. Source apportionment and source-to-sink transport of major and trace elements in coastal sediments:combining positive matrix factorization and sediment trend analysis[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2019,651:344-356.
[51] LI T,LI X J,ZHANG J Y,et al. Source identification and co-occurrence patterns of major elements in South China Sea sediments [J]. Marine Geology ,2020,428:106285.
[52] DU S H,XIANG R,LIU J G,et al. The present-day atmospheric dust deposition process in the South China Sea[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2020,223:117261.
[53] SWART P K. The geochemistry of carbonate diagenesis:the past,present and future[J]. Sedimentology,2015,62:1233-1304. doi: 10.1111/sed.12205
[54] CANFIELD D E. The geochemistry of river particulates from the continental USA:major elements[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1997,61:3349-3365. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00172-5
[55] CHEN W L,LIU G,WU S G,et al. Late Holocene lagoon succession and its response to environmental variations at Yongle atoll,Xisha Islands,South China Sea[J]. Geological Journal,2021,56:3155-3169.
[56] XU L Q,LIU X D,SUN L G,et al. Distribution of radionuclides in the guano sediments of Xisha Islands,South China Sea and its implication[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity,2010,101:362-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.02.004
[57] XU L Q,LIU X D,SUN L G,et al. Geochemical evidence for the development of coral island ecosystem in the Xisha Archipelago of South China Sea from four ornithogenic sediment profiles[J]. Chemical Geology,2011,286:135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.04.015
-



 下载:
下载: