Suitability evaluation of offshore sea sand mining based on subjective and objective weighting method
-
摘要:
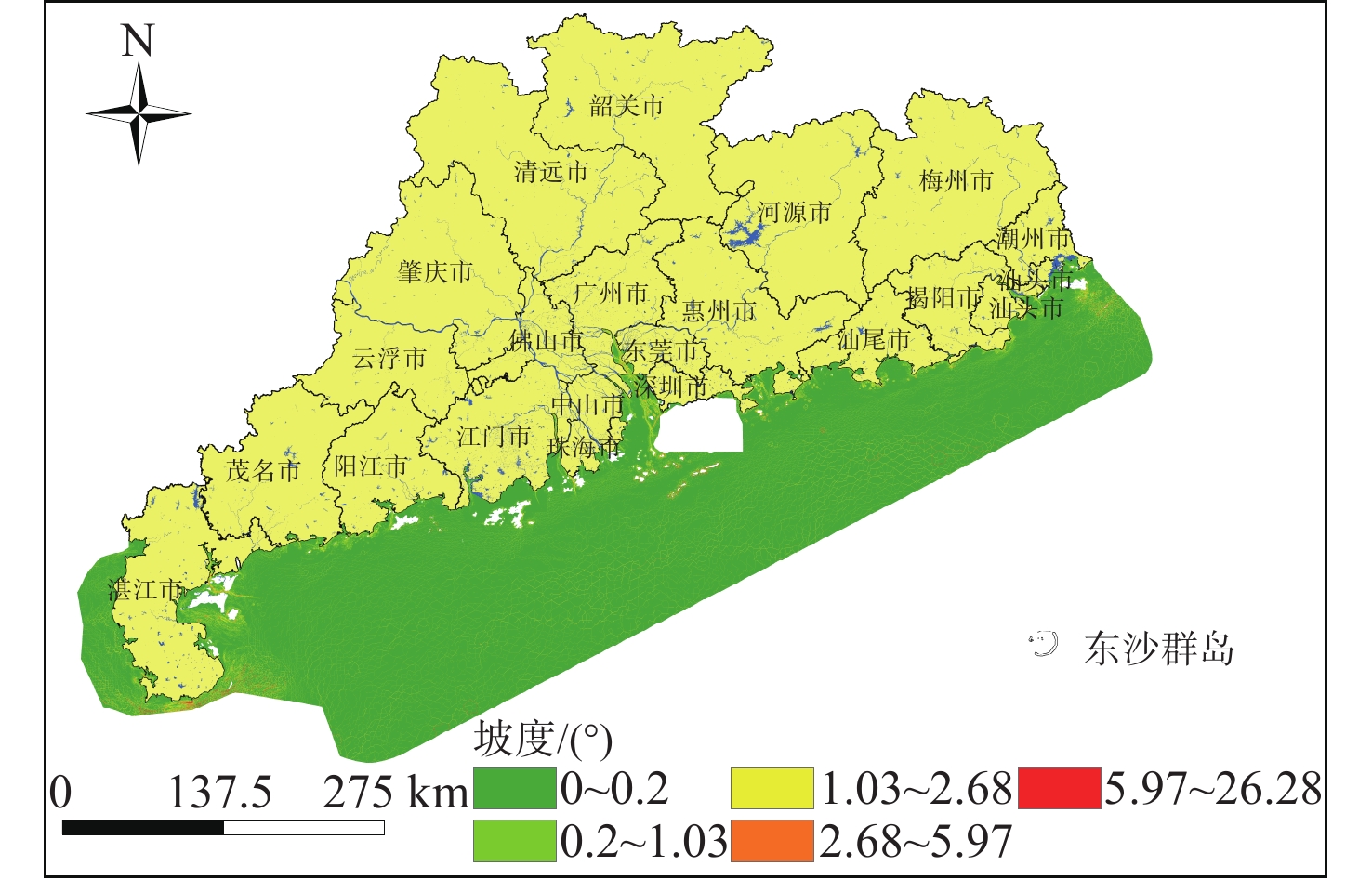
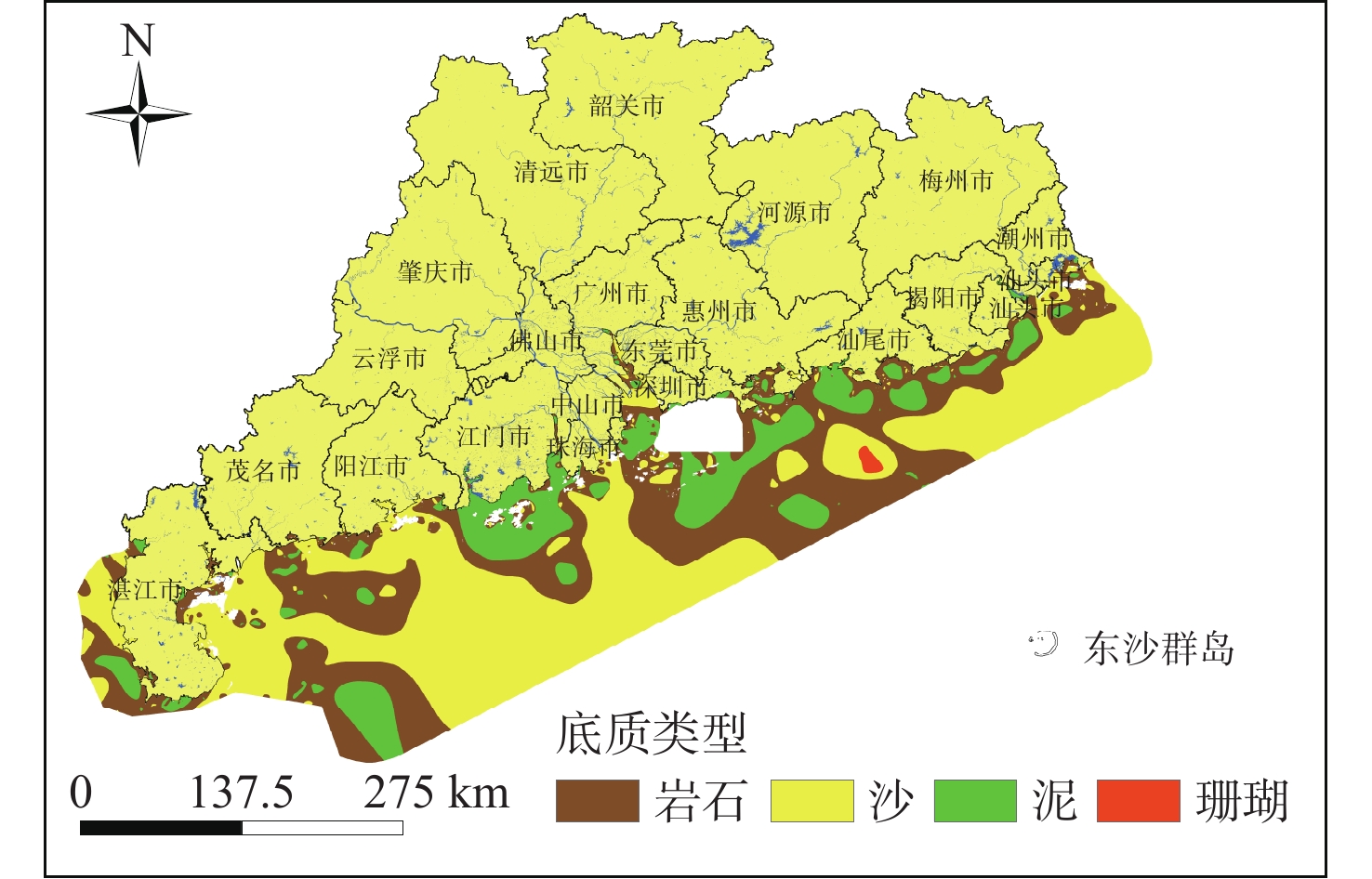
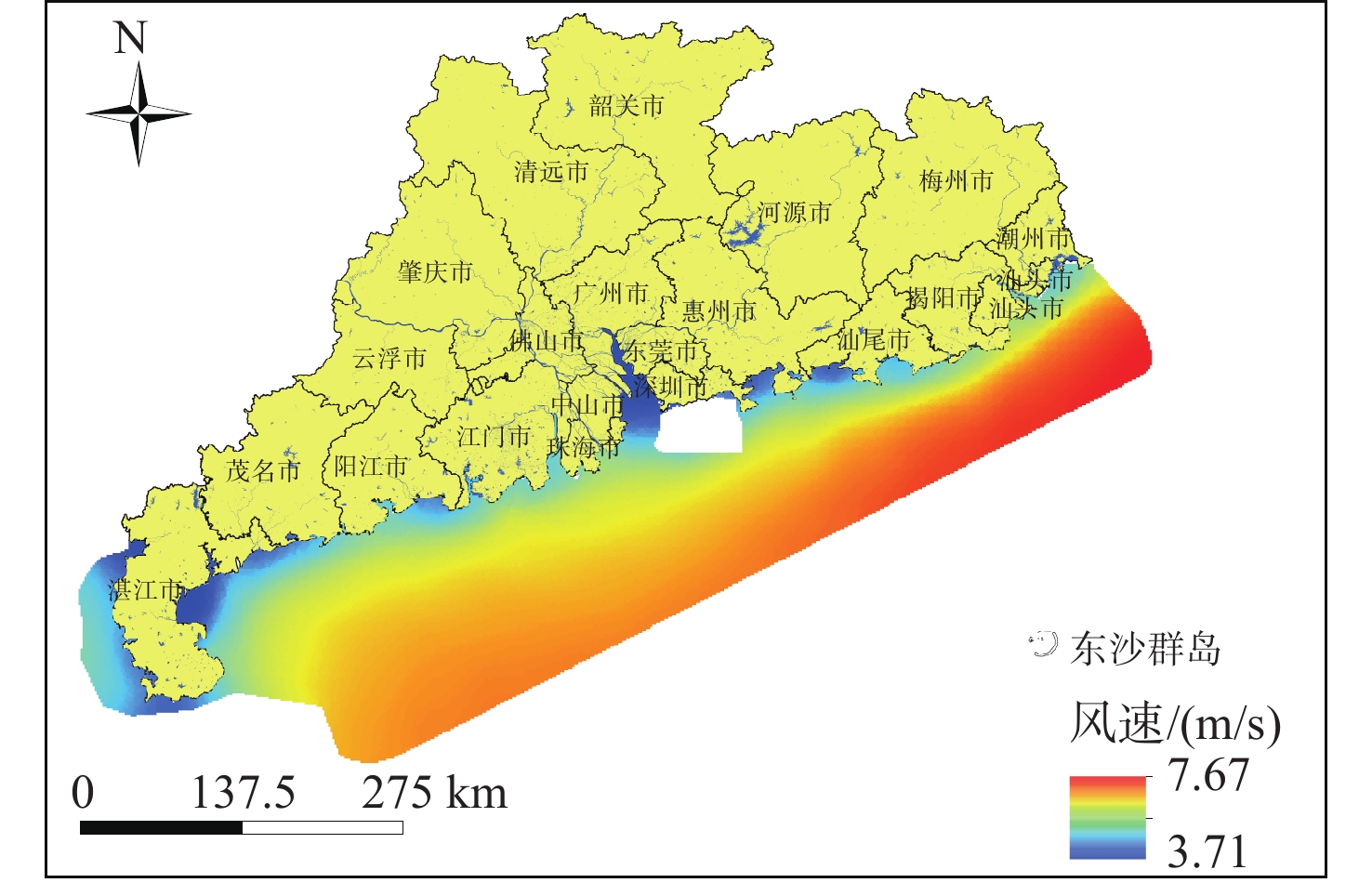
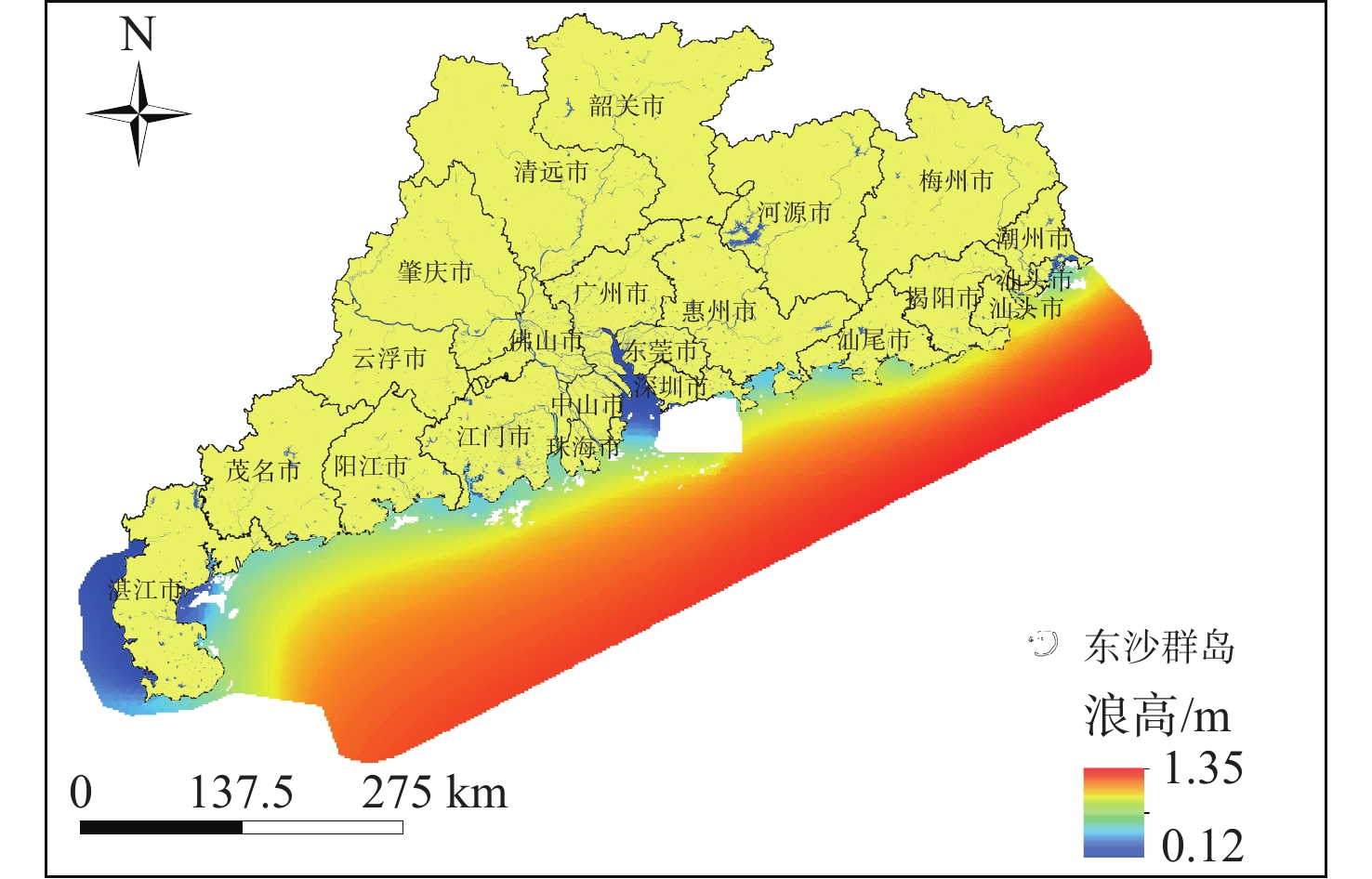
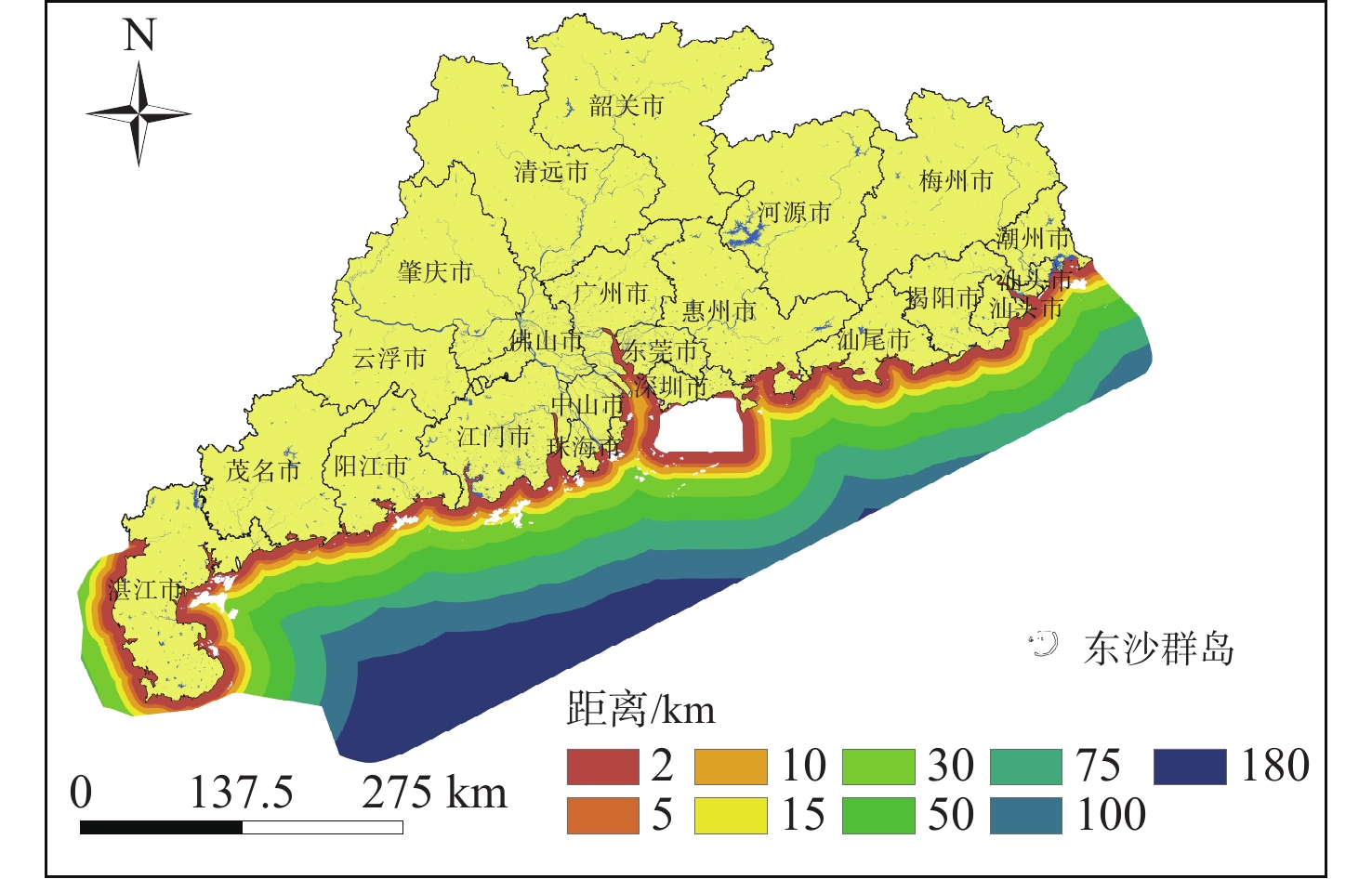
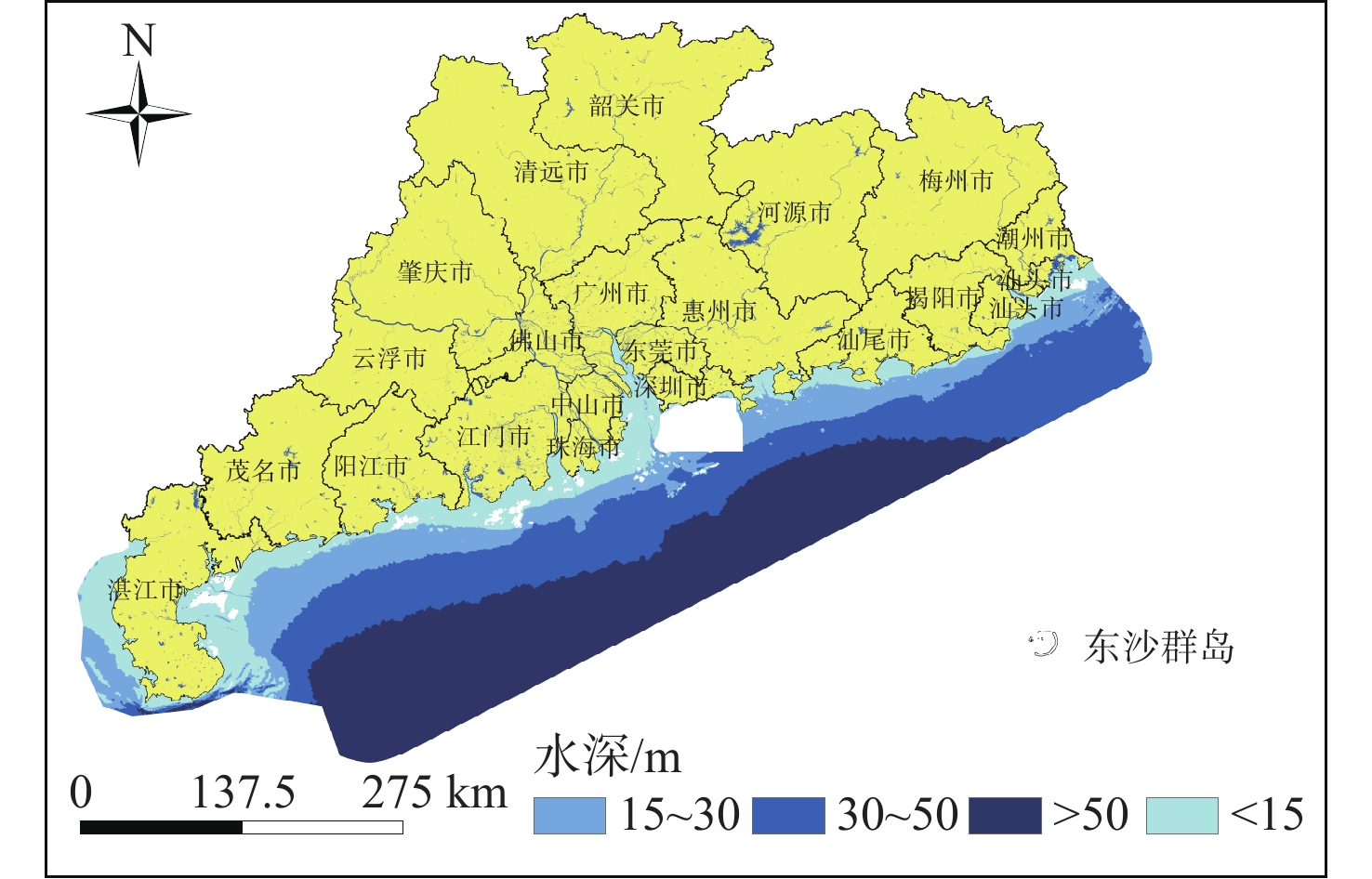
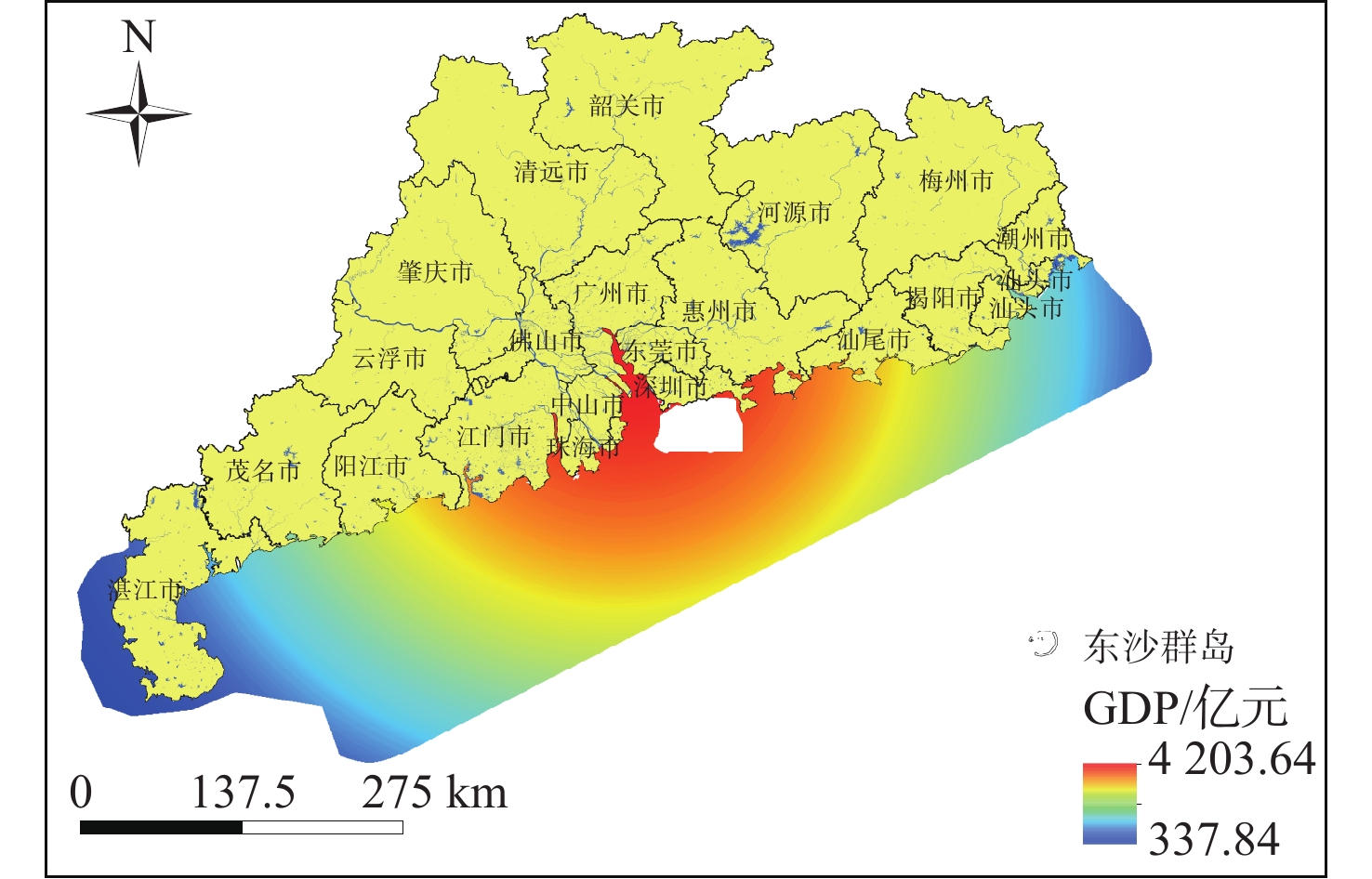
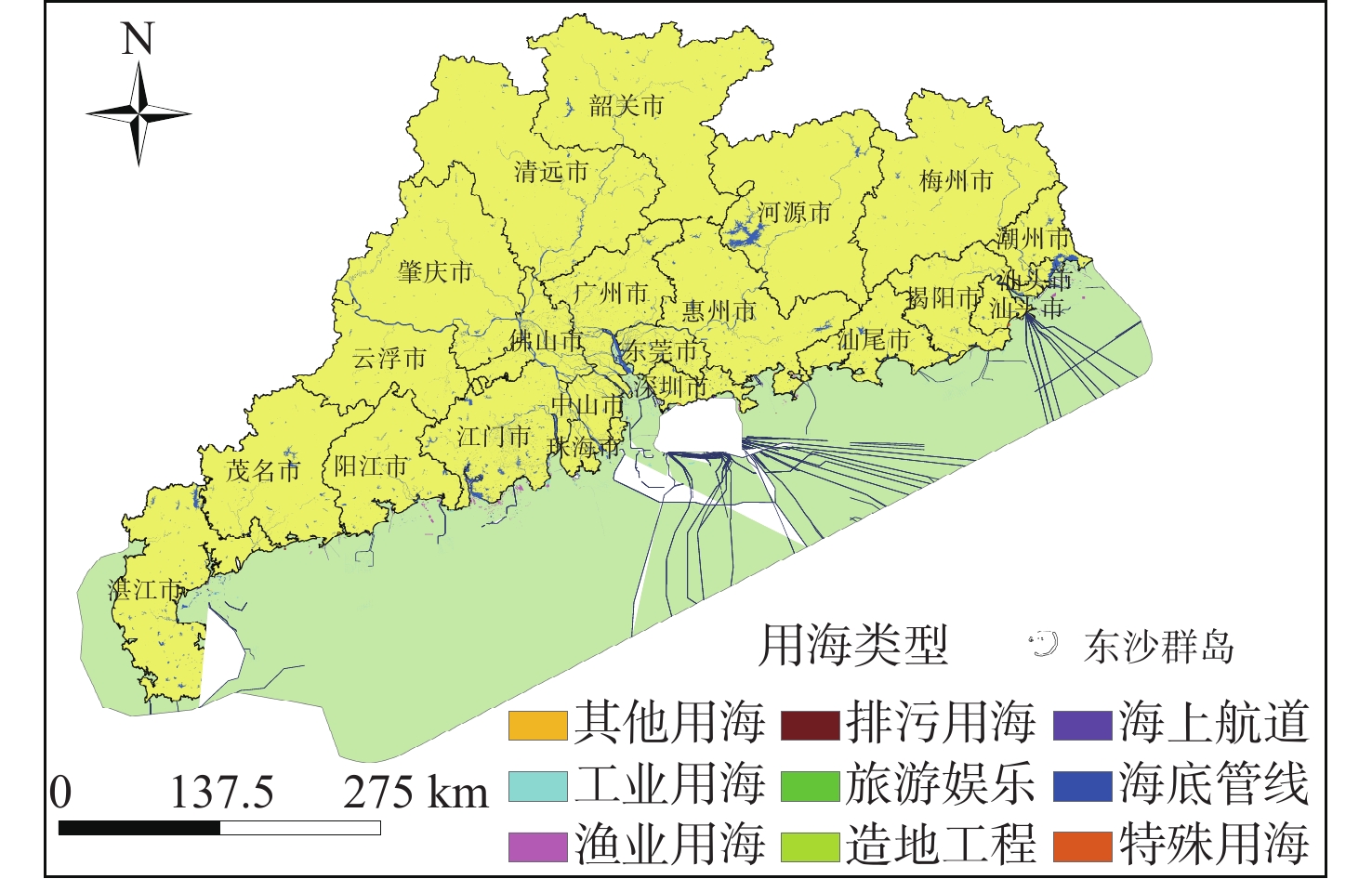
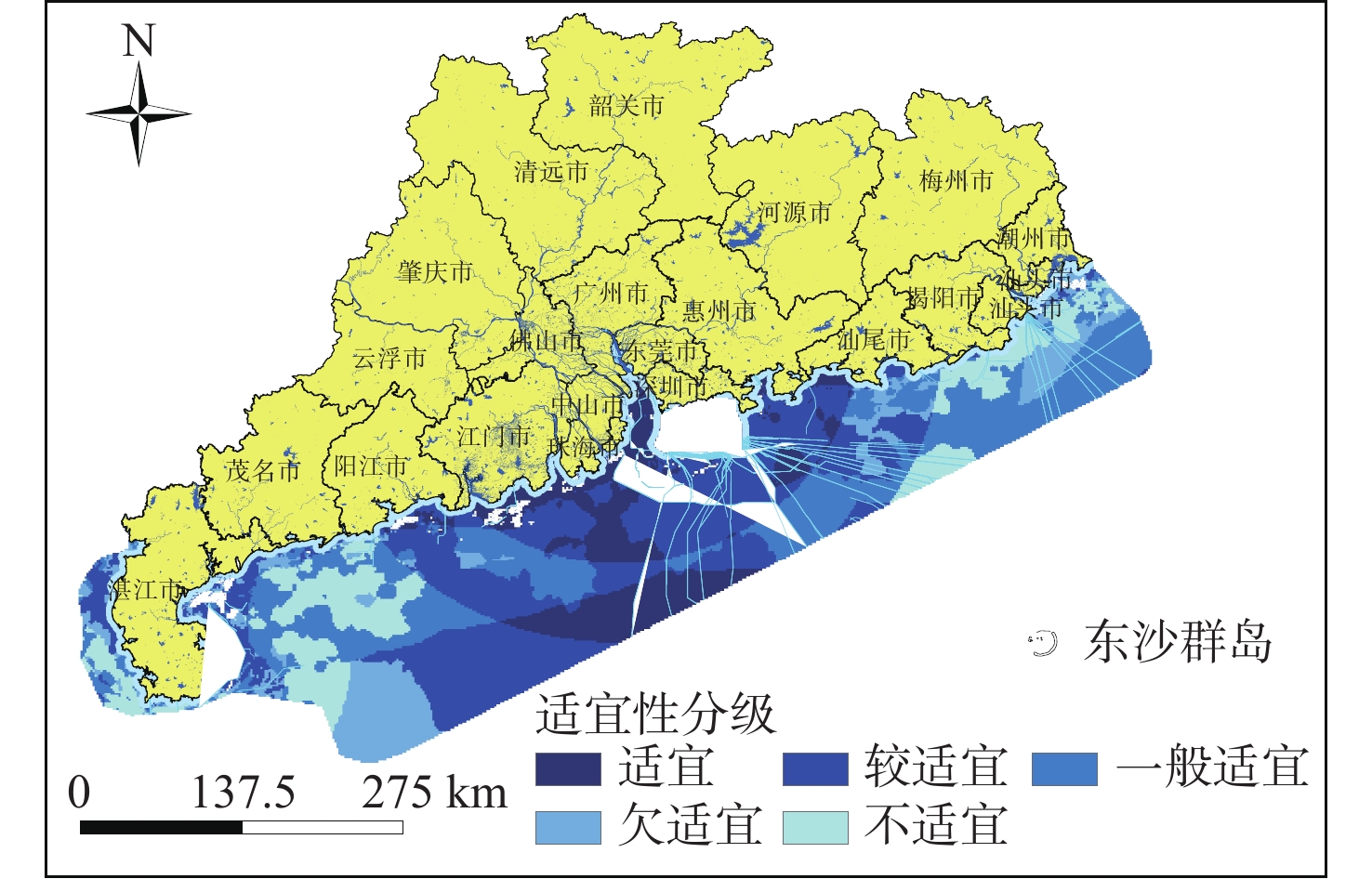
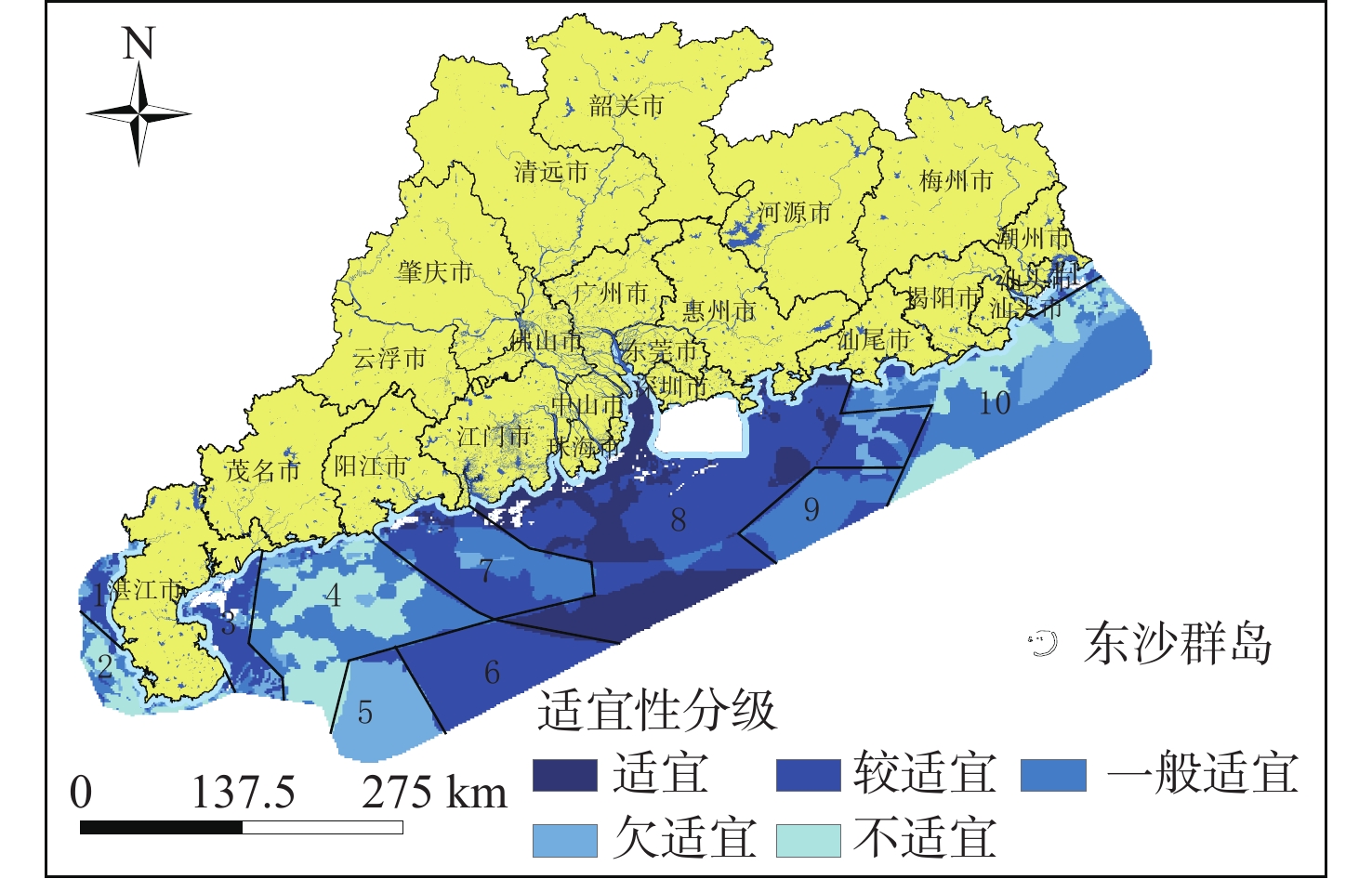
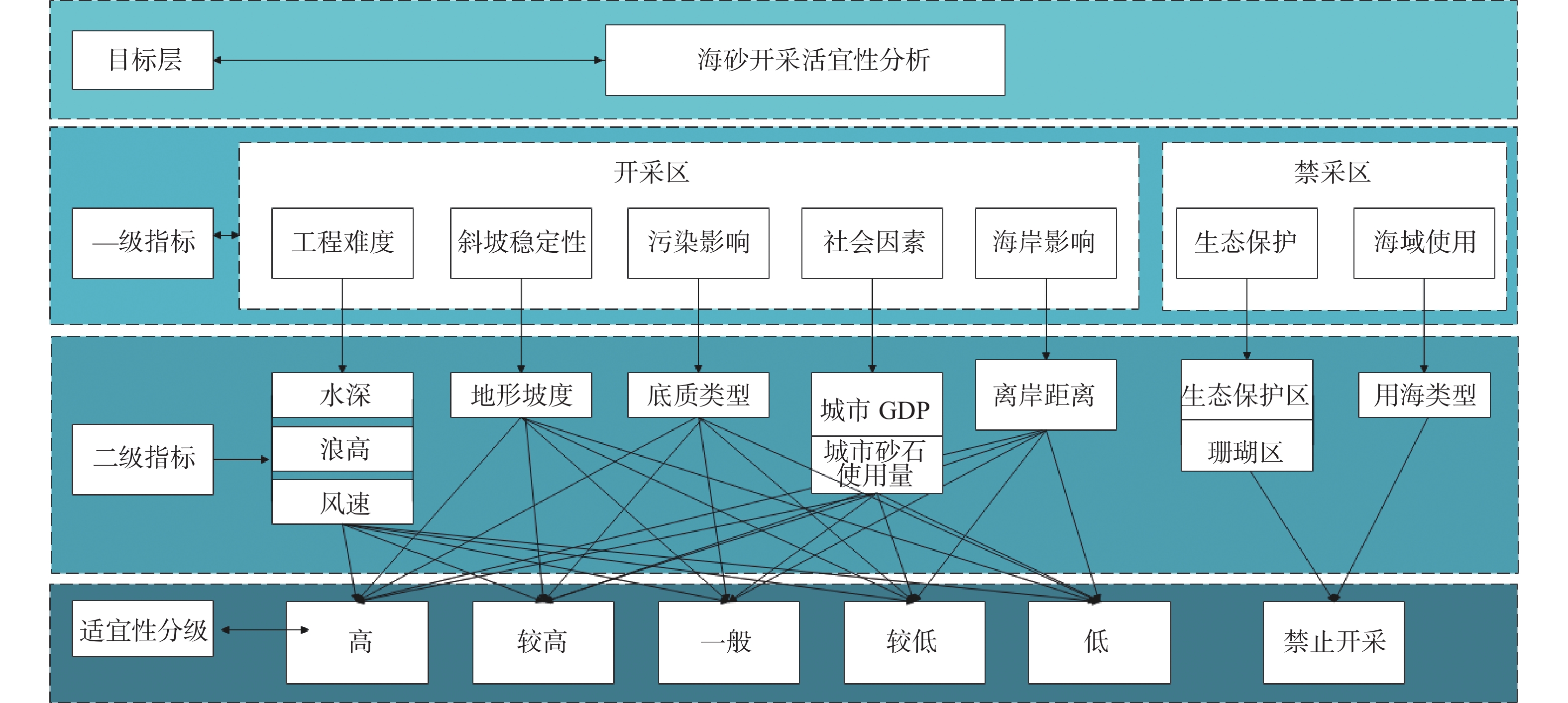
随着中国经济高速发展,砂石资源的需求量逐年攀升,在种类诸多的砂石资源中海砂以其储量丰富、用途广泛的特点在建筑业、化工业等领域被广为使用。然而近年来,海砂行业发展中存在诸多粗放式的问题,不合理的开采不仅导致国有资源的大量流失,更是引发一系列环境问题。因而,在探明海砂资源后,开展海砂开采适宜性评价十分必要。本文将污染影响、社会因素、开发难度、海岸影响、海底斜坡稳定性作为评价指标,采用主观赋权法(层次分析法)与客观赋权法(结构熵权法)分别计算指标权重,通过博弈理论将二者结合,得到指标的组合权重;然后采用自然断点法对赋权后的各因子图层进行叠加分析,得到海砂开采适宜性分区图,并对广东省近海海域进行实例分析。
Abstract:With the rapid development of China's economy, the demand for sand and gravel resources is increasing year by year. Among the many kinds of sand and gravel resources, sea sand is widely used in the construction industry, chemical industry and other fields because of its rich reserves and wide use. However, in recent years, there are many extensive problems in the development of the sea sand industry. Unreasonable mining not only leads to a large loss of state-owned resources, but also causes a series of environmental problems. After ascertaining the sea sand resources, in order to determine whether the sea sand is suitable for mining, this paper takes pollution impact, social factors, development difficulty, coastal impact and submarine slope stability as evaluation indexes, and uses subjective weighting method (analytic hierarchy process) and objective weighting method (structural entropy weight method) to calculate the index weight respectively. Through the game theory, the two are combined to obtain the combined weight of the index, and the natural breakpoint method is used for superposition analysis to obtain the sea sand mining suitability zoning map, and the offshore sea area of Guangdong Province is analyzed as an example, and the scientificity and rationality of the evaluation results are verified in combination with the actual sand mining project.
-

-
表 1 评价集判断矩阵与权重计算
Table 1. Evaluation set judgment matrix and weight calculation
海砂开采 开发
难度社会
因素污染
影响海岸
影响海底斜坡稳定性 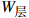
开发难度 1 1/3 3 1/4 1/3 0.290 5 社会因素 3 1 2 1/6 1/4 0.233 1 污染影响 1/2 1/3 1 1/4 1/2 0.101 4 海岸影响 4 6 5 1 2 0.223 8 海底斜坡稳定性 3 4 4 1/2 1 0.151 2 一致性:0.083 0 表 2 结构熵权法计算结果表
Table 2. Structure entropy weight method calculation results table
指标名称 B1开发
难度B2污染
影响B3社会
因素B4海岸
影响B5海底斜坡稳定性 专家1 4 3 1 4 2 专家2 3 5 3 3 3 专家3 4 4 2 4 2 专家4 2 5 4 5 1 专家5 3 3 1 4 4 专家6 4 4 3 4 1 专家7 5 3 5 4 3 专家8 3 2 1 5 5 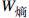
0.3115 0.1244 0.1553 0.2959 0.1147 表 3 博弈理论组合权重表
Table 3. Game theory combination weight table
指标名称 B1开发难度 B2污染影响 B3社会因素 B4海岸影响 B5海底斜坡稳定性 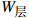
0.290 5 0.101 4 0.233 1 0.223 8 0.151 2 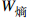
0.311 5 0.124 4 0.155 3 0.235 9 0.114 7 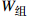
0.303 6 0.115 3 0.202 4 0.224 4 0.154 3 表 4 适宜性分值表
Table 4. Game theory chart
海砂开采适宜度级别 适宜性指数区间 Ⅰ-适宜 11.73~16.54 Ⅱ-较适宜 9.27~11.73 Ⅲ-一般适宜 7.51~9.27 Ⅳ-欠适宜 5.91~7.51 Ⅴ-不适宜 3.18~5.91 -
[1] 陈坚,胡毅. 我国海砂资源的开发与对策[J]. 海洋地质动态,2005,19(7):4-8,39.
[2] 孙岩,韩昌甫. 我国滨海砂矿资源的分布及开发[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1999,19(1):123-127. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1999.01.018.
[3] 仝长亮,王华强,张匡华,等. 海洋测绘在西南浅滩海砂资源探测中的应用[J]. 海洋测绘,2022,42(3):38-42.
[4] 史瑾瑾. 我国海砂资源开发管理问题探析及建议[J]. 中国国土资源经济,2020,33(12):80-83. doi: 10.19676/j.cnki.1672-6995.000500.
[5] 广东省自然资源厅. 广东省制定海砂开采三年行动计划加大海砂资源供应[J]. 广东建材,2020,36(6):1.
[6] 刘洪树. 我国滨海砂矿在第四系中的富集规律[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1989,10(2):41-49. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1989.02.005.
[7] 彭钰琳,马超,陈云英,等. 福建海砂开采现状及建议[J]. 海洋环境科学,2014,33(6):954-957. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2014.06.023.
[8] 尹飞龙,欧阳东,温喜廉,等. 海砂与河砂、尾砂作为建筑用砂的比较研究[J]. 混凝土,2011(12):73-75,78.
[9] 李珊,张翠萍,陈鹏. 论海砂开采存在问题及加强使用管理的建议[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2018(5):158-162. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2018.05.020.
[10] HASHIMOTO E,NAGAO M,TAKASUGI Y. Measurement of floating sand particle concentration and estimate of the flux in sea sand mining area [J]. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshu,2004,(769):35-42.
[11] 王秀卫. 论中国海砂开采管理制度的完善[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境,2012,22(S1):139-142.
[12] 张琴,余科平,陈命男. 湛江湾海砂开采对周边泥沙冲淤及波浪场的影响[J]. 人民长江,2017,48(S2):17-21. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2017.S2.006.
[13] KANG T,MIN W,HONG J S,et al. Effect of Sand Extraction on Meiobenthic Community of Jangbong-do in the Eastern Yellow Sea of Korea[J]. Korean Journal of Environmental Biology,2014,32(2):138-152.
[14] 覃茂刚,杨朝云,黄仕锐,等. 建筑用海砂资源开发利用适宜性评价初探:以琼州海峡东口为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(4):249-258. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0065.
[15] WANG P,LIN X,YU Y. Research on regularities of distribution and controlling factor of sea sand resources in Bohai Sea[C]//Education and Management Innovation(EMI2017). China Scientific Research Publishing,2017:270-276.
[16] 曹雪晴,张勇,何拥军,等. 中国近海建筑用海砂勘查回顾与面临的问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(3):121-125. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2008.03.006.
[17] 吕一河,傅微,李婷,等. 区域资源环境综合承载力研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学进展,2018,37(1):130-138.
[18] 迪力沙提·亚库甫,严金明,李强. 基于生态导向与自然条件约束的青海省国土空间开发适宜性评价研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2019,35(3):94-98,111.
[19] 梅芹芹,龚绪龙,史雅栋,等. 江苏沿海地区工程建设地质适宜性评价[J]. 地质学刊,2018,42(2):317-322.
[20] WAWAN W,NOWO D M,WARNO S U, et al. Investigating impact of sea sand mining in Tunda Island waters, Indonesia based in Mike 21 modelling[J].Croatian Journal of Fisheries,2023,81(2):73-81.
[21] 许振强. 辽东湾东部海砂开采环境效应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(6):27-34.
[22] 白凤龙,何拥军,李军. 中国海砂资源勘查、开采与可持续发展[J]. 矿床地质,2010,29(S1):771-772. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2010.s1.557.
[23] 胡泽松,张裕书,杨耀辉,等. 海滨砂矿开发中应注意的问题及建议[J]. 矿产综合利用,2011(4):3-6.
[24] 陈志亮. 船舶监管系统在外海海砂开采监管工作中的应用[J]. 福建建材,2020(10):107-108,111.
[25] KIM J H,YOO S H. Public perspective on the environmental impacts of sea sand mining:evidence from a choice experiment in South Korea [J]. Resources Policy,2020,69:101811.
[26] BOYD S E,LIMPENNY D S ,REES H L . The effects of marine sand and gravel extraction on the macrobenthos at a commercial dredging site (results 6 years post-dredging)[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science,2005,62(2):145-162.
[27] 胡幼奕. 砂石产业转型升级需考虑的若干问题及对策[J]. 混凝土世界,2015(1):30-34.
[28] 马媛,魏巍,陈静,等. 汕头东部海域海砂开采区快速回淤成因分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(7):78-82. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2013.07.014.
[29] 金永福,郑锡建,李金铎. 崎头洋海砂开采对朱家尖沿岸沙滩的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学,2006,25(3):46-49.
[30] 李婵娟. 海砂开采工程的环境影响分析[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2022,40(12):73-75.
[31] MASKUN,NUR S S,ACHMAD. Legal regulation on protecting marine environment from sea sand mining impact:a case study of spermonde archipelago[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2021,860:012092.
[32] 黄伟锋,严玉梅,黄禄萍,等. 关于海砂体积变化及松散堆积密度的研究[J]. 广东建材,2022,38((12):):43-44,11.
[33] 王玉莲,王振兴. 海砂资源调查绿色勘查实践及成效[J]. 中国水运,2024(1):63-65. doi: 10.13646/j.cnki.42-1395/u.2024.01.021.
[34] 王焰新,甘义群,邓娅敏,等. 海岸带海陆交互作用过程及其生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(1):1-10. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101.
[35] 王琼,杨伦庆. 广东海砂资源开发利用问题与对策[J]. 中国资源综合利用,2021,39(6):73-76.
[36] 李杏筠. 国内外海砂资源开采利用与权属管理探讨[J]. 合作经济与科技,2018(24):49-51. doi: 10.13665/j.cnki.hzjjykj.2018.24.017.
[37] 刘宁波,田荣燕,王海波,等. 基于AHP-模糊综合评价方法的拉萨市周边溜砂坡稳定性评价[J]. 水土保持通报,2019,39(2):161-166,171.
[38] 王海涌,张玮玥,王晓明,等. 基于ANP和VPRS的高速列车舒适性综合评价指标权重分析[J]. 铁道学报,2014,36(6):15-20.
[39] 龙星颖,葛名欢. 基于层次分析法改进ABC分类法提升带量采购药品管理的实践[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2023,43(7):799-803. doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2023.07.13.
[40] 马瑶,赵江南,廖时理. 模糊层次分析法在西南印度洋中脊46°~52°E多金属硫化物远景区预测中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(6):75-82. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0622.
[41] 王帆,廉旭刚,蔡音飞. 基于模糊层次分析法的采动地裂缝发育等级评价:以沁水煤田为例[J]. 科学技术与工程,2023,23(1):129-136.
[42] 王力召,蒋致远. 基于结构熵权法的P2P平台财务风险评价研究[J]. 系统科学学报,2020,28(2):95-99,128.
[43] 刘苏港,黄羽,倪庆国,等. 农村黑臭水体治理效果评估指标体系[J]. 长江科学院院报,2023,40(12):52-58.
[44] 俎富豪,赵秋红. 基于结构熵权法和HFWGHM算子的海上救援航空应急资源布局评价方法研究[J]. 数学的实践与认识,2019,49(19):128-138.
[45] 孙雅茹,董增川,周毅,等. 基于结构熵权法的长江下游水资源承载力评价:以南京市为例[J]. 人民长江,2018,49(7):47-51. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.07.010.
[46] 祝连波,王世笛,林陵娜,等. 基于博弈论组合赋权-物元可拓模型的地铁车站抗涝韧性评估研究[J]. 灾害学,2023,38(3):1-6,42.
[47] 李红艳,张翀,崔建国,等. 基于博弈论赋权耦合灰色关联分析的调蓄池优化选址[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(3):426-432.
[48] 廖启鹏,陈茹,黄士真. 基于模糊综合评判与GIS方法的废弃矿区景观评价[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(6):241-250. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0628.
[49] ANNAKA T, HANAYAMA S. Dynamic Water-Entry Pressure for Initially Dry Glass Beads and Sea Sand [J].Vadose Zone Journal, 2005, 4(1):127-133.
[50] 黄泽鹏,许江,胡毅,等. 泉州海域海砂资源开采区选划与管理[J]. 海洋开发与管理,2021,38(3):9-13. doi: 10.20016/j.cnki.hykfygl.2021.03.002.
-



 下载:
下载: