Cretaceous paleoclimate evolution of Yong'an Basin in western Fujian and its response to geomorphic changes along the coast of South China
-
摘要:
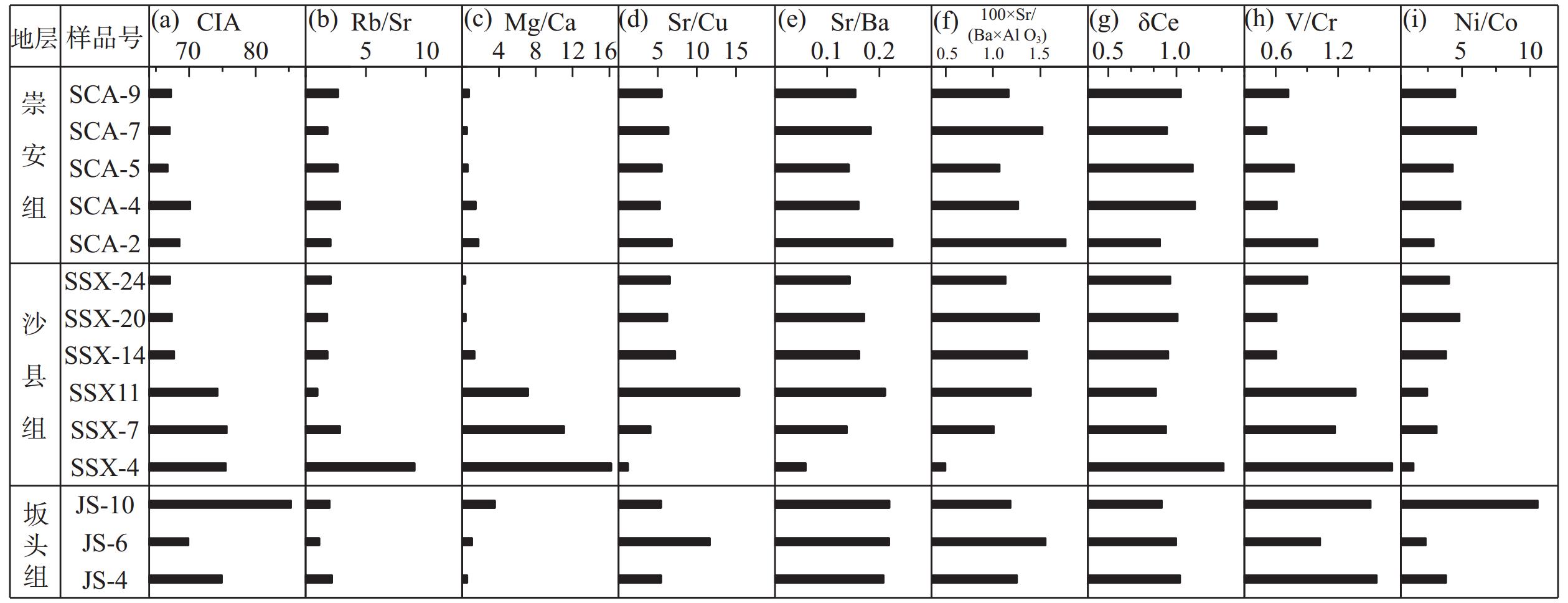
以永安盆地白垩系坂头组、沙县组、崇安组为研究对象,采集细碎屑岩样品进行了主微量元素及稀土元素测试,并与其沉积特征、古生物化石特征进行对比分析,探究白垩纪时期福建西部永安盆地的古气候演化特征,结合华南东南缘古气候变化,探讨二者与华南沿海中生代晚期地貌变化的关系。结果显示,下白垩统坂头组地层样品CIA值为69.91~85.29、Rb/Sr 值为1.13~2.21、Mg/Ca值 为0.57~3.57、Sr/Cu值为5.44~11.66、校正后古盐度指标100*Sr/(Ba*Al2O3)值为1.18~1.55,表明该区早白垩世早期气候由温暖湿润转为干旱炎热;δCe值为0.89~1.03、V/Cr值为1.03~1.57、Ni/Co值为2.34~10.58,表明早白垩世早期主要为弱氧化环境,间接指示该区当时气候由温湿向干热转变。早白垩世晚期以来,沙县组和崇安组地层样品的测试结果显示,CIA值为67.14~75.68、Rb/Sr值为0.99~9.05、Mg/Ca值为0.37~16.22、Sr/Cu值为1.20~15.46、以及校正的古盐度指标100*Sr/(Ba*Al2O3)值为0.50~1.77,指示永安盆地早白垩世晚期以来气候由干旱炎热向温暖湿润再向干旱寒冷变化;由δCe(0.89~1.03)、V/Cr值(0.51~1.72)、Ni/Co值(1.45~6.45)可以看出,早白垩世晚期以来弱氧化、弱还原环境交替出现,间接证明该区域自早白垩世晚期以来气候发生了多重转变,从干旱炎热到温暖湿润再到干旱寒冷。综上情况可以推断,永安盆地白垩纪期间古气候出现温暖湿润—干旱炎热—温暖湿润—干旱寒冷(伴有极端气候)多次转化。将研究区与周缘华南地区古气候进行统计对比,发现华南内陆古气候以温暖湿润向干旱炎热转变为主,华南沿海与内陆古气候转变的差异是对晚中生代华南沿海地貌变化的响应。
Abstract:To explore the evolution characteristics of the Cretaceous paleoclimate in the Yong'an Basin in western Fujian and the influence of the Late Mesozoic geomorphic changes along the coast of South China on the paleoclimate in the southeastern margin of South China, the Cretaceous stratigraphy of the Bantou, Shaxian, and Chong'an formations in the basin was taken as the research object. The fine-grained clastic rock samples were collected and examined for major and trace elements and rare earth elements distributions, and their sedimentary and paleontological characteristics were compared and analyzed. Variations in the paleoclimate of the Yong'an Basin in western Fujian during the Cretaceous period were clarified. Results show that the early Cretaceous Bantou Formation reflects a changing climate condition. The value ranges of CIA (chemical index of alteration) (69.91~85.29), Rb/Sr (1.13~2.21), Mg/Ca (0.57~3.57), Sr/Cu (5.44~11.66), and the calibrated paleosalinity index [100*Sr/(BaAl2O3)] (CPI) (1.18~1.55) collectively suggest a scheme transition from a warm-humid climate to a dry-hot environment. Moreover, the redox discrimination indices δCe (0.89~1.03), V/Cr (1.03~1.57), and Ni/Co (2.34~10.58) signaled a dominant weak oxidation environment, aligning with the transition to dry-hot climate in the early Cretaceous. Moving to the late Early Cretaceous to Late Cretaceous, Shaxian Formation and Chong'an Formation samples manifest further shifts in climate dynamics. The value ranges of CIA (67.14~75.68), Rb/Sr (0.99~9.05), Mg/Ca (0.37~16.22), Sr/Cu (1.20~15.46), and CPI (0.50-1.77) expose a change from hot-dry to warm-humid, followed by a transition to cold-dry climate. The δCe value (0.89~1.03), V/Cr (0.51~1.72), and Ni/Co (1.45~6.45) point to alternating weak oxidation and weak reduction environments, aligning with the multiple climate shifts during this period. Therefore, the Cretaceous paleoclimate of the Yong'an Basin exhibits a complex transitional sequence in climate, oscillating from dry-hot to warm-humid and then to dry-cold conditions, often with extreme climates. By comparing the paleoclimate between the study area and the surrounding South China region, it is evident that the predominant transformation in the inland South China paleoclimate was from warm-wet to dry-hot conditions. The paleoclimate transitions between the coastal and inland regions of South China reflect the response to late Mesozoic coastal geomorphic changes in the South China coastal areas.
-
Key words:
- western Fujian /
- Cretaceous /
- geochemistry /
- paleoclimate /
- paleogeomorphology /
- geochemistry
-

-
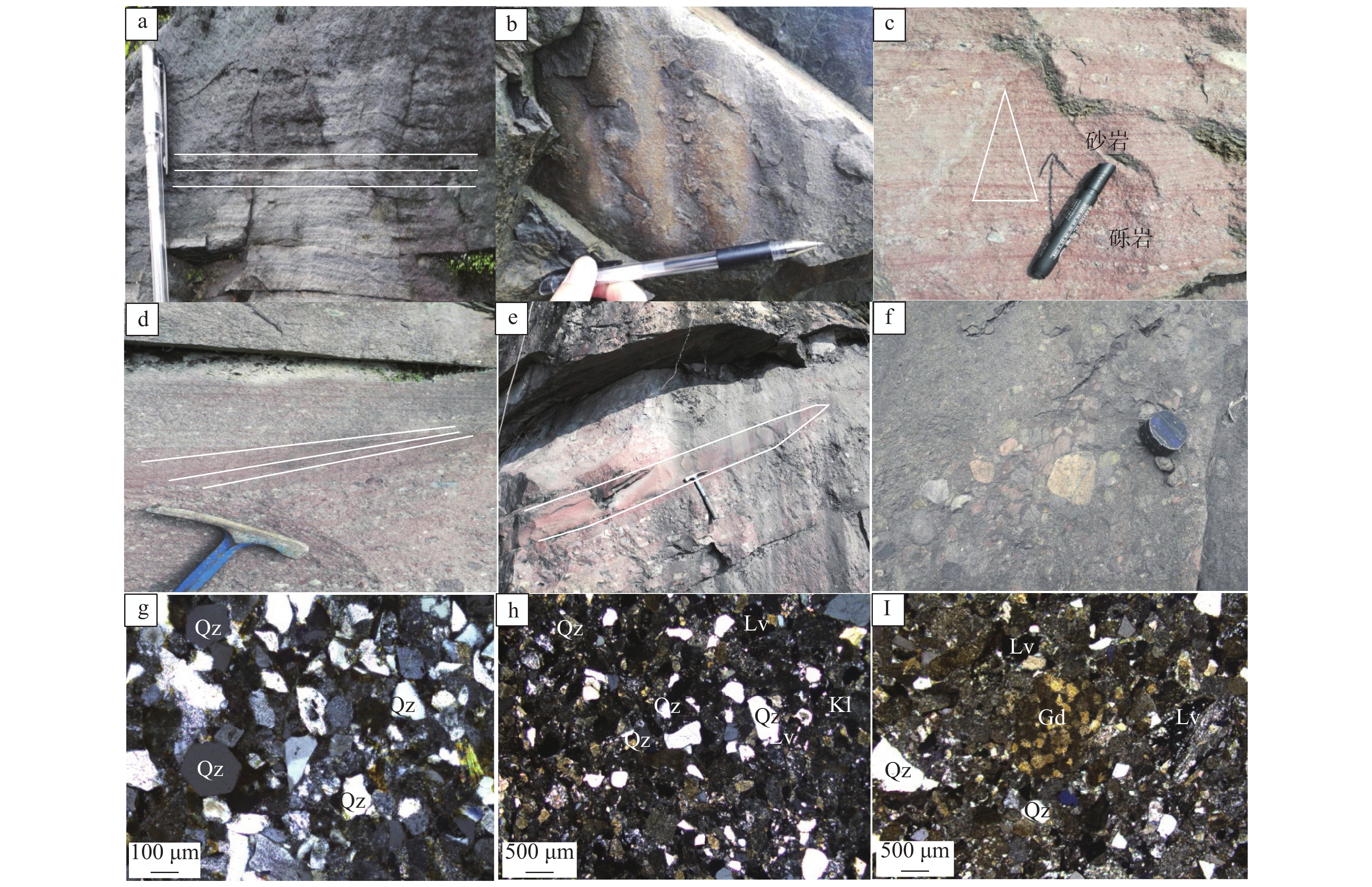
表 1 永安盆地白垩系细碎屑岩元素比值[53]
Table 1. Element ratio of fine clastic rocks of Cretaceous in Yong’an Basin
样品号 JS-4-2 JS−6 JS-10 SSX-4 SSX-7 SSX11 SSX-14 SSX-20 SSX-24 SCA-2 SCA-4 SCA-5 SCA-7 SCA-9 CIA 74.94 69.91 85.29 75.54 75.68 74.27 67.73 67.43 67.14 68.58 70.17 66.77 67.11 67.29 Rb/Sr 2.21 1.13 2.01 9.05 2.85 0.99 1.82 1.79 2.09 2.07 2.87 2.69 1.81 2.71 Mg/Ca 0.57 1.09 3.57 16.22 11.08 7.19 1.35 0.38 0.37 1.78 1.49 0.64 0.53 0.77 Sr/Cu 5.44 11.66 5.46 1.20 4.10 15.46 7.25 6.24 6.59 6.81 5.29 5.53 6.37 5.52 Sr/Ba 0.21 0.22 0.22 0.06 0.14 0.21 0.16 0.17 0.14 0.23 0.16 0.14 0.18 0.15 100×Sr/(Ba×Al2O3) 1.25 1.55 1.18 0.50 1.01 1.40 1.36 1.49 1.13 1.77 1.27 1.07 1.52 1.16 V/Cr 1.57 1.03 1.51 1.72 1.17 1.37 0.60 0.61 0.91 1.00 0.61 0.77 0.51 0.72 Ni/Co 3.83 2.34 10.58 1.45 3.13 2.44 3.83 4.81 4.05 2.91 4.88 4.32 6.05 4.49 δCe 1.03 1.00 0.89 1.35 0.93 0.85 0.94 1.01 0.96 0.88 1.14 1.12 0.93 1.04 表 2 永安盆地及周围区域白垩纪古气候特征
Table 2. Cretaceous paleoclimate characteristics of the Yong'an basin and its surrounding areas
-
[1] CHEN Y,MENG J,LIU H,et al. Detrital zircons record the evolution of the Cathaysian Coastal Mountains along the South China margin[J]. Basin Research,2022,34(2):688-701.
[2] 陈丕基. 晚白垩世中国东南沿岸山系与中南地区的沙漠和盐湖化[J]. 地层学杂志,1997,21(3):44-54.
CHEN P J. Coastal Mountains of SE China,desertization and saliniferous lakes of Central China during the Upper Cretaceous[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,1997,21(3):44-54.
[3] CHEN P J. Paleoenvironmental changes during the Cretaceous in eastern China [M]//OKADA H,MATEER N J. Cretaceous Environments of Asia. Elsevier,2000:81-90.
[4] LI J H,ZHANG Y Q,DONG S W,et al. Cretaceous tectonic evolution of South China:a preliminary synthesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2014,134:98-136. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.03.008
[5] YAN Y,HU X Q,LIN G,et al. Sedimentary provenance of the Hengyang and Mayang basins,SE China,and implications for the Mesozoic topographic change in South China Craton:evidence from detrital zircon geochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2011,41(6):494-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.012
[6] TAN J,ZHANG L,WANG C,et al. Late Cretaceous provenance change in the Jiaolai Basin,East China:implications for paleogeographic evolution of East Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2020,194:104188. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104188
[7] 陈云华. 中国东南地区晚白垩世沉积响应与古气候 [D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2008.
CHEN Y H. Late Cretaceous sedimentary responses to the “Coast Range" and paleoclimatechanges in Southeast China [D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technolog,2008.
[8] LI X M,ZOU H P. Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic exhumation of the southeastern margin of Coastal Mountains,SE China,revealed by fission-track thermochronology:implications for the topographic evolution[J]. Solid Earth Sciences,2017,2(3):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.sesci.2017.02.001
[9] DING R X,MIN K,ZOU H P. Inversion of topographic evolution using low-T thermal history:a case study from coastal mountain system in southeastern China[J]. Gondwana Research,2019,67:21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.09.009
[10] WANG Y,WANG Y J,LI S B,et al. Exhumation and landscape evolution in eastern South China since the Cretaceous:new insights from fission-track thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2020,191:104239. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104239
[11] 冯连君,储雪蕾,张同钢,等. 莲沱砂岩:南华大冰期前气候转冷的沉积记录[J]. 岩石学报,2006,22(9):2387-2393.
FENG L J,CHU X L,ZHANG T G,et al. Liantuo sandstones:sedimentary records under cold climate before the Nanhua big glaciations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2006,22(9):2387-2393.
[12] 王随继,黄杏珍,妥进才,等. 泌阳凹陷核桃园组微量元素演化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报,1997,15(1):66-71.
WANG S J,HUANG X Z,TUO J C,et al. Evolutional characteristics and their paleoclimate significance of trace elements in the Hetaoyuan Formation,Biyang Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1997,15(1):66-71.
[13] 许中杰,程日辉,沈艳杰,等. 闽西南地区晚三叠—早侏罗世温湿-干热气候转变的沉积记录 [J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2012,41(5):783-792.
XU Z J,CHENG R H,SHEN Y J,et al. Sedimentary records of the climatic transition from warm and humid to dry and hot during Late Triassic-Early Jurassic in southwestern Fujian [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2012,41(5):783-792.
[14] 徐崇凯,刘池洋,郭佩,等. 潜江凹陷古近系潜江组盐间泥岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,2018,36(3):617-629.
XU C K,LIU C Y,GUO P,et al. Geochemical characteristics and their geological significance of intrasalt mudstones from the Paleogene Qianjiang Formation in the Qianjiang Graben,Jianghan Basin,China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2018,36(3):617-629.
[15] 陈佩蓉,许中杰,孔锦涛,等. 闽西南地区中侏罗世古气候演化及其对华南构造体制转换的响应[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2020,44(5):1012-1024.
CHEN P R,XU Z J,KONG J T,et al. Paleoclimatic evolution during Middle Jurassic in southwestern Fujian and its responses to the tectonic regime transition in South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2020,44(5):1012-1024.
[16] 陈森然,许中杰,孔锦涛,等. 华南陆缘粤南地区晚三叠世—早、中侏罗世古气候演化及其对华南构造体制转换的响应[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(9):3290-3306.
CHEN S R,XU Z J,KONG J T,et al. Paleoclimatic evolution during Late Triassic-Early-Middle Jurassic in South Guangdong of South China continental margin and its responses to the tectonic regime transition[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(9):3290-3306.
[17] 李祥辉,陈斯盾,曹珂,等. 浙闽地区白垩纪中期古土壤类型与古气候 [J]. 地学前缘,2009,16(5):63-70.
LI X H,CHEN S D,CAO K,et al. Paleosols of the mid-Cretaceous:a report from Zhejiang and Fujian ,SE China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers ,2009 ,16(5):63-70.
[18] 刘玲,李祥辉,王尹,等. 浙闽地区白垩纪早中期黏土矿物组成特征及其古气候显示[J]. 沉积学报,2012,30(1):120-127.
LIU L,LI X H,WANG Y,et al. The Early-Mid Cretaceous changes of clay mineral composition from Zhejiang and Fujian Provinces,SE China:indications to paleoclimate changes[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2012,30(1):120-127.
[19] 刘友祥,胡文瑄,胡广. 浙闽地区早白垩世暗色岩系的孢粉组合与古气候特征[J]. 高校地质学报,2014,20(4):590-601.
LIU Y X,HU W X,HU G. Spores and pollen assemblages and their paleo-climate implication from the Early Cretaceous dark mudstone in Zhejiang and Fujian Provinces[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2014,20(4):590-601.
[20] CHARVET J,SHU L S,SHI Y S,et al. The building of South China:collision of Yangzi and Cathaysia blocks,problems and tentative answers[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences,1996,13(3/5):223-235.
[21] SHU L,CHARVET J. Kinematics and geochronology of the proterozoic Dongxiang-Shexian ductile shear zone:with HP metamorphism and ophiolitic melange (Jiangnan region,South China)[J]. Tectonophysics,1996,267(1/4):291-302.
[22] WANG X L,ZHOU J C,GRIFFIN W L,et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of Precambrian basement sequences in the Jiangnan orogen:dating the assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Precambrian Research,2007,159(1/2):117-131.
[23] WANG Y,FAN W,CAWOOD P A,et al. Indosinian high-strain deformation for the Yunkaidashan tectonic belt,South China:kinematics and 40Ar/ 39Ar geochronological constraints [J]. Tectonics,2007,26(6):TC6008.
[24] ZHOU J C,WANG X L,QIU J S. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic mafic rocks and sandstones from northeastern Guizhou,South China:coeval arc magmatism and sedimentation[J]. Precambrian Research,2009,170(1):27-42.
[25] ZHONG D L. Paleotethysides in West Yunnan and Sichuan,China [M]. Beijing: China Science Press,2000.
[26] WANG Y J,FAN W M,ZHANG G W,et al. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block:key observations and controversies[J]. Gondwana Research,2013,23(4):1273-1305. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.019
[27] LI J H,MA Z L,ZHANG Y Q,et al. Tectonic evolution of Cretaceous extensional basins in Zhejiang Province,eastern South China:structural and geochronological constraints[J]. International Geology Review,2014,56(13):1602-1629. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.951978
[28] LI X H. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2000,18(3):293-305. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7
[29] ZHOU X M,LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastern China:implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics,2000,326(3):269-287.
[30] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 李晓峰, 等. 华南地区中生代大规模成矿作用与岩石圈多阶段伸展[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 45-55.
MAO J W, XIE G Q, LI X F, et al. Mesozoic large scale mineralization and multiple lithospheric extension in South China.[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(1): 45-55.
[31] MAO J W,WANG Y T,LEHMANN B,et al. Molybdenite Re-Os and albite 40Ar/39Ar dating of Cu-Au-Mo and magnetite porphyry systems in the Yangtze River valley and metallogenic implications[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2006,29(3):307-324.
[32] ZHOU X M,SUN T,SHEN W Z,et al. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China:a response to tectonic evolution[J]. International Union of Geological Sciences,2006,29(1):26-33.
[33] LI Z X,LI X H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology,2007,35(2):179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
[34] HU R Z,BI X W,ZHOU M F,et al. Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary[J]. Economic Geology,2008,103(3):583-598. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.103.3.583
[35] SHU L S,ZHOU X M,DENG P,et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Southeast China Block:new insights from basin analysis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2009,34(3):376-391. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.06.004
[36] CHU Y,LIN W,FAURE M,et al. Cretaceous episodic extension in the South China Block,East Asia:evidence from the Yuechengling Massif of Central South China[J]. Tectonics,2019,38(10):3675-3702. doi: 10.1029/2019TC005516
[37] LI J,CAWOOD P A,RATSCHBACHER L,et al. Building Southeast China in the Late Mesozoic:insights from alternating episodes of shortening and extension along the Lianhuashan Fault Zone[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,201:103056. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103056
[38] YAN D P,ZHOU M F,SONG H L,et al. Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi-layer over-thrust system within the Yangtze Block (South China)[J]. Tectonophysics,2003,361(3):239-254.
[39] LIN W,WANG Q C,CHEN K. Phanerozoic tectonics of South China Block:new insights from the polyphase deformation in the Yunkai massif [J]. Tectonics,2008,27(6):TC6004
[40] LI J H,DONG S W,CAWOOD P A,et al. An Andean-type retro-arc foreland system beneath northwest South China revealed by SINOPROBE profiling[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2018,490:170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.03.008
[41] SUN W D,LING M X,YANG X Y,et al. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization:an overview[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences),2010,53(4):475-484. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-0024-0
[42] WANG Z H,LU H F. Ductile deformation and 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Changle–Nanao ductile shear zone,southeastern China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2000,22(5):561-570. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00179-0
[43] WEI W,FAURE M,CHEN Y,et al. Back-thrusting response of continental collision:Early Cretaceous NW-directed thrusting in the Changle-Nan'ao Belt (Southeast China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2015,100:98-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.005
[44] 祖辅平,舒良树,李成. 永安盆地晚古生代—中—新生代沉积构造环境演化特征[J]. 地质论评,2012,58(1):126-148.
ZU F P,SHU L S,LI C. Evolution features of depositional and tectonic setting from Late Paleozoic to Meso-Cenozoic in the Yong’an Basin[J]. Geological Review,2012,58(1):126-148.
[45] HU L S,CAWOOD P A,DU Y S,et al. Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic provenance record of paleo-Pacific subduction beneath South China[J]. Tectonics,2015,34(5):986-1008. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003803
[46] 陈金秀. 福建省永安盆地第四纪冰川遗迹的探讨 [J]. 福建地质,1984 (1):61-67.
CHEN J X. Exploration of Quaternary glacier relics in Yong'an Basin,Fujian Province [J]. Geology of Fujian,1984(1):61-67.
[47] 李兼海. 福建省岩石地层 [M]. 北京:中国地质大学出版社,1997.
LI J H. Geological Strata of Fujian Province [M]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences Press,1997.
[48] XU Q J,LIU S F,WANG Z F,et al. Provenance of the East Guangdong Basin and Yong'an Basin in Southeast China:response to the Mesozoic tectonic regime transformation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2019,185:104024. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104024
[49] LI X H,ZHANG C K,LI Y X,et al. Refined chronostratigraphy of the Late Mesozoic terrestrial strata in South China and its tectono-stratigraphic evolution[J]. Gondwana Research,2019,66:143-167. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.09.006
[50] FREYDIER R,MICHARD A,DE LANGE G,et al. Nd isotopic compositions of eastern Mediterranean sediments:tracers of the Nile influence during sapropel S1 formation?[J]. Marine Geology,2001,177(1):45-62.
[51] 赵振华. 微量元素地球化学原理 [M]. 北京:科学出版社,2016.
ZHAO Z H. Geochemistry of trace elements [M] . Beijing:Science Press,2016.
[52] NESBITT H W,YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature,1982,299(5885):715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[53] 何岸北. 东南沿海古海岸山脉演化:永安盆地晚中生代沉积及古气候响应 [D]. 广州:中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所),2022.
HE A B. Evolution of Paleo-Coastal Mountains along the Southeast Coast:Sedimentation and Paleoclimate Response in Yong'an Basin of the Late Mesozoic [D]. Guangzhou:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences),2022.
[54] MCLENNAN S M,HEMMING S,MCDANIEL D K,et al. Geochemical Approaches to Sedimentation,Provenance,and Tectonics [M]//JOHNSSON M J,BASU A. Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments. Geological Society of America,1993:21-40.
[55] CHEN J,AN Z S,HEAD J. Variation of Rb/Sr ratios in the loess-paleosol sequences of Central China during the last 130,000 years and their implications for monsoon paleoclimatology[J]. Quaternary Research,1999,51(3):215-219. doi: 10.1006/qres.1999.2038
[56] CHEN J,WANG Y J,CHEN Y,et al. Rb and Sr geochemical characterization of the Chinese loess stratigraphy and its implications for palaeomonsoon climate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition),2000,74(2):279-288. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2000.tb00462.x
[57] 田景春,张翔. 沉积地球化学 [M]. 北京:地质出版社,2016.
TIAN J C,ZHANG X. Sedimentary geochemistry [M]. Beijing:Geology Press,2016.
[58] 田晓雪,雒昆利,谭见安,等. 黑龙江嘉荫地区白垩系与古近系界线附近的古气候分析 [J]. 古地理学报,2005,7(3):425-432.
TIAN X X,LUO K L,TAN J A,et al. Analysis on palaeoclimate neighbouring the Cretaceous and Paleogene boundary in Jiayin area,Heilongjiang Province [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2005,7(3):425-432.
[59] 王益友,郭文莹,张国栋. 几种地球化学标志在金湖凹陷阜宁群沉积环境中的应用[J]. 同济大学学报,1979(2):51-60.
WANG Y Y,GUO W Y,ZHANG G D. Application of some geochemical indicators in determiring of sedimentary environment of the Funing Group (Paleogene),Jinhu Depression,Kiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Tongji University,1979(2):51-60.
[60] 王敏芳,焦养泉,王正海,等. 沉积环境中古盐度的恢复:以吐哈盆地西南缘水西沟群泥岩为例[J]. 新疆石油地质,2005,26(6):117-120.
WANG M F,JIAO Y Q,WANG Z H. Recovery paleosalinity in sedimentary environment: an example of mudstone in Shuixigou Group,southwestern margin of Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2005,26(6):117-120.
[61] WRIGHT J,SCHRADER H,HOLSER W T. Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1987,51(3):631-644. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90075-5
[62] JONES B,MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology,1994,111(1):111-129.
[63] WIGNALL P B,TWITCHETT R J. Oceanic anoxia and the end Permian mass extinction[J]. Science,1996,272(5265):1155-1158. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5265.1155
[64] 吴朝东,杨承运,陈其英. 湘西黑色岩系地球化学特征和成因意义 [J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,1999,18(1):28-29,31-41.
WU C D,YANG C Y,CHEN Q Y. The origin and geochemical characteristics of Upper Sinain Lower Cambrian black shales in western Hunan [J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica1999,18 (1):28-29,31-41.
[65] RIMMER S M. Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian-Mississippian black shales,Central Appalachian Basin (USA)[J]. Chemical Geology,2004,206(3):373-391.
[66] SCHEFFLER K,BUEHMANN D,SCHWARK L. Analysis of late Palaeozoic glacial to postglacial sedimentary successions in South Africa by geochemical proxies:response to climate evolution and sedimentary environment[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2006,240(1):184-203.
[67] 彭华,吴志才. 关于红层特点及分布规律的初步探讨 [J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),2003,42(5):109-113.
PENG H ,WU Z C. A preliminary study on the characteristics and the distribution of red beds [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis SunYatseni,2003,42(5):109-113.
[68] DOUGLAS P M J,BRENNER M,Curtis J H. Methods and future directions for paleoclimatology in the Maya lowlands[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2016,138:3-24. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.07.008
[69] 刘秀铭,吕镔,毛学刚,等. 风积地层中铁矿物随环境变化及其启示[J]. 第四纪研究,2014,34(3):443-457.
LIU X M,LYV B,MAO X G,et al. Iron minerals of aeolian deposits vary with environment and its significances[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2014,34(3):443-457.
[70] TEWARI R,CHATTERJEE S,AGNIHOTRI D,et al. Glossopteris flora in the Permian Weller Formation of Allan Hills,South Victoria Land,Antarctica:implications for paleogeography,paleoclimatology,and biostratigraphic correlation[J]. Gondwana Research,2015,28(3):905-932. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.02.003
[71] 邓胜徽,卢远征,赵怡,等. 中国侏罗纪古气候分区与演变[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(1):106-142.
DENG S H,LU Y Z,ZHAO Y,et al. The Jurassic palaeoclimate regionalization and evolution of China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2017,24(1):106-142.
[72] 岳来群,游国庆,郑宁,等. 福建坂头组沉积特征及构造背景研究[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(5):1220-1231.
YUE L Q,YOU G Q,ZHENG N,et al. Sedimentary characteristics and tectonic background of Bantou period in Fujian[J]. Geology in China,2011,38(5):1220-1231.
[73] 梁诗经,文斐成,陈润生,等. 福建泰宁白垩纪红层植物及孢粉化石组合特征[J]. 福建地质,2006(1):1-9.
LIANG S J,WEN F C,CHEN R S. The assemblage and characters of floras and sporo-pollen fossils in the Cretaceous red-bed basin of Taining County,Fujian Province[J]. Geology of Fujian,2006(1):1-9.
[74] 福建省地质调查研究院. 中国区域地质志:福建志 [M]. 北京:地质出版社,2016.
Fujian Institute Of Geological Survey. Regional Geology of China:Fujian Province [M]. Beijing:Geology Press,2016.
[75] HU G,HU W X,CAO J,et al. Deciphering the Early Cretaceous transgression in coastal southeastern China:constraints based on petrography,paleontology and geochemistry[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2012,317/318:182-195.
[76] 刘静,张金玉,葛玉魁,等. 构造地貌学:构造-气候-地表过程相互作用的交叉研究 [J]. 科学通报,2018,63(30):3070-3088.
LIU J,ZHANG J Y,GE Y K,et al. Tectonic geomorphology:an interdisciplinary study of the interaction among tectonic climatic and surface processes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2018,63(30):3070-3088.
[77] 刘芮岑. 湖南茶陵盆地晚白垩世—古新世古气候分析 [D]; 南京大学,2018.
LIU R C. Paleoclimate of the Late Cretaceous-Paleocene in the Chaling Basin,Hunan,South China [D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2018.
[78] 黄乐清,黄建中,罗来,等. 湖南衡阳盆地东缘白垩系风成沉积的发现及其古环境意义[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(4):735-748.
HUANG Y Q,HUANG J Z,LUO L,et al. The discovery of Cretaceous eolian deposits at the eastern margin of the Hengyang Basin,Hunan,and its paleoenvironmental significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2019,37(4):735-748.
[79] TENG X H,FANG X M,KAUFMAN A J,et al. Sedimentological and mineralogical records from drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin,Central China,and their implications for late Cretaceous-Early Eocene climate change[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2019,182:103936.1-103936.14.
[80] CHEN L Q,STEEL R J,GUO F S,et al. Alluvial fan facies of the Yongchong Basin:implications for tectonic and paleoclimatic changes during Late Cretaceous in SE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,134:37-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.010
[81] 李余亮. 广东省韶关市丹霞盆地长坝组沉积特征与古气候研究 [D]. 抚州:东华理工大学,2018.
LI Y L. Sedimentary Characteristics and Paleoclimate of the Changba Formation in the Danxia Basin,Shaoguan City,Guangdong Province,South China [D]. Fuzhou:East China University of Technology,2018.
[82] 王文艳,刘秀铭,马明明,等. 南雄盆地白垩纪红层沉积环境分析[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报,2016,11(3):29-37.
WANG W Y,LIU X M,MA M M,et a1. Sedimentary environment of Cretaceous red beds in Nanxiong Basin,Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment,2016,11(3):29-37.
[83] 张哲. 三水盆地下白垩统—始新统黏土矿物特征及其对区域构造-气候事件的响应 [D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018.
ZHANG Z. Clay Mineral Characteristics of Sanshui BasinfromLower Cretaceous to Eocene and Their Response to Tectonic Activities and Climate Changes in the Region [D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing ),2018.
[84] 梁西文. 中扬子区晚三叠世—新近纪层序岩相古地理演化研究 [D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2008.
LIANG X W. Study on Lithofacies Paleographic Evolution of Late Triassic-Neogene Sequence in Mid-Yangtze Region [D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2008.
[85] 王宇佳. 江西广丰晚白垩世周田组沉积特征与古气候分析 [D]. 抚州:东华理工大学,2019.
WANG Y J. Sedimentary Characteristics and Paleoclimate of the Zhoutian Formation in the Guangfeng Basin of Jiangxi Province [D]. Fuzhou:East China University of Technology,2019
[86] 刘友祥. 浙闽地区下白垩统暗色岩系的沉积环境研究 [D]. 南京:南京大学,2012.
LIU Y X. Study of Sedimentary Environment of Dark Sedimentary Rocks in Lower Cretaceous,Zhejiang and Fujian Provinces [D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2012.
-



 下载:
下载: