Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of intertidal zone in central Jiangsu Province: distribution, source, and assessment
-
摘要:
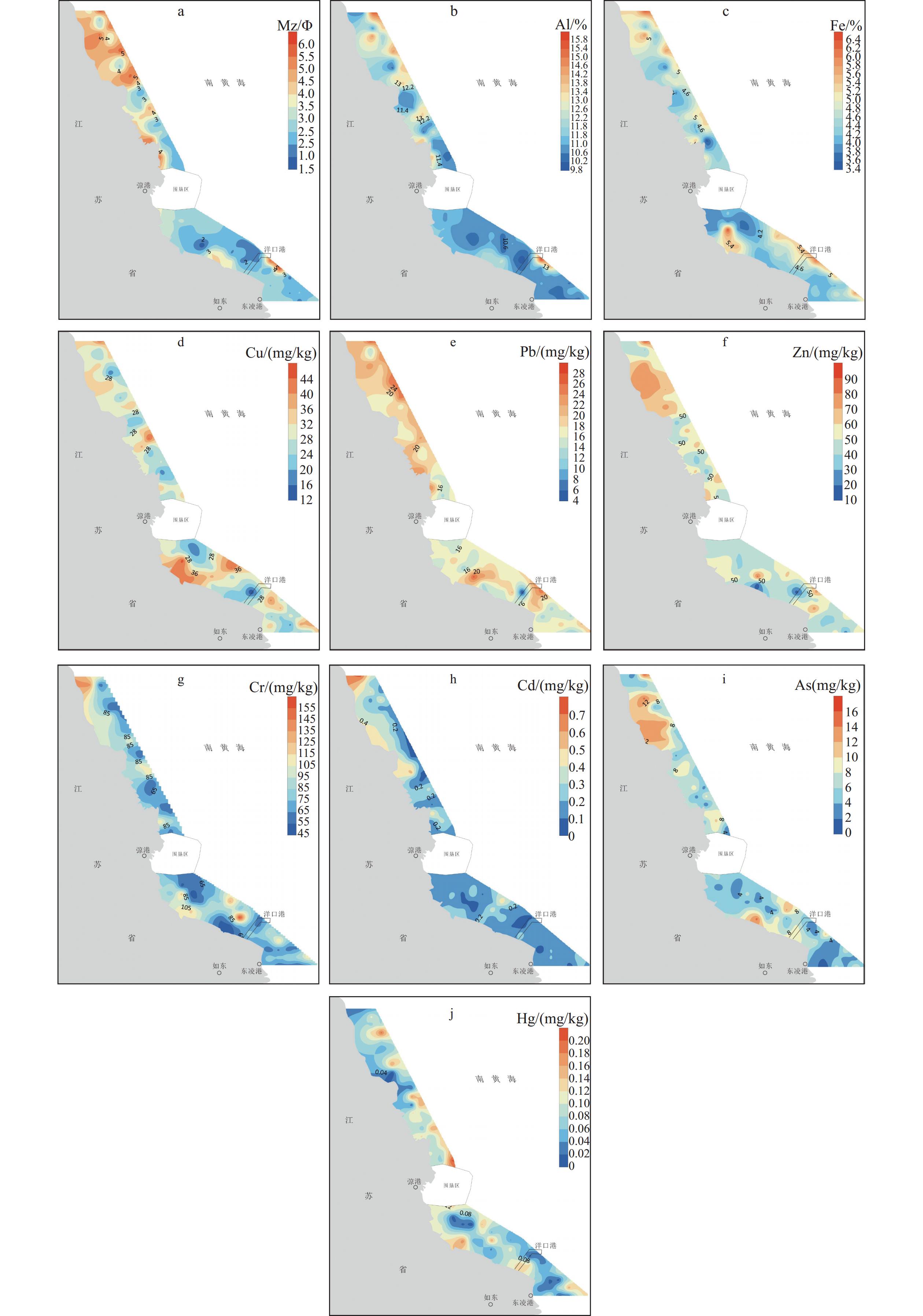
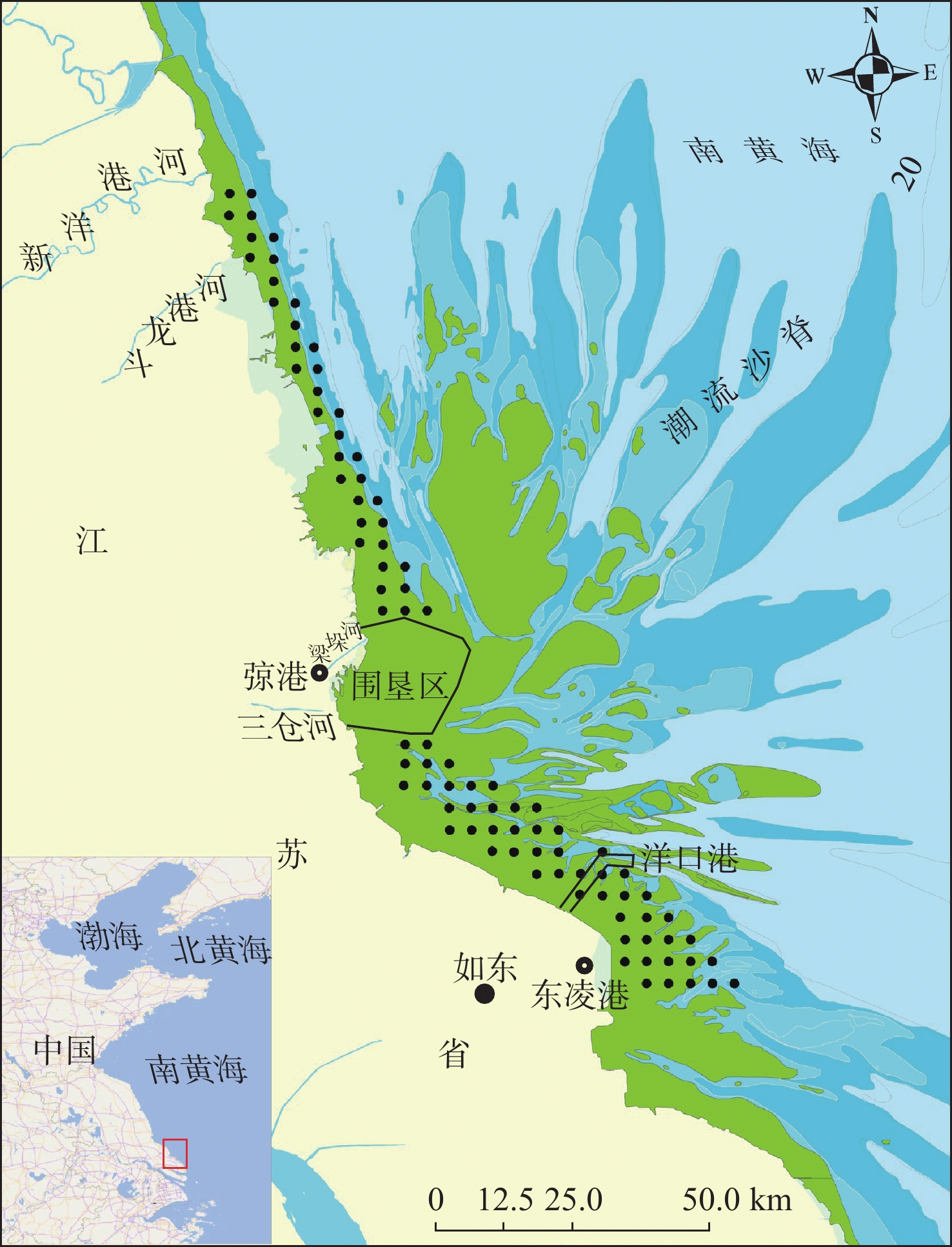
基于2015年江苏中部潮间带89个站位表层沉积物的测试分析结果和以往资料,探讨了Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr、Cd、As和Hg 7种重金属元素的含量、空间分布特征和相关性,并采用沉积物质量基准法、地累积指数法和富集系数对该区重金属状况进行了系统评价。结果表明,表层沉积物中重金属元素含量相差较大,平均含量由高至低依次为Cr>Zn>Cu>Pb>As>Cd>Hg,空间分布不均匀,高值区呈点状或片状分布。沉积物质量符合中国海洋沉积物质量第一类标准,所有站位的重金属含量均低于可能效应水平(PEL),综合潜在生态风险为低风险。元素相关性分析、地累积指数、富集系数和R型因子分析结果表明:Cu、Pb和Zn元素主要来自于地壳物质或自然风化作用,未污染、未富集;Cr元素含量受自然和人类活动共同作用的影响,部分站位轻度污染和轻度富集;Cd、As和Hg元素含量受人类活动影响较大,较为富集,污染程度较重。
Abstract:Surface sediment samples were collected at 89 stations from intertidal zone in central Jiangsu Province in 2015. The concentrations, spatial distribution patterns, and interrelations of seven heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd and Hg) were studied and compared with previous investigations. The pollution status was evaluated systematically with China’s national sediment quality guidelines, geoaccumulation index, and enrichment factor. Results show that the concentrations of heavy metals in surface sediment varies greatly, and the average concentration followed the descending order of: Cr>Zn>Cu>Pb>As>Cd>Hg. The spatial distribution was uneven. High-value areas were spot-like or in patch. The heavy metal concentrations at all stations were below the possible effect level, and the overall potential ecological risk was low. The Pearson correlation coefficients, geoaccumulation indexes, enrichment factors, and R-type factor analysis show that heavy metals Cu, Pb and Zn were not polluted or enriched, and they were mainly from crustal materials or natural weathering. Cr was slightly polluted and enriched, which were jointly affected by natural weathering and human activities. Cd, As, and Hg were enriched and heavily polluted, which were mainly derived from anthropogenic sources.
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- pollution assessment /
- surface sediments /
- intertidal zone /
- Jiangsu Province
-

-
表 1 江苏中部潮间带与其他典型区域沉积物中重金属含量对比
Table 1. Comparison of the heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments of intertidal zone in central Jiangsu Province and other representative areas
mg/kg 位置 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg 来源 江苏中部潮间带 范围 11.66~46.01 3.72~27.7 12.86~90.34 44.74~167.7 0.02~0.73 0.81~16.09 0~0.2 本文 均值 28.95 18.07 50.48 79.37 0.20 6.21 0.08 江苏南部 均值 19.02 21.34 70.77 65.56 0.07 6.25 0.03 文献[13] 江苏南通 均值 16.60 21.60 130.75 55.54 0.18 9.24 0.04 文献[29] 南黄海 均值 40.30 19.29 56.91 57.17 0.09 11.06 0.01 文献[30] 江苏沿海土壤 均值 19.54 14.52 61.06 61.71 0.12 13.06 0.01 文献[27] 江苏陆域土壤 均值 15.84 24.70 64.68 60.28 0.37 8.59 0.03 文献[31] 海洋沉积物质量第一类标准 均值 35 60 150 80 0.5 20 0.2 文献[32] 表 2 重金属元素与常量元素和平均粒径的Pearson相关系数
Table 2. Pearson's correlation matrix for the heavy metals, major element, and mean grain size
Al Fe Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg Mz Al 1 Fe 0.55** 1 Cu 0.22* 0.48** 1 Pb 0.54** 0.53** 0.47** 1 Zn 0.54** 0.45** 0.43** 0.57** 1 Cr 0.06 0.39** 0.63** 0.32** 0.23* 1 Cd −0.05 0.10 0.17 0.10 0.16 0.37** 1 As 0.30** 0.17 0.07 0.10 0.42** 0.03 0.34** 1 Hg 0.06 0.03 0.12 0.11 0.12 0.16 −0.02 0.07 1 Mz 0.89** 0.37** 0.16 0.42** 0.51** 0.12 0.14 0.35** 0.001 1 注:** 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著;* 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 3 江苏中部重金属基准阈值及不同浓度范围内的百分比
Table 3. The reference threshold of heavy metals in central Jiangsu Province and percentage of samples in different concentration ranges
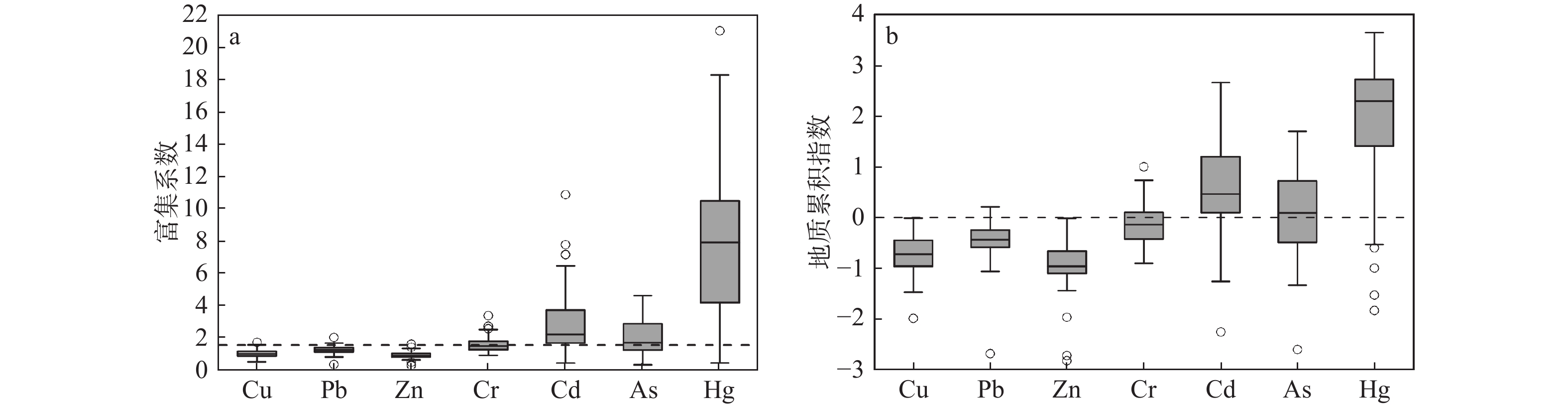
沉积物基准阈值 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg 阈值效应水平(TEL) 18.7 30.2 124 52.3 0.68 7.24 0.13 可能效应水平(PEL) 108 112 271 160 4.21 41.6 0.7 <TEL/% 5 100 100 3 99 66 85 ≥TEL,< PEL/% 95 0 0 97 1 34 15 ≥PEL /% 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 4 江苏中部潮间带表层沉积物的富集系数EF和地累积指数Igeo
Table 4. Enrichment factors and geoaccumulation index values of heavy metals in the surface sediments of intertidal zone in central Jiangsu Province
参数 Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg 背景值/(mg/kg) 31 16 61 56 0.077 3.3 0.011 EF 范围 0.46~1.67 0.28~1.96 0.22~1.55 0.86~3.32 0.38~10.82 0.27~4.56 0.38~20.99 均值 0.99 1.19 0.87 1.51 2.81 1.98 7.88 Igeo 范围 −2 ~−0.02 −2.69~0.21 −2.83 ~−0.02 −0.91~1 −2.26~2.66 −2.61~1.7 −1.84~3.65 均值 −0.72 −0.45 −0.92 −0.13 0.56 0.12 1.95 表 5 表层沉积物中特征值的总方差、方差百分比和4个主成分的特征向量(F1—F4)
Table 5. Total variance of surface sediments and their eigenvalues, percentages of variance, and eigenvectors of four principal components (F1—F4)
F1 F2 F3 F4 Al 0.80 −0.48 −0.17 0.00 Fe 0.73 0.08 −0.22 −0.19 Cu 0.63 0.58 −0.16 −0.11 Pb 0.74 0.06 −0.29 −0.02 Zn 0.81 −0.10 0.08 0.12 Cr 0.48 0.74 0.03 −0.09 Cd 0.26 0.31 0.78 −0.14 As 0.45 −0.25 0.68 0.18 Hg 0.16 0.24 −0.09 0.93 Mz 0.75 −0.48 0.05 −0.04 特征值 3.86 1.58 1.29 1.00 方差百分比/% 38.61 15.83 12.87 9.97 累积方差/% 38.61 54.44 67.30 77.27 -
[1] 雷雁翔,张斌,吴治国,等. 长岛北部海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征与风险评价及来源分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(3):40-50.
[2] THORAT B,PRASAD P,RAM A. Heavy metal accumulation in a moderately polluted Ulhas Estuary,Western India[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science,2023,60:102818. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2023.102818
[3] 王俊杰,左平,黄阳,等. 盐城新洋港表层沉积物重金属分布特征与评价[J]. 环境评价,2013,39(5):57-62.
[4] KHALEEQ A,AHMED M,HUMA R,et al. Evaluation of trace and heavy metals in different varieties of sauces to characterize their impact on human health[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,114:104789. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104789
[5] 赵雪琴,赵善道,左平,等. 江苏盐城原生湿地表层沉积物中的重金属污染评价[J]. 环境保护科学,2010,36(1):64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2010.01.020
[6] 郑江鹏,矫新明,方南娟,等. 江苏近岸海域沉积物重金属来源及风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学,2017,37(4):1514-1522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.04.039
[7] 曹柳燕,张捷,胡颢琰,等. 浙江南部近岸海域表层沉积物中重金属污染评价[J]. 环境污染与防治,2016,38(7):61-65.
[8] 高燕云. 射阳河口现代沉积速率及其重金属污染评价[D]. 南京:南京师范大学,2011.
[9] 孟昆. 苏北辐射沙洲近岸潮滩现代沉积特征及重金属时空分布规律研究[D]. 南京:南京师范大学,2018.
[10] 宋颖,李华栋,时文博,等. 黄河三角洲湿地重金属污染生态风险评价[J]. 环境保护科学,2018,44(5):118-122.
[11] 徐艳东,魏潇,杨建敏,等. 山东近岸海域表层沉积物 7 种重金属污染特征和生态风险评估研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2015,46(3):651-658. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20141200358
[12] 陈鹏. 江苏北部沿海潮间带大型底栖动物群落特征及表层沉积物重金属含量研究[D]. 南京:南京师范大学,2019.
[13] QIU J D,YIN P,LIU J,et al. Historical records of trace metals in core sediments from Jiangsu coastal area,China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2019,149:110625. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110625
[14] YUAN H M,SONG J M,LI X G,et al. Distribution and contamination of heavy metals in surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2012,64:2151-2159. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.040
[15] XIANG L,JIANG S,CHENG H,et al. Heavy metal concentration profiles and pollution assessment in the Jiangsu offshore area,China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2023,193:115187. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115187
[16] 张蓝天,杨林生,李海蓉,等. 江苏沿海滩涂土壤重金属风险分析[J]. 中国环境监测,2023,39(2):55-62.
[17] 刘超. 江苏如东潮滩重金属污染及其基于光谱响应的定量估算研究[D]. 南京:南京师范大学,2020.
[18] WU Z,DONG Y,LIU R,et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments off the Dongying coast,Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2022,180:113826. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113826
[19] 顾效源,孔祥淮,王伟,等. 山东丁字湾表层沉积物重金属分布及污染评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(3):13-21.
[20] MACDONALD D,CARR R,CALDER F,et al. Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters[J]. Ecotoxicology,1996,5(4):253-278. doi: 10.1007/BF00118995
[21] LONG E,MACDONALD D,SMITH S,et al. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments[J]. Environmental Management,1995,19(1):81-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02472006
[22] 段云莹,裴绍峰,廖名稳,等. 渤海莱州湾沉积物REE与重金属污染特征及物源判别[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(10):8-24.
[23] RUBIO B,NOMBELA M,VILAS F. Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain):an assessment of metal pollution[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2000,40(11):968-980. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00039-4
[24] GAO S,LUO T C,ZHANG B R,et al. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1998,62(11):1959-1975. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00121-5
[25] MULLER G. Heavy-metals in sediment of the rhine-changes since 1971 [M].Germany,Umschau in Wissenschaft und Technik ,1979:778-783.
[26] MÜLLER G. Die Schwermetallbelastung der sediment des Neckars und seiner Nebenflusse:eine Bestandsaufnahme[J]. Chemiker Zeitung,1981,105:157-164.
[27] LI Y,LI H G. Historical records of trace metals in core sediments from the Lianyungang coastal sea,Jiangsu,China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,116(1/2):56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.12.063
[28] HU B Q,LI J,ZHAO J T,et al. Heavy metal in surface sediments of the Liaodong Bay,Bohai Sea:distribution,contamination,and sources[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2013,185(6):5071-5083. doi: 10.1007/s10661-012-2926-0
[29] SHEN F,MAO L J,DENG X Q,et al. Reanalysis of distribution characteristics and contamination evaluation of heavy metals in coastal sediments of Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2018,39(5):62-71.
[30] XU G,LIU J,KONG X H,et al. An evaluation on heavy metal contamination in surface sediments on the west South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2012,31(2):181-185.
[31] 夏增禄. 土壤元素背景值及其研究方法[M]. 北京:气象出版社,1987.
[32] 国家海洋局国家海洋环境监测中心. GB 18668—2002,海洋沉积物质量[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社.
[33] XAVIER D,DOS SANTOS V,DE MIRANDA A,et al. Determination of background geochemistry of an Amazon estuary:the Cuñaní Estuary -Amapá[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,155:111144. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111144
[34] MADADI R,MEJJAD N,DE-LA-TORRE G. Geochemical speciation,ecological risk,and source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in sediments and waters from Musa Estuary,Persian Gulf[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2023,190:114836. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114836
[35] JEONG H,RA K. Pollution and ecological risk assessments for heavy metals in coastal,river,and road-deposited sediments from Apia City in Upolu Island,Samoa[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2023,188:114596. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114596
[36] DIAGOMANOLIN V,FARHANG M,GHAZI-KHANSARI M,et al. Heavy metals (Ni,Cr,Cu) in the karoon waterway river,Iran[J]. Toxicology Letters,2004,151(1):63-67. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.02.018
[37] 段云莹,裴绍峰,廖名稳,等. 莱州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征、污染评价与来源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(6):67-81.
[38] 江苏省国土资源厅. 江苏省工业企业用地调查分析报告(2016)[R]. 南京:江苏省国土资源厅,2017.
-



 下载:
下载: