Analysis of dynamic geomorphology at the east entrance of Qiongzhou Strait based on tidal current numerical simulation
-
摘要:
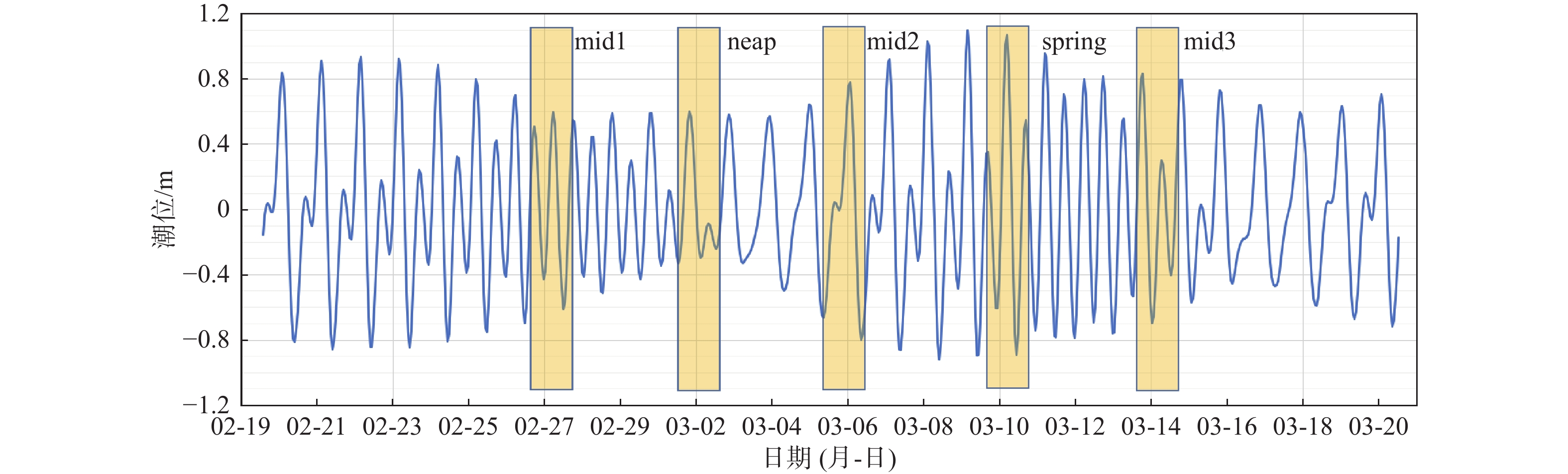
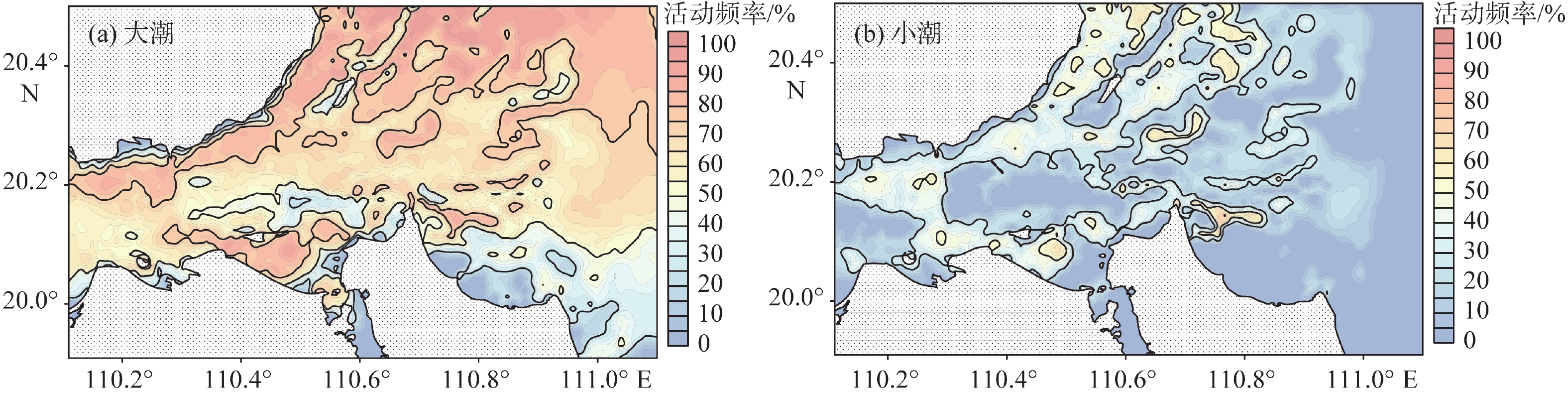
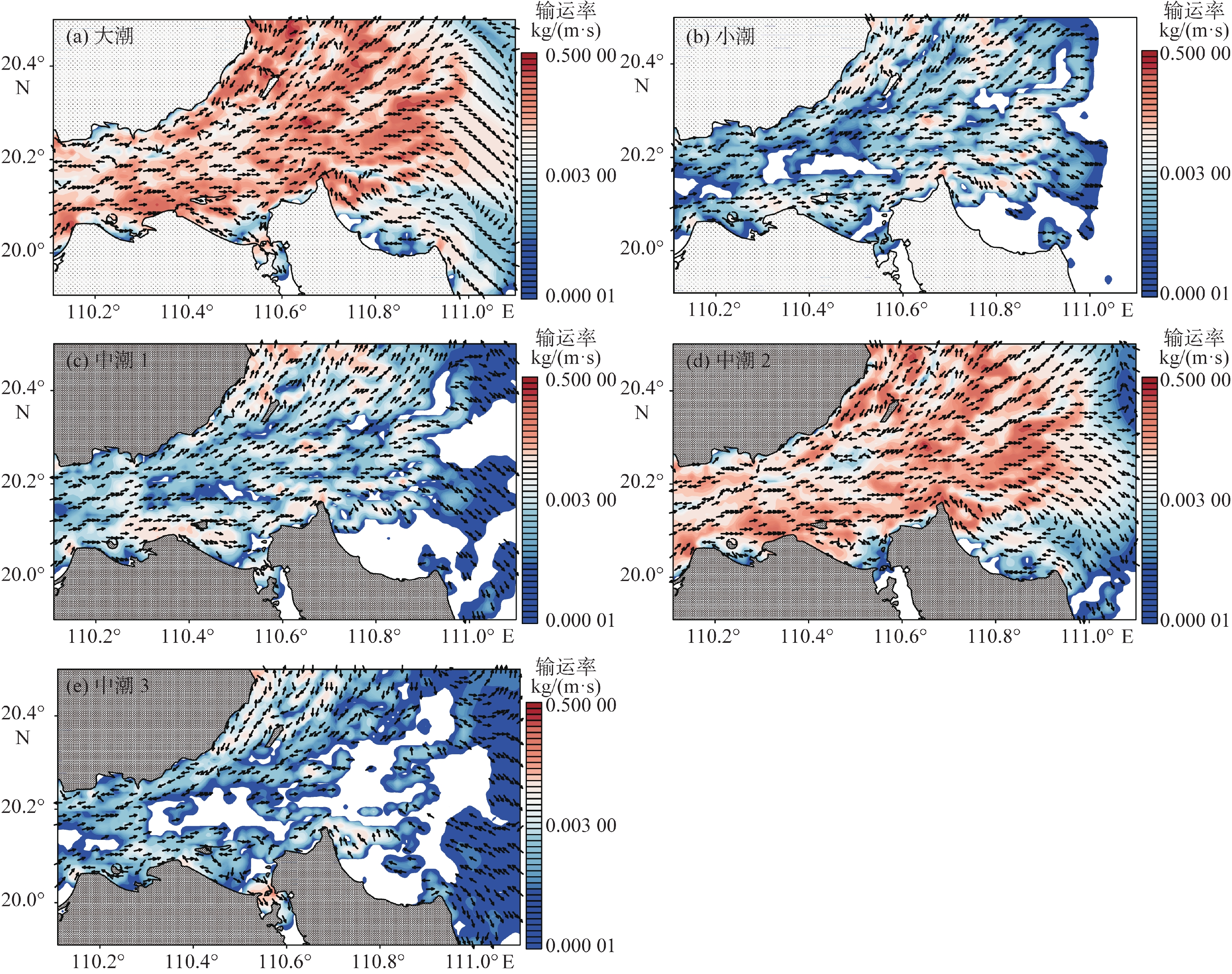
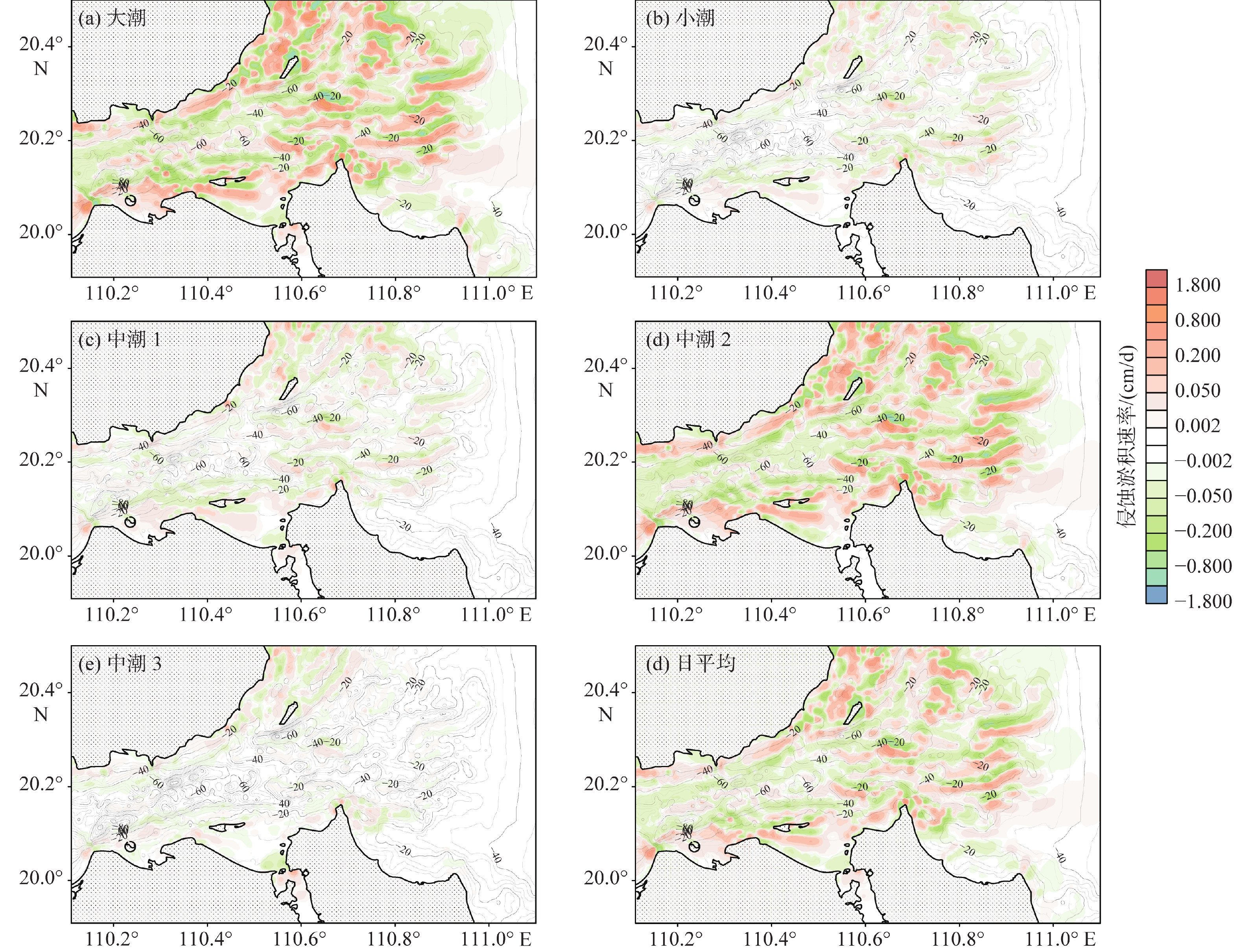
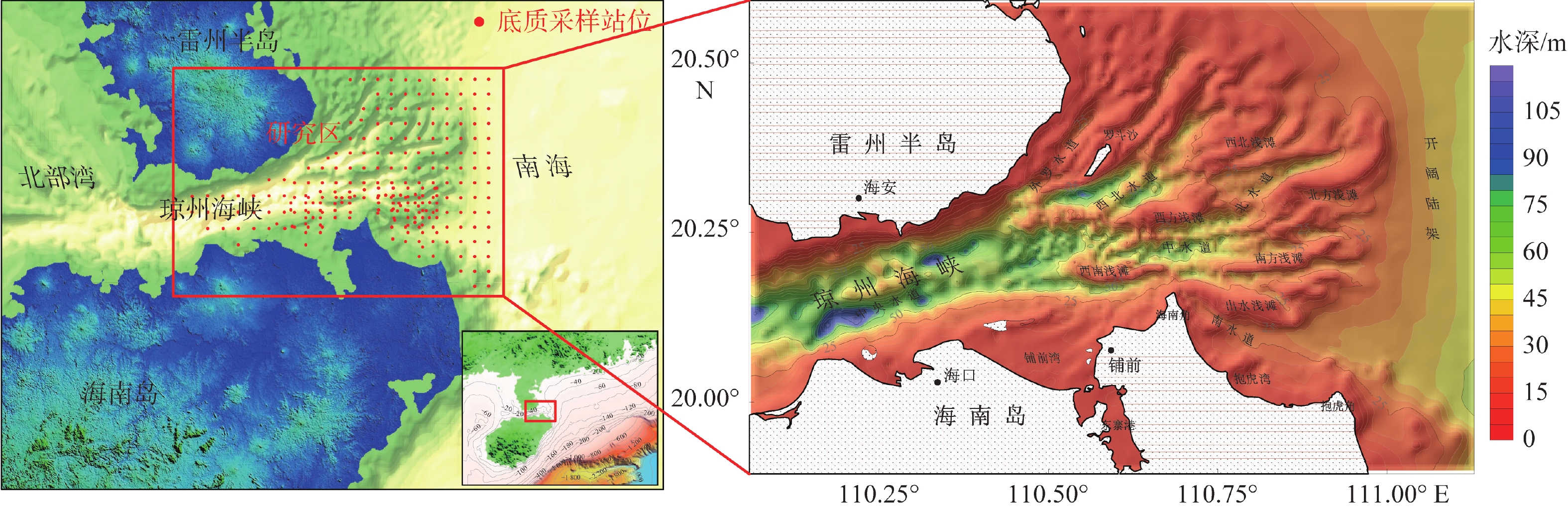
潮流是塑造琼州海峡东口海底地貌的主要动力,研究潮流作用下的沉积物运动特征,有助于更好地理解海峡的水沙通量、沉积过程和地貌演化。根据对2008和2015年研究区249个站位所采集的表层样品调查数据的研究统计,海峡东口沉积物以砂砾质为主,其分布规律与潮流的强弱和方向关系密切,运动形式主要为推移方式。为了进一步研究沉积物的运移与海底地貌的动态关系,利用沉积动力学模型估算了琼州海峡东口的潮流过程、沉积物输运率和侵蚀淤积强度等指标。结果显示,大潮时,东向急流的流速为0.9~2.0 m/s,西向急流为0.8~1.7 m/s,中潮和小潮的潮流流速约为大潮时的50%~60%。总体上,东向流强于西向流,但在海峡北岸和中央水道,西向流始终强于东向流。大潮时,全区沉积物的活动频率普遍较高,均值可达60%,其平均输运率在10−2 kg/(m·s)量级;而中小潮期间,活动频率均值仅为18%左右,平均输运率比大潮期小1~2个数量级。沉积物整体输运方向为东向,但在海峡北岸净输运方向为西向。从侵蚀淤积强度的分布可知,研究区的浅滩堆积速率较高,水道的侵蚀速率较高,量级可达10−1 m/a。
Abstract:The tidal pattern of the east entrance of Qiongzhou Strait that separating Hainan Island from Chinese mainland is irregular diurnal tide, and characterized by east-west reciprocating flow, in which strong tidal current is the main dynamic factor of shaping the seabed morohology. The study of sediment transport characteristics under tidal current is crucial for better understanding the fluxes of water and sediment, sedimentary processes and geomorphological evolution in Qiongzhou Strait. Survey data of surface sediments collected in 2008 and 2015 from 249 stations show that the sediments at the east entrance of the strait were mainly sandy and gravelly, forming the bed load that transported on seabed. To study the sediment transport and seabed morphology, the tidal current process, sediment transport rate and erosion and sedimentation intensity of the east entrance of Qiongzhou Strait were dynamically modeled. The results show that the maximum eastward flow is between 0.9 and 2.0 m/s, and the maximum westward flow is between 0.8 and 1.7 m/s, and the tidal flow in the middle and neap tides is roughly 50% to 60% of that in the spring tides. In general, the eastward flow is stronger than the westward flow, but in the north and the middle part of Qiongzhou Strait, the westward flow is always stronger than the eastward. During spring tides, the frequency of sediments movement in the study area is generally high, with an average of 60%, and the average transport rate is 10−2 kg/(m·s). During the middle and neap tides, the average frequency is only about 18%, and the average transport rate is 1-2 orders of magnitude smaller than that during the spring tides. The sediment transport direction is mainly eastward. We found that there is a higher accumulation rate near shoals and a higher erosion rate, reaching 10−1 m/a.
-

-
表 1 研究区潮流场特征统计
Table 1. Statistics of tidal current field characteristics in the study area
区域 大潮 小潮 中潮 潮差/m 东向急流时 西向急流时 潮差/m 东向急流时 西向急流时 潮差/m 东向急流时 西向急流时 流速/(m/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(m/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(m/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(m/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(m/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(m/s) 流向/(°) 北岸 1.69 0.64 89 0.96 229 0.92 0.43 82 0.50 229 1.23 0.56 84 0.60 227 南岸 1.64 0.63 137 0.46 260 0.83 0.40 106 0.27 249 1.19 0.46 132 0.36 252 中央水道 1.56 1.78 73 1.52 254 0.85 0.78 74 0.73 254 1.15 1.09 74 0.86 254 外罗水道 1.79 1.51 38 1.72 217 0.96 0.77 39 0.86 216 1.28 1.05 37 1.00 216 西北水道 1.70 1.84 59 1.60 241 0.91 0.77 58 0.71 238 1.22 1.07 57 0.87 236 北水道 1.85 1.36 71 0.93 251 0.94 0.60 67 0.43 248 1.35 0.79 61 0.54 238 中水道 1.60 2.01 82 1.24 270 0.87 0.86 82 0.59 265 1.18 1.10 80 0.69 260 南水道 1.66 0.89 106 0.77 276 0.83 0.58 103 0.40 278 1.20 0.60 106 0.47 273 罗斗沙附近 1.95 1.29 43 1.35 217 1.01 0.64 43 0.66 215 1.42 0.89 40 0.83 211 西方浅滩 1.65 1.96 81 1.40 269 0.90 0.80 82 0.63 261 1.23 1.09 76 0.74 255 西南浅滩 1.48 1.94 71 1.29 259 0.83 0.93 73 0.71 256 1.09 1.17 73 0.78 254 西北浅滩 2.07 1.70 57 1.19 237 1.01 0.74 58 0.54 231 1.49 1.00 48 0.71 223 北方浅滩 2.00 1.44 77 0.79 255 0.94 0.62 80 0.33 247 1.40 0.76 62 0.48 228 南方浅滩 1.74 1.69 104 0.96 288 0.88 0.80 103 0.42 289 1.28 0.91 97 0.49 269 出水浅滩 1.72 1.07 126 0.98 307 0.86 0.71 129 0.45 308 1.27 0.66 125 0.53 293 开阔陆架 2.06 0.52 84 0.38 247 0.93 0.27 91 0.16 228 1.38 0.31 88 0.28 209 全区 1.76 1.39 81 1.10 255 0.90 0.67 79 0.53 251 1.27 0.85 77 0.64 244 注:流速为垂向平均流速。 表 2 研究区沉积物活动频率统计
Table 2. Statistics of sediment activity frequency in study area
% 区域 大潮 小潮 中潮1 中潮2 中潮3 日平均 北岸 59.8(0~92.3) 27.9(0~69.2) 32.4(0~73.1) 55.3(0~92.3) 34.5(0~84.6) 46.2(0~83.4) 南岸 44.3(0~92.3) 15.9(0~69.2) 17.2(0~80.8) 42.2(0~92.3) 20.3(0~73.1) 32.1(0~81.4) 中央水道 64.5(19.2~92.3) 20.6(0~57.7) 20.4(0~69.2) 64.3(19.2~88.5) 13.7(0~65.4) 43.3(11.5~77.7) 外罗水道 81(34.6~96.2) 41.4(11.5~57.7) 41.8(15.4~69.2) 74(23.1~88.5) 43.6(11.5~80.8) 62.1(22.8~81.2) 西北水道 73.3(34.6~84.6) 30.2(0~57.7) 23.2(0~50) 71.3(34.6~84.6) 19.5(0~38.5) 50.6(19.1~67.2) 北水道 63.5(46.2~76.9) 5.6(0~30.8) 7.2(0~23.1) 60.3(42.3~76.9) 0.5(0~19.2) 35.9(24.5~53) 中水道 65.2(46.2~76.9) 17.4(0~46.2) 13.6(0~26.9) 65.3(50~80.8) 1.7(0~30.8) 40.2(26.4~58) 南水道 43.6(19.2~80.8) 6.8(0~69.2) 6.1(0~61.5) 46.6(23.1~76.9) 5.5(0~38.5) 27.5(11.5~65.1) 罗斗沙附近 76.8(26.9~100) 34.1(0~73.1) 37.8(0~88.5) 70(19.2~96.2) 39.3(0~92.3) 57.5(13.4~90.7) 西方浅滩 74.7(53.8~88.5) 30.8(0~65.4) 20.3(0~53.8) 74.4(53.8~88.5) 12.8(0~50) 50.1(31~73.8) 西南浅滩 65.4(26.9~84.6) 22.1(0~57.7) 17.1(0~50) 64.7(26.9~84.6) 9.5(0~50) 42.7(14.8~70.2) 西北浅滩 82.8(53.8~96.2) 31.5(0~65.4) 27.1(0~65.4) 74(46.2~92.3) 22.3(0~84.6) 55.3(27.8~84.9) 北方浅滩 71.1(23.1~88.5) 16.6(0~50) 15.9(0~38.5) 65.6(19.2~80.8) 11.1(0~50) 44.1(11.8~67) 南方浅滩 66.8(30.8~84.6) 21.1(0~65.4) 14.3(0~34.6) 66.7(23.1~84.6) 5.2(0~73.1) 42.3(15.1~74.4) 出水浅滩 60.4(11.5~96.2) 22.6(0~76.9) 14.6(0~76.9) 59.7(11.5~100) 11.9(0~80.8) 40.2(6.3~86.1) 开阔陆架 65.3(19.2~92.3) 4.6(0~34.6) 9.6(0~46.2) 52.6(0~80.8) 19.8(0~53.8) 38.7(9.1~67.6) 全区 62.9(0~100) 18(0~76.9) 18.5(0~88.5) 57.6(0~100) 18.8(0~92.3) 41.7(0~90.7) 注:数据表示均值(最小值~最大值)。 表 3 研究区侵蚀淤积速率特征统计
Table 3. Statistics of erosion and deposition rate in the study area
特征值 不同潮汐类型侵蚀淤积量/(cm/d) 日均侵蚀淤积量/(cm/d) 年侵蚀淤积量/(cm/a) 大潮 小潮 中潮1 中潮2 中潮3 平均数 0.00102 0.00004 0.00022 0.00082 0.00013 0.00057 0.20863 中位数 − 0.00054 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 − 0.00020 − 0.07340 最小值 − 2.08843 − 0.54655 − 0.53615 − 1.80270 − 0.25010 − 1.09263 − 398.81111 最大值 2.36847 0.41282 0.40163 2.33750 0.34063 1.25446 457.87946 百分位数 10 − 0.14674 − 0.01115 − 0.01454 − 0.11016 − 0.00448 − 0.07459 − 27.22413 25 − 0.03242 − 0.00157 − 0.00208 − 0.02635 − 0.00034 − 0.01741 − 6.35376 50 − 0.00054 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 − 0.00020 − 0.07340 75 0.03304 0.00146 0.00204 0.02611 0.00035 0.01707 6.22959 90 0.15087 0.01251 0.01473 0.12669 0.00498 0.08111 29.60375 -
[1] HUTHNANCE J M. On one mechanism forming linear sand banks[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,1982,14:79-99. doi: 10.1016/S0302-3524(82)80068-6
[2] 高抒,方国洪,于克俊,等. 沉积物输运对砂质海底稳定性影响的评估方法及应用实例[J]. 海洋科学集刊,2001,43:25-37.
GAO Shu,FANG Guohong,YU Kejun,et al. Methodology for evaluating the stability of sandy seabed controlled by sediment movement,with an example of application[J]. Studia Marina Sinica,2001,43:25-37.
[3] 杜晓琴,李炎,高抒. 台湾浅滩大型沙波、潮流结构和推移质输运特征[J]. 海洋学报,2008,30(5):124-136. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2008.05.017
DU Xiaoqin,LI Yan,GAO Shu. Characteristics of the large-scale sandwaves,tidal flow structure and bedload transport over the Taiwan Bank in southern China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2008,30(5):124-136. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2008.05.017
[4] 陆永军,季荣耀. 潮汐通道系统动力地貌演变的数值模拟研究进展[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2009,31(2):93-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2009.02.017
LU Yongjun,JI Rongyao. Advances in morphodynamic modeling of tidal inlet systems[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering,2009,31(2):93-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2009.02.017
[5] 吴自银,金翔龙,曹振轶,等. 东海陆架沙脊分布及其形成演化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2010,40(2):188-198.
WU Ziyin,JIN Xianglong,CAO Zhentie,et al. Distribution and evolution of sand ridges on the East China Sea Shelf [J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2009,31(2):93-104.
[6] 倪文斐,汪亚平,邹欣庆,等. 南黄海辐射沙脊群苦水洋海域的沉积动力特征及稳定性研究[J]. 海洋通报,2013,32(6):668-677. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.06.009
NI Wenfei,WANG Yaping,ZOU Xinqing,et al. Study on the sediment dynamics and stability of the Kushuiyang tidal channel at radial sand ridges in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin,2013,32(6):668-677. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.06.009
[7] YUAN B,HUIB E S,CARLES P. Modeling the finite-height behavior of offshore tidal sand ridges,a sensitivity study[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2017,137:72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.02.007
[8] 周洁琼. 台湾浅滩多尺度海底沙波特征、迁移规律及动力机制研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2019.
ZHOU Jieqiong. Characteristics,migration and dynamic mechanism of multi-scale sand waves in the Taiwan Banks[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2019
[9] 陈沈良. 琼州海峡南岸海岸动力地貌研究[J]. 热带海洋,1998,17(3):35-42.
CHEN Shenliang. Coastal dynamic geomorphological researches on south coast of Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Tropic Oceanology,1998,17(3):35-42.
[10] 李占海,柯贤坤. 琼州海峡潮流沉积物通量初步研究[J]. 海洋通报,2000,19(6):42-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2000.06.007
LI Zhanhai,KE Xiankun. Prelimary study on tidally-induced sediment fluxes of the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Marine Science Bulletin,2000,19(6):42-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2000.06.007
[11] 刘振夏,夏东兴. 中国近海潮流沉积沙体[M]. 北京:海洋出版社,2004 :185-189.
LIU Zhenxia,XIA Dongxing. Tidal sands in the China seas[M]. Beijing:Ocean Press,2004 :42-63.
[12] 赵焕庭,王丽荣,袁家义. 琼州海峡成因与时代[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,27(2):33-40.
ZHAO Huanting,WANG Lirong,YUAN Jiayi. Origin and time of Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2007,27(2):33-40.
[13] 刘振夏,夏东兴,王揆洋. 中国陆架潮流沉积体系和模式[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1998,29(2):141-147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1998.02.006
LIU Zhenxia,XIA Dongxing,WANG Kuiyang. Tidal depositional system and patterns of China’s continental shelf[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,1998,29(2):141-147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1998.02.006
[14] 仝长亮,陈飞,张匡华. 海南岛东北部海域海砂资源分布特征及开发前景分析[J]. 中国矿业,2019,28(1):58-65.
TONG Changliang,CHEN Fei,ZHANG Kuanghua. Analysis on the distribution and development of marine sand resources in the northeast sea of Hainan Island[J]. China Mining Magzine,2019,28(1):58-65.
[15] 仝长亮,张匡华,陈飞,等. 海南岛北部海域海砂资源潜力评价[J]. 中国地质,2020,47(5):1567-1576.
TONG Changliang,ZHANG Kuanghua,CHEN Fei,et al. The potential evaluation of marine sand resources in the northern sea areas of Hainan Island[J]. Geology in China,2020,47(5):1567-1575.
[16] CHENG H Q,LI J F,YIN D W,et al. Nearshore bedform instability in the eastern entrance to the Qiongzhou Strait,South China Sea[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science,2008,2(3):283-291. doi: 10.1007/s11707-008-0047-4
[17] NI Y G,ENDLER R,XIA Z,et al. The “butterfly delta” system of Qiongzhou Strait:morphology,seismic stratigraphy and sedimentation[J]. Marine Geology,2014,355:361-368. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.001
[18] 仝长亮,黎刚,陈飞,等. 海南岛东北部海域海砂资源特征及成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(1):12-19.
TONG Changliang, LI Gang,CHEN Fei, et al. Geological characteristics and origin of marine sands in the northeast sea off Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2018,34(1):12-19.
[19] 仝长亮,王华强,覃茂刚,等. 琼州海峡东口潮流沙脊表层沉积物特征及沉积环境划分[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2022,41(4):625-636.
TONG Changliang, WANG Huangqiang,QIN Maogang,et al. Sediment characteristics and sedimentary environment division of tidal sand ridge at the east entrance of Qiongzhou Strait [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography,2018,41(4):625-636.
[20] 侍茂崇. 北部湾环流研究述评[J]. 广西科学,2014,21(4):313-324.
SHI Maochong. Study comments on circulation of Beibu Gulf[J]. Guangxi Science,2014,21(4):313-324.
[21] 高抒,贾建军,于谦. 沉海岸冲淤动态的理论分析:物质收支、剖面形态、岸线进退[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(2):1-17.
GAO Shu,JIA Jianjun,YU Qian. Theoretical framework for coastal accretion-erosion analysis:material budgeting,profile morphology,shoreline change[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023,43(2):1-17.
[22] TONG C L,QIN M G,WANG X M,et al. Estimation of the spring tide bedload transport at the eastern entrance of the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Water,2023,15:724. doi: 10.3390/w15040724
[23] HARDISTY J. An assessment and calibration of formulations for Bagnold's bedload equation[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1983,53:1007-1010.
[24] SOULSBY R L. Dynamics of Marine Sands[M]. London:Thomas Telford Services Limited,1997:249.
[25] MILLER M C,MCCAVE I N,KOMAR P D. Threshold of sediment motion under unidirectional currents[J]. Sedimentology,1977,24:507-527. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1977.tb00136.x
[26] WANG Y P,GAO S. Modification to the Hardisty equation,regarding the relationship between sediment transport rate and particle size[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2001,71(1):118-121. doi: 10.1306/032100710118
[27] FOLK R L,ANDREWS P B,LEWIS D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,1970,13(4):937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[28] ZHANG Y,YE F,STANEV E V,et al. Seamless cross-scale modeling with SCHISM[J]. Ocean Modelling,2016,102:64-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2016.05.002
[29] 仝长亮,朱钰,吴祥柏,等. 基于数值模拟的琼州海峡东口推移质输运量估算[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(5):553-566.
TONG Changliang,ZHU Yu,WU Xiangbo,et al. Bedload transport estimation at the east entrance of Qiongzhou Strait based on numerical simulation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2023,30(5):553-566.
[30] 仝长亮,王华强,张匡华,等. 海洋测绘在西南浅滩海砂资源探测中的应用[J]. 海洋测绘,2022,42(3):38-42.
TONG Changliang,WANG Huaqiang,ZHANG Kuanghua,et al. Application of marine surveying and mapping in marine sand resource exploration in southwest shoal of Hainan Province[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting,2022,42(3):38-42.
[31] 陈达森,陈波,严金辉,等. 琼州海峡余流场季节性变化特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2006,28(2):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.02.003
CHEN Dasen,CHEN Bo,YAN Jinhui,et al. The seasonal variation characteristics of residual currents in the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology,2006,28(2):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2006.02.003
[32] 赵昌,吕新刚,乔方利. 北部湾潮波数值研究[J]. 海洋学报,2010,32(4):1-11.
ZHAO Chang,LYU Xingang,QIAO Fangli. Numerical study of the tidal waves in the Gulf of Tonkin[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2010,32(4):1-11.
[33] 夏综万,廖世智,冯砚青. 粤东甲子海域潮波异常和南海北部潮波的传播[J]. 海洋学报,2013,35(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2013.01.001
XIA Zongwan,LIAO Shizhi,FENG Yanqing. Traveling of tidal wave in the north part of the South China Sea and the tidal energy divergence appearing in the area of Jiazi Station[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2013,35(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2013.01.001
[34] 任叙合,尤启明,郭静,等. 海南岛东北海域海流和余流特征分析[J]. 广西科学,2018,25(4):418-422.
REN Xuhe,YOU Qiming,GUO Jing,et al. Characteristics analysis of current and residual current in the northeastern sea area of Hainan Island[J]. Guangxi Sciences,2018,25(4):418-422.
[35] 侍茂崇,陈春华,黄方,等. 琼州海峡冬末春初潮余流场特征[J]. 海洋学报,1998,20(1):1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.1998.01.001
SHI Maochong,CHEN Chunhua,HUANG Fang,et al. Characteristics of tidal current and residual current in the Qiongzhou Straits in period between end of winter and beginning of spring[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,1998,20(1):1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.1998.01.001
[36] 陈妙红,高抒,邹欣庆,等. 海南博鳌港枯水期海底活动性的初步研究[J]. 海洋通报,2002,21(6):39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.06.006
CHEN Miaohong,GAO Shu,ZOU Xinqing,et al. Preliminary study on seabed mobility during low river discharge periods,Boao Harbour,Hainan Island[J]. Marine Science Bulletin,2002,21(6):39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.06.006
[37] 田壮才,郭秀军,乔路正,等. 南海北部海底沉积物临界起动流速空间分布特征分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(S2):4287-4294.
TIAN Zhuangcai,GUO Xiujun,QIAO Luzheng,et al. Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics of seabed sediments critical starting velocity in the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(S2):4287-4294.
[38] 郑淑贤. 基于FVCOM的琼州海峡潮汐潮流数值模拟与研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学,2015.
ZHENG Shuxian. Numerical simulation of tide and tidal currents in the Qiongzhou Strait based on FVCOM[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China,2015.
[39] CHEN C L,LI P L,SHI M C,et al. Numerical study of the tides and residual currents in the Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology,
[40] 储鏖,徐怡,陈永平,等. 潮致泥沙全沙净输运解析模式[J]. 海洋工程,2020,38(4):61-72.
CHU Ao,XU Yi,CHEN Yongping,et al. Analytical model for tidal-induced net sediment transport[J]. The Ocean Engineering,2020,38(4):61-72.
[41] 程和琴,胡红兵,蒋智勇,等. 琼州海峡东口底形平衡域谱分析[J]. 海洋工程,2003,21(4):97-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2003.04.016
CHENG Heqin,HU Hongbing,JIANG Zhiyong,et al. Equilibrium range spectra analysis of nearshore bedforms in the East Qiongzhou Strait[J]. The Ocean Engineering,2003,21(4):97-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2003.04.016
[42] 肖政,蒋昌波,夏波. 琼州海峡罗斗沙岛岸滩演变分析[J]. 水道港口,2007,28(1):16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2007.01.004
XIAO Zheng,JIANG Changbo,XIA Bo. Analysis of the beach evolvement near Luodousha Island in Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor,2007,28(1):16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2007.01.004
[43] 董志华. 台风对东方岸外沙波沙脊和海底地貌的影响[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学,2004.
DONG Zhihua. The influence on current ridge,sand wave and topography of Dongfang offshore by typhoon[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China,2004.
[44] 陈宜展. 南海海洋响应台风过程数值研究[D]. 广州:中山大学,2010.
CHEN Yizhan. Numerical study of the response of the South China Sea to typhoon[D]. Guangzhou:Sun Yat-sen University,2010.
[45] 周其坤,孙永福,胡光海,等. 南海北部海底沙波迁移规律及其在台风作用下的响应研究[J]. 海洋学报,2018,40(9):78-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.007
ZHOU Qikun,SUN Yongfu,HU Guanghai,et al. Research on the migration rule and the typhoon impact on the submarine sand waves of the northern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao,2018,40(9):78-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.09.007
-



 下载:
下载: