A numerical simulation study for controlling seawater intrusion by using hydraulic and physical barriers
-
摘要:
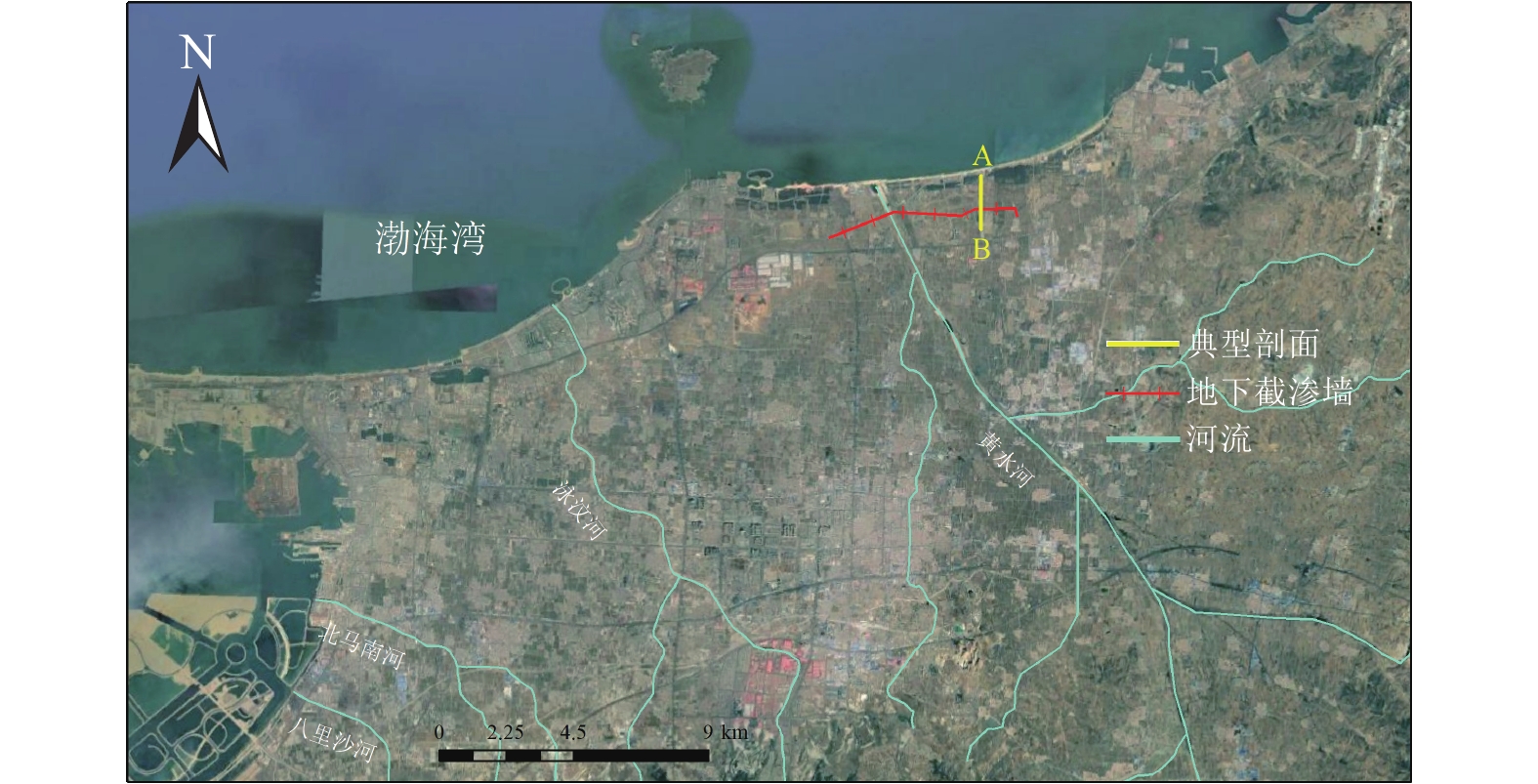
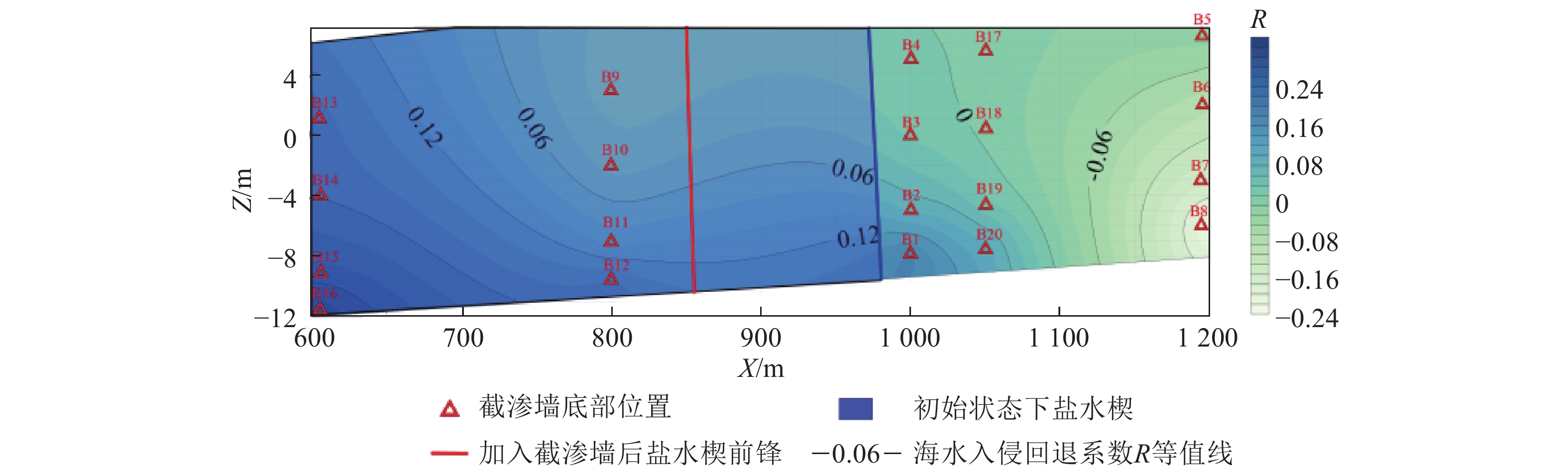
基于SEAWAT-2000程序构建室内二维砂箱试验中咸水入侵数值模型,利用该模型分析了针对不同补给井井位、补给井流量、截渗墙位置及贯穿深度等多种情景下的咸淡水界面运移规律。二维砂箱实验模拟结果表明,当注水井位于盐水楔前锋附近,距咸水边界40 cm、砂箱顶部边界5 cm处时,注水井工程措施能达到最佳海水入侵驱退效果,回退系数达21.5%。当截渗墙布设于距咸水边界10 cm处,贯穿深度为35 cm时,截渗墙工程措施能达到最佳海水入侵驱退效果,回退系数达81.1%。在此基础上,结合实际场地条件,构建山东龙口地区滨海含水层中某典型二维剖面的海水入侵数值模型,探讨了不同截渗墙布设情景模式下海水入侵状况。模拟结果表明,当截渗墙布设于距海岸线600 m处,贯穿深度为18 m时,截渗墙工程措施达到最佳海水入侵驱退效果,回退系数达28.4%。研究结果揭示了补给井井位、补给井流量、截渗墙位置及贯穿深度等因素对咸淡水界面运移规律的影响,可为场地条件下滨海含水层海水入侵防治中的工程管理措施优化提供参考依据。
Abstract:Seawater intrusion (SI) has become a global concern for groundwater environment. SI not only seriously threatens freshwater resources in coastal aquifers, but also undermines the balance of coastal ecosystem and further restricts the socioeconomic development. This paper simulates the SI process in a 2D synthetic aquifer constructed from sandbox experiment using the simulator SEAWAT-2000. The transport phenomenon of the brackish water interface is investigated by altering the location and injection rate of a recharge well and the layout of the physical barrier. The results show that when the recharge well is located near the toe of the salt water wedge of 40 cm from the coastline and 5 cm from the surface, the optimal performance of the recharge scheme is achieved with the repulsion rate up to 21.5%. When the physical barrier is located 10 cm from the coastline and the penetration depth is 35 cm, the toe of saltwater wedge is effectively driven to the coastline with the repulsion rate up to 81.8%. Moreover, we simulate the variable-density groundwater flow and transport in a typical two-dimensional section of coastal aquifer in the Longkou District of Shandong Province. The SI model is established to evaluate the influences of different management schemes (i.e., physical barrier and recharge well) on the prevention of seawater intrusion. The results show that when the physical barrier is located 600 m from the coastline and the penetration depth is 18 m, the toe of salt water wedge is effectively driven back to the coastline with the repulsion rate up to 28.4%. The results reveal the influence of hydraulic and physical barriers under different settings on the migration rule of the brackish water interface. The findings may provide insights into the optimization suggestions for coastal groundwater management under site conditions.
-
Key words:
- seawater intrusion /
- numerical simulation /
- SEAWAT-2000 /
- flow barrier /
- physical barrier /
- recharge well
-

-
表 1 理想砂箱试验地下水数值模型主要参数[26]
Table 1. Input parameters for the numerical model of the ideal sandbox
参数 参数值 有效孔隙度θ 0.4 渗透系数K/(cm·s−1) 1.31 纵向弥散度αL/cm 0.1 横向弥散度αT/cm 0.01 分子扩散系数D/(cm2·s−1) 1×10−5 表 2 山东龙口地区典型剖面地下水数值模型参数
Table 2. Input parameters used in the numerical model for the typical profile in Longkou
参数 参数值 水平渗透系数Kx/(m·d−1) 85 垂向渗透系数Kz/(m·d−1) 0.85 纵向弥散度αL/m 50 横向弥散度αT/m 5 给水度 0.01 贮水系数 1×10−5 -
[1] WERNER A D. On the classification of seawater intrusion[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2017,551:619 − 631. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.012
[2] 李雪, 叶思源. 海水入侵调查方法研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(6):211 − 217. [LI Xue, YE Siyuan. Progress in seawater intrusion[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2016,36(6):211 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] WERNER A D, BAKKER M, POST V E A, et al. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2013,51:3 − 26. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.03.004
[4] KETABCHI H, MAHMOODZADEH D, ATAIEASHTIANI B, et al. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2016,535:235 − 255. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.01.083
[5] SHERIF M M, SINGH V P. Effect of climate change on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers[J]. Hydrological Processes,1999,13(8):1277 − 1287. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19990615)13:8<1277::AID-HYP765>3.0.CO;2-W
[6] NAEEM M F A A, YUSOFF I, NG T F, et al. A study on the impact of anthropogenic and geogenic factors on groundwater salinization and seawater intrusion in Gaza coastal aquifer, Palestine: An integrated multi-techniques approach[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,2019,156:75 − 93. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.05.006
[7] 王玉广, 王传珺, 刘志华, 等. 地下水位和海平面变化对绥中砂质海岸海水入侵影响[J]. 海洋环境科学,2019,38(3):347 − 352. [WANG Yuguang, WANG Chuanjun, LIU Zhihua, et al. Impact to the the seawater intrusion around sand Coast in Suizhong with the variations of groundwater level and sea level[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2019,38(3):347 − 352. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190305
[8] BADARUDDIN S, WERNER A D, MORGAN L K. Water table salinization due to seawater intrusion[J]. Water Resources Research,2015,51(10):8397 − 8408. doi: 10.1002/2015WR017098
[9] WERNER A D, SIMMONS C T. Impact of sea-level rise on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers[J]. Groundwater,2009,47(2):197 − 204. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2008.00535.x
[10] 崔相飞, 周训, 徐中平, 等. 海岸带咸淡水界面的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):29 − 35. [CUI Xiangfei, ZHOU Xun, XU Zhongping, et al. Advances in research on the fresh water-salt water interface in coastal zones[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):29 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] ZHOU X, SONG C, LI T. Estimation of the inland extending length of the freshwater-saltwater interface in coastal unconfined aquifers[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal,2016,61(13):2367 − 2375. doi: 10.1080/02626667.2015.1111516
[12] 赵洁, 林锦, 吴剑锋, 等. 大连周水子海水入侵区地下水多目标优化管理模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):25 − 32. [ZHAO Jie, LIN Jin, WU Jianfeng, et al. A multi-objective simulation-optimization model for optimal control of seawater intrusion in the Zhoushuizi district of Dalian[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] JAVADI A, HUSSAIN M, SHERIF M, et al. Multi-objective optimization of different management scenarios to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers[J]. Water Resources Management,2015,29(6):1843 − 1857. doi: 10.1007/s11269-015-0914-1
[14] 梁越, 陈建生, 陈亮. 注水井水力帷幕防治海水入侵的机理与应用[J]. 长江科学院院报,2009,26(10):133 − 136. [LIANG Yue, CHEN Jiansheng, CHEN Liang. Mechanism and application of water injecting hydraulic curtain stopping seawater intrusion[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2009,26(10):133 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2009.10.031
[15] ARMANUOS A M, AL-ANSARI N, YASEEN Z M. Assessing the effectiveness of using recharge Wells for controlling the saltwater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers with sloping beds: numerical study[J]. Sustainability,2020,12(7):2685. doi: 10.3390/su12072685
[16] 武雅洁, 冯峰, 雷鑫. 地下截渗墙影响下的咸水入侵规律研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(8):131 − 138. [WU Yajie, FENG Feng, LEI Xin. Study on the behavior of saltwater intrusion under the installation of subsurface cutoff wall[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2018,48(8):131 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] EBELING P, HÄNDEL F, WALTHER M. Potential of mixed hydraulic barriers to remediate seawater intrusion[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,693:133478. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.284
[18] KALERIS V K, ZIOGAS A I. The effect of cutoff walls on saltwater intrusion and groundwater extraction in coastal aquifers[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2013,476:370 − 383. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.007
[19] ABDOULHALIK A, AHMED A, HAMILL G A. A new physical barrier system for seawater intrusion control[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2017,549:416 − 427. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.04.005
[20] ALLOW K A. The use of injection wells and a subsurface barrier in the prevention of seawater intrusion: a modelling approach[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2012,5(5):1151 − 1161. doi: 10.1007/s12517-011-0304-9
[21] JANARDHANA M R, KHAIRY H. Simulation of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: a case study on the Amol–Ghaemshahr coastal aquifer system, Northern Iran[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(24):1 − 19.
[22] CHANG Y W, HU B X, XU Z X, et al. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2018,215:1 − 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2018.06.002
[23] 陈开荣, 陈汉宝, 赵海亮. 基于SEAWAT的海水入侵数值模拟[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2012,23(6):140 − 145. [CHEN Kairong, CHEN Hanbao, ZHAO Hailiang. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of seawater intrusion based on SEAWAT[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2012,23(6):140 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] LANGEVIN C D, THORNE JR D T, DAUSMAN A M, et al. SEAWAT version 4: a computer program for simulation of multi-species solute and heat transport[R]. Reston: United state Geological Survey, 2008.
[25] SIMPSON M J. SEAWAT-2000: variable-density flow processes and integrated MT3DMS transport processes[J]. Ground Water,2004,42(5):642 − 646. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2004.tb02717.x
[26] LUYUN R, MOMII K, NAKAGAWA K. Effects of recharge wells and flow barriers on seawater intrusion[J]. Groundwater,2011,49(2):239 − 249. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00719.x
-




 下载:
下载: