In-situ Fenton oxidation experiment of compound benzene pollutants in high salt and strong acid groundwater
-
摘要:
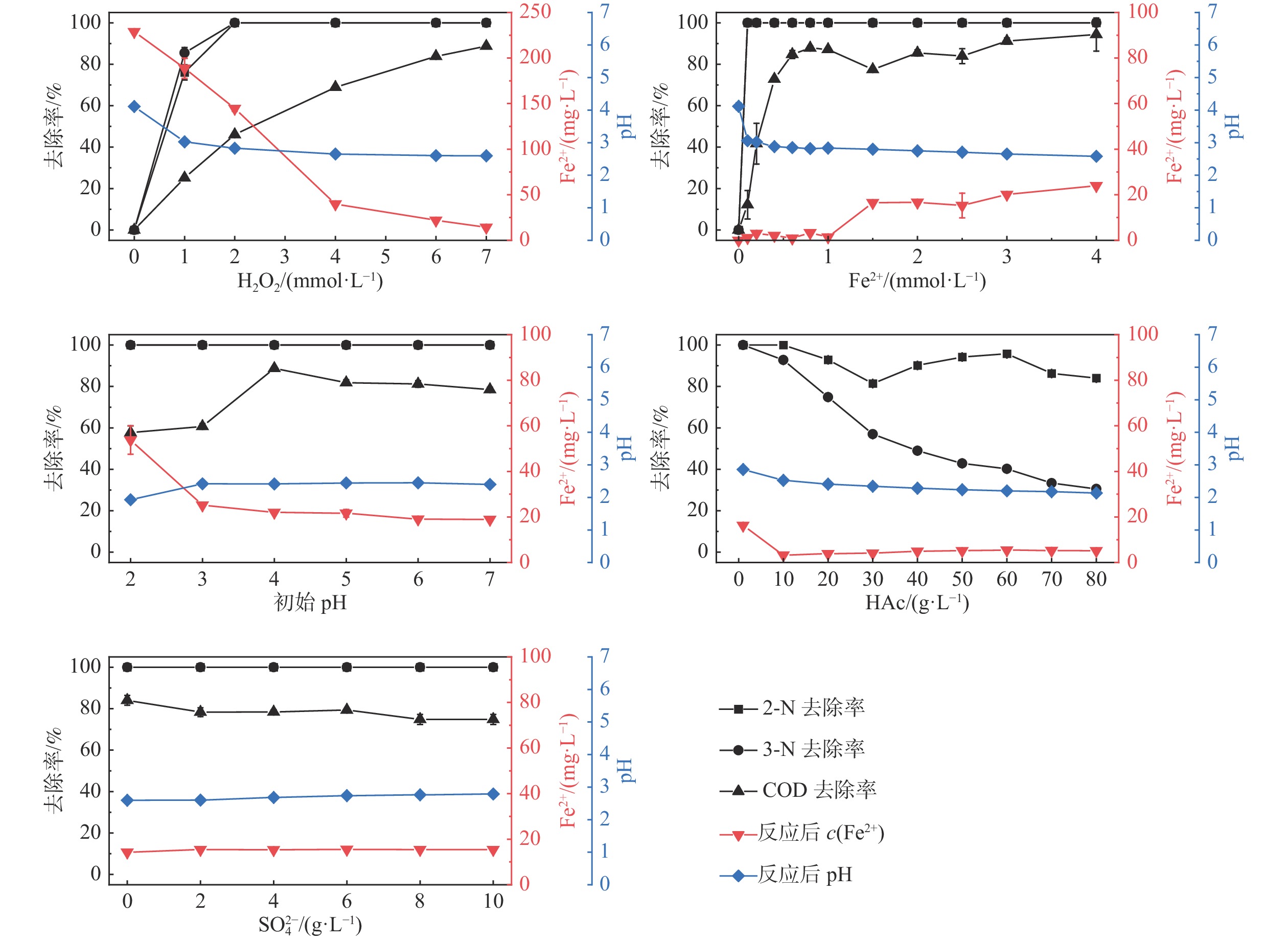
在原位氧化过程中,实际场地地下水和含水介质的物化特征是影响氧化效果的重要因素,而目前对此影响的研究较少。以某场地实际高盐强酸性复合苯系污染地下水为研究对象,以地下水中2-硝基-4-甲氧基苯胺(2-nitro-4-methoxyaniline,2-N)和3-硝基-4-甲氧基苯胺(3-nitro-4-methoxyaniline,3-N)为特征污染物,探究芬顿(Fenton)试剂原位氧化特征,并研究液相环境因素(初始H2O2浓度、初始Fe2+浓度、初始pH值、初始醋酸(Acetic acid,HAc)浓度、初始
< span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210203181048.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210203181048.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210203181048.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210203181118.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210203181118.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210203181118.png'/ > -
关键词:
- 芬顿 /
- 原位氧化 /
- 2-硝基-4-甲氧基苯胺 /
- 3-硝基-4-甲氧基苯胺 /
- 地下水污染 /
- 含水层介质
Abstract:In the process of in-situ oxidation, the physical and chemical characteristics of actual ground water and water-bearing media are the important factors affecting the oxidation effect, but there are few specific studies on this effect at present. The actual high-salt and strong-acid compound benzene contaminated groundwater in a certain site is used as the research object, and 2-nitro-4-methoxyaniline (2-N) and 3-nitro-4-methoxyaniline (3-N) in groundwater are characteristic pollutants. The in-situ oxidation characteristics of Fenton’s reagent are explored, and the liquid environmental factors (initial H2O2 concentration, initial Fe2+ concentration, initial pH value, initial acetic acid (HAc) concentration, initial
< span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112508.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112515.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112515.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112515.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112508.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112515.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112515.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='202012021_Z-20210310112515.png'/ > -

-
表 1 场地地下水特征污染物浓度
Table 1. Concentrations of the characteristic pollutants in groundwater of the site
指标 2-N/(mg·L−1) 3-N/(mg·L−1) HAc/(g·L−1) 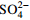 /(g·L−1)
/(g·L−1)
pH 浓度 32.78 60.58 1.06×104 4.04×103 4.18 表 2 实验方案概括表
Table 2. Summary of the experimental program
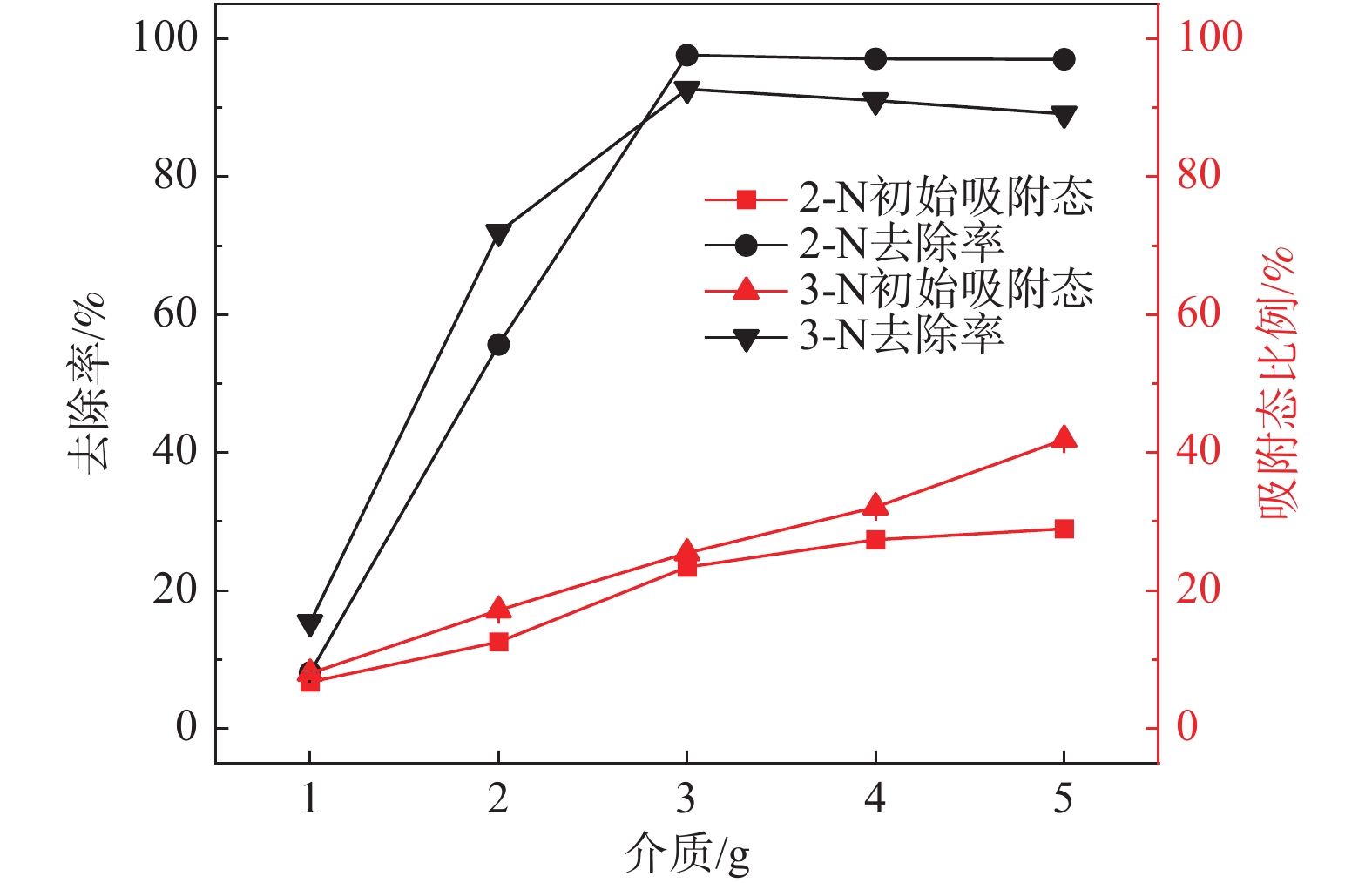
序号 实验类型 序号 实验内容 影响因素初始值( X) 1 纯液相环境 1.1 初始H2O2浓度的影响 c(H2O2)=0,1,2,4,6,7 mmol/L 1.2 初始Fe2+浓度的影响 c(Fe2+)=0,0.1,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1.0,1.5,2.0,2.5,3.0,4.0 mmol/L 1.3 初始pH值的影响 pH=2,3,4,5,6,7 1.4 初始HAc浓度的影响 c(HAc)=1,10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80 g/L 1.5 初始 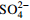 浓度的影响
浓度的影响
c( 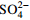 )=0,2,4,6,8,10 g/L
)=0,2,4,6,8,10 g/L
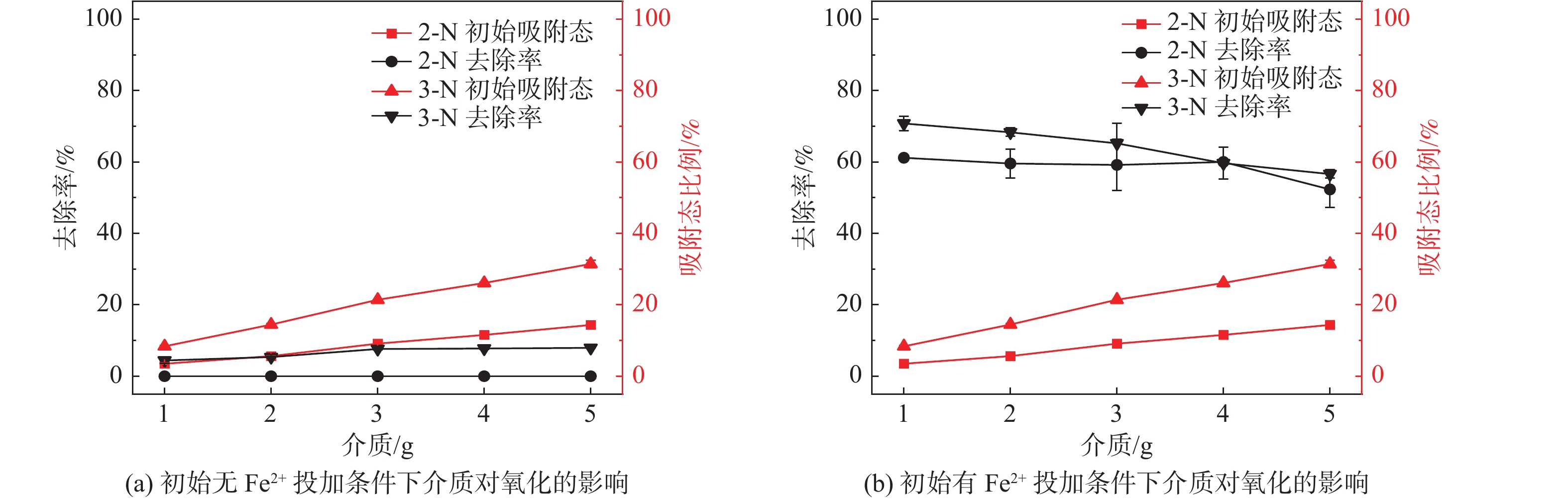
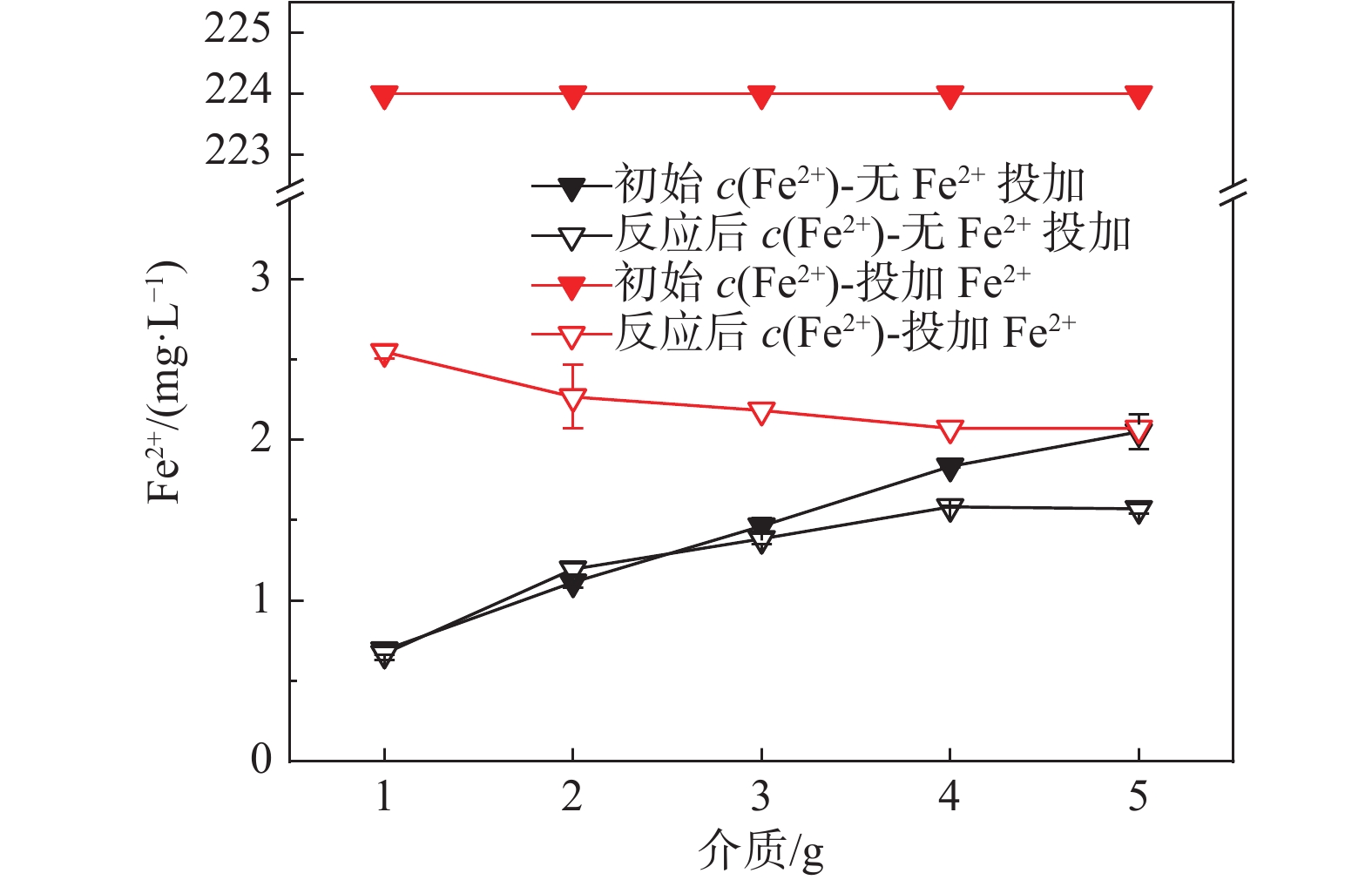
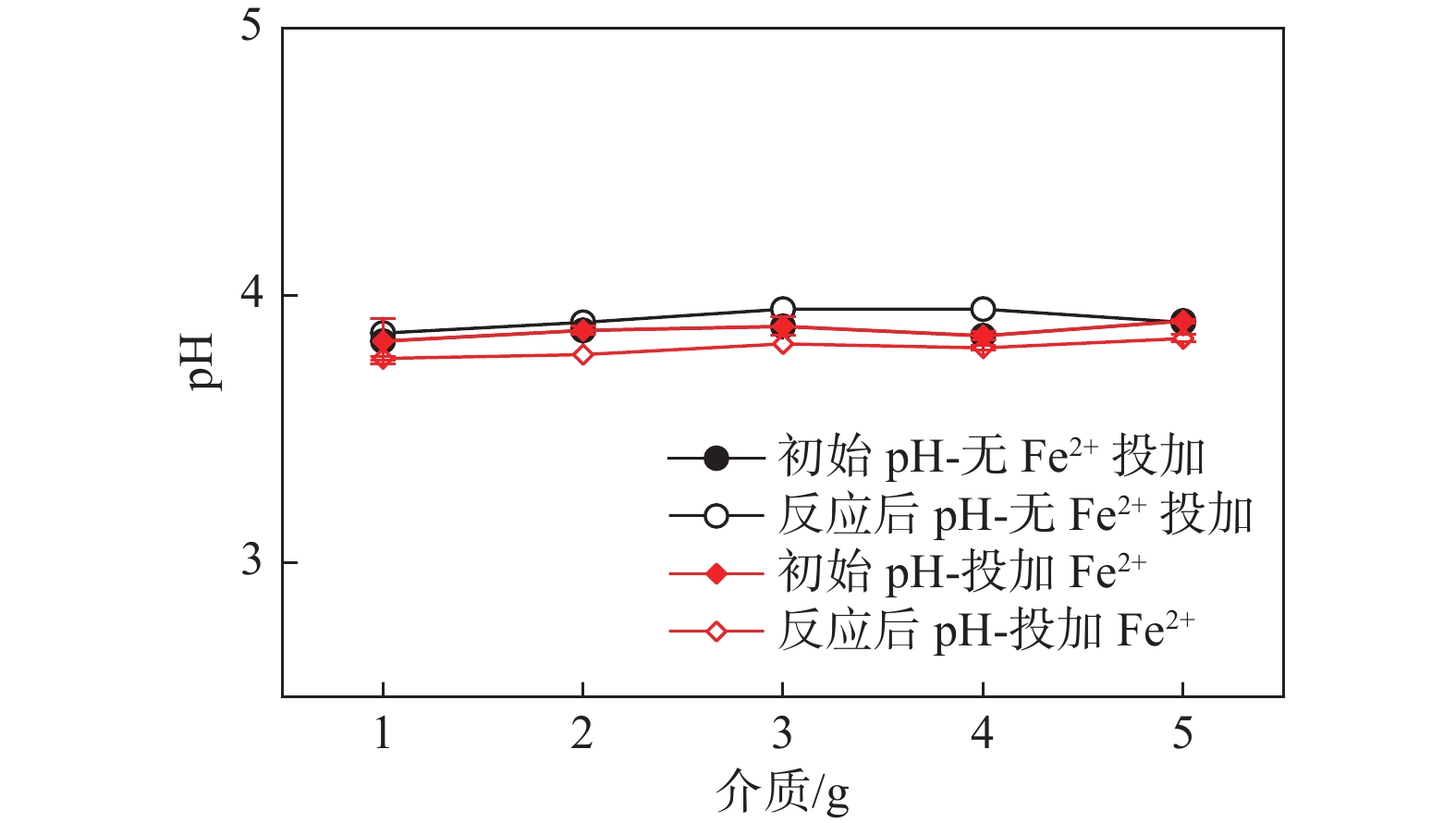
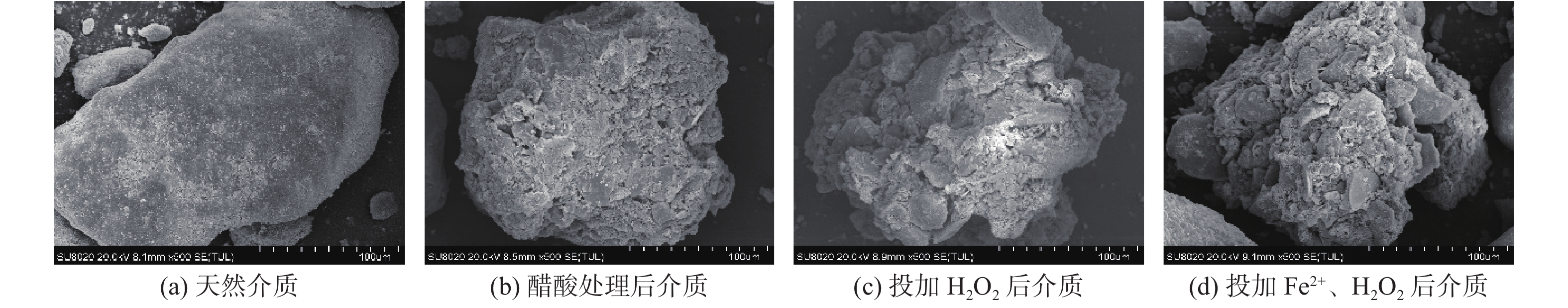
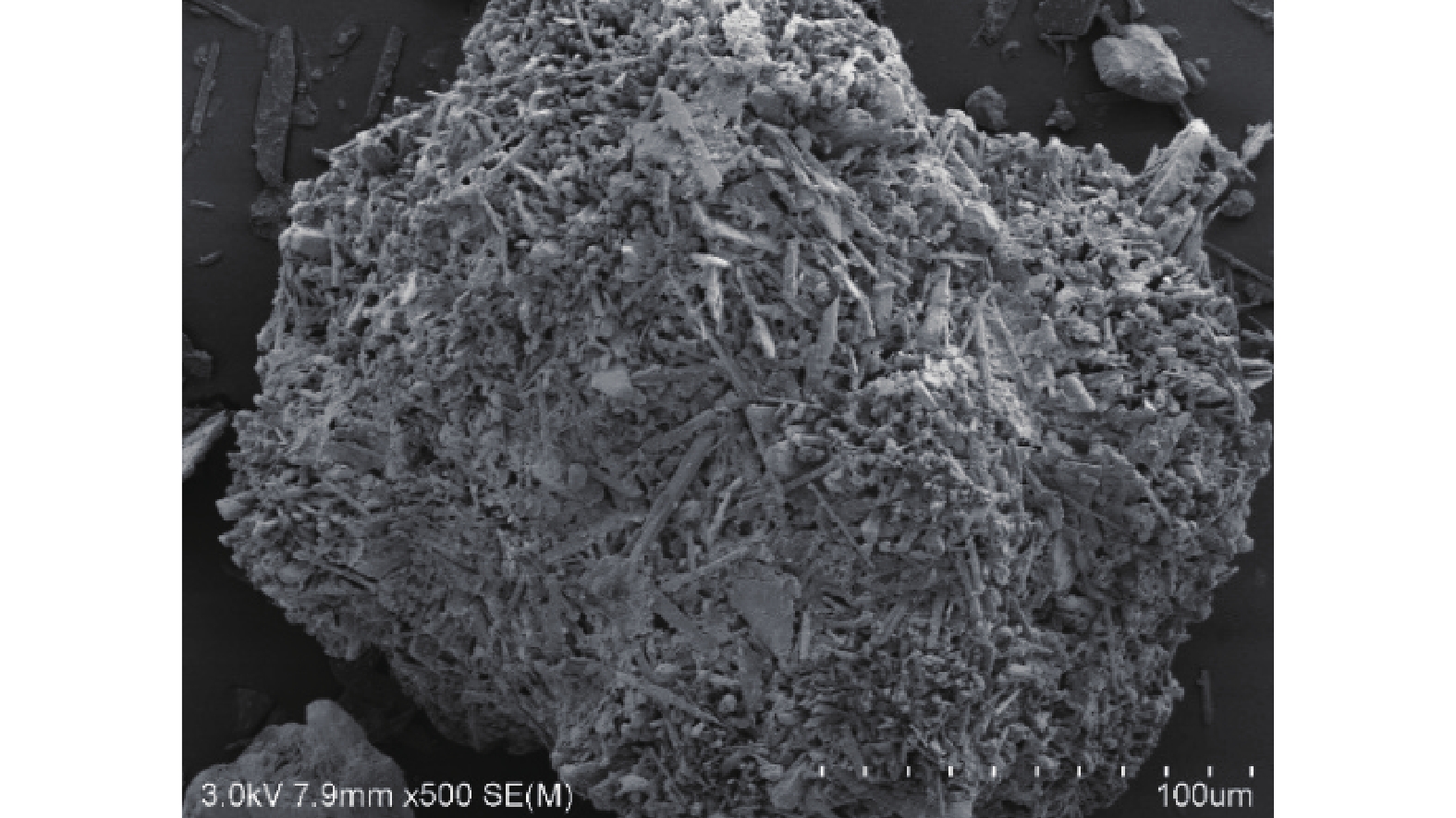
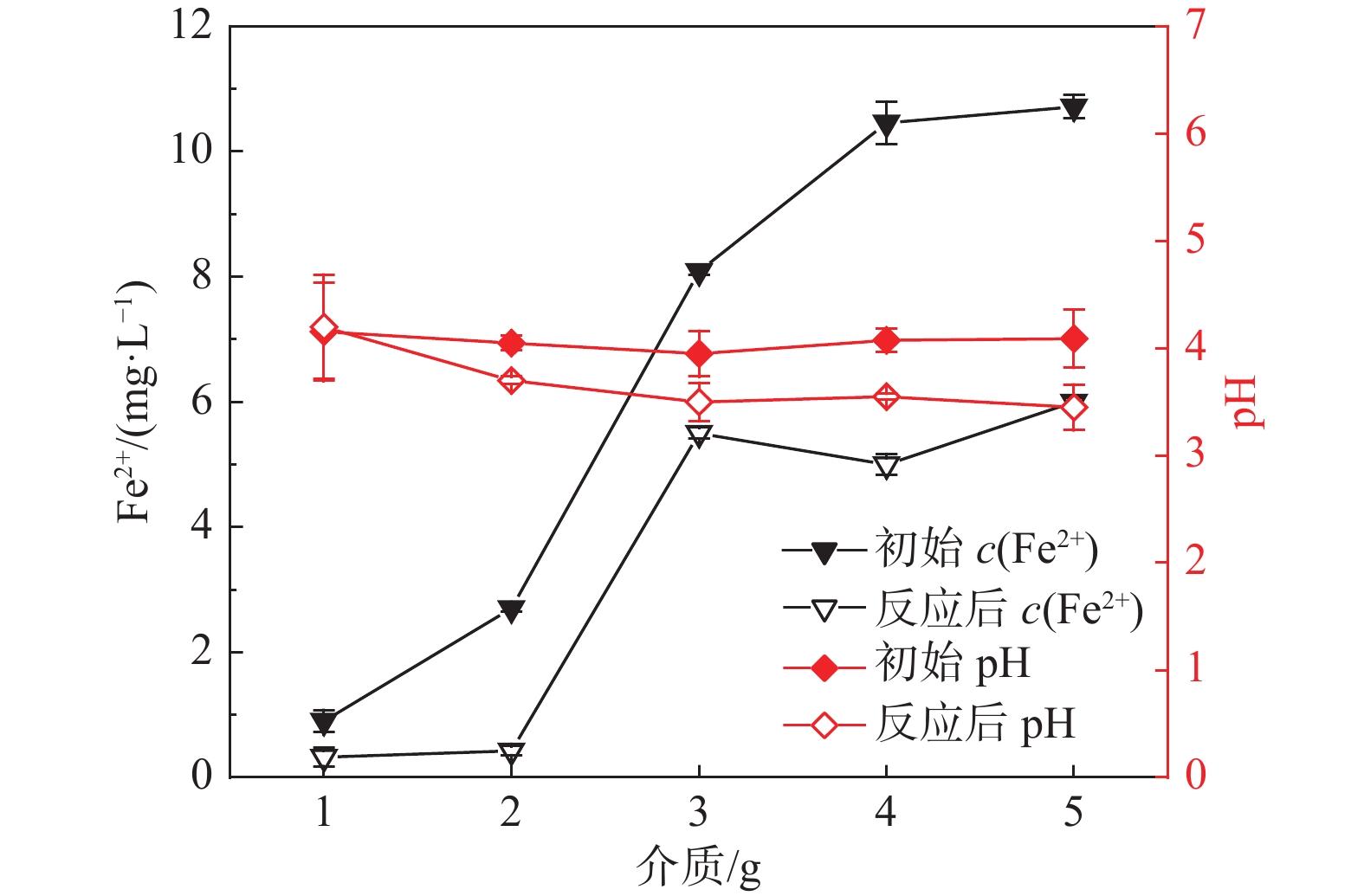
2 固液双相环境 2.1 醋酸环境介质影响-不加Fe2+ 介质质量:1,2,3,4,5 g 醋酸环境介质影响-添加Fe2+ 介质质量:1,2,3,4,5 g 2.2 硫酸环境介质影响实验 介质质量:1,2,3,4,5 g 表 3 各实验初始条件对照表
Table 3. Comparison of the initial conditions of each experiment
实验影响因素 2-N/(mg·L−1) 3-N/(mg·L−1) H2O2/(mmol·L−1) Fe2+/(mmol·L−1) pH HAc/(g·L−1) 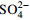 /(g·L−1)
/(g·L−1)
介质/g 初始H2O2浓度的影响 30 60 X 4 4 0 0 0 初始Fe2+浓度的影响 30 60 7 X 4 0 0 0 初始pH值的影响 30 60 7 4 X 0 0 0 初始HAc浓度的影响 30 60 7 4 4 X 0 0 初始 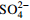 浓度的影响
浓度的影响
30 60 7 4 4 0 X 0 醋酸环境介质影响-不加Fe2+ 30 60 7 0 4 60 0 X 醋酸环境介质影响-添加Fe2+ 30 60 7 4 4 60 0 X 硫酸环境介质影响实验 30 60 7 0 4 0 9.6 X 注:表3中的X表示表2影响因素初始值一列中对应实验内容的数值。 表 4 含水层介质中各矿物质量占比
Table 4. Mass ratio of each mineral in the aquifer medium
矿物名称 石英 斜长石 微斜长石 云母 方解石 绿泥石 白云石 黄铁矿 质量百分比/% 43 26 9 9 5 4 3 1 -
[1] 方玲, 孟冠华, 魏旺, 等. 苯系染料中间体生产废水的处理技术现状与发展[J]. 染料与染色,2016,53(4):42 − 50. [FANG Ling, MENG Guanhua, WEI Wang, et al. Application status and development of treatment for wastewater from benzene-dye intermediates[J]. Dyestuffs and Coloration,2016,53(4):42 − 50. (in Chinese)
[2] GUO Y, XUE Q, CUI K P, et al. Study on the degradation mechanism and pathway of benzene dye intermediate 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline via multiple methods in Fenton oxidation process[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(20):10764 − 10775. doi: 10.1039/C8RA00627J
[3] 郭莹, 陈鸿汉, 张焕祯, 等. 基于Box-Behnken响应曲面法优化Fenton预处理高浓度染料中间体生产废水[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(5):775 − 783. [GUO Ying, CHEN Honghan, ZHANG Huanzhen, et al. Optimization of Fenton pre-treatment of high concentration dye intermediate wastewater based on box-behnken response surface methodology[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(5):775 − 783. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] TSUBOKURA Y, ASO S, KOGA T, et al. Combined repeated dose and reproductive/developmental toxicity screening test of 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline in rats[J]. Drug and Chemical Toxicology,2015,38(4):361 − 374. doi: 10.3109/01480545.2014.973962
[5] GUO Y, XUE Q, ZHANG H Z, et al. Treatment of real benzene dye intermediates wastewater by the Fenton method: characteristics and multi-response optimization[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(1):80 − 90. doi: 10.1039/C7RA09404C
[6] CONTRERAS R H, DE KOWALEWSKI D G, FACELLI J C. ChemInform abstract: the NMR analysis of the methoxy-group conformation in 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline[J]. Chemischer Informationsdienst,1982,13(31).
[7] AZHAGIRI S, JAYAKUMAR S, GUNASEKARAN S, et al. Molecular structure, Mulliken charge, frontier molecular orbital and first hyperpolarizability analysis on 2-nitroaniline and 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline using density functional theory[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2014,124:199 − 202. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.12.106
[8] ZHANG M H, DONG H, ZHAO L, et al. A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,670:110 − 121. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.180
[9] AMETA R, CHOHADIA A K, JAIN A, et al. Fenton and photo-Fenton processes[J]//Advanced Oxidation Processes for Waste Water Treatment. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 49-87.
[10] FERRENTINO R, MERZARI F, ANDREOTTOLA G. Optimisation of Fe2+/H2O2 ratio in Fenton process to increase dewaterability and solubilisation of sludge[J]. Environmental Technology,2020,41(22):2946 − 2954. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2019.1589583
[11] SUTTON N B, GROTENHUIS J T C, LANGENHOFF A A M, et al. Efforts to improve coupled in situ chemical oxidation with bioremediation: a review of optimization strategies[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2011,11(1):129 − 140. doi: 10.1007/s11368-010-0272-9
[12] CHAPELLE F H, BRADLEY P M, CASEY C C. Behavior of a chlorinated ethene plume following source-area treatment with Fenton's reagent[J]. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation,2005,25(2):131 − 141.
[13] 王平, 韩占涛, 张海领, 等. 某氨氮污染地下水体抽出-处理系统优化模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):34 − 43. [WANG Ping, HAN Zhantao, ZHANG Hailing, et al. Simulation and optimization of a pumping and treating system for the remediation of ammonia polluted groundwater[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):34 − 43. (in Chinese)
[14] JONSSON S, PERSSON Y, FRANKKI S, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in contaminated soils by Fenton's reagent: a multivariate evaluation of the importance of soil characteristics and PAH properties[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2007,149(1):86 − 96. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.057
[15] BERGENDAHL J, HUBBARD S, GRASSO D. Pilot-scale Fenton's oxidation of organic contaminants in groundwater using autochthonous iron[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2003,99(1):43 − 56. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00356-4
[16] 崔英杰, 杨世迎, 王萍, 等. Fenton原位化学氧化法修复有机污染土壤和地下水研究[J]. 化学进展,2008,20(7):1196 − 1201. [CUI Yingjie, YANG Shiying, WANG Ping, et al. Organically polluted soil and groundwater remediation by in situ Fenton oxidation[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2008,20(7):1196 − 1201. (in Chinese)
[17] AMBIKA S, DEVASENA M, MANIVANNAN NAMBI I. Assessment of meso scale zero valent iron catalyzed Fenton reaction in continuous-flow porous media for sustainable groundwater remediation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,334:264 − 272. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.046
[18] KANG N, LEE D S, YOON J. Kinetic modeling of Fenton oxidation of phenol and monochlorophenols[J]. Chemosphere,2002,47(9):915 − 924. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00067-X
[19] HANSSON H, KACZALA F, MARQUES M, et al. Photo-Fenton and Fenton oxidation of recalcitrant wastewater from the wooden floor industry[J]. Water Environment Research,2015,87(6):491 − 497. doi: 10.2175/106143015X14212658614559
[20] HAJIAN M, MIRBAGHERI S A, JAVID A H. Comparison of classical Fenton and Fenton-like using µ-ZVI processes for the degradation of cresol in the wastewater[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2018,109:132 − 138. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2018.21836
[21] 何正坤, 马小兰, 孙猛, 等. 地下水水化学成分对类Fenton法氧化硝基苯的影响[J]. 生态环境学报,2011,20(11):1731 − 1734. [HE Zhengkun, MA Xiaolan, SUN Meng, et al. Influences of chemical composition of groundwater on Fenton-like oxidation of nitrobenzene[J]. Ecology and Environment,2011,20(11):1731 − 1734. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.11.025
[22] 郭莹, 陈鸿汉, 张焕祯, 等. Fenton氧化降解2-硝基-4-甲氧基苯胺的特性和动力学特征[J]. 环境科学研究,2017,30(10):1613 − 1621. [GUO Ying, CHEN Honghan, ZHANG Huanzhen, et al. Characteristics and kinetics of oxidative degradation of 2-nitro-4-methoxyaniline by Fenton oxidation process[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2017,30(10):1613 − 1621. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 秦俊豪. 微摩尔H2O2介导的Fenton效应对几种污染物环境行为的影响[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016.
[QIN Junhao. Effect of micromolar hydrogen peroxide mediated Fenton-driven on environmental behavior of several environmental pollutants[D]. Guangzhou:South China Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
[24] 展惠英. 多环芳烃类污染物在黄土中的迁移转化[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2004.
ZHAN Huiying.Transfer and transform of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) in loess soils[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-






 下载:
下载: