Deformation and movement characteristics of debris flow landslide: A case study of the Shaziba landslide in Enshi, China
-
摘要:
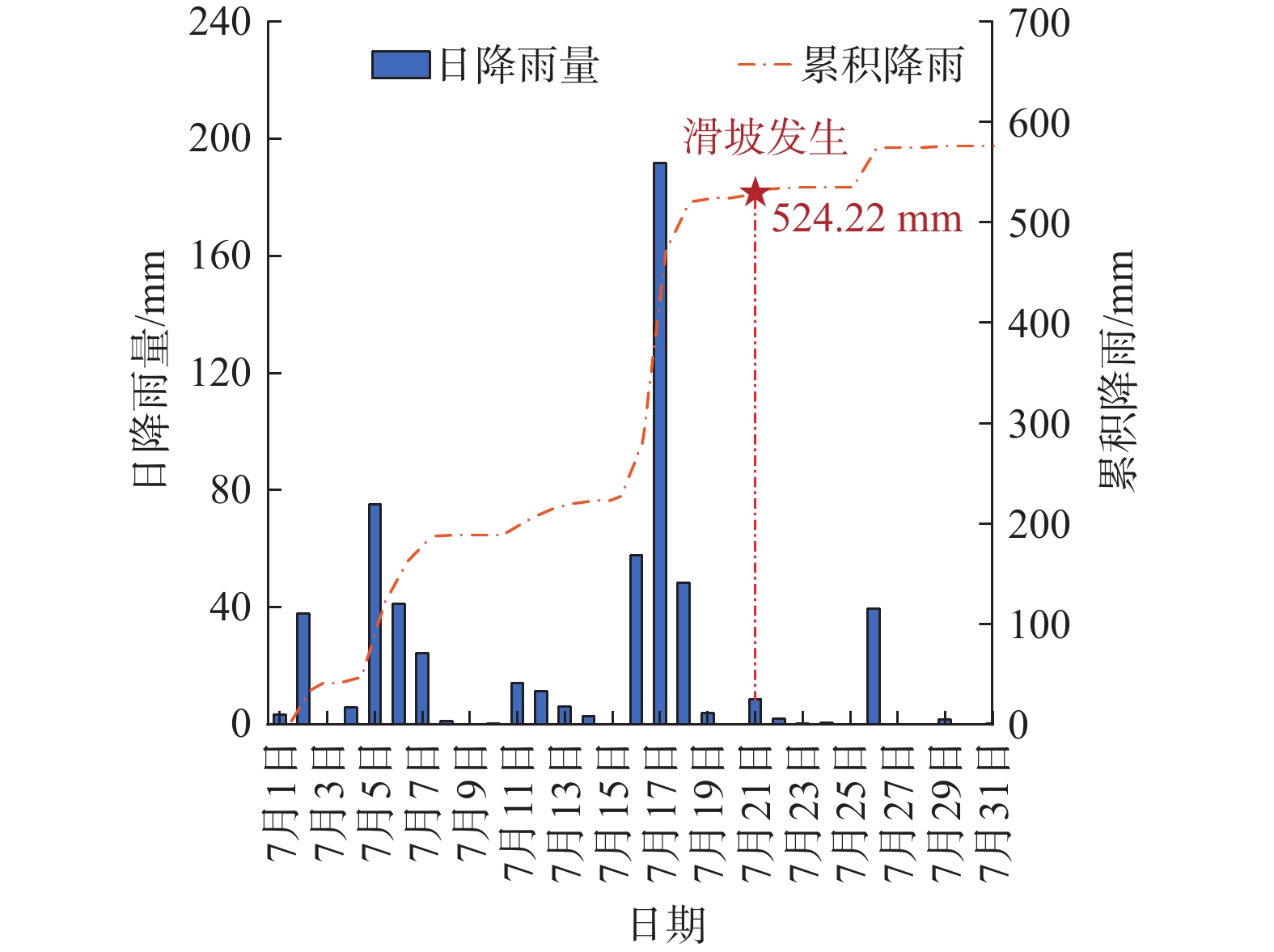
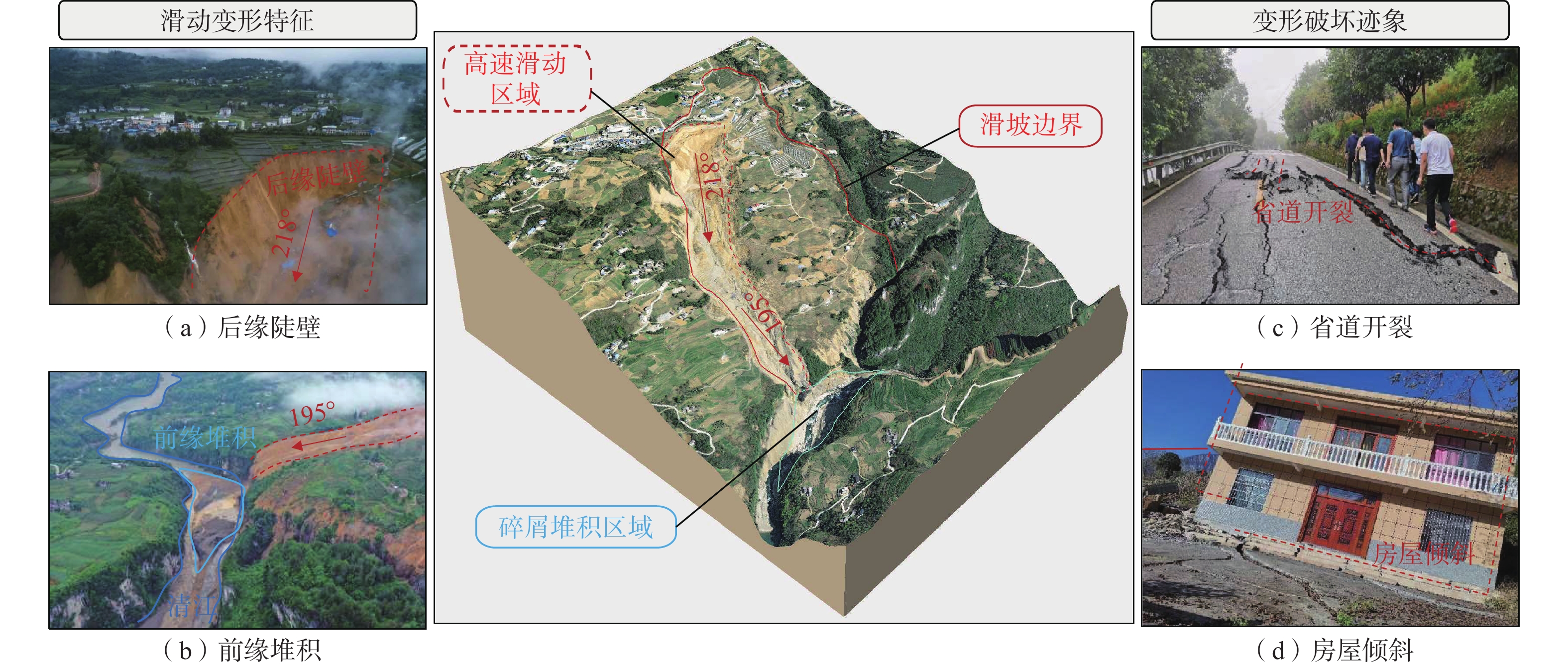
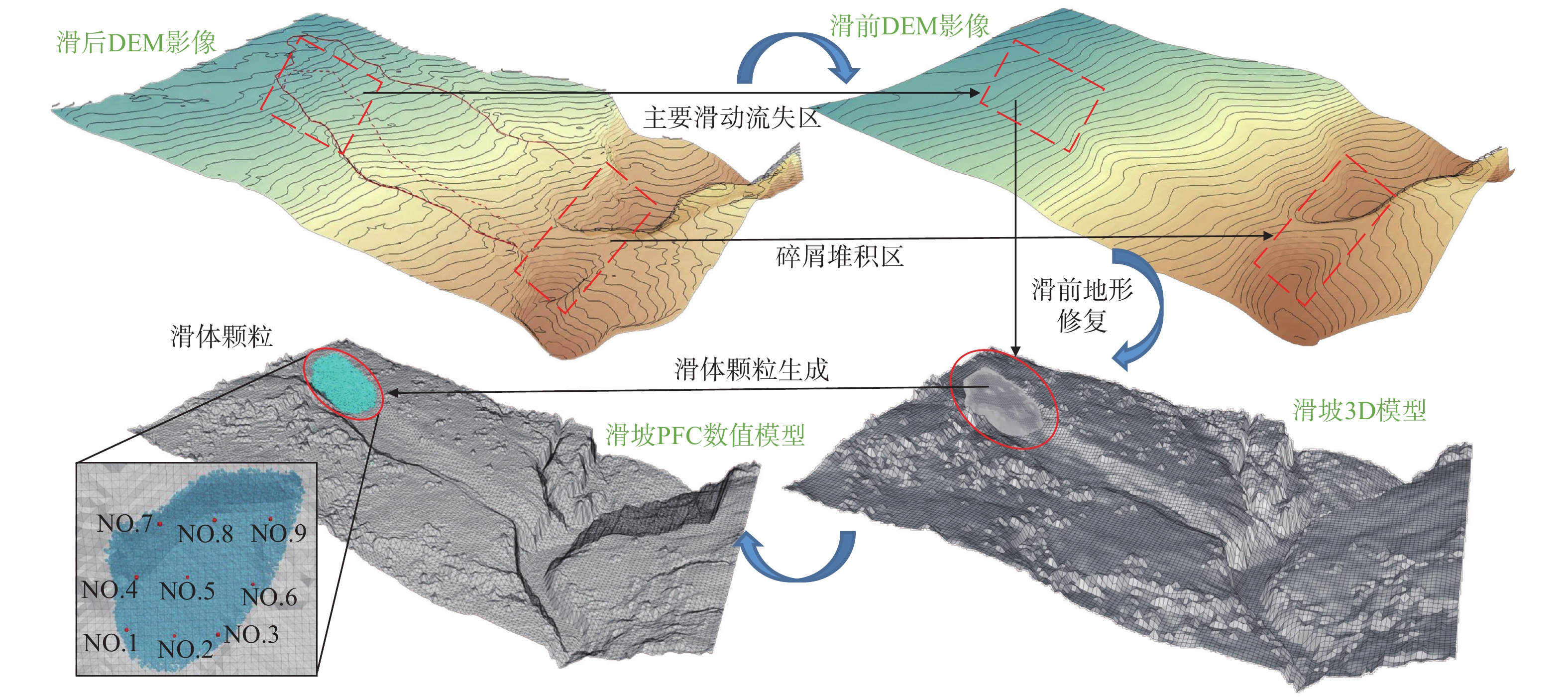
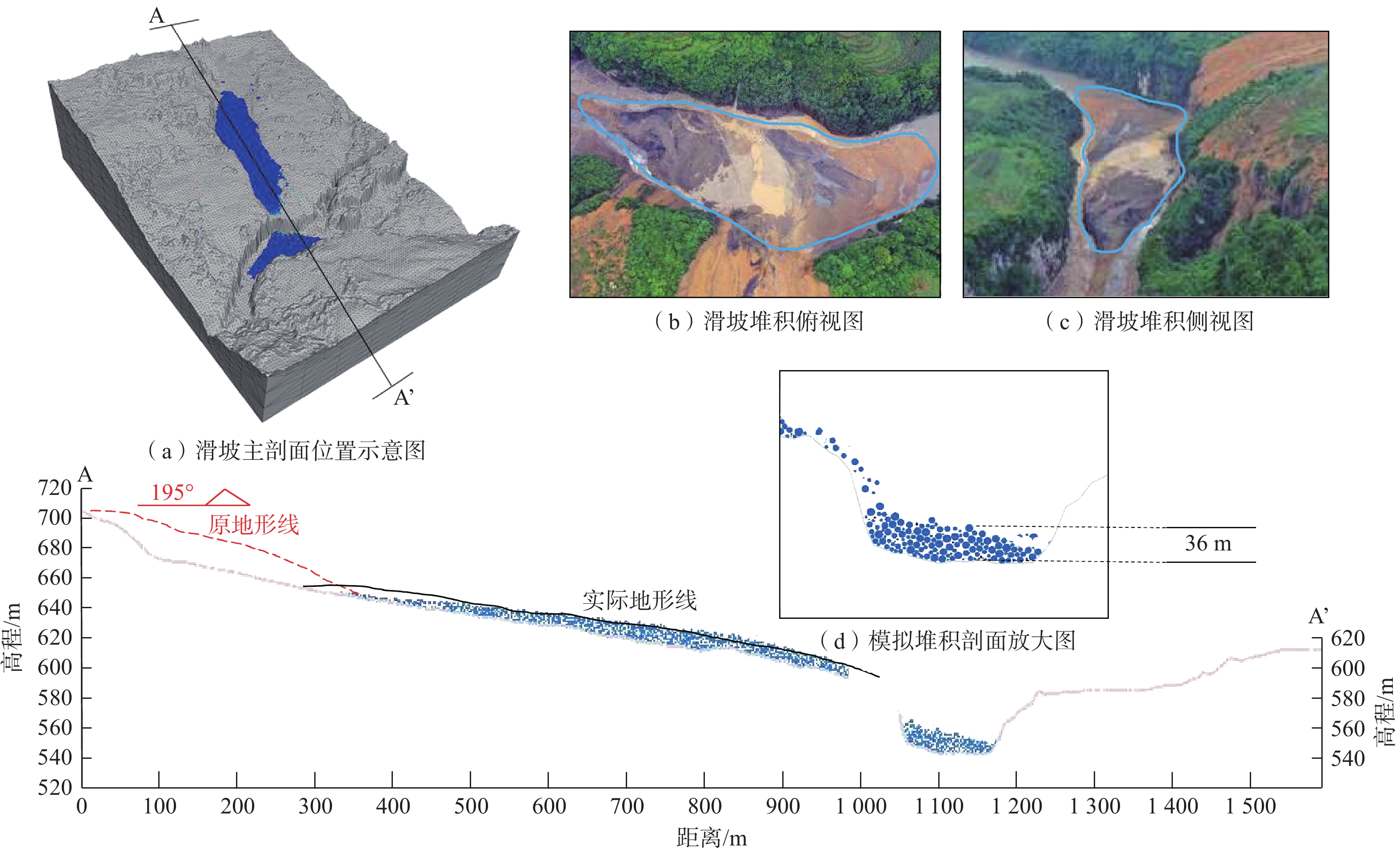
碎屑流滑坡往往具有高滑动速度及远距离滑移的运动学特征,并且滑坡滑动易对周边环境造成严重的破坏和巨大的财产损失。2020年7月21日,在特大暴雨的持续影响下,恩施沙子坝滑坡失稳滑动并发展为碎屑流滑坡,最终在清江堆积形成堰塞湖。为了探究沙子坝滑坡滑动速度和位移等运动特征及运动演化规律,通过高精度无人机正射影像构建滑坡三维数值模型,基于室内试验获取滑体力学数据对模型细观参数进行标定,最后,使用颗粒流PFC3D软件模拟滑坡从失稳到堆积的过程。通过模拟可得:沙子坝滑坡运动时间约757 s,平均速度可达4.9 m/s,平均滑移距离约960 m。滑坡动力学过程可分为失稳滑动(0~18 s)、流态传播(18~331 s)及低速堆积(331~757 s)3个阶段,且在滑动过程中表现出了碎屑流滑坡的“超距、失距”特征以及碎屑流滑坡的体积增大效应。滑体在清江的堆积体呈现靠近滑出崖口方向堆积较厚,远离滑坡方向较薄的类锥形堆积形态,模拟结果与实际情况吻合较好。模型较好地再现了沙子坝滑坡从失稳到堆积的滑动过程,可为类似碎屑流滑坡地质灾害的防治与研究提供参考。
Abstract:Debris flow landslides usually exhibit high sliding speed and long-distance slip, and their unstable slide is easy to cause serious damage to the surrounding area and significant property loss. On July 21, 2020, under the continuous influence of heavy rainfall, the Shaziba landslide in Enshi lost stability and transformed into a debris flow landslide, ultimately depositing within the Qing River, forming a dammed lake. To explore its kinematic features, such as velocity and displacement, during the Shaziba landslide’s sliding process and the evolving patterns of the landslide mass, a three-dimensional numerical model of the landslide was constructed using high-precision ortho-images obtained from unmanned aerial vehicles (drones). The parameters of the model were calibrated based on the mechanical properties of the landslide mass obtained from laboratory tests. Finally, the Particle Flow Code (PFC3D) software was used to simulate the process of the Shaziba debris flow landslide from sliding to deposition. It is determined that the movement time of the landslide was approximately 757 seconds, with a maximum average velocity of 4.9 m/s, and an average sliding distance of about 960 m. The dynamic process of the landslide can be divided into three stages: unstable sliding (0~18 s), flow propagation (18~331 s), and low-speed deposition (331~757 s). Throughout the sliding process, it exhibited the characteristics of hyper-distance and loss-distance, as well as the volume-increasing effect of debris flow landslides. The deposition pattern of the landslide mass in the Qing River displayed a conical accumulation shape, with thick accumulation near the landslide exit and thin accumulation in the opposite direction of the landslide, which closely matched the actual situation. The model effectively reproduces the sliding process of the Shaziba landslide from instability to deposition. This study can provide valuable insights for the prevention and study of geological hazards related to debris flow landslides.
-
Key words:
- debris flow landslide /
- numerical simulation /
- PFC /
- deformation evolution /
- motion process
-

-
表 1 滑体物理力学参数表
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of slip mass
干重度/(g·cm−3) 含水率/% 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 粉质黏土 15.56 35.3 24.42 12.02 表 2 滑坡模型细观参数表
Table 2. Microscopic parameters of landslide model
细观参数 关键词 参数值 颗粒密度/(kg·m−3) density 2.07×103 黏结半径/m bond_gap R×0.01 有效模量/Pa emod 1.2×107 刚度比 kratio 1.5 黏结有效刚度/Pa pb_emod 1.2×107 黏结刚度比/Pa pb_krat 1.2 摩擦系数 fric 0.3 抗拉强度/Pa pb_ten 1.7×105 黏结强度/Pa pb_coh 1.0×107 颗粒摩擦角/(°) pb_fa 34 -
[1] 张明,殷跃平,吴树仁,等. 高速远程滑坡-碎屑流运动机理研究发展现状与展望[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(6):805 − 817. [ZHANG Ming,YIN Yueping,WU Shuren,et al. Development status and prospects of studies on kinematics of long runout rock avalanches[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(6):805 − 817. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.001
ZHANG Ming, YIN Yueping, WU Shuren, et al. Development status and prospects of studies on kinematics of long runout rock avalanches[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(6): 805 − 817. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.001
[2] 文宝萍,王凡. 1965年烂泥沟滑坡前兆、高速远程运动及后期演化特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):72 − 80. [WEN Baoping,WANG Fan. Precursors and motion characteristics of the 1965 lannigou rockslides and the subsequent evolution[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):72 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEN Baoping, WANG Fan. Precursors and motion characteristics of the 1965 lannigou rockslides and the subsequent evolution[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 72 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 杨海平,王金生. 长江三峡工程库区千将坪滑坡地质特征及成因分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2):233 − 239. [YANG Haiping,WANG Jinsheng. Geological features and cause analysis of Qianjiangping landslide of July 13,2003 on Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(2):233 − 239. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.013
YANG Haiping, WANG Jinsheng. Geological features and cause analysis of Qianjiangping landslide of July 13, 2003 on Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2): 233 − 239. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.013
[4] 易连兴. 西南岩溶山区复合水动力场滑坡影响模式——以关岭县大寨滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):43 − 50. [YI Lianxing. Impact model of landslide with complex hydrodynamic field in Karst Mountain areas of southwest China:A case study of the Dazhai landslide in Guanling County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YI Lianxing. Impact model of landslide with complex hydrodynamic field in Karst Mountain areas of southwest China: A case study of the Dazhai landslide in Guanling County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4): 43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 殷跃平,王文沛,张楠,等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(5):827 − 841. [YIN Yueping,WANG Wenpei,ZHANG Nan,et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area:A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12029/gc20170501
YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei, ZHANG Nan, et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area: A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(5): 827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20170501
[6] ZHAO Weihua,WANG Rui,LIU Xiuwei,et al. Field survey of a catastrophic high-speed long-runout landslide in Jichang Town,Shuicheng County,Guizhou,China,on July 23,2019[J]. Landslides,2020,17(6):1415 − 1427. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01380-z
[7] 张磊,周银朋,庄宇,等. 贵州水城尖山营滑坡动力学特性分析与隐患点致灾范围预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):1 − 7. [ZHANG Lei,ZHOU Yinpeng,ZHUANG Yu,et al. Dynamic analysis and prediction of rear slope affected area of the Jianshanying landslide in Shuicheng County,Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Yinpeng, ZHUANG Yu, et al. Dynamic analysis and prediction of rear slope affected area of the Jianshanying landslide in Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 高浩源,高杨,殷跃平,等. 青藏高原高位远程滑坡动力学研究的新问题[J]. 地质力学学报,2022,28(6):1090 − 1103. [GAO Haoyuan,GAO Yang,YIN Yueping,et al. New scientific issues in the study of high-elevation and long-runout landslide dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2022,28(6):1090 − 1103. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222831
GAO Haoyuan, GAO Yang, YIN Yueping, et al. New scientific issues in the study of high-elevation and long-runout landslide dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(6): 1090 − 1103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222831
[9] MUCEKU Y,KORINI O. Landslide and slope stability evaluation in the historical town of Kruja,Albania[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2014,14(3):545 − 556. doi: 10.5194/nhess-14-545-2014
[10] FAN Xuanmei,XU Qiang,SCARINGI G,et al. Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24th 2017 Xinmo landslide,Maoxian,Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,2017,14(6):2129 − 2146. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0907-7
[11] SCHEIDEGGER A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics,1973,5(4):231 − 236. doi: 10.1007/BF01301796
[12] DAVIES T R H. Spreading of rock avalanche debris by mechanical fluidization[J]. Rock Mechanics,1982,15(1):9 − 24. doi: 10.1007/BF01239474
[13] XIN Peng,LIANG Changyu,WU Shuren,et al. Kinematic characteristics and dynamic mechanisms of large-scale landslides in a Loess Plateau:A case study for the north bank of the Baoji stream segment of the Wei River,China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2016,75(2):659 − 671. doi: 10.1007/s10064-015-0824-8
[14] 杨明钰,陈红旗,祁小博,等. 基于可靠度理论的地震滑坡运动距离预测模型[J]. 中国地质调查,2023,10(3):102 − 109. [YANG Mingyu,CHEN Hongqi,QI Xiaobo,et al. Prediction model for the landslide movement distance induced by earthquake based on the reliability theory[J]. Geological Survey of China,2023,10(3):102 − 109. (in Chinese)]
YANG Mingyu, CHEN Hongqi, QI Xiaobo, et al. Prediction model for the landslide movement distance induced by earthquake based on the reliability theory[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2023, 10(3): 102 − 109. (in Chinese)
[15] SULPIZIO R,CASTIONI D,RODRIGUEZ-SEDANO L A,et al. The influence of slope-angle ratio on the dynamics of granular flows:Insights from laboratory experiments[J]. Bulletin of Volcanology,2016,78(11):77. doi: 10.1007/s00445-016-1069-5
[16] DEANGELI C. Laboratory granular flows generated by slope failures[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2008,41(1):199 − 217. doi: 10.1007/s00603-007-0131-1
[17] 雷先顺,朱大勇,刘诚,等. 考虑滑道坡度和宽度的滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(5):1281 − 1288. [LEI Xianshun,ZHU Dayong,LIU Cheng,et al. Model test study of the effect of slope angle and chute width on landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(5):1281 − 1288. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LEI Xianshun, ZHU Dayong, LIU Cheng, et al. Model test study of the effect of slope angle and chute width on landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(5): 1281 − 1288. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 胡晓波,樊晓一,唐俊杰. 基于离散元的高速远程滑坡运动堆积特征及能量转化研究——以三溪村滑坡为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(4):527 − 535. [HU Xiaobo,FAN Xiaoyi,TANG Junjie. Accumulation characteristics and energy conversion of high-speed and long-distance landslide on the basis of Dem:A case study of sanxicun landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(4):527 − 535. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.051
HU Xiaobo, FAN Xiaoyi, TANG Junjie. Accumulation characteristics and energy conversion of high-speed and long-distance landslide on the basis of Dem: A case study of sanxicun landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4): 527 − 535. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.051
[19] ZHU Yuxuan,DAI Fuchu. Insights into the kinetic and fragmentation characteristics of a ridge-top rock avalanche based on field investigation and discrete element simulation[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(3):2085 − 2099. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-02079-0
[20] 吴伟乐,贺凯,高杨,等. 强降雨条件下碎屑岩滑坡远程运动模拟分析——以牛儿湾滑坡为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2022,28(6):1115 − 1126. [WU Weile,HE Kai,GAO Yang,et al. Long-runout fluidization disaster simulation analysis of clastic landslide under heavy rainfall:A case study of the Niuerwan landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2022,28(6):1115 − 1126. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222833
WU Weile, HE Kai, GAO Yang, et al. Long-runout fluidization disaster simulation analysis of clastic landslide under heavy rainfall: A case study of the Niuerwan landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(6): 1115 − 1126. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222833
[21] WANG Huanling,LIU Shiqi,XU Weiya,et al. Numerical investigation on the sliding process and deposit feature of an earthquake-induced landslide:A case study[J]. Landslides,2020,17(11):2671 − 2682. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01446-y
[22] WEI Li,CHENG Hualin,DAI Zili. Propagation modeling of rainfall-induced landslides:A case study of the shaziba landslide in Enshi,China[J]. Water,2023,15(3):424. doi: 10.3390/w15030424
[23] TANG Chaolung,HU Jyrching,LIN Minglang,et al. The Tsaoling landslide triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake,Taiwan:Insights from a discrete element simulation[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,106(1/2):1 − 19.
[24] 郭长宝,王磊,李任杰,等. 西藏贡觉粉砂质泥岩工程地质特性与蠕变强度研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):54 − 64. [GUO Changbao,WANG Lei,LI Renjie,et al. Engineering geology properties and creeping strength characteristics of the silty mudstone in Gongjue County in Tibet of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):54 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Changbao, WANG Lei, LI Renjie, et al. Engineering geology properties and creeping strength characteristics of the silty mudstone in Gongjue County in Tibet of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 54 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 陈果,钮志林,樊晓一,等. 高速远程滑坡沿程速度演化与冲击力分布研究——以三溪村滑坡为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2022,31(3):232 − 241. [CHEN Guo,NIU Zhilin,FAN Xiaoyi,et al. Velocity evolution and impact force distribution of high-velocity and long-runout landslide debris flow along the way:A case study of Sanxi Village landslide[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2022,31(3):232 − 241. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Guo, NIU Zhilin, FAN Xiaoyi, et al. Velocity evolution and impact force distribution of high-velocity and long-runout landslide debris flow along the way: A case study of Sanxi Village landslide[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2022, 31(3): 232 − 241. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] DUMAN T Y. The largest landslide dam in Turkey:Tortum landslide[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,104(1/2):66 − 79.
[27] XU Zhenhao,WANG Wenyang,LIN Peng,et al. A parameter calibration method for PFC simulation:Development and a case study of limestone[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering,2020,22:97 − 108.
[28] 赵国彦,戴兵,马驰. 平行黏结模型中细观参数对宏观特性影响研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(7):1491 − 1498. [ZHAO Guoyan,DAI Bing,MA Chi. Study of effects of microparameters on macroproperties for parallel bonded model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(7):1491 − 1498. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.07.024
ZHAO Guoyan, DAI Bing, MA Chi. Study of effects of microparameters on macroproperties for parallel bonded model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(7): 1491 − 1498. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.07.024
[29] 阿比尔的,郑颖人,冯夏庭,等. 平行黏结模型宏细观力学参数相关性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(4):1289 − 1301. [ABI ERDI,ZHENG Yingren,FENG Xiating,et al. Relationship between particle micro and macro mechanical parameters of parallel-bond model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(4):1289 − 1301. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ABI ERDI, ZHENG Yingren, FENG Xiating, et al. Relationship between particle micro and macro mechanical parameters of parallel-bond model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(4): 1289 − 1301. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 周博,汪华斌,赵文锋,等. 黏性材料细观与宏观力学参数相关性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(10):3171 − 3175. [ZHOU Bo,WANG Huabin,ZHAO Wenfeng,et al. Analysis of relationship between particle mesoscopic and macroscopic mechanical parameters of cohesive materials[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(10):3171 − 3175. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Bo, WANG Huabin, ZHAO Wenfeng, et al. Analysis of relationship between particle mesoscopic and macroscopic mechanical parameters of cohesive materials[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(10): 3171 − 3175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 葛云峰,周婷,霍少磊,等. 高速远程滑坡运动堆积过程中的能量传递机制[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(11):3939 − 3949. [GE Yunfeng,ZHOU Ting,HUO Shaolei,et al. Energy transfer mechanism during movement and accumulation of rockslide avalanche[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(11):3939 − 3949. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GE Yunfeng, ZHOU Ting, HUO Shaolei, et al. Energy transfer mechanism during movement and accumulation of rockslide avalanche[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(11): 3939 − 3949. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 陶伟,胡晓波,姜元俊,等. 颗粒粒径对滑坡碎屑流动力特征及能量转化的影响——以四川省三溪村滑坡为例[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(9):1610 − 1619. [TAO Wei,HU Xiaobo,JIANG Yuanjun,et al. Influence of particle size on energy evolution of debris flow in landslide based on DEM:A case study of Sanxicun landslide[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(9):1610 − 1619. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.09.015
TAO Wei, HU Xiaobo, JIANG Yuanjun, et al. Influence of particle size on energy evolution of debris flow in landslide based on DEM: A case study of Sanxicun landslide[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(9): 1610 − 1619. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.09.015
-




 下载:
下载: