Research progress on the response characteristics and indicative significance of microorganisms to seawater intrusion
-
摘要:
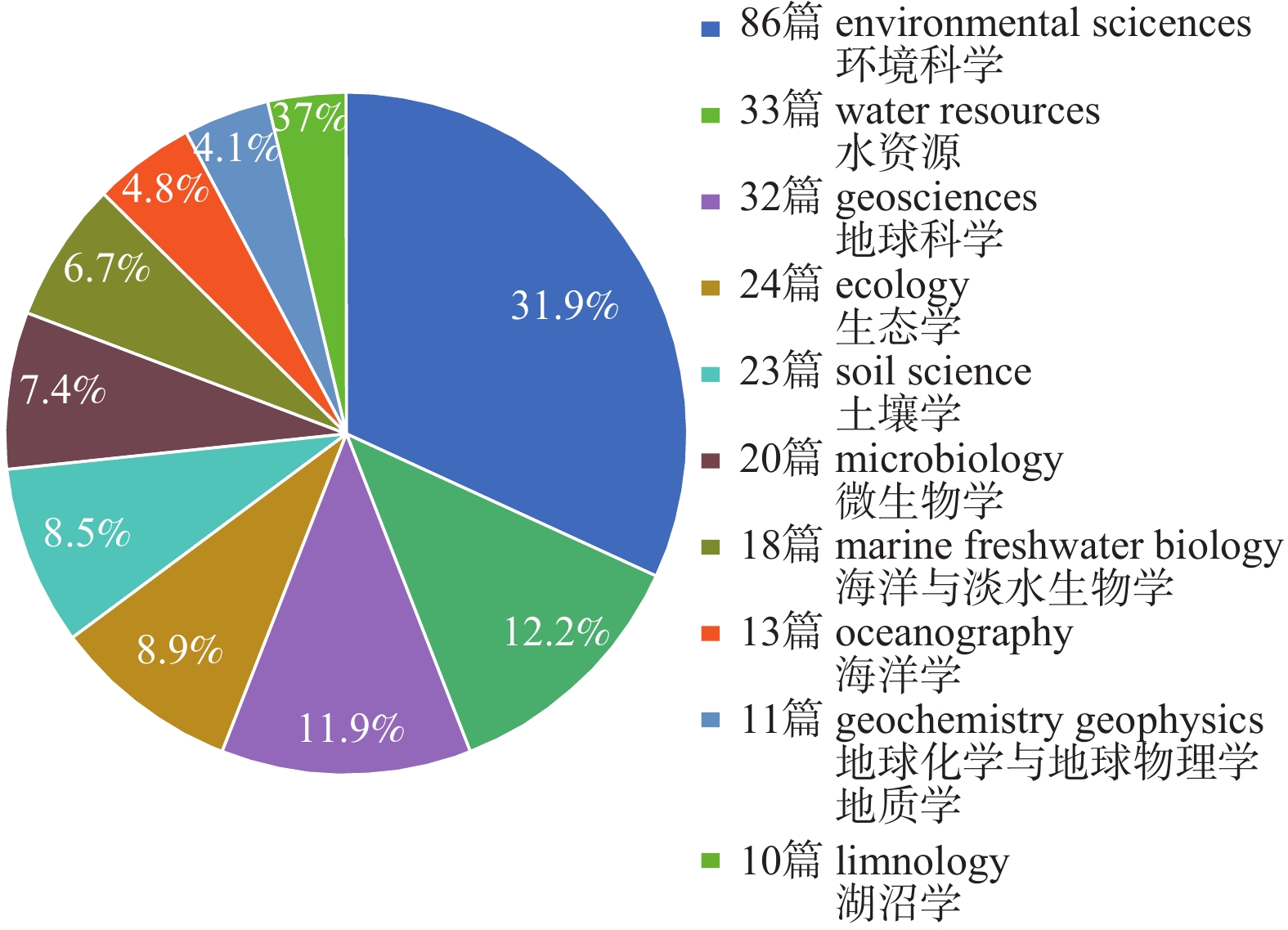
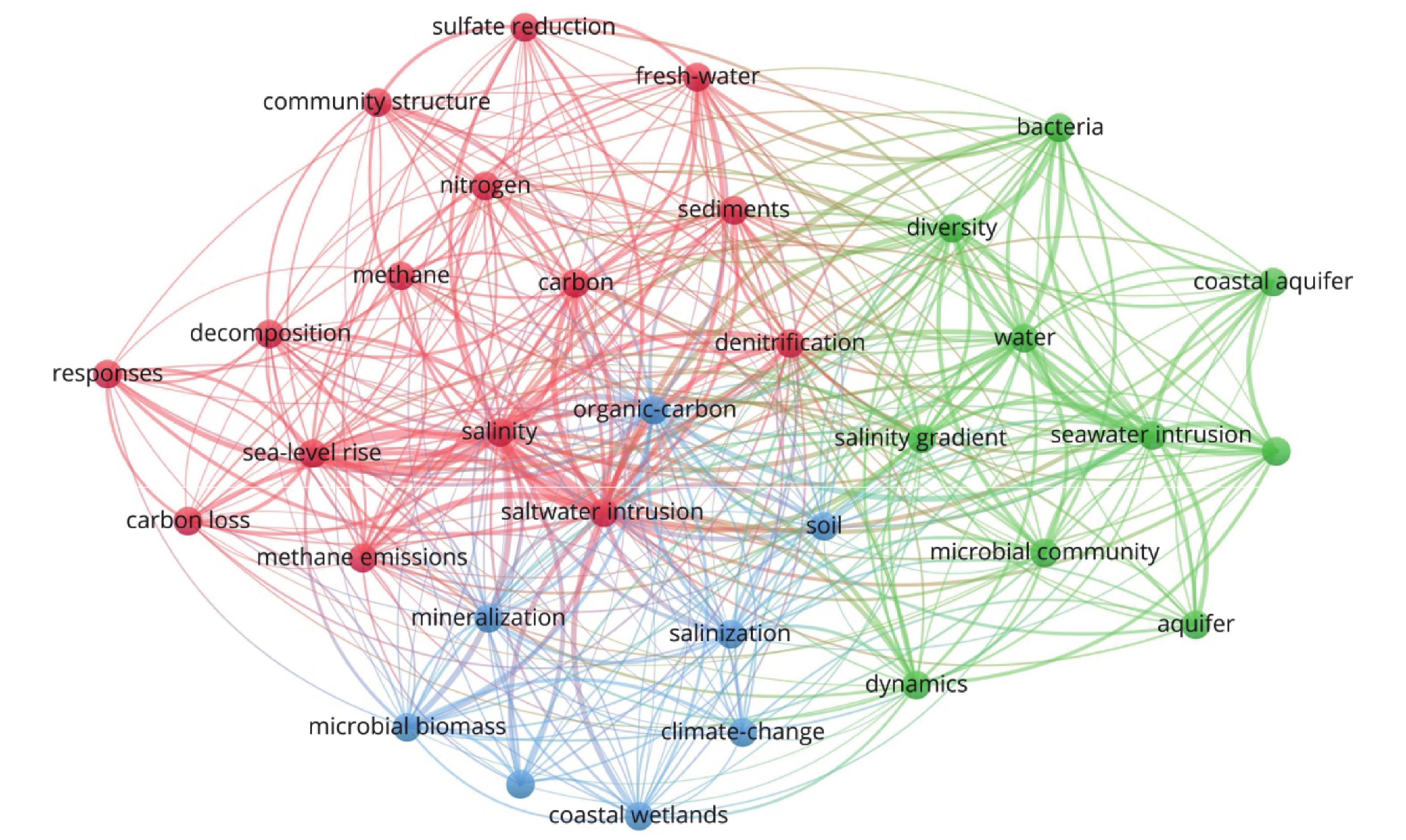
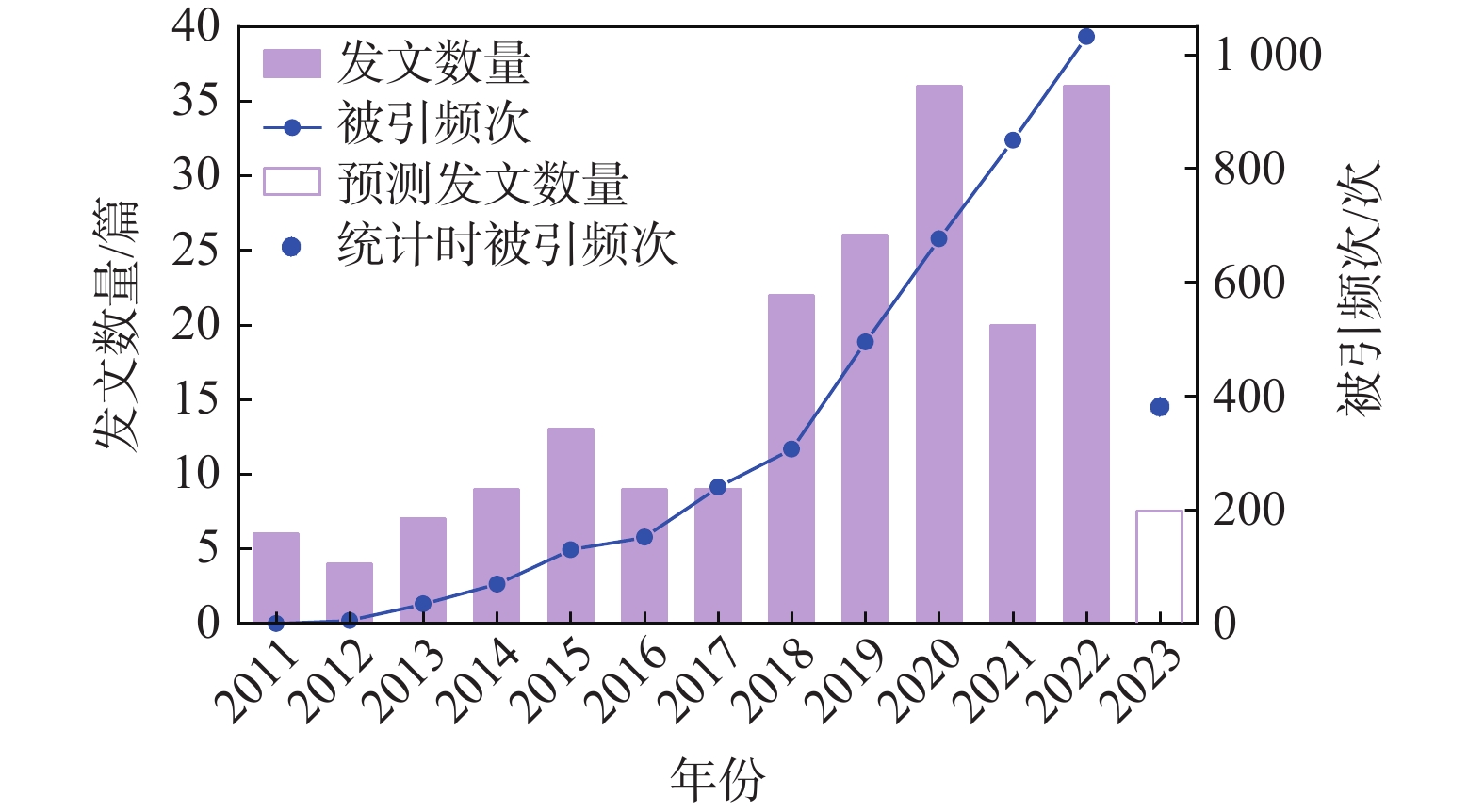
海水入侵是全球性环境地质问题,对沿海城市的供水安全及生态环境造成严重威胁。微生物对环境变化具有高度的敏感性,近年来许多学者开始关注微生物对海水入侵的响应特征,为海水入侵调查研究提供了新的思路与方法。为了充分认识该领域的研究进展,基于Web of Science 核心数据库,利用文献计量学可视化分析方法对海水入侵微生物响应特征研究现状、热点及趋势进行分析。文献分析结果表明:该新兴研究领域的成果集中出现在2011年以后,发文量和引文量呈现上升趋势;中国积极参与海水入侵微生物响应特征研究,其发文量及高引用指数均位居世界第二位,研究成果具有较高的学术影响力;由关键词聚类分析可知,该领域热门研究方向包括地下水微生物群落对海水入侵的响应研究、土壤微生物群落对海水入侵的响应研究、元素地球化学循环与微生物作用研究。研究结果表明:咸-淡水交互区微生物群落演替受盐度、溶解氧、温度、有机碳、pH值等多种因子的共同影响,其主控因子随水文地质条件的不同而变化;海水入侵会影响微生物介导的碳、氮、硫、铁等物质循环过程;在含水层中发现的典型海洋细菌及嗜盐古菌对海水入侵的识别具有重要指示意义,相关技术是海水入侵传统调查方法的有力补充,在古海水入侵、现代海水入侵的辨别应用中具有较大优势和潜力。
Abstract:Seawater intrusion is a global environmental geological issue that poses a serious threat to the water supply security and ecological environment of coastal cities. Microorganisms exhibit a high sensitivity to environmental changes, and in recent years, numerous scholars have turned their attention to the response characteristics of microorganisms to seawater intrusion, offering new perspectives and methodologies for research in this field. To completely understand the research progress in this field, this study, based on the Web of Science core database, employed bibliometric visualization analysis methods to analyze the current status, hotspots, and trends of research on microbial response characteristics to seawater intrusion. The results indicate that significant developments in this emerging research area have mainly occurred after 2011, with a consistent increase in publication volume and citation counts. Chinese scholars actively engage in the research of microbial responses to seawater intrusion, ranking second in terms of both publication output and h-index, with a significant academic impact. Keyword cluster analysis reveals that popular research topics in this field encompass the response of groundwater microbial communities to seawater intrusion, investigations into soil microbial communities’ response to seawater intrusion, and the geochemical cycling of elements in conjunction with microbial processes. The study indicates that the succession of microbial communities in brackish-saline water transition zones is jointly influenced by factors such as salinity, dissolved oxygen, temperature, organic carbon, and pH. The primary controlling factors vary with hydrogeological conditions. The intrusion of seawater impacts microbial-mediated processes involved in the cycling of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, iron, and other substances. The identification of typical marine bacteria and halophilic archaea found in aquifers holds significant indicative value concerning seawater intrusion. This serves as a potent complement to traditional investigative methods for seawater intrusion, offering substantial potential and advantages in distinguishing paleoseawater intrusion and seawater intrusion.
-
Key words:
- seawater intrusion /
- groundwater /
- microbial community /
- geochemistry /
- bibliometric
-

-
表 1 传统海水入侵调查方法
Table 1. Traditional investigation methods of seawater intrusion
方法 地下水监测 地球化学示踪 地球物理探测 数值模拟 水化学示踪 同位素示踪 分类 水位、电导率、
水温等溶解性总固体、Cl−、 ${\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 、
Cl/Br、Na/Cl、Ca/Mg等2H、18O、3H、14C、34S、37Cl、
81Br、87Sr、11B、7Li等电阻率法(ERI、VES),
电磁法(TDEM、FDEM、AEM),
激发极化法(IP)等突变界面模型、
单一组分过渡带模型、
多组分过渡带模型等优点 结果直观,可初步限定咸-淡水界面位置 结果直观,可反映
海水入侵程度可识别地下水咸化的
不同来源可快速识别咸水界面的
空间分布可模拟、预测海水入侵
发生及发展过程缺点 建设成本高;无法
识别地下水盐分来源数据代表性取决于取样密度;
难以准确识别地下水盐分来源结果的解释相对复杂,需要多种同位素
进行追踪;示踪时间有限;成本高昂地层岩性、含水层特征等会
干扰海水入侵物探结果解译需要掌握详细的地质资料
及水文地质参数文献 [4, 20 − 21] [22 − 23] [9, 24 − 25] [26 − 27] [12, 28 − 29] 表 2 2011—2023年发文量前10的国家
Table 2. Top 10 countries in terms of the number of published papers from 2011 to 2023
排序 国家 收录/篇 发文量
占比/%h指数 被引次数
总计每篇平均
被引次数1 美国 83 40.69 24 2273 27.39 2 中国 53 25.98 18 1143 21.57 3 德国 20 9.80 11 433 21.65 4 意大利 12 5.88 9 382 31.83 5 西班牙 10 4.90 5 280 28.00 6 澳大利亚 9 4.41 7 88 9.78 7 法国 9 4.41 6 293 32.56 8 韩国 8 3.92 6 110 13.75 9 加拿大 7 3.43 4 70 10.00 10 印度 7 3.43 4 90 12.86 表 3 典型研究区海水入侵指示微生物
Table 3. Signature microorganism of seawater intrusion in the typical study areas
研究区 赋存环境 Cl−质量浓度/(mg·L-1) 微生物分类 分类水平(目/科/属) 所属门类 主要影响因子 参考文献 中国山东省龙口市 孔隙水 126~796 细菌 海洋螺菌目(Oceanospirillales)、交替单胞菌科(Alteromonadaceae) 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) 溶解氧、氧化还原电位、Cl−浓度 [47] 中国广东省珠江三角洲 孔隙水 93~13442 细菌 海杆菌属(Marinobacter)、交替单胞菌目(Alteromonadales) 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) 盐度、温度、pH [18, 74] 古菌 海洋古菌MG Ⅰ(Marine group Ⅰ) 奇古菌门(Thaumarchaeota) 中国广西省北海市 孔隙水 379~1396 细菌 甲基单胞菌科(Methylomonadaceae )、 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) Cl−浓度,水产养殖及地表水体富营养化程度 [55] 帕斯氏细菌科(Paceibacteraceae) 髌骨菌门(Patescibacteria) 古菌 乌斯古菌目(Woesearchaeales)、 纳古菌门(Nanoarchaeota) 硝化古菌科(Nitrosotaleaceae)、球形硝化古菌科(Nitrososphaeraceae) 泉古菌门(Crenarchaeota) 韩国济州岛 孔隙水 350~15427 细菌 红杆菌科( Rhodobacteraceae)、 黄杆菌科(Flavobacteriaceae) 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) Cl−浓度 [16, 46] 西班牙 岩溶水 472~20028 细菌 硫氧化细菌(Sulfuriflexus mobilis)、杆状脱硫微菌(Desulfomicrobium baculatum) 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) 盐度、有机碳、pH、二氧化碳分压 [43, 66] 印度尼西亚爪哇岛 孔隙水 4169~10249 蓝藻细菌 聚球藻(Synechococcus sp. CC9902) 蓝藻门(Cyanobacteria) 盐度、温度 [42] 细菌 海杆菌属(Marinobacter)、盐单胞菌属(Halomonas) 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) 美国东部特拉华州 孔隙水 2700~18900 细菌 脱硫菌属(Desulfovibrio、 Desulfopila、 Desulfurispora) 变形菌门(Proteobacteria) 二价铁浓度、总铁浓度、盐度、溶解氧 [17] -
[1] 薛禹群,谢春红,吴吉春. 海水入侵研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1992,19(6):29 − 33. [XUE Yuqun,XIE Chunhong,WU Jichun. Seawater intrusion[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,1992,19(6):29 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XUE Yuqun, XIE Chunhong, WU Jichun . Seawater intrusion[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,1992 ,19 (6 ):29 −33 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 孙金华,吴永祥,林锦,等. 黄渤海沿海地区海水入侵防治与地下水管理研究[J]. 中国水利,2021(7):20 − 23. [SUN Jinhua,WU Yongxiang,LIN Jin,et al. Seawater intrusion prevention and groundwater management and study in the coastal area of the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea[J]. China Water Resources,2021(7):20 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Jinhua, WU Yongxiang, LIN Jin, et al . Seawater intrusion prevention and groundwater management and study in the coastal area of the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea[J]. China Water Resources,2021 (7 ):20 −23 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 李雪,叶思源. 海水入侵调查方法研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(6):211 − 217. [LI Xue,YE Siyuan. Progress in seawater intrusion[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2016,36(6):211 − 217. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Xue, YE Siyuan . Progress in seawater intrusion[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2016 ,36 (6 ):211 −217 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 张康,韩冬梅,曹天正,等. 基岩海岛地下水与海水相互作用研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(1):3 − 12. [ZHANG Kang,HAN Dongmei,CAO Tianzheng,et al. Interaction between groundwater and seawater in bedrock islands[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(1):3 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Kang, HAN Dongmei, CAO Tianzheng, et al . Interaction between groundwater and seawater in bedrock islands[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (1 ):3 −12 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 侯国华,高茂生,党显璋. 唐山曹妃甸浅层地下水水化学特征及咸化成因[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(6):49 − 57. [HOU Guohua,GAO Maosheng,DANG Xianzhang. Hydrochemical characteristics and salinization causes of shallow groundwater in Caofeidian,Tangshan City[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2019,26(6):49 − 57. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HOU Guohua, GAO Maosheng, DANG Xianzhang . Hydrochemical characteristics and salinization causes of shallow groundwater in Caofeidian, Tangshan City[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2019 ,26 (6 ):49 −57 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 郭明华,王敬,戴长国,等. 文登区浅层地下水化学演化与海水入侵研究[J]. 海洋科学,2021,45(7):57 − 65. [GUO Minghua,WANG Jing,DAI Changguo,et al. Study on the hydrochemical evolution of groundwater and seawater intrusion in the shallow layer of Wendeng District[J]. Marine Sciences,2021,45(7):57 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Minghua, WANG Jing, DAI Changguo, et al . Study on the hydrochemical evolution of groundwater and seawater intrusion in the shallow layer of Wendeng District[J]. Marine Sciences,2021 ,45 (7 ):57 −65 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 熊贵耀,付腾飞,韩江波,等. 大沽河流域地下水水化学及同位素特征[J]. 海洋科学进展,2019,37(4):626 − 637. [XIONG Guiyao,FU Tengfei,HAN Jiangbo,et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Dagu River Basin[J]. Advances in Marine Science,2019,37(4):626 − 637. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIONG Guiyao, FU Tengfei, HAN Jiangbo, et al . Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Dagu River Basin[J]. Advances in Marine Science,2019 ,37 (4 ):626 −637 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 侯国华,高茂生,党显璋,等. 江苏盐城滨海地区浅层地下咸水的水盐来源及咸化成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(4):48 − 59. [HOU Guohua,GAO Maosheng,DANG Xianzhang,et al. Water and salt sources and salinization of shallow saline groundwater in the coastal area of Yancheng,Jiangsu[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2021,41(4):48 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HOU Guohua, GAO Maosheng, DANG Xianzhang, et al . Water and salt sources and salinization of shallow saline groundwater in the coastal area of Yancheng, Jiangsu[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2021 ,41 (4 ):48 −59 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] QI Huihui,MA Chuanming,HE Zekang,et al. Lithium and its isotopes as tracers of groundwater salinization:A study in the southern coastal plain of Laizhou Bay,China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment,2019,650(Pt 1):878-890.
[10] 苏永军,范翠松,赵更新,等. 综合电法在探测海水入侵界面中的研究与应用——以莱州湾地区为例[J]. 物探与化探,2020,44(3):704 − 708. [SU Yongjun,FAN Cuisong,ZHAO Gengxin,et al. Research and application of comprehensive electrical method in detecting saltwater intrusion interface:A case study of Laizhou Bay Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2020,44(3):704 − 708. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SU Yongjun, FAN Cuisong, ZHAO Gengxin, et al . Research and application of comprehensive electrical method in detecting saltwater intrusion interface: A case study of Laizhou Bay Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2020 ,44 (3 ):704 −708 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] KAZAKIS N,PAVLOU A,VARGEMEZIS G,et al. Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data. An application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf,Greece[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2016,543:373 − 387. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.041
[12] 董健,曾献奎,吴吉春. 不同类型海岸带海水入侵数值模拟研究进展[J]. 高校地质学报,2018,24(3):442 − 449. [DONG Jian,ZENG Xiankui,WU Jichun. Advances in numerical simulation of seawater intrusion in different coastal zones[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2018,24(3):442 − 449. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DONG Jian, ZENG Xiankui, WU Jichun . Advances in numerical simulation of seawater intrusion in different coastal zones[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2018 ,24 (3 ):442 −449 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 王佳琪,郭芷琳,田勇,等. 海水入侵模拟方法VFT3D及应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(2):184 − 194. [WANG Jiaqi,GUO Zhilin,TIAN Yong,et al. Development and application of sea water intrusion models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(2):184 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jiaqi, GUO Zhilin, TIAN Yong, et al . Development and application of sea water intrusion models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (2 ):184 −194 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] GUO Huaming,ZHOU Yinzhu,JIA Yongfeng,et al. Sulfur cycling-related biogeochemical processes of arsenic mobilization in the western Hetao Basin,China:Evidence from multiple isotope approaches[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(23):12650 − 12659.
[15] PEARCE A R,RIZZO D M,MOUSER P J. Subsurface characterization of groundwater contaminated by landfill leachate using microbial community profile data and a nonparametric decision-making process[J]. Water Resources Research,2011,47(6):W06511.
[16] LEE E,SHIN D,HYUN S P,et al. Periodic change in coastal microbial community structure associated with submarine groundwater discharge and tidal fluctuation[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2017,62(2):437 − 451. doi: 10.1002/lno.10433
[17] MCALLISTER S M,BARNETT J M,HEISS J W,et al. Dynamic hydrologic and biogeochemical processes drive microbially enhanced iron and sulfur cycling within the intertidal mixing zone of a beach aquifer[J]. Limnology and Oceanography,2015,60(1):329 − 345. doi: 10.1002/lno.10029
[18] SANG Shilei,DAI Heng,HU B X,et al. The study of hydrogeochemical environments and microbial communities along a groundwater salinity gradient in the Pearl River Delta,China[J]. Water,2019,11(4):804. doi: 10.3390/w11040804
[19] ZHANG Xiaoying,MIAO Jinjie,HU B X,et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in intruded coastal brine aquifers (Laizhou Bay,China)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24(26):21073 − 21090. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9641-x
[20] SREEKANTH J,DATTA B. Review:Simulation-optimization models for the management and monitoring of coastal aquifers[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2015,23(6):1155 − 1166. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1272-z
[21] FAN Yue,LU Wenxi,MIAO Tiansheng,et al. Optimum design of a seawater intrusion monitoring scheme based on the image quality assessment method[J]. Water Resources Management,2020,34(8):2485 − 2502. doi: 10.1007/s11269-020-02565-w
[22] ZHI Chuanshun,CAO Wengeng,ZHANG Zhuo,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and processes of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Water,2021,13(4):534. doi: 10.3390/w13040534
[23] NAIR I S,RAJAVENI S P,SCHNEIDER M,et al. Geochemical and isotopic signatures for the identification of seawater intrusion in an alluvial aquifer[J]. Journal of Earth System Science,2015,124(6):1281 − 1291. doi: 10.1007/s12040-015-0600-y
[24] HAN Dongmei,SONG Xianfang,CURRELL M J,et al. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay,China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2014,508:12 − 27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.10.040
[25] WERNER A D,BAKKER M,POST V E A,et al. Seawater intrusion processes,investigation and management:Recent advances and future challenges[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2013,51:3 − 26. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.03.004
[26] GOEBEL M,PIDLISECKY A,KNIGHT R. Resistivity imaging reveals complex pattern of saltwater intrusion along Monterey coast[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2017,551:746 − 755. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.037
[27] 王亮,戴云峰,刘冰,等. 基于等值反磁通瞬变电磁法快速探测海水入侵研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2023,38(3):1397 − 1407. [WANG Liang,DAI Yunfeng,LIU Bing,et al. Research on rapid detection of seawater intrusion based on opposing-coil transient electromagnetic method[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2023,38(3):1397 − 1407. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Liang, DAI Yunfeng, LIU Bing, et al . Research on rapid detection of seawater intrusion based on opposing-coil transient electromagnetic method[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2023 ,38 (3 ):1397 −1407 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[28] MIAO Tiansheng,LU Wenxi,LIN Jin,et al. Simulation of seawater intrusion and optimization of cutoff wall schemes based on surrogate model[J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment,2019,25(1/2):297 − 313.
[29] COBANER M,YURTAL R,DOGAN A,et al. Three dimensional simulation of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers:A case study in the Goksu Deltaic Plain[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2012,464/465:262 − 280. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.07.022
[30] 王广才,王焰新,刘菲,等. 基于文献计量学分析水文地球化学研究进展及趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2022,29(3):25 − 36. [WANG Guangcai,WANG Yanxin,LIU Fei,et al. Advances and trends in hydrogeochemical studies:Insights from bibliometricanalysis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2022,29(3):25 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Guangcai, WANG Yanxin, LIU Fei, et al . Advances and trends in hydrogeochemical studies: Insights from bibliometricanalysis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2022 ,29 (3 ):25 −36 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[31] 汪美华,赵慧,倪天翔,等. 近30年滑坡研究文献图谱可视化分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4):75 − 85. [WANG Meihua,ZHAO Hui,NI Tianxiang,et al. Visualization analysis of research literature map on landslides in the past 30 years[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(4):75 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Meihua, ZHAO Hui, NI Tianxiang, et al . Visualization analysis of research literature map on landslides in the past 30 years[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (4 ):75 −85 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[32] 严恺,粱其荀. 海岸工程[M]. 北京:海洋出版社,2002. [YAN Kai,LIANG Qixun. Coastal engineering[M]. Beijing:Ocean Press,2002. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Kai, LIANG Qixun. Coastal engineering[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2002. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 许宁. 中国大陆海岸线及海岸工程时空变化研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学,2016. [XU Ning. Study on temporal and spatial changes of Chinese mainland coastline and coastal engineering[D]. Beijing:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Ning. Study on temporal and spatial changes of Chinese mainland coastline and coastal engineering[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 王庆兵,陈麟,支传顺等. 不同海岸带地下水微生物群落结构与多样性差异研究[J/OL]. 中国地质,(2022-08-22) [2023-10-11] [WANG Qingbing,CHEN Lin,ZHI Chuanshun,et al. Difference study on microbial community structure and diversity of groundwater in different coastal zones[J/OL]. Geology in China,(2022-08-22) [2023-10-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.0958.004.html.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Qingbing, CHEN Lin, ZHI Chuanshun, et al. Difference study on microbial community structure and diversity of groundwater in different coastal zones[J/OL]. Geology in China, (2022-08-22) [2023-10-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20220822.0958.004.html.(in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 尹霞,许晓晴,王勋功,等. 潮汐作用对黄河口滨海浅层地下水细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学,2022,41(4):526 − 533. [YIN Xia,XU Xiaoqing,WANG Xungong,et al. Tide effects on bacterial community structure in the shallow groundwater from Yellow River estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2022,41(4):526 − 533. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YIN Xia, XU Xiaoqing, WANG Xungong, et al . Tide effects on bacterial community structure in the shallow groundwater from Yellow River estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2022 ,41 (4 ):526 −533 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[36] WU Qinglong,ZWART G,SCHAUER M,et al. Bacterioplankton community composition along a salinity gradient of sixteen high-mountain lakes located on the Tibetan Plateau,China[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2006,72(8):5478 − 5485.
[37] HUANG Xiaolin,LIN Juan,YE Xiuyun,et al. Molecular characterization of a thermophilic and salt- and alkaline-tolerant xylanase from planococcus sp. SL4,a strain isolated from the sediment of a soda lake[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2015,25(5):662 − 671. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1408.08062
[38] WEI Jiaming,CUI Lijuan,LI Wei,et al. Denitrifying bacterial communities in surface-flow constructed wetlands during different seasons:Characteristics and relationships with environment factors[J]. Scientific Reports,2021,11:4918. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82438-3
[39] ZHANG Yi,ALAM M A,KONG Xiaoying,et al. Effect of salinity on the microbial community and performance on anaerobic digestion of marine macroalgae[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology,2017,92(9):2392 − 2399.
[40] ANANTHARAMAN K,BROWN C T,HUG L A,et al. Thousands of microbial genomes shed light on interconnected biogeochemical processes in an aquifer system[J]. Nature Communications,2016,7:13219. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13219
[41] KIM K,HEISS J. Methods in capturing the spatiotemporal dynamics of flow and biogeochemical reactivity in sandy beach aquifers:A review[J]. Water,2021,13(6):782. doi: 10.3390/w13060782
[42] ADYASARI D,HASSENRÜCK C,OEHLER T,et al. Microbial community structure associated with submarine groundwater discharge in northern Java (Indonesia)[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,689:590 − 601. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.193
[43] HÉRY M,VOLANT A,GARING C,et al. Diversity and geochemical structuring of bacterial communities along a salinity gradient in a carbonate aquifer subject to seawater intrusion[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology,2014,90(3):922 − 934. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12445
[44] HONG Yiguo,WU Jiapeng,WILSON S,et al. Vertical stratification of sediment microbial communities along geochemical gradients of a subterranean estuary located at the Gloucester beach of Virginia,United States[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2019,9:3343. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03343
[45] CHEN Lin,ZHANG Jin,DAI Heng,et al. Comparison of the groundwater microbial community in a salt-freshwater mixing zone during the dry and wet seasons[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2020,271:110969. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110969
[46] UNNO T,KIM J,KIM Y,et al. Influence of seawater intrusion on microbial communities in groundwater[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2015,532:337 − 343. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.111
[47] CHEN Lin,HU B X,DAI Heng,et al. Characterizing microbial diversity and community composition of groundwater in a salt-freshwater transition zone[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,678:574 − 584. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.017
[48] DEL CARMEN V G M,SOLA F,VALLEJOS Á. Comparative study of microbial diversity in different coastal aquifers:Determining factors[J]. Water,2023,15(7):1337. doi: 10.3390/w15071337
[49] VALLERO M V G,HULSHOFF POL L W,LETTINGA G,et al. Effect of NaCl on thermophilic (55℃) methanol degradation in sulfate reducing granular sludge reactors[J]. Water Research,2003,37(10):2269 − 2280. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00024-1
[50] 宋延静,张晓黎,付娆,等. 滨海盐渍化土壤中氨氧化微生物丰度和多样性特征[J]. 土壤,2022,54(6):1157 − 1164. [SONG Yanjing,ZHANG Xiaoli,FU Rao,et al. Patterns of activity and community of ammonia oxidizers along salinity gradient in salinized soils[J]. Soils,2022,54(6):1157 − 1164. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SONG Yanjing, ZHANG Xiaoli, FU Rao, et al . Patterns of activity and community of ammonia oxidizers along salinity gradient in salinized soils[J]. Soils,2022 ,54 (6 ):1157 −1164 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[51] 李寒,张晓黎,郭晓红,等. 滨海盐渍化土壤中蓝细菌多样性及分布[J]. 微生物学通报,2015,42(5):957 − 967. [LI Han,ZHANG Xiaoli,GUO Xiaohong,et al. Diversity and distribution of cyanobacteria in coastal saline soils[J]. Microbiology China,2015,42(5):957 − 967. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Han, ZHANG Xiaoli, GUO Xiaohong, et al . Diversity and distribution of cyanobacteria in coastal saline soils[J]. Microbiology China,2015 ,42 (5 ):957 −967 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[52] ZHAO Qingqing,BAI Junhong,GAO Yongchao,et al. Shifts in the soil bacterial community along a salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Land Degradation & Development,2020,31(16):2255 − 2267.
[53] SANG Shilei,ZHANG Xiaoying, DAI Heng,et al. Diversity and predictive metabolic pathways of the prokaryotic microbial community along a groundwater salinity gradient of the Pearl River Delta,China[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8:17317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35350-2
[54] JIANG Shan,ZHANG Yixue,JIN Jie,et al. Organic carbon in a seepage face of a subterranean estuary:Turnover and microbial interrelations[J]. The Science of the Total Environment,2020,725:138220. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138220
[55] MA Zhonglin,GAO Long,SUN Mingxue,et al. Microbial diversity in groundwater and its response to seawater intrusion in Beihai city,southern China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2022,13:876665. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.876665
[56] MAZHAR S,PELLEGRINI E,CONTIN M,et al. Impacts of salinization caused by sea level rise on the biological processes of coastal soils :A review[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science,2022,10:909415.
[57] 陈香,李卫民,刘勤. 基于文献计量的近30年国内外土壤微生物研究分析[J]. 土壤学报,2020,57(6):1458 − 1470. [CHEN Xiang,LI Weimin,LIU Qin. Bibliometric-based analysis of researches on soil microbes at home and abroad in the past 30 years[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2020,57(6):1458 − 1470. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Xiang, LI Weimin, LIU Qin . Bibliometric-based analysis of researches on soil microbes at home and abroad in the past 30 years[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2020 ,57 (6 ):1458 −1470 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[58] FIERER N,JACKSON R B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2006,103(3):626 − 631.
[59] JACKSON C R,VALLAIRE S C. Effects of salinity and nutrients on microbial assemblages in Louisiana wetland sediments[J]. Wetlands,2009,29(1):277 − 287. doi: 10.1672/08-86.1
[60] SERRANO R. Salt tolerance in plants and microorganisms:Toxicity targets and defense responses[J]. International Review of Cytology,1996,165:1 − 52.
[61] SHAO Pengshuai,HAN Hongyan,SUN Jingkuan,et al. Salinity effects on microbial derived-C of coastal wetland soils in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution,2022,10:872816. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.872816
[62] 桑石磊. 海水入侵对地下水水文地球化学及微生物群落的影响研究[D]. 广州:暨南大学,2019. [SANG Shilei. Effects of seawater intrusion on hydrogeocheistry and microbial communities of groundwater[D]. Guangzhou:Jinan University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SANG Shilei. Effects of seawater intrusion on hydrogeocheistry and microbial communities of groundwater[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) [63] HUANG Shan,SHERMAN A,CHEN Chen,et al. Tropical cyclone effects on water and sediment chemistry and the microbial community in estuarine ecosystems[J]. Environmental Pollution,2021,286:117228. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117228
[64] FENG Lijuan,ZHANG Zeliang,YANG Guangfeng,et al. Microbial communities and sediment nitrogen cycle in a coastal eutrophic lake with salinity and nutrients shifted by seawater intrusion[J]. Environmental Research,2023,225:115590. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115590
[65] XIONG Guiyao,ZHU Xiaobin,WU Jichun,et al. Seawater intrusion alters nitrogen cycling patterns through hydrodynamic behavior and biochemical reactions:Based on Bayesian isotope mixing model and microbial functional network[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2023,867:161368. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161368
[66] SOLA F,DEL CARMEN V G M,VALLEJOS A. Interrelation prokaryotic community-aquifer in a carbonate coastal environment[J]. Aquatic Sciences,2019,82(1):13.
[67] POFFENBARGER H J,NEEDELMAN B A,MEGONIGAL J P. Salinity influence on methane emissions from tidal marshes[J]. Wetlands,2011,31(5):831 − 842. doi: 10.1007/s13157-011-0197-0
[68] NEUBAUER S C,FRANKLIN R B,BERRIER D J. Saltwater intrusion into tidal freshwater marshes alters the biogeochemical processing of organic carbon[J]. Biogeosciences,2013,10(12):8171 − 8183. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-8171-2013
[69] SEGARRA K E A,COMERFORD C,SLAUGHTER J,et al. Impact of electron acceptor availability on the anaerobic oxidation of methane in coastal freshwater and brackish wetland sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2013,115:15 − 30. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.03.029
[70] GONG Shanggui,IZON G,PENG Yongbo,et al. Multiple sulfur isotope systematics of pyrite for tracing sulfate-driven anaerobic oxidation of methane[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2022,597:117827. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2022.117827
[71] PATHAK H,RAO D L N. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization from added organic matter in saline and alkali soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,1998,30(6):695 − 702. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00208-3
[72] TOBIAS C,NEUBAUER S C. Salt marsh biogeochemistry:An overview[M]//Coastal Wetlands. Amsterdam:Elsevier,2019:539-596.
[73] WESTON N B,DIXON R E,JOYE S B. Ramifications of increased salinity in tidal freshwater sediments:Geochemistry and microbial pathways of organic matter mineralization[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences,2006,111(G1):G01009.
[74] 桑石磊,黄柏强. 基于基因测序的地下咸水微生物多样性研究[J]. 农技服务,2021,38(6):104 − 106. [SANG Shilei,HUANG Baiqiang. Study on microbial diversity of underground salt water based on gene sequencing[J]. Agricultural Technology Service,2021,38(6):104 − 106. (in Chinese)]
SANG Shilei, HUANG Baiqiang . Study on microbial diversity of underground salt water based on gene sequencing[J]. Agricultural Technology Service,2021 ,38 (6 ):104 −106 . (in Chinese)[75] SELIVANOVA E A,POSHVINA D V,KHLOPKO Y A,et al. Diversity of prokaryotes in planktonic communities of saline Sol-Iletsk Lakes (Orenburg Oblast,Russia)[J]. Microbiology,2018,87(4):569 − 582. doi: 10.1134/S0026261718040161
[76] 刘吉文,刘姣,黄付燕,等. 海洋奇古菌门认知的拓展:从新类群到新功能[J]. 微生物学报,2022,62(12):4628 − 4645. [LIU Jiwen,LIU Jiao,HUANG Fuyan,et al. The expanding knowledge of marine Thaumarchaeota:From new groups to new functions[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2022,62(12):4628 − 4645. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jiwen, LIU Jiao, HUANG Fuyan, et al . The expanding knowledge of marine Thaumarchaeota: From new groups to new functions[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2022 ,62 (12 ):4628 −4645 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[77] HUANG Wencong ,LIU Yang,ZHANG Xinxu,et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals metabolic flexibility of Woesearchaeota[J]. Nature Communications,2021,12:5281.
-



 下载:
下载: