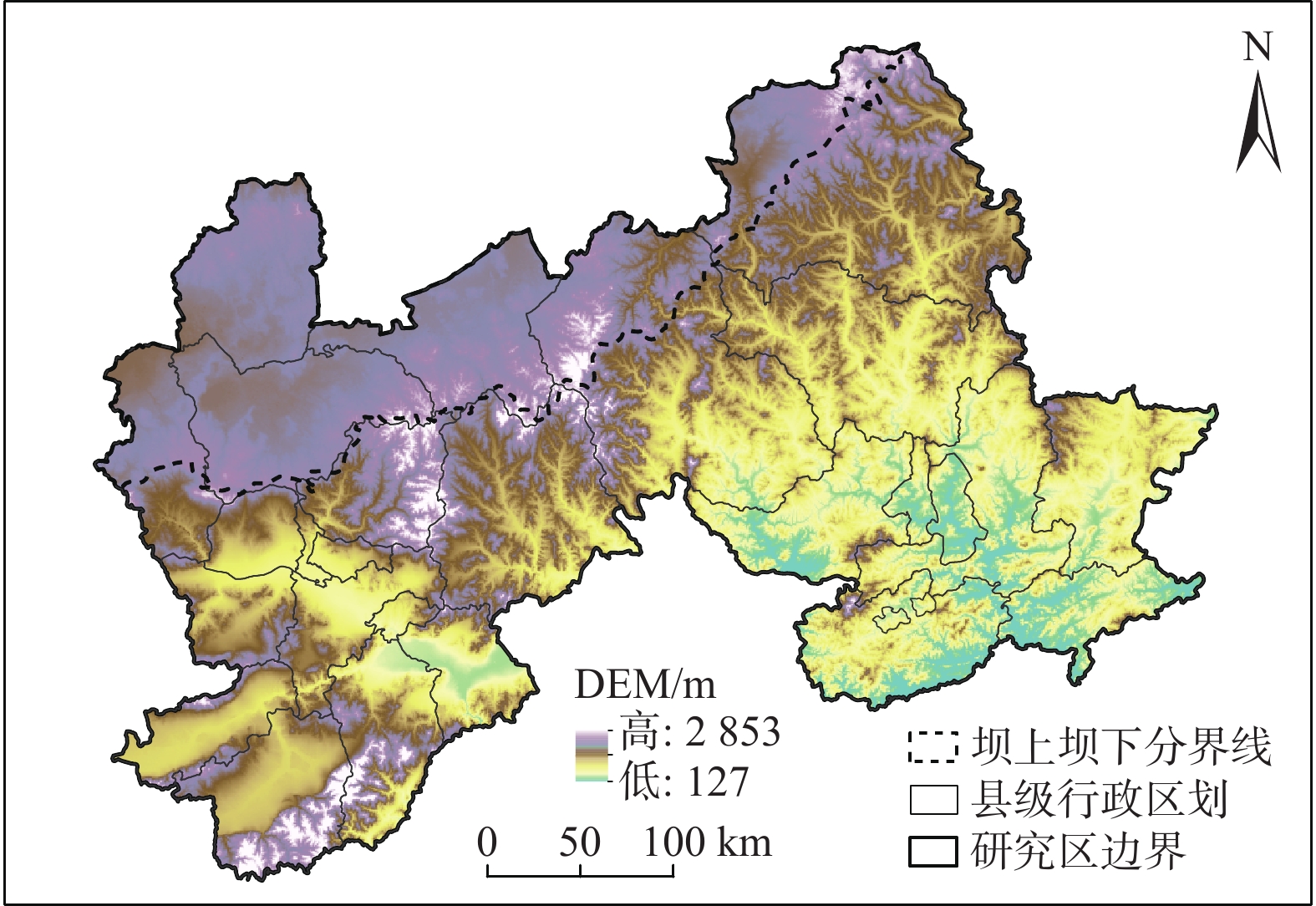
Driving factors analysis of surface soil moisture variation in Zhangjiakou-Chengde district based on geodetector
-
摘要:
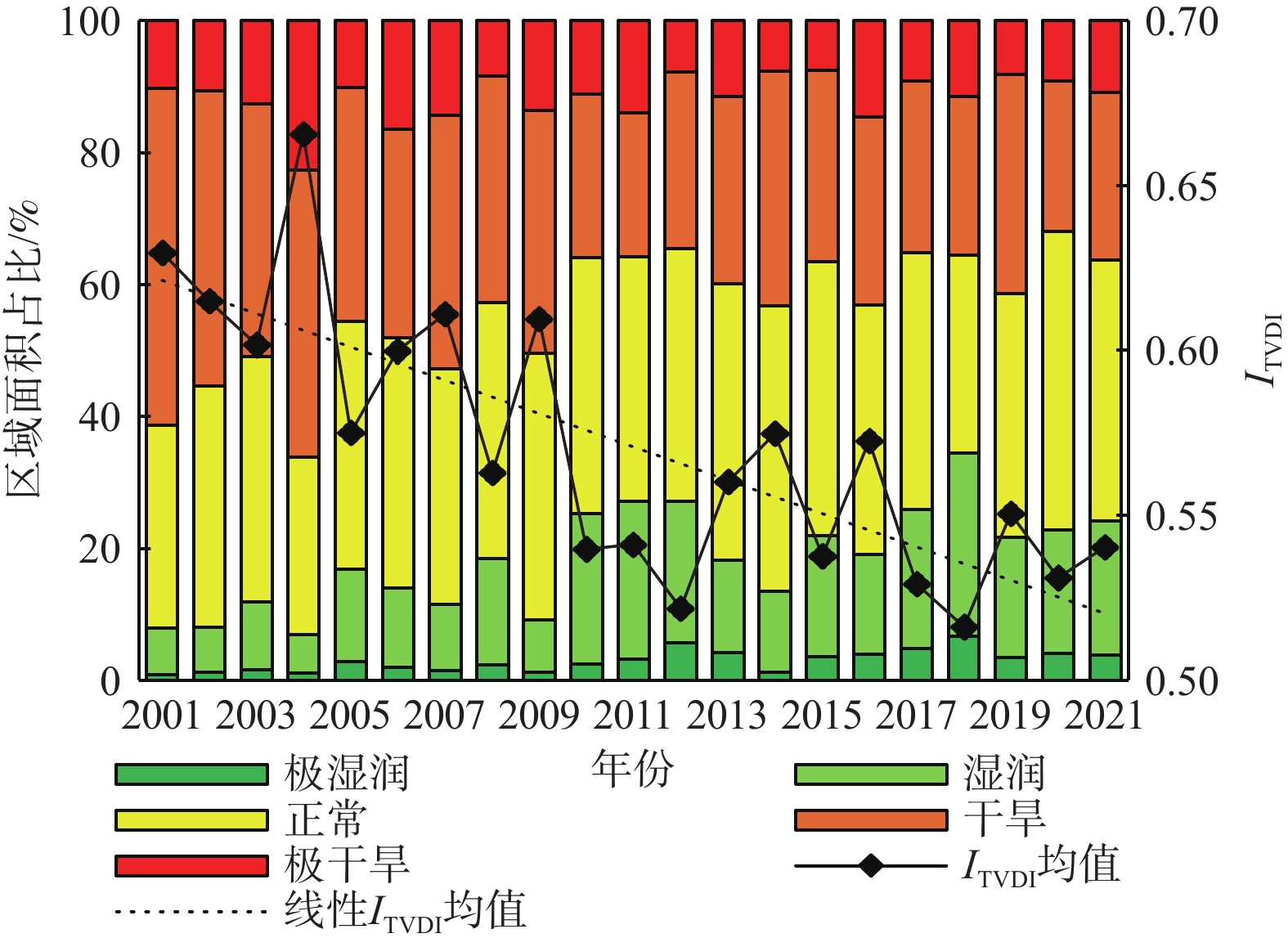
河北张家口、承德地区(以下简称“张承地区”)作为京津冀地区的生态屏障、重要的水源保护地和风沙阻隔区,近年来开展了一系列生态治理工程。土壤湿度作为综合反映气候、植被覆盖、土壤性质的重要指标,在大气水—地表水—地下水的循环中至关重要。但张承地区地处半干旱区,水资源相对匮乏,且现有研究忽视了对其土壤湿度空间变化特征及驱动因素的分析。研究以中等分辨率成像光谱仪数据、全球陆地数据同化系统数据集等为基础,基于温度-植被干旱指数模型反演并分析张承地区2001—2021年土壤湿度及时空变化特征,利用地理探测器方法分析8个驱动因子对张承地区土壤湿度时空异质性的解释力。结果表明:(1)2001—2021年张承地区的土壤湿度呈现波动上升趋势,土壤湿度分布为东部高,西部低,张家口低于承德;空间上,研究区83.09%区域的土壤湿度呈现逐年上升的趋势;(2)研究区土壤湿度的驱动因素解释力大小排序为:归一化植被指数>土壤类型>年均降水>土地利用类型>坡度>高程>年均气温>坡向,其中归一化植被指数和土壤类型的解释力均高于30%,为主导驱动因素;(3)在交互作用分析中,多因子共同作用的影响大于单因子作用, 归一化植被指数与高程的交互影响作用最强。研究结果对于张承地区水资源的高效利用及生态环境保护具有重要的参考作用。
-
关键词:
- 地理探测器 /
- 温度-植被干旱指数模型 /
- 土壤湿度 /
- 驱动因子 /
- 张承地区
Abstract:As an important water conservation and sand-windy barrier, Zhangjiakou and Chengde (Zhang-Cheng) district of Hebei Province is very important for ecological protection in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The soil moisture is an important comprehensive indicator for climate, vegetation cover, and soil property, and is essential in the cycle of atmospheric−surface water−underground water. However, few studies focused on the soil moisture change and its impact factors in the Zhang-Cheng district, an area with semi-arid climate and scarce water resources. Based on moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) and global land data assimilation system data (GLDAS), the spatiotemporal variation of surface soil moisture in Zhang-Cheng district was simulated during the period of 2001−2021 using temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) model. Moreover, the geodetector method was also employed to identify the contribution of 8 impact factors on soil moisture. The results indicate that the soil moisture is generally fluctuating increase during the period of 2001−2021. Spatially, the soil moisture is higher in the east and lower in the west part of the study area and approximately 83.09% of the the study area experienced a progressive increase in soil moisture. In terms of driving factors, normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), soil type, annual precipitation, land use type, slope, elevation, annual temperature, and aspect were analyzed in descending order of their effect on soil moisture variation. NDVI and soil type are the dominant drivers, with each contribution exceeding 30%. As to interaction analysis, it indicates that the effect of multiple factors is greater than that of individual factor. The synergistic interaction between NDVI and elevation is the largest influence on soil moisture. This study has great significance for efficient utilization of water resources and eco-environmental protection in the Zhang-Cheng district.
-
Key words:
- geodetector /
- TVDI model /
- soil moisture /
- driving factors /
- Zhang-Cheng district
-

-
表 1 土壤湿度等级划分标准
Table 1. Standard for classification of soil moisture levels
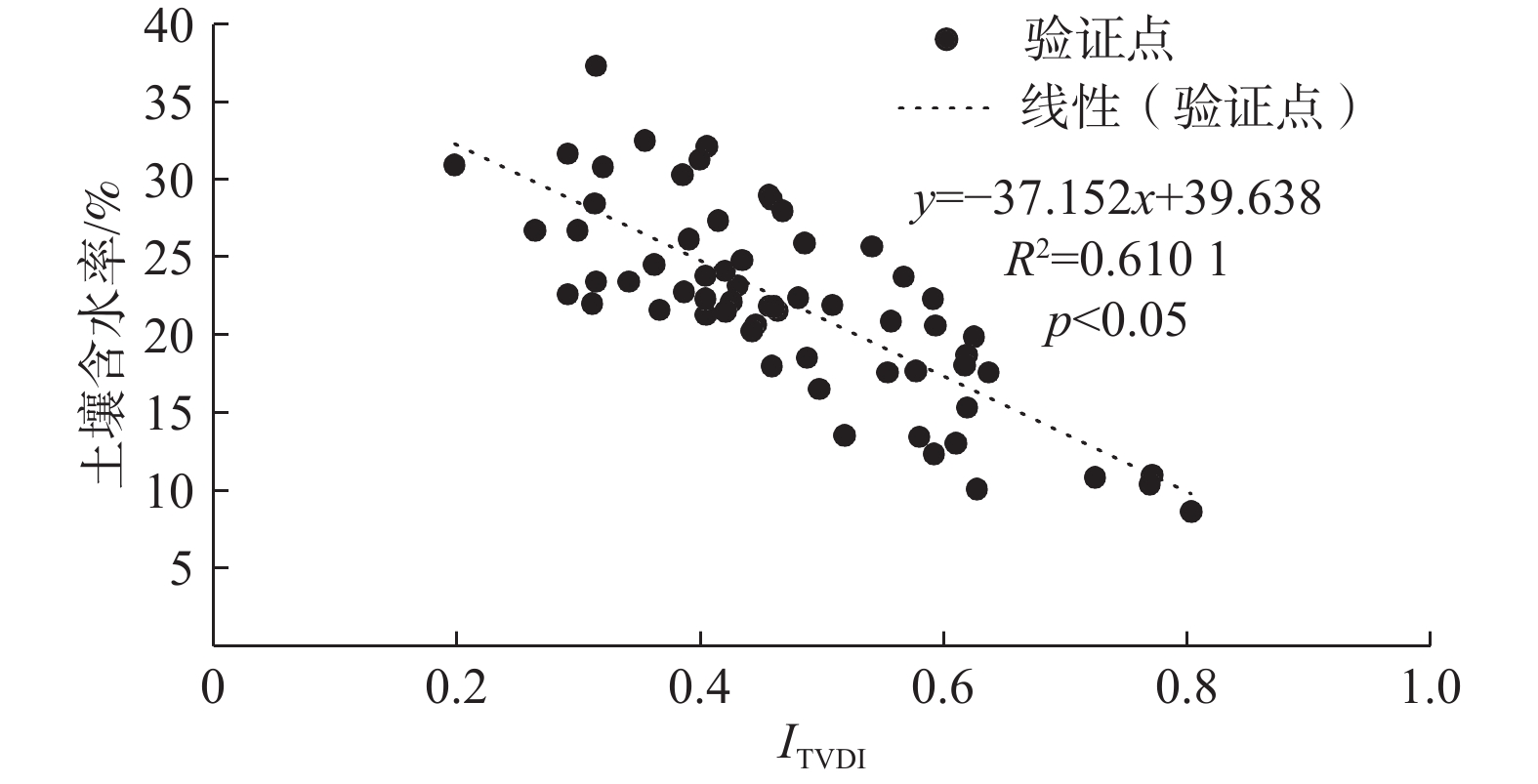
ITVDI值 土壤湿度等级 实测土壤含水率区间/% 0<ITVDI≤0.2 极湿润 30~32 0.2<ITVDI≤0.4 湿润 24~31 0.4<ITVDI≤0.6 正常 16~25 0.6<ITVDI≤0.8 干旱 10~18 0.8<ITVDI≤1 极干旱 注:表中“ITVDI”为TVDI值;空白为无数据,是由于实测土壤湿度的测量季节为夏季,受季节和测量位置影响,测量位置的ITVDI值均<0.8,因此无极干旱等级实测土壤含水率数据。 表 2 Z绝对值的显著性检验表
Table 2. Significance test table of absolute value of Z
|Z| ≥1.64 ≥1.96 ≥2.58 信度/% 90 95 99 表 3 交互作用类型
Table 3. Interaction types
判据 交互作用 q(X1∩X2)<Min(q(X1),q(X2)) 非线性减弱 Min(q(X1),q(X2))<q(X1∩X2)<Max(q(X1),q(X2)) 单因子
非线性减弱q(X1∩X2)>Max(q(X1),q(X2)) 双因子增强 q(X1∩X2)=q(X1)+q(X2) 独立 q(X1∩X2)>q(X1)+q(X2) 非线性增强 注:表中“Min”为取最小值;“Max”为取最大值;“X1”、“X2”分别为2个不同的驱动因子。 表 4 TVDI值空间变化趋势面积统计
Table 4. Areal statistics of spatial change in ITVDI
TVDI值变化趋势 等级 面积占比/% β<0.001,|Z|>1.96 显著下降 45.16 β<0.001, |Z|≤1.96 轻微下降 37.93 −0.001≤β≤0.001 基本不变 7.62 β>0.001, |Z|≤1.96 轻微上升 6.92 β>0.001, |Z|>1.96 显著上升 2.38 表 5 分异及因子探测器探测结果
Table 5. Detection results of differentiation and factor detectors
驱动因子 p值 q值 q值排序 NDVI 0.000 0.417 1 年均气温 0.000 0.098 7 年均降水 0.000 0.297 3 高程 0.000 0.146 6 坡度 0.000 0.154 5 坡向 0.506 0.006 8 土壤类型 0.000 0.369 2 土地利用类型 0.000 0.274 4 表 6 交互作用探测器探测结果
Table 6. Detection results of interaction detector
驱动因子 NDVI 年均气温 年均降水 高程 坡度 土壤类型 土地利用类型 NDVI 0.417 年均气温 0.584 0.098 年均降水 0.470 0.534 0.297 高程 0.615 0.239 0.529 0.146 坡度 0.427 0.304 0.339 0.294 0.154 土壤类型 0.509 0.512 0.453 0.580 0.409 0.369 土地利用类型 0.472 0.397 0.422 0.403 0.301 0.466 0.274 注:绿色代表非线性增强,黄色代表双因子增强。 -
[1] 程梦园,曹广超,赵美亮,等. 香日德-柴达木河流域土壤湿度时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 干旱区研究,2022,39(2):615 − 624. [CHENG Mengyuan,CAO Guangchao,ZHAO Meiliang,et al. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and influencial factors of soil moisture in the Xiangride-Qaidam River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research,2022,39(2):615 − 624. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHENG Mengyuan, CAO Guangchao, ZHAO Meiliang, et al . Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and influencial factors of soil moisture in the Xiangride-Qaidam River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research,2022 ,39 (2 ):615 −624 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 王德应,杨永崇,王涛,等. 基于TVDI的河南省土壤湿度时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2022(6):138 − 146. [WANG Deying,YANG Yongchong,WANG Tao,et al. Spatial-temporal variation characteristics of soil moisture and its relationship with meteorological factors in Henan Province based on TVDI[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2022(6):138 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Deying, YANG Yongchong, WANG Tao, et al. Spatial-temporal variation characteristics of soil moisture and its relationship with meteorological factors in Henan Province based on TVDI[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2022(6): 138 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 杨曦,武建军,闫峰,等. 基于地表温度-植被指数特征空间的区域土壤干湿状况[J]. 生态学报,2009,29(3):1205 − 1216. [YANG Xi,WU Jianjun,YAN Feng,et al. Assessment of regional soil moisture status based on characteristics of surface temperature/vegetation index space[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009,29(3):1205 − 1216. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Xi, WU Jianjun, YAN Feng, et al . Assessment of regional soil moisture status based on characteristics of surface temperature/vegetation index space[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009 ,29 (3 ):1205 −1216 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] LIU Yi,LI Peng,ZHANG Zhiwei. Resilient or not:A comparative case study of ten local water markets in China[J]. Sustainability,2018,10(11):4020. doi: 10.3390/su10114020
[5] HUANG Guangwei. From water-constrained to water-driven sustainable development:A case of water policy impact evaluation[J]. Sustainability,2015,7(7):8950 − 8964. doi: 10.3390/su7078950
[6] MOORE S M. The development of water markets in China:Progress,peril,and prospects[J]. Water Policy,2015,17(2):253 − 267. doi: 10.2166/wp.2014.063
[7] 梁韶卿. 温度植被干旱指数(TVDI)的优化与评价[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2021. [LIANG Shaoqing. Optimization and evaluation of temperature vegetation drought index (TVDI)[D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIANG Shaoqing. Optimization and evaluation of temperature vegetation drought index (TVDI)[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 郭铌,李栋梁,蔡晓军,等. 1995年中国西北东部特大干旱的气候诊断与卫星监测[J]. 干旱区地理,1997,20(3):69 − 74. [GUO Ni,LI Dongliang,Cai Xiaojun,et al. Climatic diagnosis and satellite monitoring of a severe drought over eastern Northwest China in 1995[J]. Arid Land Geography,1997,20(3):69 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Ni, LI Dongliang, Cai Xiaojun, et al . Climatic diagnosis and satellite monitoring of a severe drought over eastern Northwest China in 1995[J]. Arid Land Geography,1997 ,20 (3 ):69 −74 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 刘泽,陈建平. 北京植被时空变化与气候因子相关性[J]. 地质通报,2021,40(12):2159 − 2166. [LIU Ze,CHEN Jianping. Correlation between temporal-spatial changes of vegetation and climate factors in Beijing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021,40(12):2159 − 2166. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Ze, CHEN Jianping . Correlation between temporal-spatial changes of vegetation and climate factors in Beijing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2021 ,40 (12 ):2159 −2166 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] KOGAN F,SULLIVAN J. Development of global drought-watch system using NOAA/AVHRR data[J]. Advances in Space Research,1993,13(5):219 − 222. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(93)90548-P
[11] 冯强,田国良,王昂生,等. 基于植被状态指数的土壤湿度遥感方法研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2004,13(3):81 − 88. [FENG Qiang,TIAN Guoliang,WANG Angsheng,et al. Remote sensing monitoring of soil humidity using vegetation condition index[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2004,13(3):81 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FENG Qiang, TIAN Guoliang, WANG Angsheng, et al . Remote sensing monitoring of soil humidity using vegetation condition index[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2004 ,13 (3 ):81 −88 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] Liu Huiqing,HUETE A. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,1995,33(2):457 − 465. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1995.8746027
[13] 杨文杰. 基于Landsat 8生长时序遥感信息的玉米干旱监测研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2017. [YANG Wenjie. The research of monitoring on drought of maize based on landsat 8 growing time series remote sensing data[D]. Shihezi:Shihezi University,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Wenjie. The research of monitoring on drought of maize based on landsat 8 growing time series remote sensing data[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 王劲峰,徐成东. 地理探测器:原理与展望[J]. 地理学报,2017,72(1):116 − 134. [WANG Jinfeng,XU Chengdong. Geodetector:Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2017,72(1):116 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jinfeng, XU Chengdong . Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2017 ,72 (1 ):116 −134 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 覃星铭, 马国斌, 蒋忠诚, 等. 典型石漠化峰丛洼地土壤重金属的空间分异特征及其影响因素[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(5):283 − 292. [QIN Xingming, MA Guobin, JIANG Zhongcheng, et al. Spatial variations and influencing factors analysis of heavy metals in the soil of typical rocky desertification peak cluster depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(5):283 − 292. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QIN Xingming, MA Guobin, JIANG Zhongcheng, et al . Spatial variations and influencing factors analysis of heavy metals in the soil of typical rocky desertification peak cluster depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022 ,41 (5 ):283 −292 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 胡清清, 杨晓霞. 我国地质文化村(镇)空间分布特征及影响因素研究[J]. 地质论评,2024,70(1):277 − 286. [HU Qingqing, YANG Xiaoxia. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Geological Culture Villages (Towns) in China[J]. Geological Review,2024,70(1):277 − 286. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Qingqing, YANG Xiaoxia . Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Geological Culture Villages (Towns) in China[J]. Geological Review,2024 ,70 (1 ):277 −286 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 马靖宣,金晓媚,张绪财,等. 基于InVEST模型的张承地区水源涵养功能时空变化特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):54 − 64. [MA Jingxuan,JIN Xiaomei,ZHANG Xucai,et al. Spatio-temporal change characteristics of water conservation function in the Zhang-Cheng district based on the InVEST model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):54 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MA Jingxuan, JIN Xiaomei, ZHANG Xucai, et al . Spatio-temporal change characteristics of water conservation function in the Zhang-Cheng district based on the InVEST model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (3 ):54 −64 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 邵雅琪,姜群鸥,胡中民,等. 张承地区植被指数时空演变特征及其与气候因子的关系[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2018,23(7):96 − 106. [SHAO Yaqi,JIANG Qunou,HU Zhongmin,et al. Spatio-temporal evolution of the vegetation index and its relationship with climatic factors in the Zhangjiakou-Chengde Region[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University,2018,23(7):96 − 106. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHAO Yaqi, JIANG Qunou, HU Zhongmin, et al . Spatio-temporal evolution of the vegetation index and its relationship with climatic factors in the Zhangjiakou-Chengde Region[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University,2018 ,23 (7 ):96 −106 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 王盛,李亚文,李庆,等. 变化环境影响下张承地区水源涵养和土壤保持服务及其权衡与协同关系研究[J]. 生态学报,2022,42(13):5391 − 5403. [WANG Sheng,LI Yawen,LI Qing,et al. Water and soil conservation and their trade-off and synergistic relationship under changing environment in Zhangjiakou-Chengde Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42(13):5391 − 5403. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Sheng, LI Yawen, LI Qing, et al . Water and soil conservation and their trade-off and synergistic relationship under changing environment in Zhangjiakou-Chengde Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022 ,42 (13 ):5391 −5403 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] 闫峰,王艳姣,武建军. 基于Ts-EVI特征空间的春旱遥感监测——以河北省为例[J]. 干旱区地理,2009,32(5):769 − 775. [YAN Feng,WANG Yanjiao,WU Jianjun. Application of Ts-EVI character space to monitor spring drought:A case study in Hebei China[J]. Arid Land Geography,2009,32(5):769 − 775. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Feng, WANG Yanjiao, WU Jianjun . Application of Ts-EVI character space to monitor spring drought: A case study in Hebei China[J]. Arid Land Geography,2009 ,32 (5 ):769 −775 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 薄燕飞,白建军,刘永林. 基于TVDI及气象干旱指数的河北省春旱时空变化特征[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2016,52(2):188 − 195. [BO Yanfei,BAI Jianjun,LIU Yonglin. The spatial-temporal variations of spring drought in Hebei Province based on TVDI and meteorological drought index[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2016,52(2):188 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
BO Yanfei, BAI Jianjun, LIU Yonglin . The spatial-temporal variations of spring drought in Hebei Province based on TVDI and meteorological drought index[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2016 ,52 (2 ):188 −195 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 朱彦儒,赵红莉,黄艳艳,等. 基于双指数联合模型的土壤含水量反演——以河北省为例[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文),2020,18(4):71 − 80. [ZHU Yanru,ZHAO Hongli,HUANG Yanyan,et al. Soil water content inversion based on double-index combined model:Taking Hebei Province as an example[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2020,18(4):71 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Yanru, ZHAO Hongli, HUANG Yanyan, et al . Soil water content inversion based on double-index combined model: Taking Hebei Province as an example[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2020 ,18 (4 ):71 −80 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[23] 王嘉杰. 基于TVDI的河北省干旱监测及其滞后性研究[D]. 邯郸:河北工程大学,2022. [WANG Jiajie. Study on drought monitoring and its lag in Hebei Province based on TVDI[D]. Handan:Hebei University of Engineering,2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jiajie. Study on drought monitoring and its lag in Hebei Province based on TVDI[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] SANDHOLT I,RASMUSSEN K,ANDERSEN J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2002,79(2/3):213 − 224.
[25] 沙莎,郭铌,李耀辉,等. 我国温度植被旱情指数TVDI的应用现状及问题简述[J]. 干旱气象,2014,32(1):128 − 134. [SHA Sha,GUO Ni,LI Yaohui,et al. Introduction of application of temperature vegetation dryness index in China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2014,32(1):128 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHA Sha, GUO Ni, LI Yaohui, et al . Introduction of application of temperature vegetation dryness index in China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology,2014 ,32 (1 ):128 −134 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[26] 孙振蓉. 京津冀地区冬小麦面积估算和旱情遥感监测研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2015. [SUN Zhenrong. Estimation of winter wheat area and drought monitoring research based on remote sensing data in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SUN Zhenrong. Estimation of winter wheat area and drought monitoring research based on remote sensing data in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 程伟,辛晓平. 基于TVDI的内蒙古草地干旱变化特征分析[J]. 中国农业科学,2020,53(13):2728 − 2742. [CHENG Wei,XIN Xiaoping. Analysis of spatial-temporal characteristics of drought variation in grassland area of inner Mongolia based on TVDI[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020,53(13):2728 − 2742. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHENG Wei, XIN Xiaoping . Analysis of spatial-temporal characteristics of drought variation in grassland area of inner Mongolia based on TVDI[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020 ,53 (13 ):2728 −2742 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[28] 唐海, 张代磊, 周文纳. 广东阳江盆地遥感数据地温反演及地热异常靶区圈定[J]. 地质论评,2022,68(6):2396 − 2404. [TANG Hai, ZHANG Dailei, ZHOU Wenna. Inversion of ground temperature from remote sensing data and delineation of geothermal anomaly targets in Yangjiang Basin, Guangdong Province[J]. Geological Review,2022,68(6):2396 − 2404. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TANG Hai, ZHANG Dailei, ZHOU Wenna . Inversion of ground temperature from remote sensing data and delineation of geothermal anomaly targets in Yangjiang Basin, Guangdong Province[J]. Geological Review,2022 ,68 (6 ):2396 −2404 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[29] 陈振,刘涛,梁守真,等. 基于Modis-TVDI方法的山东小麦生长季旱情遥感监测[J]. 江苏农业科学,2018,46(19):323 − 328. [CHEN Zhen,LIU Tao,LIANG Shouzhen,et al. Remote sensing monitoring of drought in wheat growing season in Shandong Province based on Modis-TVDI method[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(19):323 − 328. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Zhen, LIU Tao, LIANG Shouzhen, et al . Remote sensing monitoring of drought in wheat growing season in Shandong Province based on Modis-TVDI method[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2018 ,46 (19 ):323 −328 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[30] 刘一哲,冯文兰,扎西央宗,等. 基于MODIS TVDI和模糊数学方法的藏北地区旱情等级遥感监测[J]. 干旱区研究,2020,37(1):86 − 96. [LIU Yizhe,FENG Wenlan,ZHA Xiyangzong,et al. Remote sensing monitoring of drought level in North Tibet based on MODIS TVDI and fuzzy mathematics[J]. Arid Zone Research,2020,37(1):86 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Yizhe, FENG Wenlan, ZHA Xiyangzong, et al . Remote sensing monitoring of drought level in North Tibet based on MODIS TVDI and fuzzy mathematics[J]. Arid Zone Research,2020 ,37 (1 ):86 −96 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[31] 陈丙寅,杨辽,陈曦,等. 基于改进型TVDI在干旱区旱情监测中的应用研究[J]. 干旱区地理,2019,42(4):902 − 913. [CHEN Bingyin,YANG Liao,CHEN Xi,et al. Application of modified TVDI in drought monitoring in arid areas[J]. Arid Land Geography,2019,42(4):902 − 913. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Bingyin, YANG Liao, CHEN Xi, et al . Application of modified TVDI in drought monitoring in arid areas[J]. Arid Land Geography,2019 ,42 (4 ):902 −913 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[32] 林楠,姜然哲,刘强,等. 近20年三江平原地表蒸散发时空特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(5):1392 − 1407. [LIN Nan,JIANG Ranzhe,LIU Qiang,et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of surface evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain in recent 20 years[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(5):1392 − 1407. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIN Nan, JIANG Ranzhe, LIU Qiang, et al . Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of surface evapotranspiration in Sanjiang Plain in recent 20 years[J]. Geology in China,2021 ,48 (5 ):1392 −1407 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[33] 童威,郎丰铠. 基于地理探测器的武汉市土地利用变化及其驱动机制探讨[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文),2021,52(4):45 − 56. [TONG Wei,LANG Fengkai. Geodetector-based analysis on land-use variation and its driving force in Wuhan[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2021,52(4):45 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TONG Wei, LANG Fengkai . Geodetector-based analysis on land-use variation and its driving force in Wuhan[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2021 ,52 (4 ):45 −56 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[34] 王倩,金晓媚,张绪财,等. 河北省张承地区2001—2020年植被动态变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 现代地质,2023,37(4):881 − 891. [WANG Qian,JIN Xiaomei,ZHANG Xucai,et al. Vegetation dynamics and driving factors in Zhangjiakou-Chengde Area of Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020[J]. Geoscience,2023,37(4):881 − 891. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Qian, JIN Xiaomei, ZHANG Xucai, et al . Vegetation dynamics and driving factors in Zhangjiakou-Chengde Area of Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020[J]. Geoscience,2023 ,37 (4 ):881 −891 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[35] HEIN L,DE RIDDER N,HIERNAUX P,et al. Desertification in the Sahel:Towards better accounting for ecosystem dynamics in the interpretation of remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Arid Environments,2011,75(11):1164 − 1172. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.05.002
[36] 马梓策. 华北地区干旱时空变化特征及其影响因素分析[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学. [MA Zice. Spatial and temporal characteristics of drought and its influencing factors in north china[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Normal University. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MA Zice. Spatial and temporal characteristics of drought and its influencing factors in north china[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University. (in Chinese with English abstract) -



 下载:
下载: