Changes of glaciers and glacier lakes in alpine and extremely alpine regions using remote sensing technology:A case study in the Shisha Pangma area of southern Tibet
-
摘要:
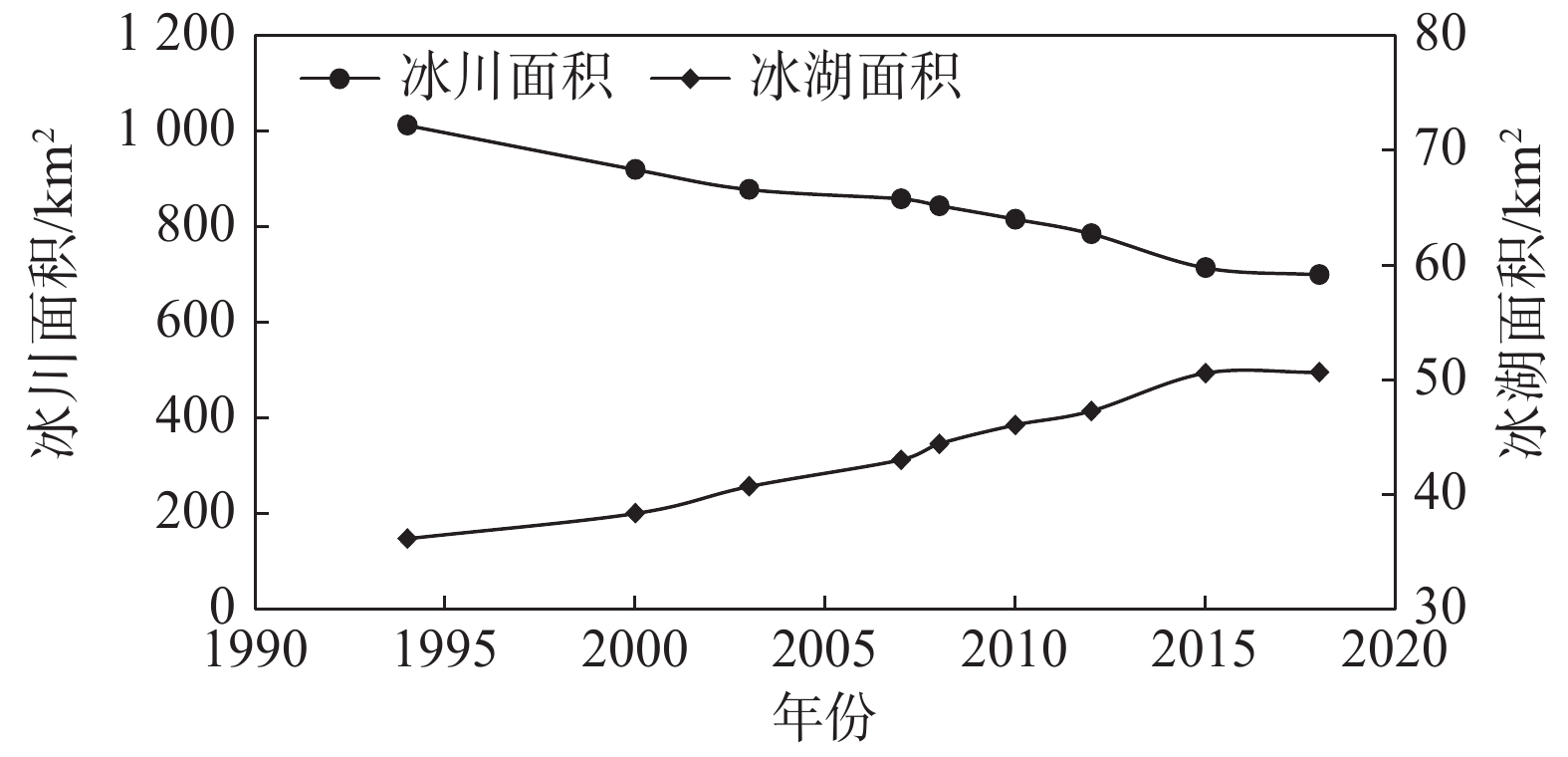
在全球变暖的大背景下,我国藏南地区冰川持续退缩,冰湖不断扩张,从而引发了一系列的地质灾害问题。文章利用Landsat系列影像,在面向对象分类方法的基础上采用波段比值法和NDWI指数提取了藏南希夏邦玛峰地区1994—2018年共9期冰川和冰湖的面积。研究表明,希夏邦玛峰地区净冰川持续退缩,总体速率为(1.28±0.32)%/a,冰湖的扩张速率约为(1.88±1.07)%/a。同时,面积小于1 km2的冰川退缩极为严重,高达33.25%。其次气象再分析数据表明夏季气温和降水的增加可能是该地区净冰川退缩加快的重要原因,并且共同促进了冰湖的加速扩张,大大提高了该地区冰湖溃决的风险。
Abstract:Under the background of global warming, glaciers in southern Tibet continue to retreat and glacier lakes continue to expand, resulting in a series of geological disasters. In this paper, based on the object-oriented classification method, the area of glaciers and glacier lakes in Shisha Pangma peak region of South Tibet from 1994 to 2018 were extracted by using band ratio method and NDWI index. The results show that the net glaciers in Shisha Pangma peak region continue to retreat, with an overall rate of (1.28 ± 0.32)%per year, and the expansion rate of the glacier lakes are about (1.88 ±1. 07) %per year. At the same time, glaciers with an area of less than 1 km2 retreat seriously, up to 33.25%. Secondly, the meteorological reanalysis data show that the increase of summer temperature and precipitation may be important reasons for the accelerated retreat of net glaciers in the region, and jointly promote the expansion of glacier lakes, greatly increasing the risk of glacier lakes outburst in the region.
-
Key words:
- glaciers /
- remote sensing /
- glacial lakes /
- glacial lakes outburst
-

-
表 1 中国各地冰川面积分布
Table 1. Glacier area distribution in China
地区 冰川面积/km2 占全国冰川百分比/% 昆仑山 12082.95 20.34 念青唐古拉山 10818.45 18.21 天山 9235.96 15.55 喜马拉雅山 8411.96 14.16 喀喇昆仑山 4897.37 8.24 羌塘高原 3355.34 5.65 帕米尔 2849.36 4.80 唐古拉山 2217.23 3.73 祁连山 1930.49 3.25 冈底斯山 1572.82 2.65 横断山 1462.46 2.46 阿尔泰山 279.91 0.47 阿尔金山 275.00 0.46 萨吾尔山 16.84 0.03 表 2 光学影像数据详情
Table 2. Details of optical image data
影像时间 传感器类型 条带号
/行号空间分辨率 1994年10月 TM5 141/40 30 m多光谱 1994年10月 TM5 140/40 30 m多光谱 2000年11月 ETM 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2000年11月 ETM 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2003年10月 ETM+ 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2003年11月 ETM+ 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2007年10月 ETM+ 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2007年9月 ETM+ 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2008年11月 ETM+ 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2008年10月 ETM+ 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2010年10月 ETM+ 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2010年10月 ETM+ 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2012年11月 ETM+ 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2012年10月 ETM+ 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2015年11月 OIL8 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2015年11月 OIL8 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2018年11月 OIL8 141/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 2018年10月 OIL8 140/40 30 m多光谱+15 m全色 表 3 9期冰川冰湖面积表
Table 3. Area of glaciers and glacial lakes in Phase 9
年份 1994 2000 2003 2007 2008 2010 2012 2015 2018 冰川面积/km2 1012.66 920.10 878.23 858.81 844.55 816.30 785.59 714.45 699.89 冰湖面积/km2 36.15 38.35 40.70 43.04 44.43 46.07 47.29 50.59 50.65 表 4 不同角度下冰川的退缩率
Table 4. Retreat rates of glaciers with multipectives
冰川面积/km2 变化率
均值/%纬度
位置变化率
均值/%经度
位置变化率
均值/%流向 变化率
均值/%0~1 −33.25 低 −21.91 西 −17.52 北 −31.11 1~2 −30.04 中 −21.75 中 −20.13 东北 −14.28 2~3 −22.08 高 −17.11 东 −22.67 东南 −26.10 3~4 −17.91 南 −20.61 4~7 −18.37 西南 −22.02 7~20 −13.98 西北 −17.10 -
[1] ZHANG Z, LIU S Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Glacier variations at Aru Co in western Tibet from 1971 to 2016 derived from remote-sensing data[J]. Journal of Glaciology,2018,64(245):397 − 406. doi: 10.1017/jog.2018.34
[2] LI G, LIN H, YE Q H. Heterogeneous decadal glacier downwasting at the Mt. Everest (Qomolangma) from 2000 to 2012 based on multi-baseline bistatic SAR interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2018,206:336 − 349. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.12.032
[3] DING Y J, LIU S Y, LI J, et al. The retreat of glaciers in response to recent climate warming in Western China[J]. Annals of Glaciology,2006,43:97 − 105. doi: 10.3189/172756406781812005
[4] 吴珊珊, 姚治君, 姜丽光, 等. 现代冰川体积变化研究方法综述[J]. 地球科学进展,2015,30(2):237 − 246. [WU Shanshan, YAO Zhijun, JIANG Liguang, et al. Method review of modern glacier volume change[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2015,30(2):237 − 246. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2015.02.0237
[5] 周玉杉. 基于多源遥感数据的青藏高原及其周边区域冰川物质平衡变化研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2019,35(4):142. [ZHOU Yushan. Investigation of glacier mass balance in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau and its surroundings based on multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2019,35(4):142. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.04.023
[6] 邬光剑, 姚檀栋, 王伟财, 等. 青藏高原及周边地区的冰川灾害[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2019,34(11):1285 − 1292. [WU Guangjian, YAO Tandong, WANG Weicai, et al. Glacial hazards on Tibetan Plateau and surrounding alpines[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2019,34(11):1285 − 1292. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] NIE Y, LIU Q, LIU S Y. Glacial lake expansion in the central Himalayas by landsat images, 1990–2010[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(12):e83973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083973
[8] 舒梅海. 近25年阿尔泰山区冰川冰湖变化及特征[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2017.
SHU Meihai. Variations and characters of glacier and glacial lakesin Altai mountains in recent 25 years[D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] GARDELLE J, BERTHIER E, ARNAUD Y, et al. Region-wide glacier mass balances over the Pamir-Karakoram-Himalaya during 1999–2011[J]. The Cryosphere,2013,7(4):1263 − 1286. doi: 10.5194/tc-7-1263-2013
[10] HEWITT K. The karakoram anomaly glacier expansion and the ‘elevation effect’ karakoram Himalaya[J]. Mountain Research and Development,2005,25(4):332 − 340. doi: 10.1659/0276-4741(2005)025[0332:TKAGEA]2.0.CO;2
[11] 刘时银, 姚晓军, 郭万钦, 等. 基于第二次冰川编目的中国冰川现状[J]. 地理学报,2015,70(1):3 − 16. [LIU Shiyin, YAO Xiaojun, GUO Wanqin, et al. The contemporary glaciers in China based on the Second Chinese Glacier Inventory[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2015,70(1):3 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11821/dlxb201501001
[12] 许艾文. 近40年中国喀喇昆仑山冰川变化的遥感监测[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017.
XU Aiwen. Monitoring glacier change based on remote sensing in China karakoram for the last four decades[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 冀琴. 1990—2015年喜马拉雅山冰川变化及其对气候波动的响应[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018.
JI Qin. Glacier variations in response to climate change in the Himalaya during 1990—2015[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王欣, 吴坤鹏, 蒋亮虹, 等. 近20年天山地区冰湖变化特征[J]. 地理学报,2013,68(7):983 − 993. [WANG Xin, WU Kunpeng, JIANG Lianghong, et al. Wide expansion of glacial lakes in Tianshan mountains during 1990—2010[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2013,68(7):983 − 993. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 柴开国. 珠峰地区冰湖变化及其影响研究[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2017.
CHAI Kaiguo. The change of glacial lake and its influence in the Everest region[D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王欣, 刘时银, 姚晓军, 等. 我国喜马拉雅山区冰湖遥感调查与编目[J]. 地理学报,2010,65(1):29 − 36. [WANG Xin, LIU Shiyin, YAO Xiaojun, et al. Glacier lake investigation and inventory in the Chinese Himalayas based on the remote sensing data[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2010,65(1):29 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11821/xb201001004
[17] 蒋亮虹. 基于多源遥感数据的喜马拉雅中段冰川变化监测与分析[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2015.
JIANG Lianghong. Variation and implication of glaciers based on multi-source remote sensing data in central Himalaya[D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 吕卉. 近40年喜马拉雅山冰川波动对气候变化的响应[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013.
LYU Hui. Response of glacier variation to climate change in the Himalayan mountains, during the last 40 years[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 汪宙峰, 张廷山, 王成武. 西藏喜马拉雅山地区冰湖溃决的预测模型及其应用研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2016,38(2):388 − 394. [WANG Zhoufeng, ZHANG Tingshan, WANG Chengwu. Prediction model and its application for glacial lake outburst in the Himalayas area, Tibet[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2016,38(2):388 − 394. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 徐道明, 冯清华. 西藏喜马拉雅山区危险冰湖及其溃决特征[J]. 地理学报,1989,44(3):343 − 351. [XU Daoming, FENG Qinghua. Dangerous glacial lake and outburst featuresin Xizang Himalayas[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,1989,44(3):343 − 351. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.03.011
[21] 姚晓军, 刘时银, 孙美平, 等. 20世纪以来西藏冰湖溃决灾害事件梳理[J]. 自然资源学报,2014,29(8):1377 − 1390. [YAO Xiaojun, LIU Shiyin, SUN Meiping, et al. Study on the glacial lake outburst flood events in Tibet since the 20th Century[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2014,29(8):1377 − 1390. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2014.08.010
[22] 车涛, 晋锐, 李新, 等. 近20a来西藏朋曲流域冰湖变化及潜在溃决冰湖分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2004,26(4):397 − 402. [CHE Tao, JIN Rui, LI Xin, et al. Glacial lakes variation and the potentially dangerous glacial lakes in the Pumqu basin of Tibet during the last two decades[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2004,26(4):397 − 402. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2004.04.004
[23] WANG X, LIU S Y, GUO W Q, et al. Using remote sensing data to quantify changes in glacial lakes in the Chinese Himalaya[J]. Mountain Research and Development,2012,32(2):203 − 212. doi: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-11-00044.1
[24] 吕儒仁, 等. 西藏泥石流与环境[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1999.
LYU Ruren, et al. Tibet autonomous region debris flow and environment in Tibet[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[25] 刘春玲, 童立强, 祁生文, 等. 喜马拉雅山地区冰川湖溃决灾害隐患遥感调查及影响因素分析[J]. 国土资源遥感,2016,28(3):110 − 115. [LIU Chunling, TONG Liqiang, QI Shengwen, et al. Remote sensing investigation and influence factor analysis of glacier lake outburst potential in the himalayas[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2016,28(3):110 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] JAIN S K, MIR R A. Glacier and glacial lake classification for change detection studies using satellite data: A case study from Baspa basin, western Himalaya[J]. Geocarto International,2019,34(4):391 − 414. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2017.1404145
[27] KOLECKA N, KOZAK J. Assessment of the accuracy of SRTM C- and X-band high mountain elevation data: A case study of the polish Tatra mountains[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics,2014,171(6):897 − 912. doi: 10.1007/s00024-013-0695-5
[28] 祁威, 张镱锂, 高俊刚, 等. 1971—2009年珠穆朗玛峰地区尼泊尔境内气候变化[J]. 地理学报,2013,68(1):82 − 94. [QI Wei, ZHANG Yili, GAO Jungang, et al. Climate change on southern slope of Mt. Qomolangma region in Nepal from 1971 to 2009[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2013,68(1):82 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11821/xb201301010
[29] 杨续超, 张镱锂, 张玮, 等. 珠穆朗玛峰地区近34年来气候变化[J]. 地理学报,2006,61(7):687 − 696. [YANG Xuchao, ZHANG Yili, ZHANG Wei, et al. Climate change in Mt.Qomolangma region in China during the last 34 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2006,61(7):687 − 696. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.07.002
[30] XIE P P, CHEN M Y, YANG S, et al. A gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over east Asia[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology,2007,8(3):607 − 626. doi: 10.1175/JHM583.1
[31] FAN Y, VAN DEN DOOL H. A global monthly land surface air temperature analysis for 1948-present[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,2008,113(D1):D01103.
[32] HUANG L, LI Z, HAN H D, et al. Analysis of thickness changes and the associated driving factors on a debris-covered glacier in the Tienshan Mountain[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2018,206:63 − 71. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.12.028
[33] LIPPL S, VIJAY S, BRAUN M. Automatic delineation of debris-covered glaciers using InSAR coherence derived from X-, C- and L-band radar data: a case study of Yazgyl Glacier[J]. Journal of Glaciology,2018,64(247):811 − 821. doi: 10.1017/jog.2018.70
[34] LI D S, CUI B L, WANG Y, et al. Glacier extent changes and possible causes in the Hala Lake Basin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2019,16(7):1571 − 1583. doi: 10.1007/s11629-018-5198-5
[35] 王欣, 刘时银, 郭万钦, 等. 我国喜马拉雅山区冰碛湖溃决危险性评价[J]. 地理学报,2009,64(7):782 − 790. [WANG Xin, LIU Shiyin, GUO Wanqin, et al. Hazard assessment of moraine-dammed lake outburst floods in the Himalayas, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2009,64(7):782 − 790. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.07.002
[36] 车涛, 李新, MOOL P, 等. 希夏邦马峰东坡冰川与冰川湖泊变化遥感监测[J]. 冰川冻土,2005,27(6):801 − 805. [CHE Tao, LI Xin, MOOL P, et al. Monitoring glaciers and associated glacial lakes on the east slopes of mount Xixia Bangma from remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2005,27(6):801 − 805. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2005.06.003
[37] WAKE C P, MAYEWSKI P A, XIE Z C, et al. Regional distribution of monsoon and desert dust signals recorded in Asian glaciers[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,1993,20(14):1411 − 1414. doi: 10.1029/93GL01682
-




 下载:
下载: