Probabilistic inverse-analysis and reliability prediction of rainfall-induced landslides for slope with multi-source information
-
摘要:
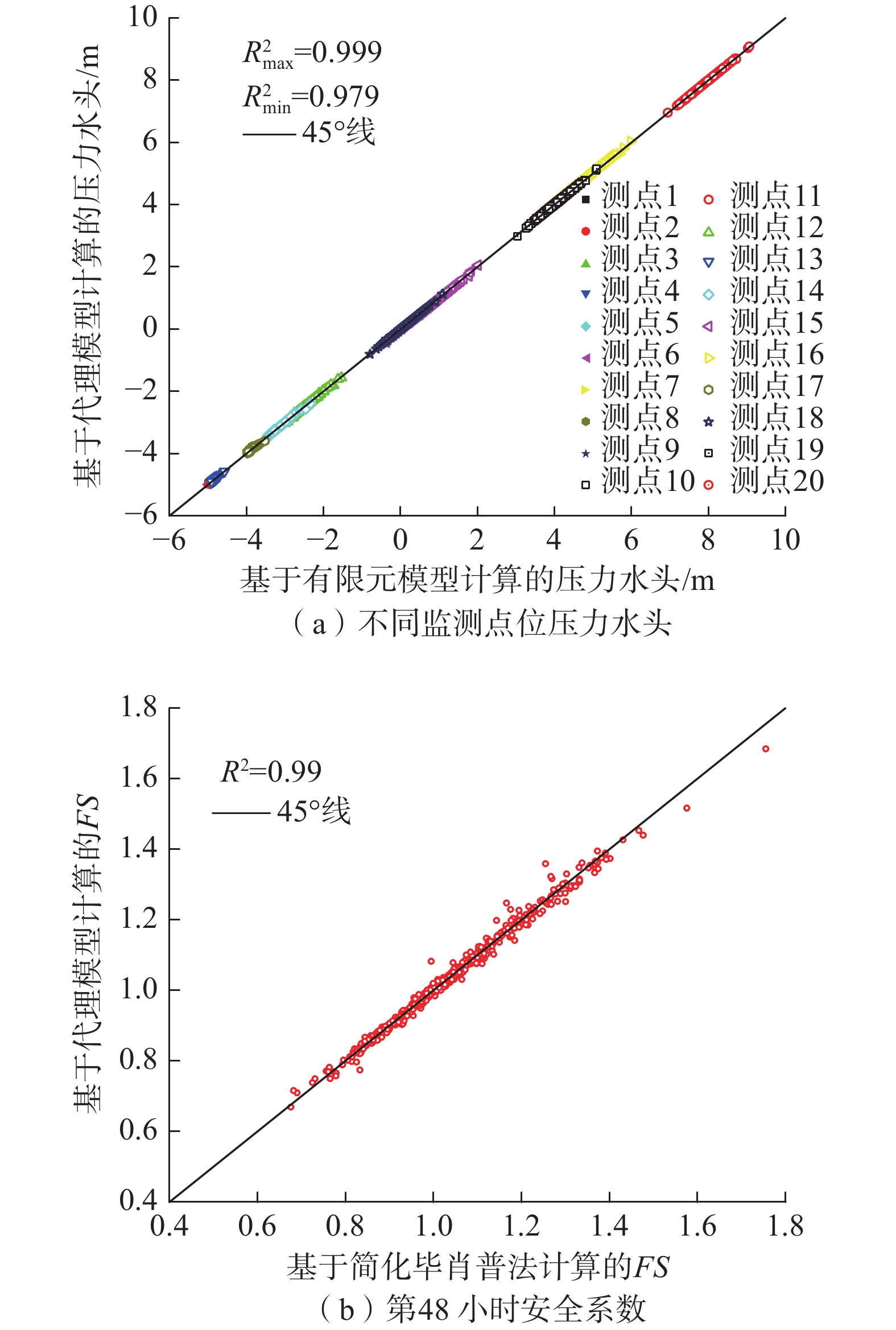
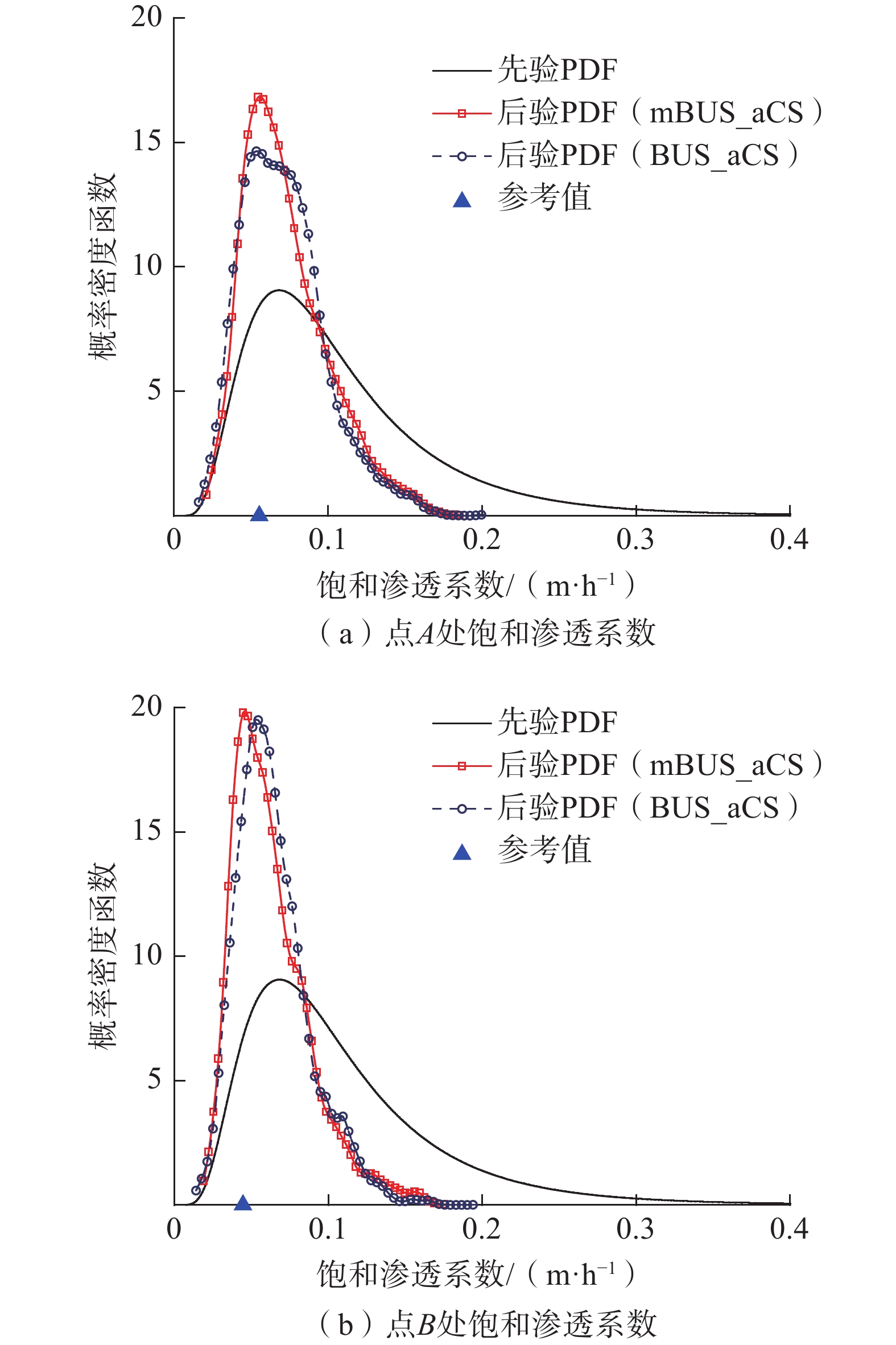
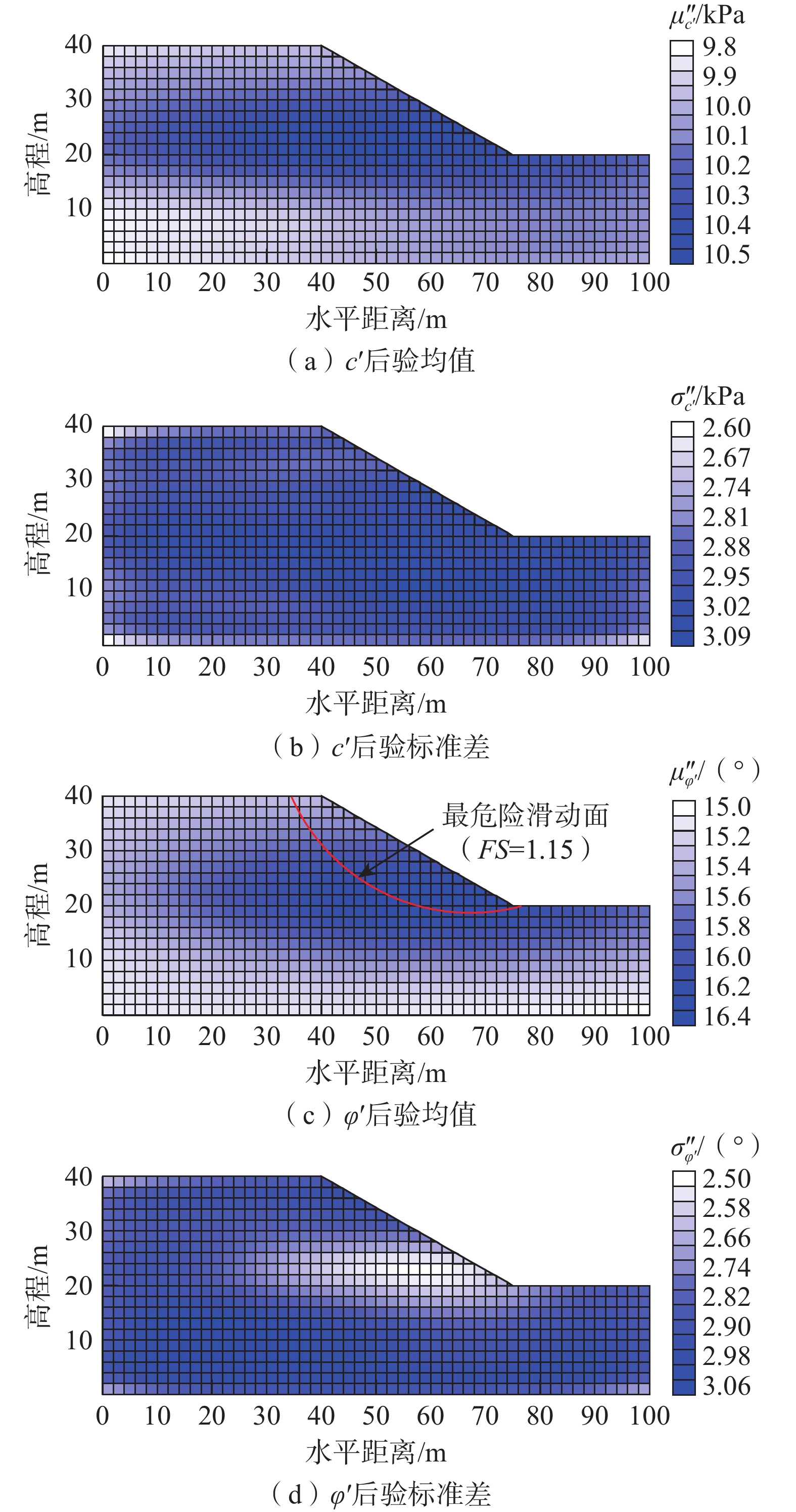
概率反分析是推断不确定土体参数统计特征的重要手段,可以使边坡可靠度评估更接近工程实际。然而目前的概率反分析很少使用多源信息(包括监测数据、观测信息和边坡服役记录),因为这通常涉及数千个随机变量和高维似然函数的评估。因此融合多源信息对空间变异土体参数进行概率反分析进而预测降雨条件下的边坡可靠度是一项具有挑战性的难题。文章将改进的基于子集模拟的贝叶斯更新(mBUS)方法与自适应条件抽样(aCS)算法相结合,构建了空间变异土体参数概率反分析和边坡可靠度预测的框架,并以某一公路边坡为例验证了该框架的有效性。研究结果表明:通过融合多源信息所获得的土体参数后验统计特征与现场观测结果基本吻合;用更新后的土体参数预测得到2004年9月12日该边坡在暴雨工况下的失效概率为23.1%,符合实际边坡失稳情况,说明在此框架下可以充分利用多源信息解决高维概率反分析问题。
Abstract:Probabilistic inverse-analysis is an essential approach to infer statistical characteristics of uncertain soil parameters, making the slope reliability assessment closer to engineering reality. However, current probabilistic inverse analysis rarely integrates multi-source information, including monitored data, field observation information, and slope survival records. Conducting the probabilistic inverse-analysis of spatially varying soil parameters and slope reliability prediction under rainfalls by integrating the multi-source information is a challenging issue due to the involvement of thousands of random variables and the evaluation of high-dimensional likelihood functions. In this paper, a modified Bayesian updating with subset simulation (mBUS) method is combined with adaptive conditional sampling (aCS) algorithm to establish a framework for probabilistic inverse analysis of spatially variable soil parameters and reliability prediction of slopes. The effectiveness of this framework is validated using a highway slope as a case study. The research results show that the posterior statistical characteristics of soil parameters obtained by integrating multi-source information are in good agreement with field observation results. Additionally, the probability of slope failure under heavy rainfall on September 12, 2004 with the updated soil parameters is 23.1 %, which is in line with the actual slope instability. Within this framework, multi-source information can be fully utilized to address high-dimensional probabilistic inverse analysis problems.
-

-
表 1 回填层岩土体参数先验信息
Table 1. Prior statistical characteristics of soil parameters for the backfill layer
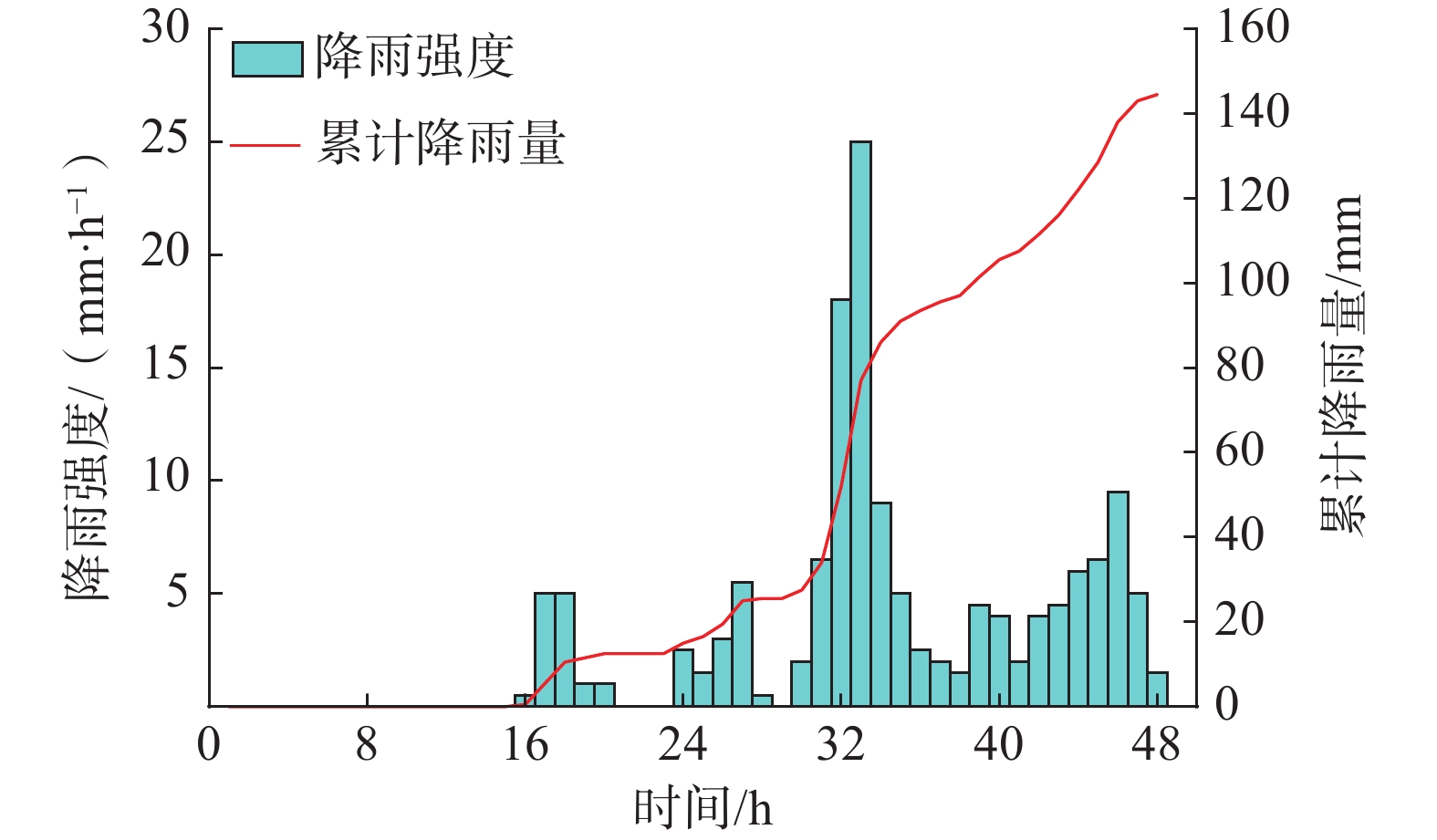
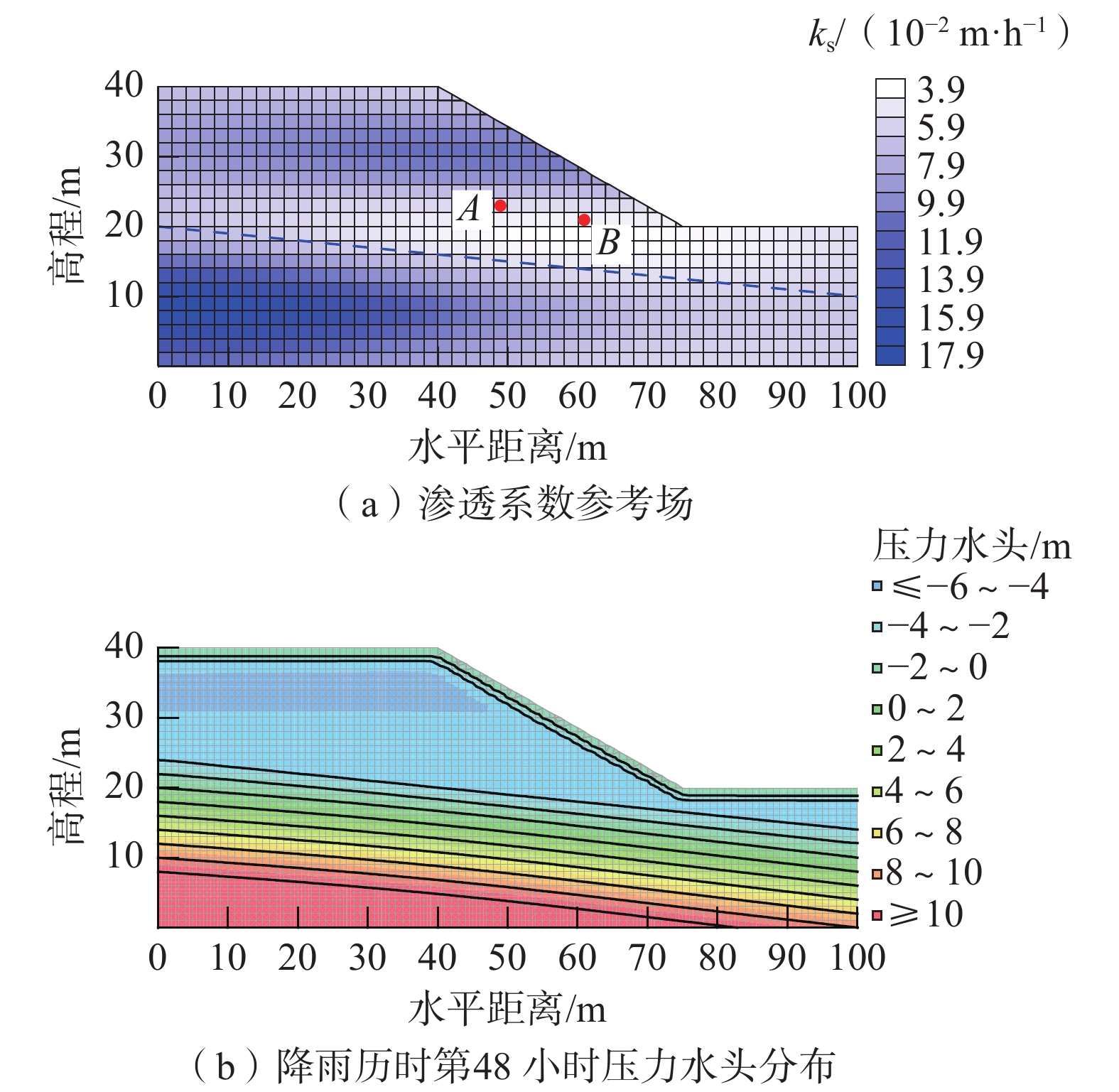
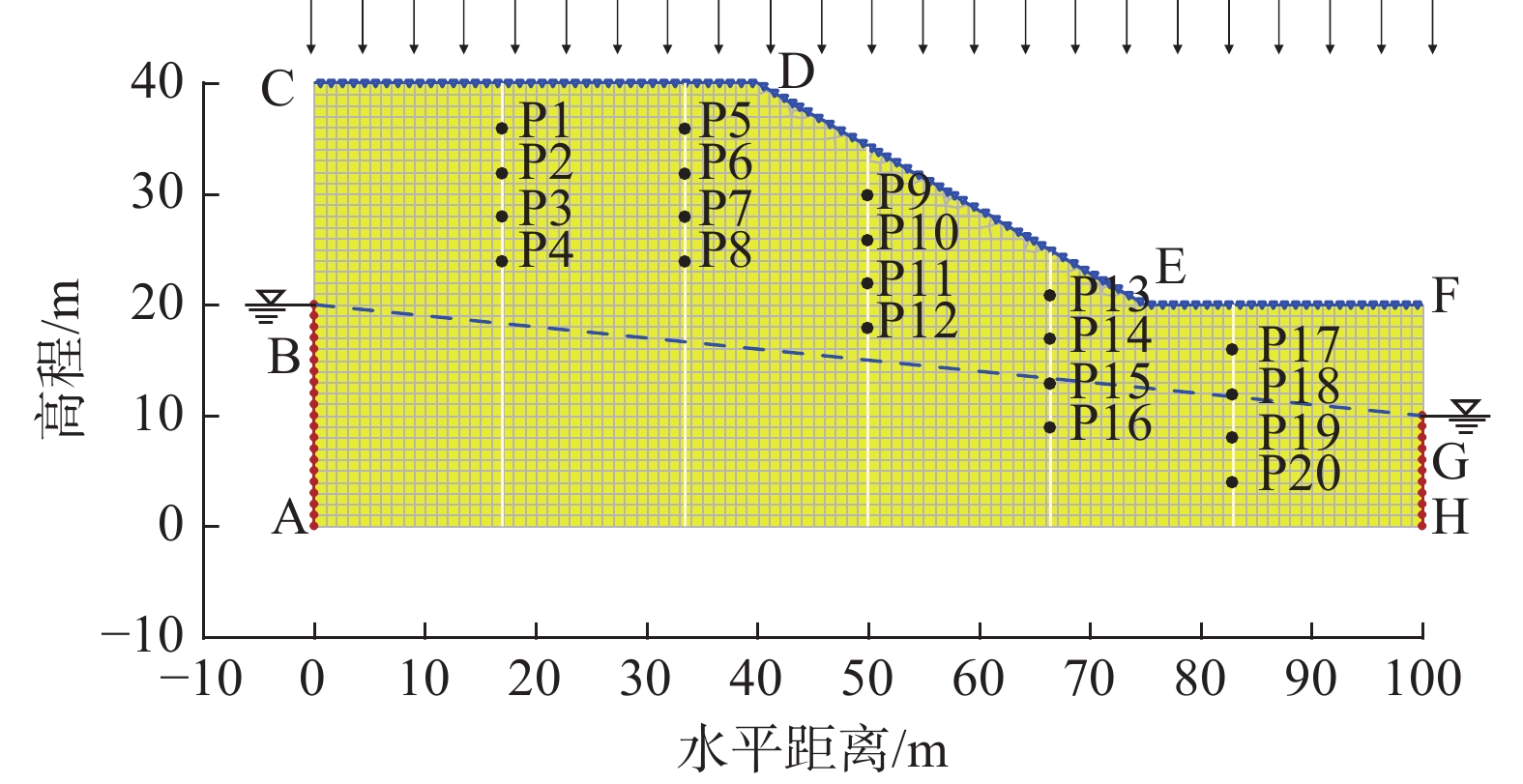
土体类型 土体参数 μ σ COV 概率分布 回填层 饱和渗透系数/(m·h−1) 0.108 0.0648 0.6 对数正态分布 黏聚力/kPa 10 3 0.3 对数正态分布 内摩擦角/(°) 15 3 0.2 对数正态分布 饱和体积含水量 0.315 — — — 饱和重度/(kN·m−3) 20 — — — -
[1] 文海家, 张岩岩, 付红梅, 等. 降雨型滑坡失稳机理及稳定性评价方法研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报,2018,31(2):15 − 29. [WEN Haijia, ZHANG Yanyan, FU Hongmei, et al. Research status of instability mechanism of rainfall-induced landslide and stability evaluation methods[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2018,31(2):15 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEN Haijia, ZHANG Yanyan, FU Hongmei, et al . Research status of instability mechanism of rainfall-induced landslide and stability evaluation methods[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2018 ,31 (2 ):15 −29 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 胡康,任光明,常文娟,等. 基于节理不确定性的可靠度分析——以西藏某岩质边坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):53 − 60. [HU Kang, REN Guangming, CHANG Wenjuan, et al. Reliability analysis based on joint uncertainty:A case study of a rock slope in Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):53 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Kang, REN Guangming, CHANG Wenjuan, et al . Reliability analysis based on joint uncertainty: A case study of a rock slope in Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (2 ):53 −60 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 陈忠源, 戴自航, 简文彬. 基于因子权重反分析的新近失稳土质边坡稳定性评价云模型[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4):125 − 133. [CHEN Zhongyuan, DAI Zihang, JIAN Wenbin. Cloud model for stability evaluation of recently failed soil slopes based on weight inversion of influencing factors[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(4):125 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Zhongyuan, DAI Zihang, JIAN Wenbin . Cloud model for stability evaluation of recently failed soil slopes based on weight inversion of influencing factors[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (4 ):125 −133 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[4] 王继玲, 周维博, 孙梨梨, 等. 石川河富平地下水库渗透系数空间变异性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):34 − 43. [WANG Jiling, ZHOU Weibo, SUN Lili, et al. Study on the spatial vriability of hydraulic conductivity of underground reservoir in Fuping section of Shichuan River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):34 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jiling, ZHOU Weibo, SUN Lili, et al . Study on the spatial vriability of hydraulic conductivity of underground reservoir in Fuping section of Shichuan River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (3 ):34 −43 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] YANG Haoqing,ZHANG Lulu,PAN Qiujing,et al. Bayesian estimation of spatially varying soil parameters with spatiotemporal monitoring data[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2021,16(1):263 − 278. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-00991-z
[6] CAO Zijun,WANG Yu,LI Dianqing. Site-specific characterization of soil properties using multiple measurements from different test procedures at different locations–A Bayesian sequential updating approach[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,211:150 − 161. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.06.021
[7] DIAZDELAO F A,GARBUNO-INIGO A,AU S K,et al. Bayesian updating and model class selection with Subset Simulation[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2017,317:1102 − 1121. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2017.01.006
[8] STRAUB D,PAPAIOANNOU I. Bayesian updating with structural reliability methods[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2015,141(3):04014134. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000839
[9] 刘贤, 揭鸿鹄, 蒋水华, 等. 融合历史降雨下斜坡稳定性观测信息的可靠度分析[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1865 − 1874. [LIU Xian, JIE Honghu, JIANG Shuihua, et al. Slope reliability analysis incorporating observation of stability performance under a past rainfall event[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1865 − 1874. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Xian, JIE Honghu, JIANG Shuihua, et al . Slope reliability analysis incorporating observation of stability performance under a past rainfall event[J]. Earth Science,2023 ,48 (5 ):1865 −1874 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 曹子君, 胡超, 苗聪, 等. 基于分层贝叶斯学习的滨海软土地层高效识别方法[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1730 − 1741. [CAO Zijun, HU Chao, MIAO Cong, et al. Efficient identification method of coastal soft soil stratum based on hierarchical Bayesian learning[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1730 − 1741. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CAO Zijun, HU Chao, MIAO Cong, et al . Efficient identification method of coastal soft soil stratum based on hierarchical Bayesian learning[J]. Earth Science,2023 ,48 (5 ):1730 −1741 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] DEPINA I,OGUZ E A,THAKUR V. Novel Bayesian framework for calibration of spatially distributed physical-based landslide prediction models[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2020,125:103660. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103660
[12] PAPAIOANNOU I,BETZ W,ZWIRGLMAIER K,et al. MCMC algorithms for subset simulation[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics,2015,41:89 − 103. doi: 10.1016/j.probengmech.2015.06.006
[13] ZHANG J,ZHANG L M,TANG W H. Slope reliability analysis considering site-specific performance information[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2011,137(3):227 − 238. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000422
[14] AU S K,BECK J L. Estimation of small failure probabilities in high dimensions by subset simulation[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics,2001,16(4):263 − 277. doi: 10.1016/S0266-8920(01)00019-4
[15] WANG C H,FANG Li,CHANG D T T,et al. Back-analysis of a rainfall-induced landslide case history using deterministic and random limit equilibrium methods[J]. Engineering Geology,2023,317:107055. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107055
[16] 蒋水华, 李典庆, 周创兵, 等. 考虑参数空间变异性的非饱和土坡可靠度分析[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(9):2569 − 2578. [JIANG Shuihua, LI Dianqing, ZHOU Chuangbing, et al. Reliability analysis of unsaturated slope considering spatial variability[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(9):2569 − 2578. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIANG Shuihua, LI Dianqing, ZHOU Chuangbing, et al . Reliability analysis of unsaturated slope considering spatial variability[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014 ,35 (9 ):2569 −2578 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] FREDLUND D G,XING Anqing,HUANG Shangyan. Predicting the permeability function for unsaturated soils using the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1994,31(4):533 − 546. doi: 10.1139/t94-062
[18] YANG Haoqing,ZHANG Lulu,XUE Jianfeng,et al. Unsaturated soil slope characterization with Karhunen–Loève and polynomial chaos via Bayesian approach[J]. Engineering with Computers,2019,35(1):337 − 350. doi: 10.1007/s00366-018-0610-x
[19] HUANG J,GRIFFITHS D V. Determining an appropriate finite element size for modelling the strength of undrained random soils[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2015,69:506 − 513. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.06.020
[20] LIU Xin,WANG Yu,KOO R C H,et al. Development of a slope digital twin for predicting temporal variation of rainfall-induced slope instability using past slope performance records and monitoring data[J]. Engineering Geology,2022,308:106825. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106825
[21] ZHANG J,ZHANG L M,TANG W H. Bayesian framework for characterizing geotechnical model uncertainty[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2009,135(7):932 − 940. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000018
-



 下载:
下载: