Landslide susceptibility modeling and interpretability based on CatBoost-SHAP model
-
摘要:
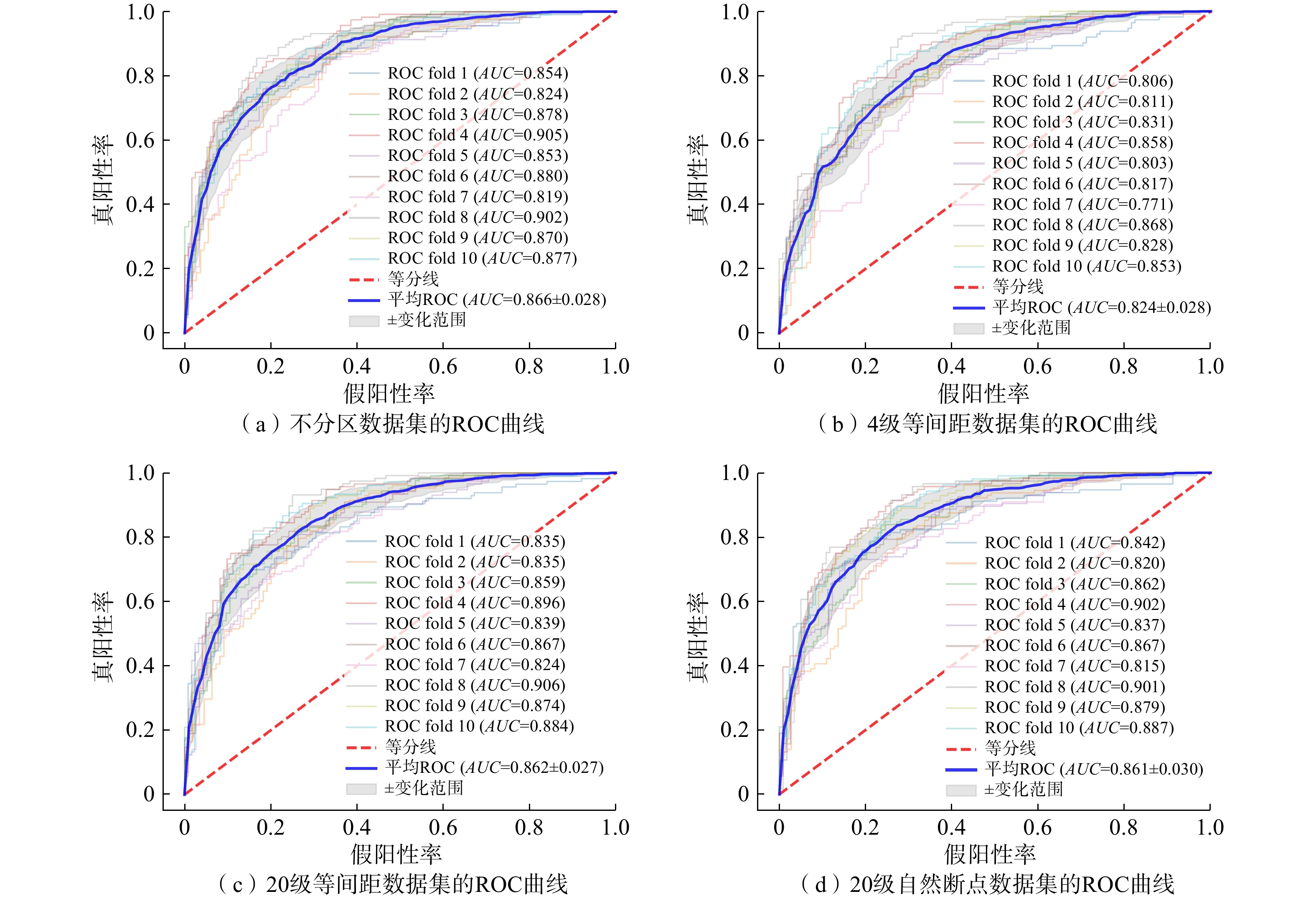
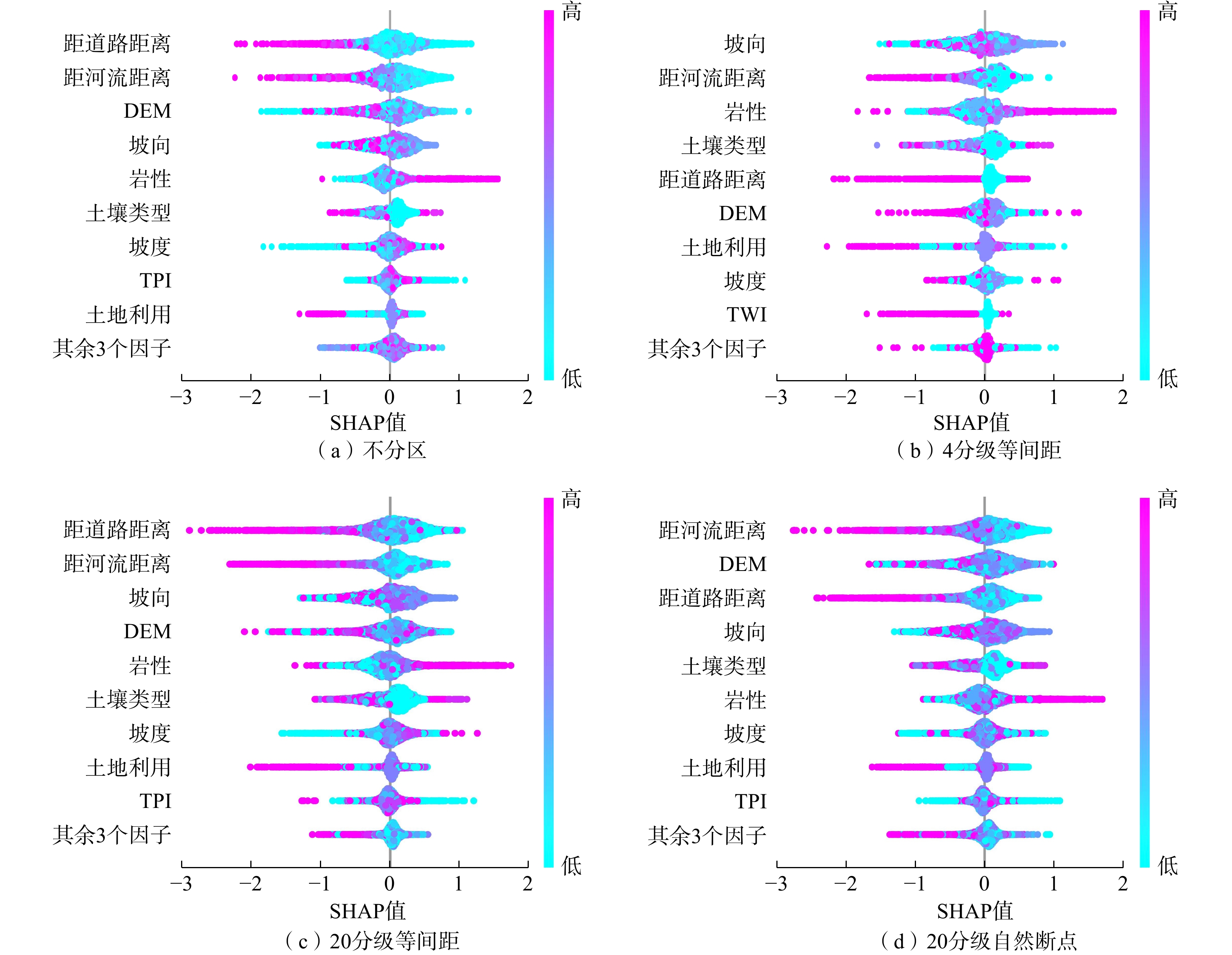
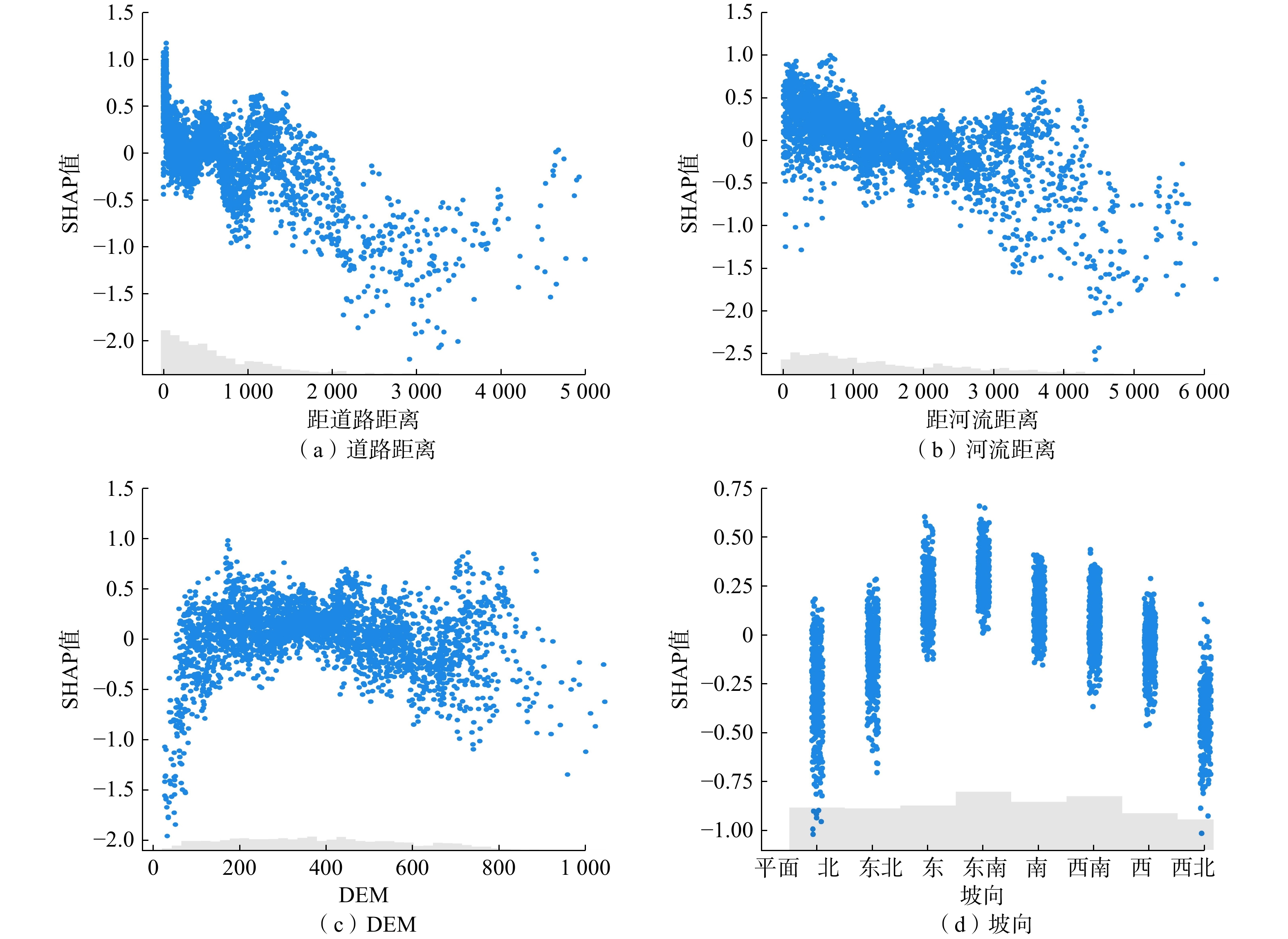
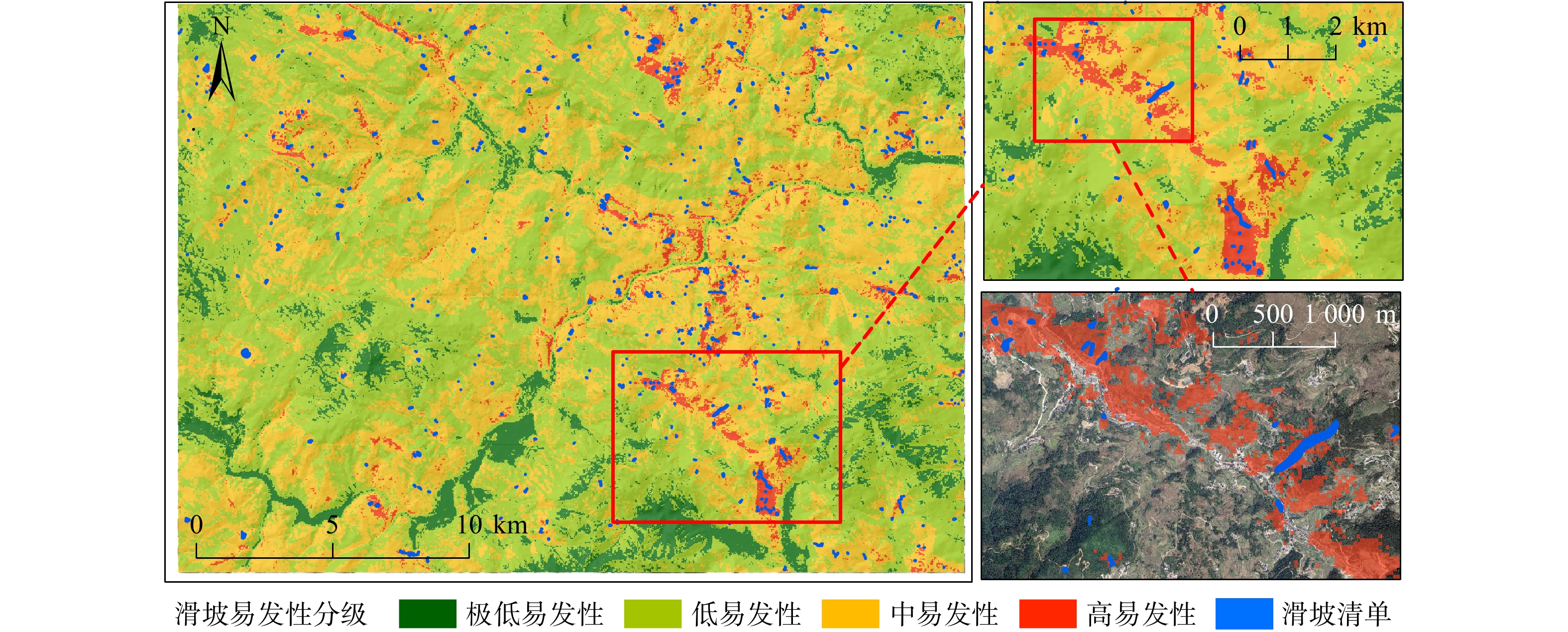
文章致力于深入探索滑坡易发性建模中集成学习模型的不确定性和可解释性。以浙江省东部沿海山区为研究对象,利用谷歌历史影像与Sentinel-2A影像,记录了2016年超级台风“鲇鱼”触发的552起浅层滑坡事件。研究首先对连续型因子进行了不分级、等间距法和自然断点法的工况设计,进一步划分为4,6,8,12,16,20级。随后,引入了类别增强提升树模型(CatBoost)以评估不同工况下的滑坡易发性值,再结合受试者曲线与沙普利加性解释法分析,对建模过程中的不确定性和可解释性进行了深入研究,目的在于确定最优建模策略。结果表明:(1) 在CatBoost模型计算中,河流距离成为最关键的影响因子,其次是与地质条件、人类活动相关的因子;(2) 不分级工况下,模型能够获得最高的AUC值,达到0.866;(3)相较于等间距法,自然断点法的划分策略展现出更佳的泛化能力,且模型预测性能随着分级数量的增加而增加;(4)沙普利加性解释法模型揭示了主要影响因子道路距离、河流距离、DEM和坡向对台风诱发滑坡的控制机制。研究成果能够加深对滑坡易发性的理解,提高滑坡预测的准确性和可靠性,为相关地区的防灾减灾工作提供科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 滑坡;易发性建模 /
- 可解释性 /
- CatBoost模型 /
- 沙普利加性解释法模型 /
- 台风诱发滑坡
Abstract:This study is dedicated to delving deeply into the uncertainty and interpretability of ensemble learning models in landslide susceptibility modeling. Focusing on the eastern coastal mountainous region of Zhejiang Province as the study area, this research utilizes historical Google imagery and Sentinel-2A imagery to document 552 shallow landslide events triggered by the super typhoon "Megi" in 2016. Initially, the study designs scenarios for continuous factors using non-grading, equal interval method, and natural breaks method, subsequently subdividing them into 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20 levels. Thereafter, the Category Boosting Model (CatBoost) is introduced to assess landslide susceptibility values under different scenarios. Coupled with the analysis of ROC (receiver operating characteristic) curves and SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanation), in-depth investigation into uncertainty and interpretability during the modeling process is conducted, with the aim of determining the optimal modeling strategy. The results indicate that: (1) In the computations of the CatBoost model, aspect emerges as the most critical influencing factor, followed by factors related to water and geological conditions; (2) Under the non-grading scenario, the model achieves the highest AUC value, reaching 0.866; (3) Compared to the equal interval method, the natural breaks method demonstrates superior generalization capability, and the model’s predictive performance imrpoves with an increase in the number of classifications; (4) The SHAP model reveals the controlling mechanisms of the principal influencing factors (aspect, lithology, elevation, and road distance) on typhoon-induced landslides. The findings of this research can deepen our understanding of landslide susceptibility, enhance the accuracy and reliability of landslide predictions, and provide a scientific basis for disaster prevention and mitigation efforts in the related regions.
-

-
[1] 郭子正,何俊,黄达,等. 降雨诱发浅层滑坡危险性的快速评估模型及应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(5):1188 − 1201. [GUO Zizheng,HE Jun,HUANG Da,et al. Fast assessment model for rainfall-induced shallow landslide hazard and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(5):1188 − 1201. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Zizheng, HE Jun, HUANG Da, et al . Fast assessment model for rainfall-induced shallow landslide hazard and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023 ,42 (5 ):1188 −1201 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 刘谢攀,殷坤龙,肖常贵,等. 基于I-D-R阈值模型的滑坡气象预警[J]. 地球科学,2022:1 − 15. [LIU Xiepan,YIN Kunlong,XIAO Changgui,et al. Meteorological early warning of landslide based on I-D-R threshold model[J]. Earth Science,2022:1 − 15. ( in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Xiepan, YIN Kunlong, XIAO Changgui, et al. Meteorological early warning of landslide based on I-D-R threshold model[J]. Earth Science, 2022: 1 − 15. ( in Chinese with English abstract) [3] CUI Yulong,JIN Jiale,HUANG Qiangbing,et al. A data-driven model for spatial shallow landslide probability of occurrence due to a typhoon in Ningguo city,Anhui Province,China[J]. Forests,2022,13(5):732. doi: 10.3390/f13050732
[4] 黄发明,陈佳武,范宣梅,等. 降雨型滑坡时间概率的逻辑回归拟合及连续概率滑坡危险性建模[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(12):4609 − 4628. [HUANG Faming,CHEN Jiawu,FAN Xuanmei,et al. Logistic regression fitting of rainfall-induced landslide occurrence probability and continuous landslide hazard prediction modelling[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(12):4609 − 4628. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, CHEN Jiawu, FAN Xuanmei, et al . Logistic regression fitting of rainfall-induced landslide occurrence probability and continuous landslide hazard prediction modelling[J]. Earth Science,2022 ,47 (12 ):4609 −4628 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 郭子正,殷坤龙,黄发明,等. 基于滑坡分类和加权频率比模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(2):287 − 300. [GUO Zizheng,YIN Kunlong,HUANG Faming,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(2):287 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Zizheng, YIN Kunlong, HUANG Faming, et al . Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on landslide classification and weighted frequency ratio model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019 ,38 (2 ):287 −300 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[6] 黄发明,李金凤,王俊宇,等. 考虑线状环境因子适宜性和不同机器学习模型的滑坡易发性预测建模规律[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):44 − 59. [HUANG Faming,LI Jinfeng,WANG Junyu,et al. Modelling rules of landslide susceptibility prediction considering the suitability of linear environmental factors and different machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):44 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, LI Jinfeng, WANG Junyu, et al . Modelling rules of landslide susceptibility prediction considering the suitability of linear environmental factors and different machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022 ,41 (2 ):44 −59 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 黄发明,陈佳武,唐志鹏,等. 不同空间分辨率和训练测试集比例下的滑坡易发性预测不确定性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(6):1155 − 1169. [HUANG Faming,CHEN Jiawu,TANG Zhipeng,et al. Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction due to different spatial resolutions and different proportions of training and testing datasets[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(6):1155 − 1169. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, CHEN Jiawu, TANG Zhipeng, et al . Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction due to different spatial resolutions and different proportions of training and testing datasets[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021 ,40 (6 ):1155 −1169 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 曾韬睿,殷坤龙,桂蕾,等. 基于滑坡致灾强度预测的建筑物易损性定量评价[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1807 − 1824. [ZENG Taorui,YIN Kunlong,GUI Lei,et al. Quantitative vulnerability analysis of buildings based on landslide intensity prediction[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1807 − 1824. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZENG Taorui, YIN Kunlong, GUI Lei, et al . Quantitative vulnerability analysis of buildings based on landslide intensity prediction[J]. Earth Science,2023 ,48 (5 ):1807 −1824 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 杜国梁,杨志华,袁颖,等. 基于逻辑回归–信息量的川藏交通廊道滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):102 − 111. [DU Guoliang,YANG Zhihua,YUAN Ying,et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
DU Guoliang, YANG Zhihua, YUAN Ying, et al . Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor using logistic regression-information value method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (5 ):102 −111 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] 闫举生,谭建民. 基于不同因子分级法的滑坡易发性评价——以湖北远安县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):52 − 60. [YAN Jusheng,TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods:A case study in Yuan’an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Jusheng, TAN Jianmin . Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods: A case study in Yuan’an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019 ,30 (1 ):52 −60 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[11] 黄发明,曹中山,姚池,等. 基于决策树和有效降雨强度的滑坡危险性预警[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2021,55(3):472 − 482. [HUANG Faming,CAO Zhongshan,YAO Chi,et al. Landslides hazard warning based on decision tree and effective rainfall intensity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2021,55(3):472 − 482. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, CAO Zhongshan, YAO Chi, et al . Landslides hazard warning based on decision tree and effective rainfall intensity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2021 ,55 (3 ):472 −482 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 黄发明,曹昱,范宣梅,等. 不同滑坡边界及其空间形状对滑坡易发性预测不确定性的影响规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(增刊2):3227 − − 3240. [HUANG Faming,CAO Yu,FAN Xuanmei,et al. Influence of different landslide boundaries and their spatial shapes on the uncertainty of landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(Sup 2):3227-3240. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, CAO Yu, FAN Xuanmei, et al. Influence of different landslide boundaries and their spatial shapes on the uncertainty of landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(Sup 2): 3227-3240. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 宋昭富,张勇,佘涛,等. 基于易发性分区的区域滑坡降雨预警阈值确定——以云南龙陵县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(4):22 − 29. [SONG Zhaofu,ZHANG Yong,SHE Tao,et al. Determination of regional landslide rainfall warning threshold based on susceptibility zoning:a case study in Longling County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(4):22 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SONG Zhaofu, ZHANG Yong, SHE Tao, et al . Determination of regional landslide rainfall warning threshold based on susceptibility zoning: a case study in Longling County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (4 ):22 −29 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] 黄发明,叶舟,姚池,等. 滑坡易发性预测不确定性:环境因子不同属性区间划分和不同数据驱动模型的影响[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(12):4535 − 4549. [HUANG Faming,YE Zhou,YAO Chi,et al. Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction:different attribute interval divisions of environmental factors and different data-based models[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(12):4535 − 4549. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, YE Zhou, YAO Chi, et al . Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction: different attribute interval divisions of environmental factors and different data-based models[J]. Earth Science,2020 ,45 (12 ):4535 −4549 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[15] 仉文岗,何昱苇,王鲁琦,等. 基于水系分区的滑坡易发性机器学习分析方法:以重庆市奉节县为例[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):2024 − 2038. [ZHANG Wengang,HE Yuwei,WANG Luqi,et al. Machine learning solution for landslide susceptibility based on hydrographic division:case study of Fengjie County in Chongqing[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):2024 − 2038. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Wengang, HE Yuwei, WANG Luqi, et al . Machine learning solution for landslide susceptibility based on hydrographic division: case study of Fengjie County in Chongqing[J]. Earth Science,2023 ,48 (5 ):2024 −2038 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[16] 杨得虎, 朱杰勇, 刘帅, 等. 基于信息量、加权信息量与逻辑回归耦合模型的云南罗平县崩滑灾害易发性评价对比分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(5):43 − 53. [YANG Dehu, ZHU Jieyong, LIU Shuai, et al. Comparative analyses of susceptibility assessment for landslide disasters based on information value, weighted information value and logistic regression coupled model in Luoping County, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(5):43 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Dehu, ZHU Jieyong, LIU Shuai, et al . Comparative analyses of susceptibility assessment for landslide disasters based on information value, weighted information value and logistic regression coupled model in Luoping County, Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (5 ):43 −53 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 贾雨霏,魏文豪,陈稳,等. 基于SOM-I-SVM耦合模型的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):125 − 137. [JIA Yufei,WEI Wenhao,CHEN Wen,et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on the SOM-I-SVM model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):125 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
JIA Yufei, WEI Wenhao, CHEN Wen, et al . Landslide susceptibility assessment based on the SOM-I-SVM model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (3 ):125 −137 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 刘海知,徐辉,包红军,等. 基于集成学习的山区中小流域滑坡易发区早期识别优化试验[J]. 工程科学与技术,2022,54(6):12 − 20. [LIU Haizhi,XU Hui,BAO Hongjun,et al. Optimization experiment of early identification of landslides susceptibility areas in medium and small mountainous catchment based on ensemble learning[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2022,54(6):12 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Haizhi, XU Hui, BAO Hongjun, et al . Optimization experiment of early identification of landslides susceptibility areas in medium and small mountainous catchment based on ensemble learning[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2022 ,54 (6 ):12 −20 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] 曾韬睿,邬礼扬,金必晶,等. 基于stacking集成策略和SBAS-InSAR的滑坡动态易发性制图[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(9):2266 − 2282. [ZENG Taorui,WU Liyang,JIN Bijing,et al. Landslide dynamic susceptibility mapping based on stacking ensemble strategy and SBAS-InSAR[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(9):2266 − 2282. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZENG Taorui, WU Liyang, JIN Bijing, et al . Landslide dynamic susceptibility mapping based on stacking ensemble strategy and SBAS-InSAR[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023 ,42 (9 ):2266 −2282 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[20] 黄发明,陈彬,毛达雄,等. 基于自筛选深度学习的滑坡易发性预测建模及其可解释性[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1696 − 1710. [HUANG Faming,CHEN Bin,MAO Daxiong,et al. Landslide susceptibility prediction modeling and interpretability based on self-screening deep learning model[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1696 − 1710. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, CHEN Bin, MAO Daxiong, et al . Landslide susceptibility prediction modeling and interpretability based on self-screening deep learning model[J]. Earth Science,2023 ,48 (5 ):1696 −1710 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] LUNDBERG S M,LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. December 4 - 9,2017,Long Beach,California,USA. ACM,2017:4768 − 4777.
[22] 陈丹璐,孙德亮,文海家,等. 基于不同因子筛选方法的LightGBM-SHAP滑坡易发性研究[J/OL]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),(2023-08-08)[2023-09-26] https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1991.N.20230808.1452.003. [CHEN Danlu,SUN Deliang,WEN Haijia,etal. A study on landslide susceptibility of LightGBMSHAP based on different factor screening methods[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science),(2023-08-08)[2023-09-26]. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Danlu, SUN Deliang, WEN Haijia, etal. A study on landslide susceptibility of LightGBMSHAP based on different factor screening methods[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), (2023-08-08)[2023-09-26]. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] DAHAL A,LOMBARDO L. Explainable artificial intelligence in geoscience:a glimpse into the future of landslide susceptibility modeling[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2023,176:105364.
[24] 黄发明,曾诗怡,姚池,等. 滑坡易发性预测建模的不确定性:不同“非滑坡样本”选择方式的影响[J]. 工程科学与技术,2023,56(1):1 − 14. [HUANG Faming, ZENG Shiyi, CHI Yao, et al. Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction modeling:influence of different selection methods of "non-landslide samples"[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2023,56(1):1 − 14. ( in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Faming, ZENG Shiyi, CHI Yao, et al. Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction modeling: influence of different selection methods of "non-landslide samples"[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2023, 56(1): 1 − 14. ( in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 罗路广,裴向军,崔圣华,等. 九寨沟地震滑坡易发性评价因子组合选取研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(11):2306 − 2319. [LUO Luguang,PEI Xiangjun,CUI Shenghua,et al. Combined selection of susceptibility assessment factors for Jiuzhaigou earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(11):2306 − 2319. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LUO Luguang, PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, et al . Combined selection of susceptibility assessment factors for Jiuzhaigou earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021 ,40 (11 ):2306 −2319 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[26] 宋宇飞,曹琰波,范文,等. 基于贝叶斯方法的降雨诱发滑坡概率型预警模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(3):558 − 574. [SONG Yufei,CAO Yanbo,FAN Wen,et al. Probabilistic early warning model for rainfall-induced landslides based on Bayesian approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(3):558 − 574. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SONG Yufei, CAO Yanbo, FAN Wen, et al . Probabilistic early warning model for rainfall-induced landslides based on Bayesian approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023 ,42 (3 ):558 −574 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[27] PROKHORENKOVA L,GUSEV G,VOROBEV A,et al. CatBoost:unbiased boosting with categorical features[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. December 3 - 8,2018,Montréal,Canada. ACM,2018:6639–6649.
[28] 高秉海,何毅,张立峰,等. 顾及In SAR形变的CNN滑坡易发性动态评估——以刘家峡水库区域为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(2):450 − 465. [GAO Binghai,HE Yi,ZHANG Lifeng,et al. Dynamic evaluation of landslide susceptibility by CNN considering InSAR deformation:A case study of Liujiaxia Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(2):450 − 465. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Binghai, HE Yi, ZHANG Lifeng, et al . Dynamic evaluation of landslide susceptibility by CNN considering InSAR deformation: A case study of Liujiaxia Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023 ,42 (2 ):450 −465 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[29] 张俊,殷坤龙,王佳佳,等. 三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):284 − 296. [ZHANG Jun,YIN Kunlong,WANG Jiajia,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):284 − 296. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Jun, YIN Kunlong, WANG Jiajia, et al . Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou district of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016 ,35 (2 ):284 −296 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[30] HUANG Faming,ZHANG Jing,ZHOU Chuangbing,et al. A deep learning algorithm using a fully connected sparse autoencoder neural network for landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Landslides,2020,17(1):217 − 229. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01274-9
[31] XING Yin,CHEN Yang,HUANG Saipeng,et al. Research on the uncertainty of landslide susceptibility prediction using various data-driven models and attribute interval division[J]. Remote Sensing,2023,15(8):2149. doi: 10.3390/rs15082149
[32] 李文彬,范宣梅,黄发明,等. 不同环境因子联接和预测模型的滑坡易发性建模不确定性[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(10):3777 − 3795. [LI Wenbin,FAN Xuanmei,HUANG Faming,et al. Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility modeling under different environmental factor connections and prediction models[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(10):3777 − 3795. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Wenbin, FAN Xuanmei, HUANG Faming, et al . Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility modeling under different environmental factor connections and prediction models[J]. Earth Science,2021 ,46 (10 ):3777 −3795 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[33] 方然可, 刘艳辉, 黄志全. 基于机器学习的区域滑坡危险性评价方法综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(4):1 − 8. [FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, HUANG Zhiquan. A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(4):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, HUANG Zhiquan . A review of the methods of regional landslide hazard assessment based on machine learning[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021 ,32 (4 ):1 −8 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[34] 陈水满, 赵辉龙, 许震, 等. 基于人工神经网络模型的福建南平市滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):133 − 140. [CHEN Shuiman, ZHAO Huilong, XU Zhen, et al. Landslide risk assessment in Nanping City based on artificial neural networks model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):133 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Shuiman, ZHAO Huilong, XU Zhen, et al . Landslide risk assessment in Nanping City based on artificial neural networks model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022 ,33 (2 ):133 −140 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[35] 阳清青, 余秋兵, 张廷斌, 等. 基于GDIV模型的大渡河中游地区滑坡危险性评价与区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(5):130 − 140. [YANG Qingqing,YU Qiubing,ZHANG Tingbin,et al. Landslide hazard assessment in the middle reach area of the Dadu River based on the GDIV model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(5):130 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Qingqing, YU Qiubing, ZHANG Tingbin, et al . Landslide hazard assessment in the middle reach area of the Dadu River based on the GDIV model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023 ,34 (5 ):130 −140 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[36] 刘甲美,王涛,杜建军,等. 四川泸定MS6.8级地震诱发崩滑灾害快速评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):84 − 94. [LIU Jiamei, WANG Tao, DU Jianjun, et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding MS6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):84 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jiamei, WANG Tao, DU Jianjun, et al . Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding MS6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023 ,50 (2 ):84 −94 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: