Spatio-temporal differentiation of landslide after the Ms6.5 Ludian earthquake in Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
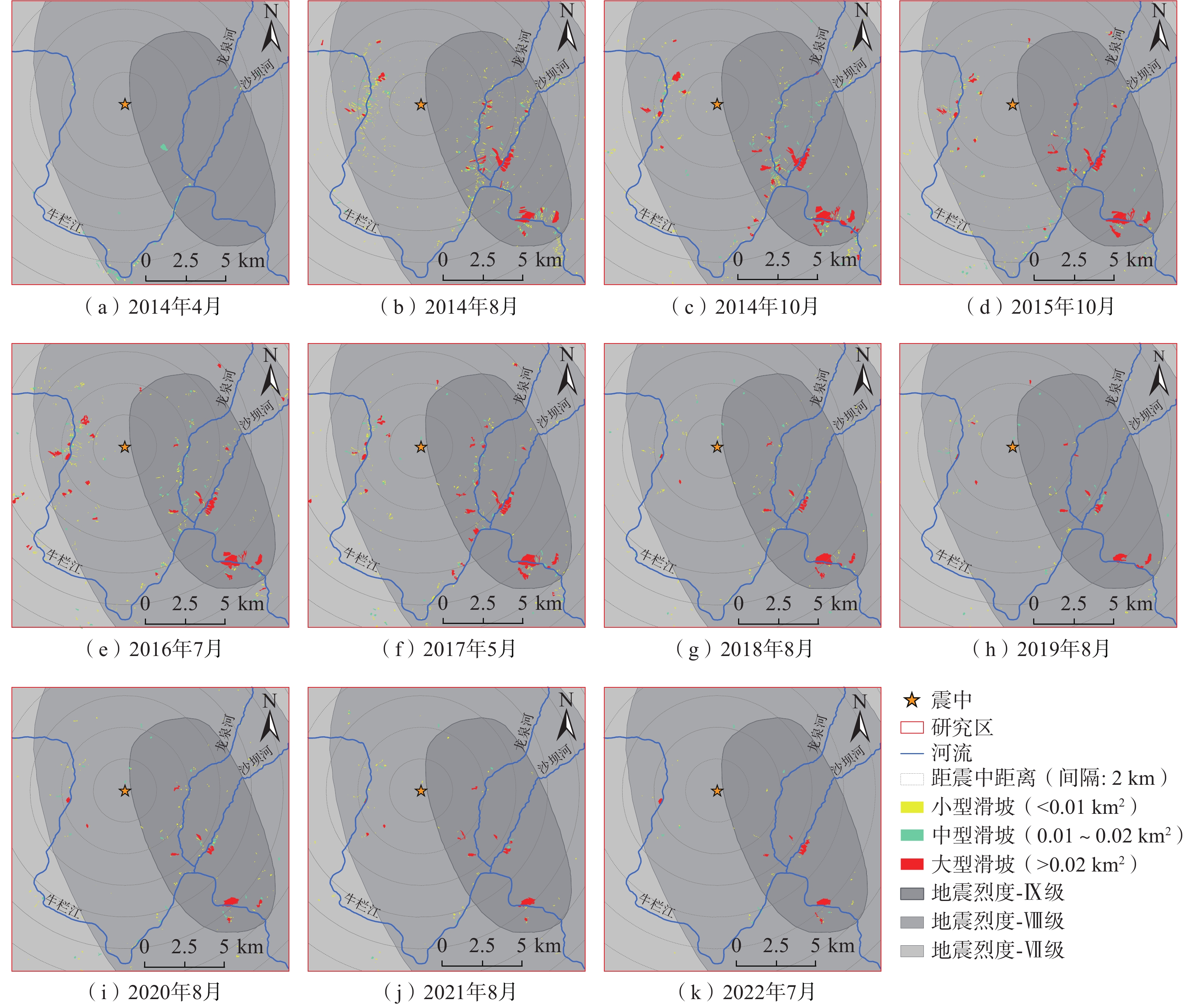
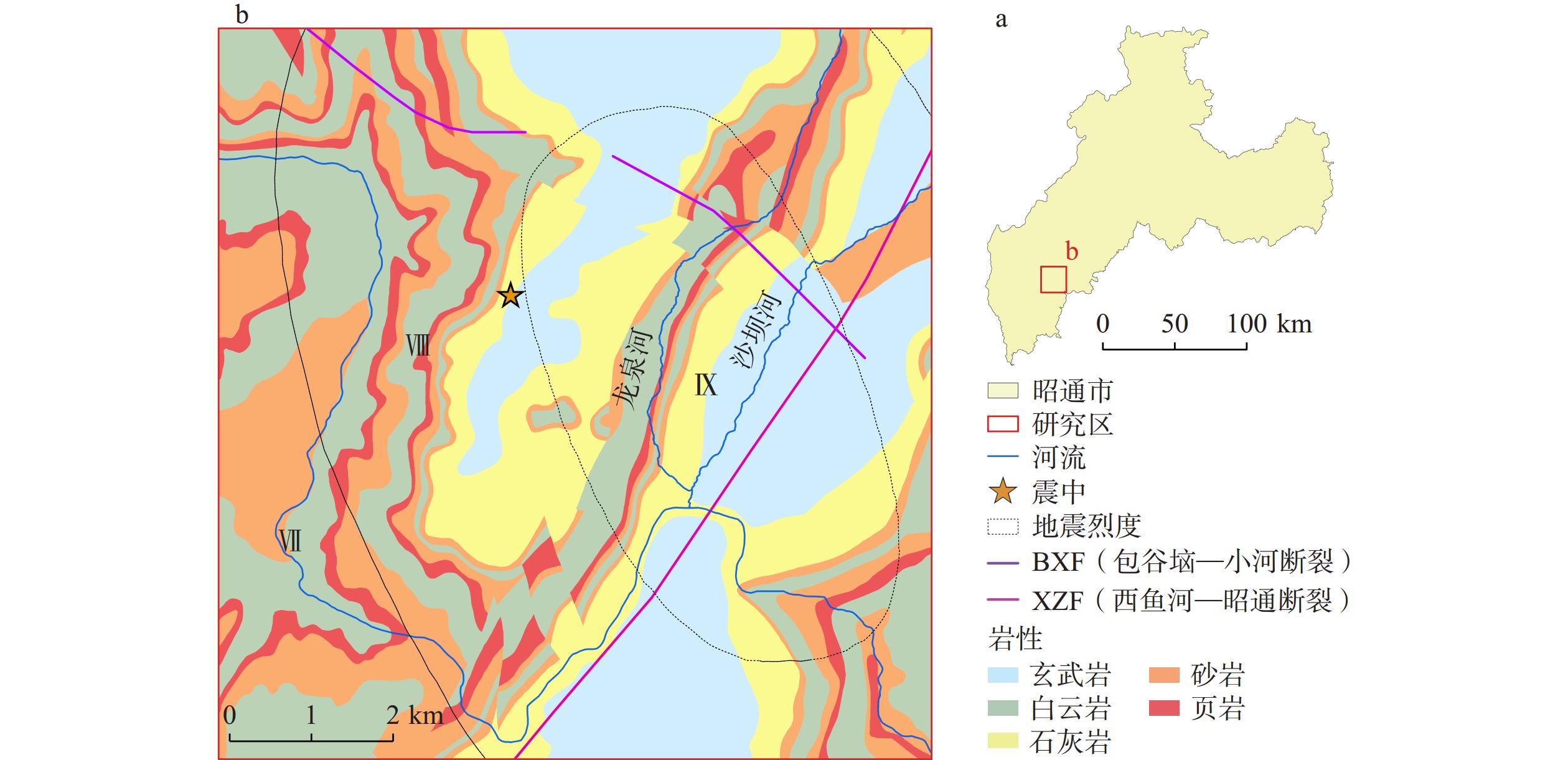
2014年8月3日云南鲁甸发生的Ms6.5级地震触发了大量滑坡,受强烈地震触发的滑坡震后恢复速度慢、恢复难度大且具有扩大复发的可能,会对道路、水体、生态环境造成长期影响,因此,探究其长时间时空分异具有必要性。以受地震影响的314 km2为研究区域,首先基于ENVI深度学习方法提取震后滑坡并编制其多时相数据清单,在此基础上,从滑坡时空分布特征、滑坡时空面积变化特征以及滑坡活动演化进行时空分异分析。结果表明:(1)地震后,滑坡数量和面积急剧增加,在随后的8 a时间内,总体呈现逐渐减少趋势,地震触发滑坡以面积小于0.01 km2的小型滑坡为主,集中分布于河谷两侧,同时距震中
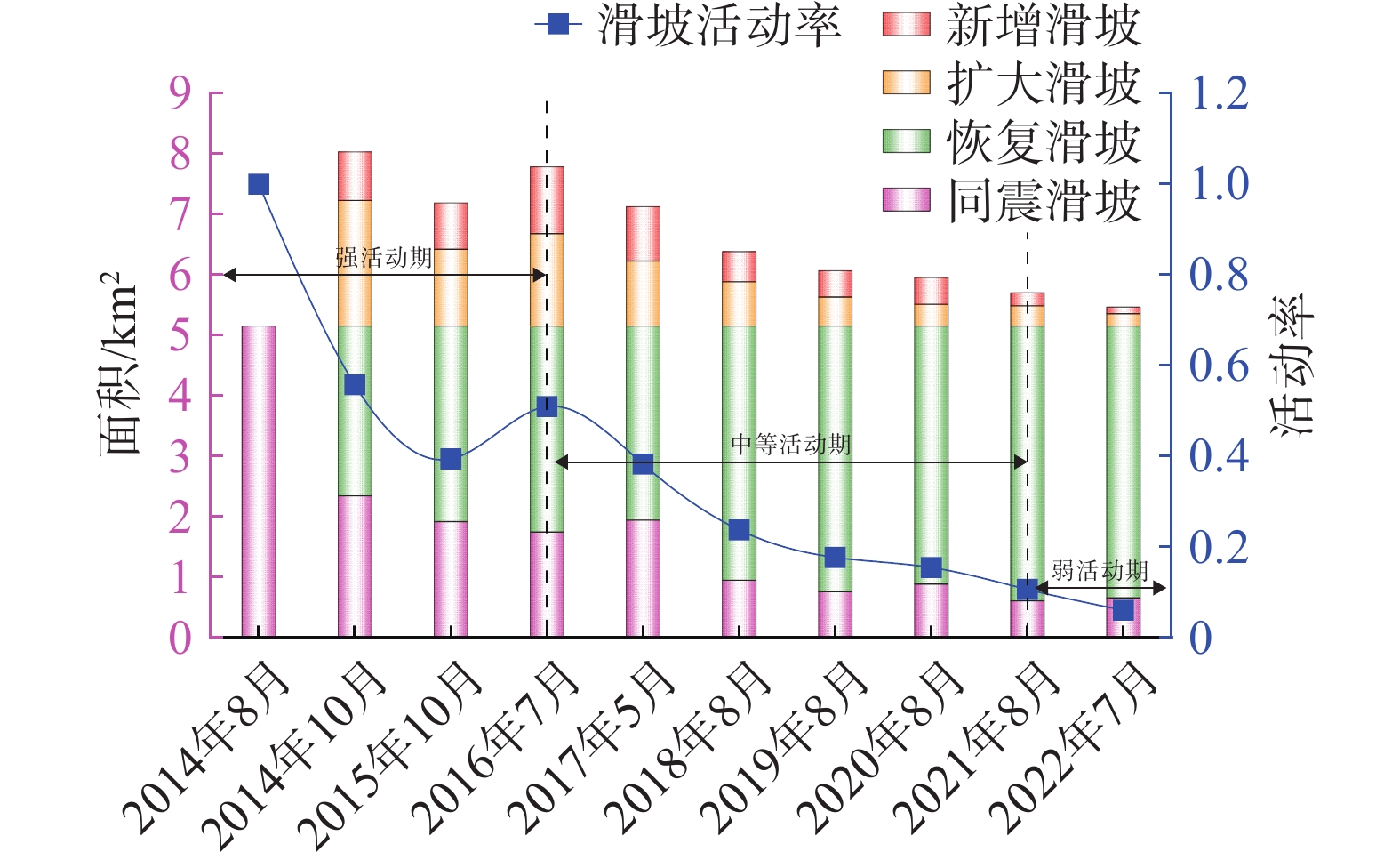
2000 m、地震烈度Ⅸ级范围内分布较为明显;(2)随时间推移,震后滑坡活动率总体表现为逐渐减弱趋势,截至2022年7月,地震触发滑坡只有6.08%的滑坡仍处于活动状态,表明地震对滑坡的影响已经逐渐减弱;(3)地震后滑坡的活动演化可以分为3个阶段:滑坡强活动期(2014年8月—2016年7月)、中等活动期(2016年8月—2021年8月)、弱活动期(2021年9月—2022年7月)。Abstract:A large number of landslides were triggered by the Ms6.5 magnitude earthquake that occurred in Ludian, Yunnan Province, on August 3, 2014. Landslides triggered by strong earthquakes exhibit slow post-earthquake recovery, high recovery difficulty, and tend to recur and expand, which can have long-term impacts on roads, water bodies, and ecological environments. Therefore, it is necessary to explore their long-time spatial and temporal variability. Taking the 314 km2 area affected by the earthquake as the study area, post-earthquake landslides were first extracted and a multi-temporal data list was compiled using the ENVI deep learning method. Based on this, the spatial-temporal differentiation analysis was carried out focusing on the spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of landslides, changes in spatio-temporal area, and the evolution of landslide activities. The results show that: (1) following the earthquake, the number and area of landslides increased dramatically, gradually decreasing over the subsequent 8 years. Earthquake-triggered landslides were primarily small-scale, with an area of less than 0.01 km2, concentrated on both sides of the river valley, and distributed more prominently within 2 000 meters from the epicenter and within seismic intensity Ⅸ; (2) over time, the post-earthquake landslide activity rate generally showed a gradual weakening trend, with only 6.08% of the earthquake-triggered landslides still active as of July 2022, indicating a gradual weakening of the earthquake's impact on landslides; (3) the activity evolution of post-earthquake landslides can be divided into three phases: the period of strong landslide activity (August 2014-July 2016), the period of moderate activity (August 2016-August 2021), and the period of weak activity (September 2021-July 2022).
-

-
表 1 影像数据信息
Table 1. Image data information
日期 2014年
4月13日2014年
10月26日2015年
10月29日2016年
7月11日2017年
5月13日2018年
8月24日2019年
8月18日2020年
8月27日2021年
8月2日2022年
7月16日数据
来源资源3号
(ZY3)高分1号
(GF1)高分1号
(GF1)高分2号
(GF2)资源3号
(ZY3)高分1号
(GF1)高分2号
(GF2)高分1号
(GF1)高分2号
(GF2)高分1号B卫星
(GF1B)数量/景 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 4 2 分辨率/m 2.1 2 2 0.8 2.1 2 0.8 2 0.8 2 表 2 滑坡活动期分类标准
Table 2. Classification standard of landslide activity period
滑坡活动期 滑坡活动率/% 扩大滑坡面积/km2 新增滑坡面积/km2 震后滑坡强活动期 P>50 >1.5 >1 震后滑坡中等活动期 10<P≤50 >0.2且≤1.5 >0.2且≤1 震后滑坡弱活动期 P≤10 ≤0.2 ≤0.2 表 3 精度验证结果
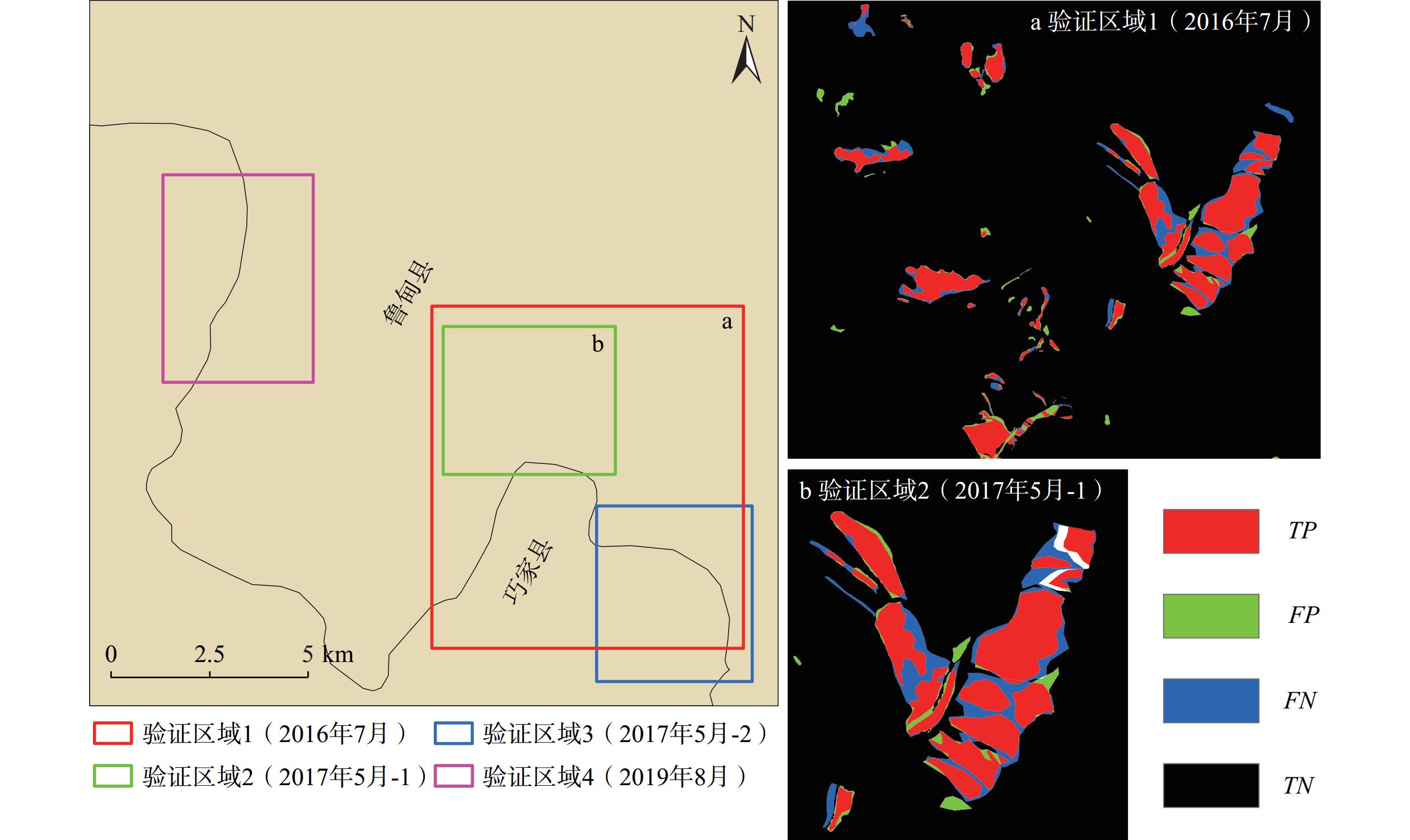
Table 3. Accuracy verification results
区域 影像类型 Precision Recall CE OE F1 验证区域1 GF2 0.8614 0.8281 0.1386 0.1719 0.8444 验证区域2 ZY3 0.8573 0.8439 0.1427 0.1561 0.8506 验证区域3 ZY3 0.8650 0.7499 0.1350 0.2490 0.8034 验证区域4 GF2 0.8634 0.7561 0.1366 0.2439 0.8062 表 4 地震震后滑坡规模分布情况统计
Table 4. Statistical distribution of landslide scale after earthquake
2014年4月 2014年8月 2014年10月 2015年10月 2016年7月 2017年5月 2018年8月 2019年8月 2020年8月 2021年8月 2022年7月 小型滑坡/个 36 908 408 300 367 307 179 107 153 85 42 中型滑坡/个 25 64 56 37 54 37 27 25 24 9 8 大型滑坡/个 0 42 49 37 45 42 16 15 11 13 9 表 5 2014—2022年鲁甸地区降水统计
Table 5. Statistics of precipitation in Ludian area from 2014 to 2022
年份 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 年降水量/mm 941.0 976.4 1107.1 955.4 879.7 721.9 794.5 742.2 861.4 表 6 滑坡活动面积变化及活动率统计
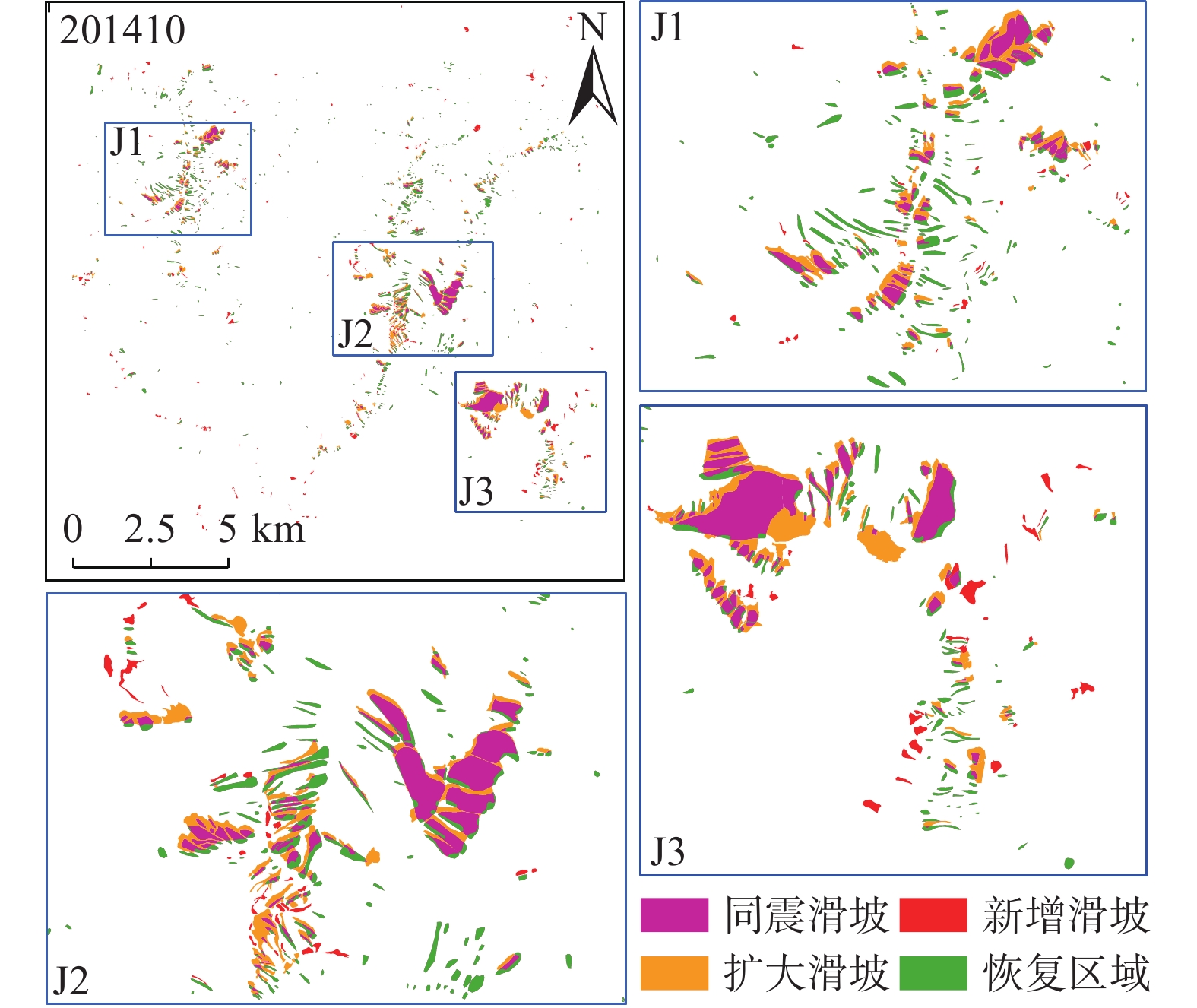
Table 6. Landslide activity area change and activity rate statistics
年月 恢复区域
/km2扩大面积
/km2新增面积
/km2活动面积
/km2活动率
/%2014年10月 2.81 2.08 0.80 2.88 55.78 2015年10月 3.23 1.27 0.77 2.03 39.44 2016年7月 3.41 1.52 1.10 2.63 50.98 2017年5月 3.21 1.07 0.90 1.97 38.28 2018年8月 4.20 0.73 0.50 1.23 23.79 2019年8月 4.39 0.48 0.44 0.91 17.70 2020年8月 4.27 0.36 0.44 0.80 15.48 2021年8月 4.55 0.33 0.22 0.55 10.67 2022年7月 4.50 0.20 0.11 0.31 6.08 -
[1] 黄润秋. 汶川地震地质灾害后效应分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(2):145 − 151. [HUANG Runqiu. After effect of geohazards induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(2):145 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.02.001
HUANG Runqiu. After effect of geohazards induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(2): 145 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.02.001
[2] KEEFER D K. The importance of earthquake-induced landslides to long-term slope erosion and slope-failure hazards in seismically active regions[M]//Geomorphology and Natural Hazards. Amsterdam:Elsevier,1994:265 − 284.
[3] 祁生文,许强,刘春玲,等. 汶川地震极重灾区地质背景及次生斜坡灾害空间发育规律[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(1):39 − 49. [QI Shengwen,XU Qiang,LIU Chunling,et al. Slope instabilities in the severest disaster areas of 5·12 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(1):39 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.005
QI Shengwen, XU Qiang, LIU Chunling, et al. Slope instabilities in the severest disaster areas of 5·12 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(1): 39 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.005
[4] 田颖颖,许冲,徐锡伟,等. 2014年鲁甸Ms6.5地震震前与同震滑坡空间分布规律对比分析[J]. 地震地质,2015,37(1):291 − 306. [TIAN Yingying,XU Chong,XU Xiwei,et al. Spatial distribution analysis of coseismic and pre-earthquake landslides triggered by the 2014 Ludian Ms6.5 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2015,37(1):291 − 306. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.023
TIAN Yingying, XU Chong, XU Xiwei, et al. Spatial distribution analysis of coseismic and pre-earthquake landslides triggered by the 2014 Ludian Ms6.5 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2015, 37(1): 291 − 306. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.023
[5] ZOU Yu,QI Shengwen,GUO Songfeng,et al. Factors controlling the spatial distribution of coseismic landslides triggered by the Mw 6.1 Ludian earthquake in China[J]. Engineering Geology,2022,296:106477. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106477
[6] 韩征,方振雄,傅邦杰,等. 同震崩塌滑坡的光学遥感影像多特征融合解译方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):103 − 113. [HAN Zheng,FANG Zhenxiong,FU Bangjie,et al. Interpretation method for regional co-seismic collapses based on multi-feature fusion of optical remote sensing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):103 − 113. ( in Chinese with English abstract]
HAN Zheng, FANG Zhenxiong, FU Bangjie, et al. Interpretation method for regional co-seismic collapses based on multi-feature fusion of optical remote sensing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 103 − 113. ( in Chinese with English abstract
[7] 许冲,田颖颖,沈玲玲,等. 2015年尼泊尔廓尔喀Mw7.8地震滑坡数据库[J]. 地震地质,2018,40(5):1115 − 1128. [XU Chong,TIAN Yingying,SHEN Lingling,et al. Database of landslides triggered by 2015 Gorkha (Nepal) Mw7.8 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology,2018,40(5):1115 − 1128. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Chong, TIAN Yingying, SHEN Lingling, et al. Database of landslides triggered by 2015 Gorkha (Nepal) Mw7.8 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2018, 40(5): 1115 − 1128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] GUO Xinyi,FU Bihong,DU Jie,et al. Monitoring and assessment for the susceptibility of landslide changes after the 2017 Ms7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake using the remote sensing technology[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9:43.
[9] 杨华阳,许向宁,杨鸿发. 基于证据权法的九寨沟地震滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):20 − 29. [YANG Huayang,XU Xiangning,YANG Hongfa. The Jiuzhaigou co-seismic landslide hazard assessment based on weight of evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):20 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Huayang, XU Xiangning, YANG Hongfa. The Jiuzhaigou co-seismic landslide hazard assessment based on weight of evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3): 20 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陈博,李振洪,黄武彪,等. 2022年四川泸定Mw6.6级地震诱发地质灾害空间分布及影响因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2022,44(6):971 − 985. [CHEN Bo,LI Zhenhong,HUANG Wubiao,et al. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of geohazards induced by the 2022 Mw6.6 luding (Sichuan,China)earthquake[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2022,44(6):971 − 985. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Bo, LI Zhenhong, HUANG Wubiao, et al. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of geohazards induced by the 2022 Mw6.6 luding (Sichuan, China)earthquake[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(6): 971 − 985. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 范宣梅,王欣,戴岚欣,等. 2022年Ms6.8级泸定地震诱发地质灾害特征与空间分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(5):1504 − 1516. [FAN Xuanmei,WANG Xin,DAI Lanxin,et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of Ms6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5,2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(5):1504 − 1516. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FAN Xuanmei, WANG Xin, DAI Lanxin, et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of Ms6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5, 2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(5): 1504 − 1516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘甲美,王涛,杜建军,等. 四川泸定Ms6.8级地震诱发崩滑灾害快速评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):84 − 94. [LIU Jiamei,WANG Tao,DU Jianjun,et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding Ms6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):84 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jiamei, WANG Tao, DU Jianjun, et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding Ms6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 84 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 杨志华, 吴瑞安, 郭长宝, 等. 川西巴塘断裂带地质灾害效应与典型滑坡发育特征[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(2):355 − 368. [YANG Zhihua, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(2):355 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Zhihua, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Geo-hazard effects and typical landslide characteristics of the Batang fault zone in the western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(2): 355 − 368. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李明威,熊江,陈明,等. 汶川震区植被恢复与同震滑坡活动性动态演化分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):182 − 192. [LI Mingwei,XIONG Jiang,CHEN Ming,et al. Vegetation restoration and dynamic evolution analysis of landslide activity in the Wenchuan Earthquake area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):182 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Mingwei, XIONG Jiang, CHEN Ming, et al. Vegetation restoration and dynamic evolution analysis of landslide activity in the Wenchuan Earthquake area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(3): 182 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 龙玉洁,李为乐,黄润秋,等. 汶川地震震后10 a绵远河流域滑坡遥感自动提取与演化趋势分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(11):1792 − 1800. [LONG Yujie,LI Weile,HUANG Runqiu,et al. Automatic extraction and evolution trend analysis of landslides in Mianyuan River Basin in the 10 years after Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1792 − 1800. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LONG Yujie, LI Weile, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Automatic extraction and evolution trend analysis of landslides in Mianyuan River Basin in the 10 years after Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1792 − 1800. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] LIN Ching weei,LIU Shouheng,LEE Senyuan,et al. Impacts of the Chi-Chi earthquake on subsequent rainfall-induced landslides in central Taiwan[J]. Engineering Geology,2006,86(2):87 − 101.
[17] SHAFIQUE M. Spatial and temporal evolution of co-seismic landslides after the 2005 Kashmir earthquake[J]. Geomorphology,2020,362:107228. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107228
[18] CHEN Ming,TANG Chuan,XIONG Jiang,et al. The long-term evolution of landslide activity near the epicentral area of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in China[J]. Geomorphology,2020,367:107317. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107317
[19] 许冲,徐锡伟,沈玲玲,等. 2014年鲁甸Ms6.5地震触发滑坡编录及其对一些地震参数的指示[J]. 地震地质,2014,36(4):1186 − 1203. [XU Chong,XU Xiwei,SHEN Lingling,et al. Inventory of landslides triggered by the 2014 Ms6.5 Ludian earthquake and its implications on several earthquake parameters[J]. Seismology and Geology,2014,36(4):1186 − 1203. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.04.020
XU Chong, XU Xiwei, SHEN Lingling, et al. Inventory of landslides triggered by the 2014 Ms6.5 Ludian earthquake and its implications on several earthquake parameters[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2014, 36(4): 1186 − 1203. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.04.020
[20] 张鹏飞. 地震滑坡的遥感影像自动提取研究[D]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所,2021. [ZHANG Pengfei. Research on automatic extraction of remote sensing images of co-seismic landslides[D]. Beijing:Institute of Geology,China Earthquake Administration,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Pengfei. Research on automatic extraction of remote sensing images of co-seismic landslides[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] YANG Ruilin,ZHANG Feng,XIA Junshi,et al. Landslide extraction using mask R-CNN with background-enhancement method[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(9):2206. doi: 10.3390/rs14092206
[22] 蒋涛,崔圣华,冉耀. 开挖和降雨耦合诱发滑坡机理分析——以四川万源前进广场滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):20 − 30. [JIANG Tao,CUI Shenghua,RAN Yao. Analysis of landslide mechanism induced by excavation and rainfall:A case study of the Qianjin square landslide in Wanyuan City,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):20 − 30. ( in Chinese with English abstract]
JIANG Tao, CUI Shenghua, RAN Yao. Analysis of landslide mechanism induced by excavation and rainfall: A case study of the Qianjin square landslide in Wanyuan City, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 20 − 30. ( in Chinese with English abstract
[23] 胡爱国,周伟. 地震与强降雨作用下堆积体滑坡变形破坏机理及防治方案分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):27 − 34. [HU Aiguo,ZHOU Wei. Deformation and failure mechanism and analysis on prevention measures of colluction landslide under earthquake and heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):27 − 34. ( in Chinese with English abstract]
HU Aiguo, ZHOU Wei. Deformation and failure mechanism and analysis on prevention measures of colluction landslide under earthquake and heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 27 − 34. ( in Chinese with English abstract
[24] HE Xiangli,XU Chong,QI Wenwen,et al. Landslides triggered by the 2020 Qiaojia Mw5.1 earthquake,Yunnan,China:distribution,influence factors and tectonic significance[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2021,32(5):1056 − 1068. doi: 10.1007/s12583-021-1492-1
[25] 明小娜,周洋,钟玉盛,等. 2017年云南鲁甸Ms4.9地震房屋震害特征与烈度评定[J]. 地震研究,2017,40(2):295 − 302. [MING Xiaona,ZHOU Yang,ZHONG Yusheng,et al. Building damage characteristics and earthquake intensity evaluation of the Ludian Ms4.9 earthquake in 2017[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,2017,40(2):295 − 302. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2017.02.017
MING Xiaona, ZHOU Yang, ZHONG Yusheng, et al. Building damage characteristics and earthquake intensity evaluation of the Ludian Ms4.9 earthquake in 2017[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2017, 40(2): 295 − 302. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2017.02.017
-



 下载:
下载: