Analysis of geological hazards caused by the “23 • 7” heavy rainfall in the northern section of Taihang Mountain in Hebei Province
-
摘要:
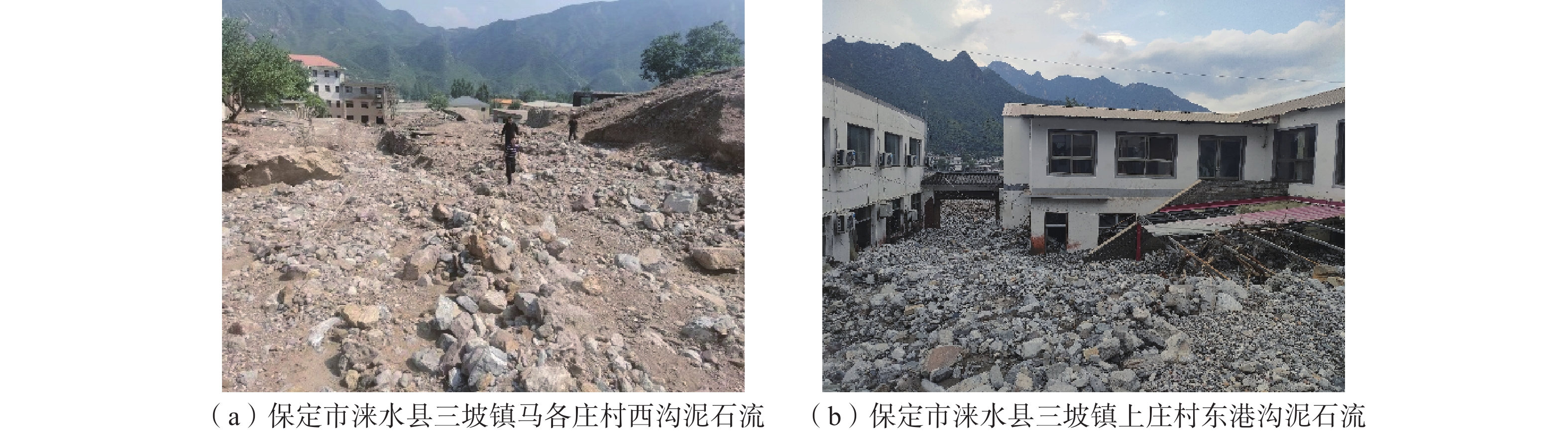
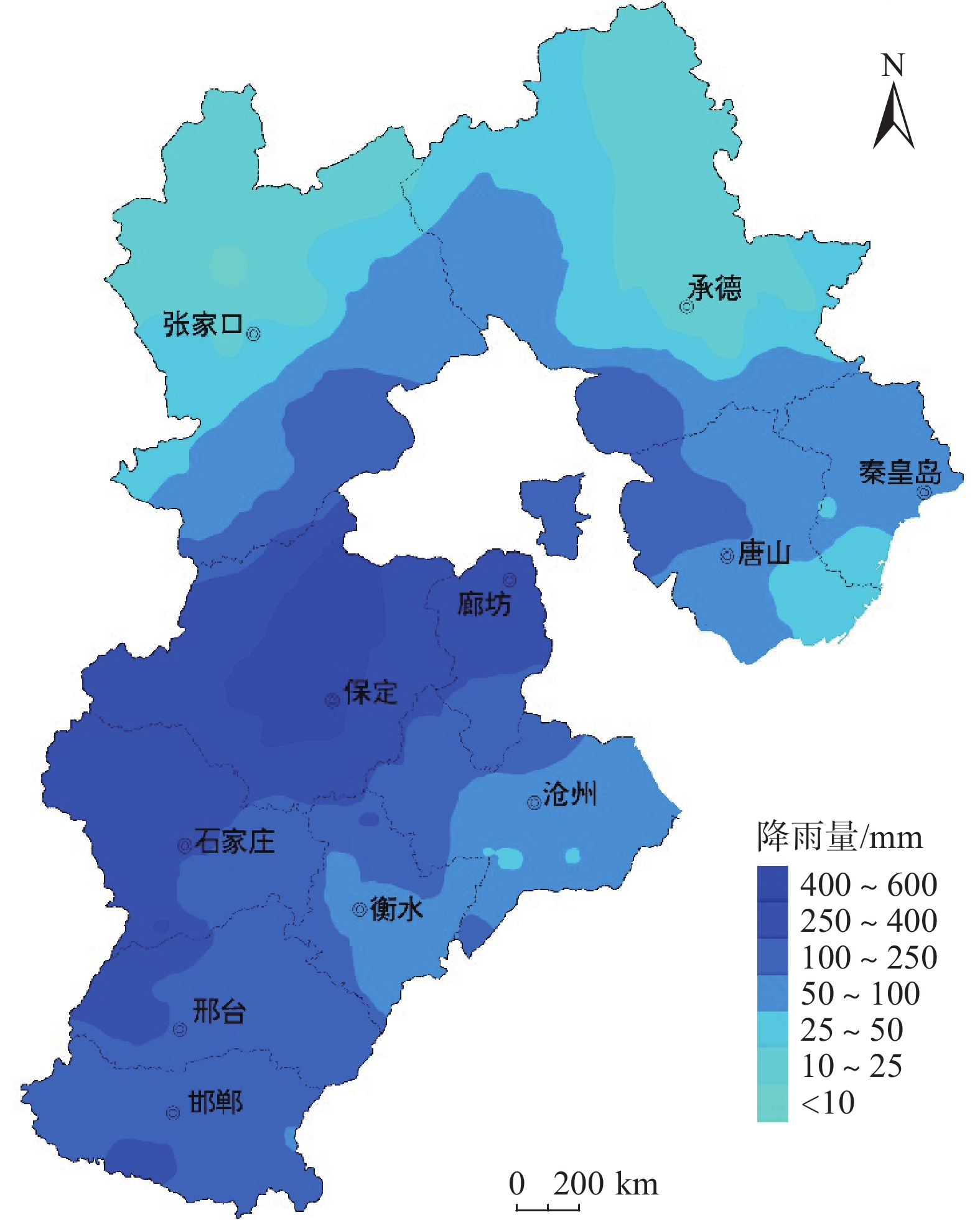
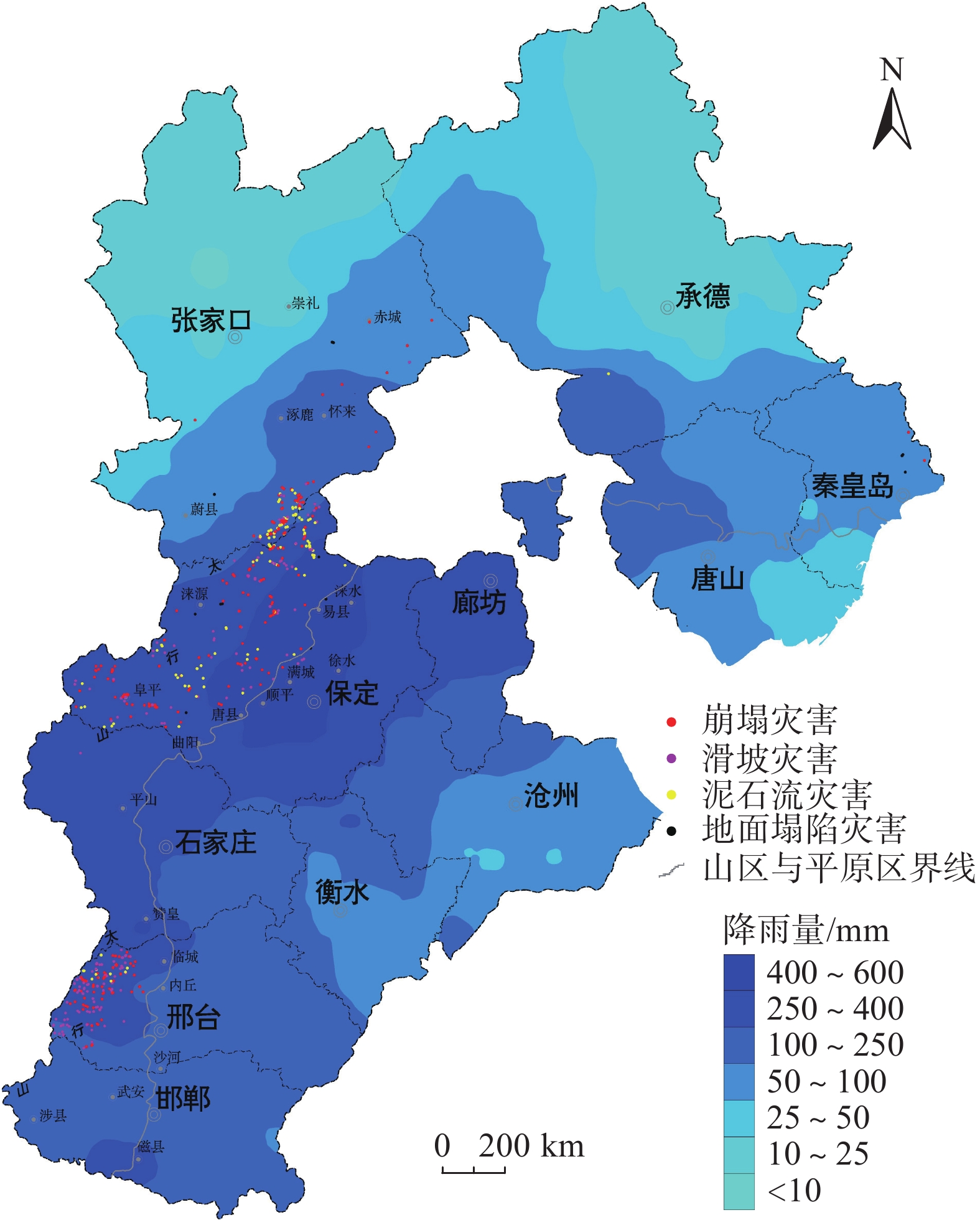
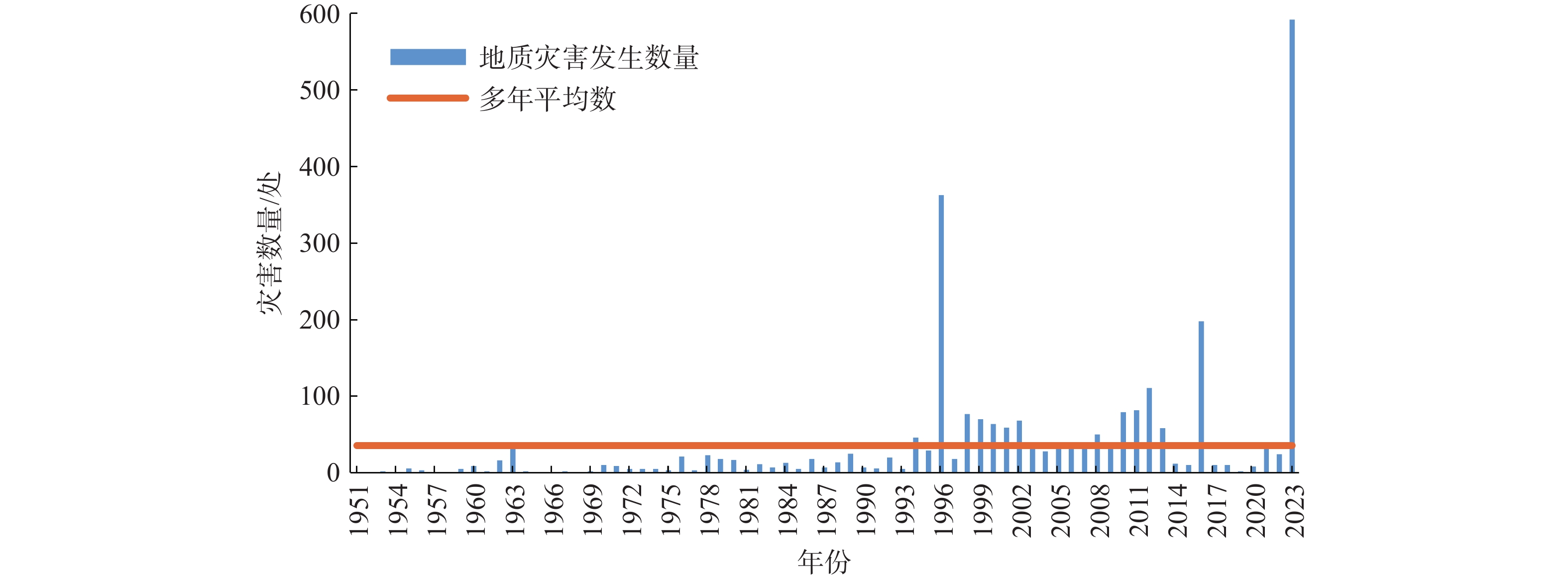
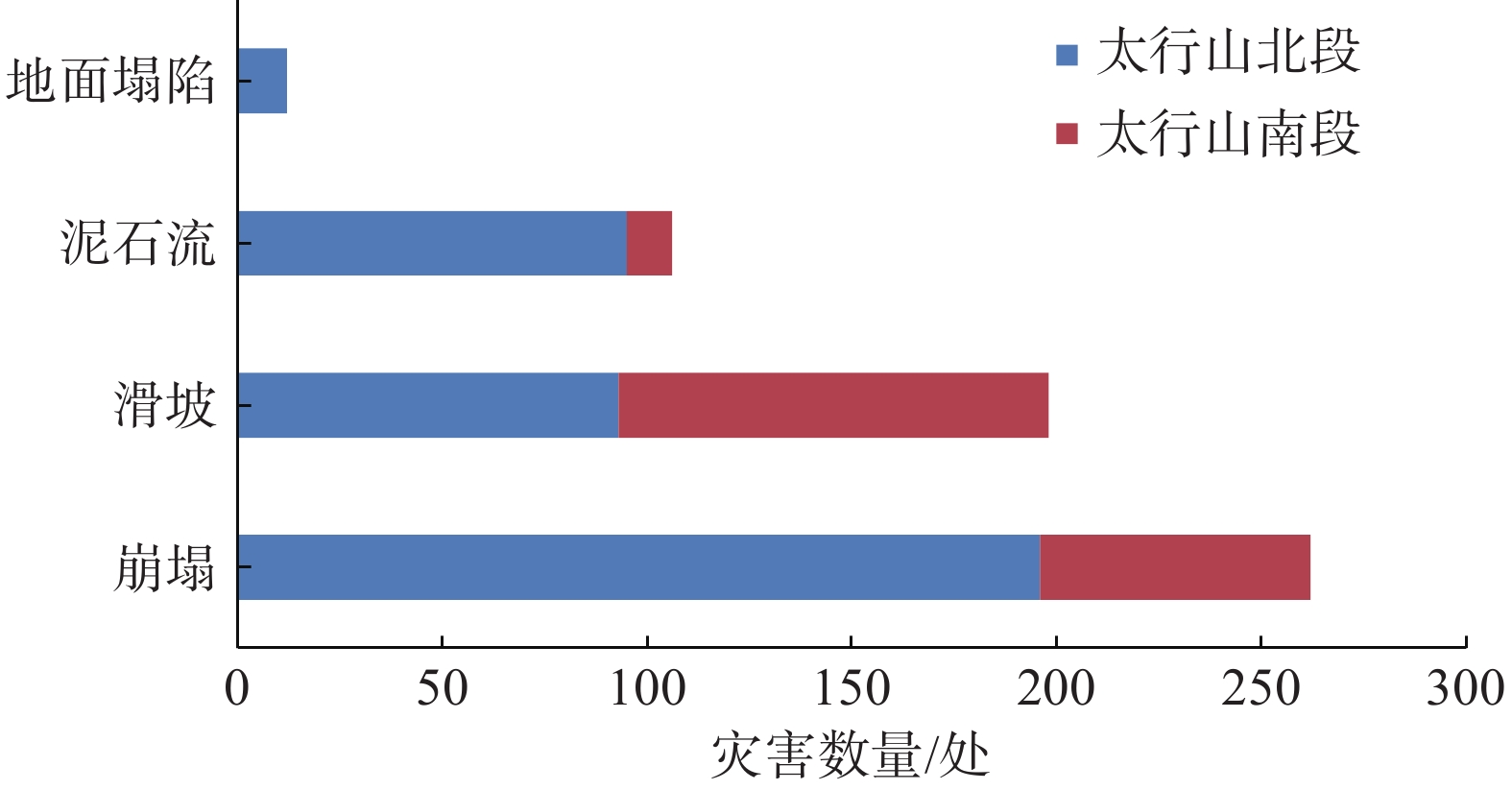
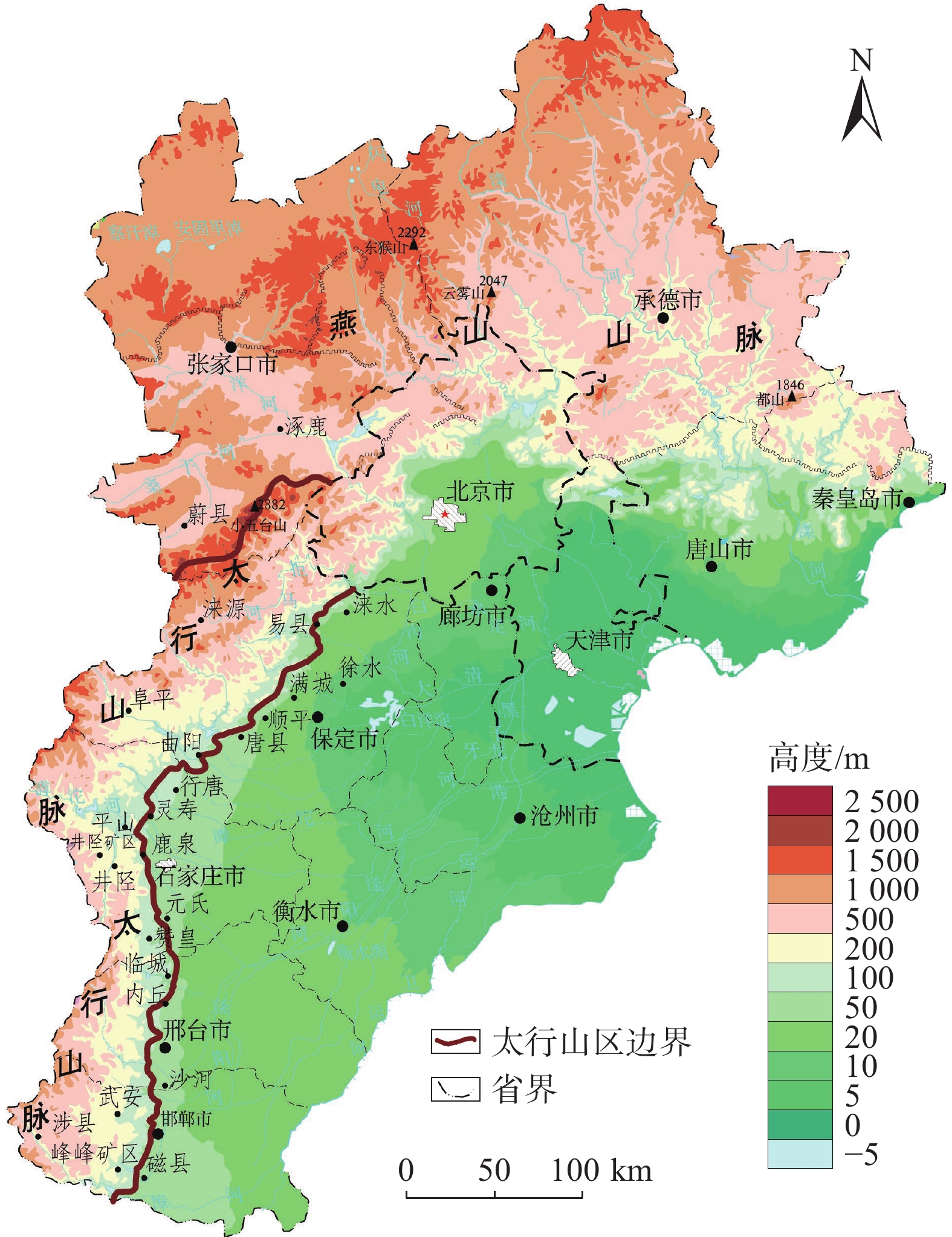
强降雨是引发地质灾害的主要因素。中国北方地区目前多侧重短时强降雨引发地质灾害方面的研究,对区域性极端降水条件下地质灾害特征规律方面研究尚存在不足。基于“23•7”强降雨引发的地质灾害样本分析,研究了太行山河北段地质灾害发生的规律特征。结果表明:(1)地质灾害呈现出多发、群发性态势,发生数量达历史新高,类型以崩塌、滑坡、泥石流为主,激发新的地质灾害明显增多;(2)地质灾害发生时空范围与强降雨区域高度吻合,太行山南段和北段呈现差异性分布;(3)泥石流造成的损失最大,坡面型泥石流明显多发,松散物覆盖型滑坡多发易发。研究结果可为极端降水条件下地质灾害防范提供参考。
Abstract:Heavy rainfall is the main factor triggering geological disasters. In the northern region of China, most of the researches focus on the geologic disasters caused by short-term heavy rainfall, and the researches on the characteristics of geologic disasters under regional extreme precipitation conditions are still insufficient. Based on the sample analysis of geological disasters triggered by the “23•7” heavy rainfall, the regular characteristics of geological disasters in the Hebei section of the Taihang Mountains were studied. The results show that: (1) geologic hazards show the trend of multiple and group occurrence, and the number of occurrences reaches a new high in history, and the types of avalanches, landslides, and mudslides are the main ones, which stimulate new geologic hazards to increase significantly; (2) the spatial and temporal scales of occurrence of geologic hazards and the area of heavy rainfall are highly coincident with each other, and the south and north sections of the Taihang Mountains show a differentiated distribution; (3) mudslides cause the most damage, and slope-type mudslides are obviously more frequent, and the loose material-covered landslides are more frequent and easier to occur. cover type landslides are more frequent and prone to occur. The results of the study can provide a reference for the prevention of geologic disasters under extreme precipitation conditions.
-
Key words:
- Doksuri /
- extreme precipitation /
- geological disaster /
- characteristic pattern /
- Taihang Mountain
-

-
表 1 河北省特大暴雨洪地质灾害灾情汇总表
Table 1. Summary table of extraordinarily heavy rainfall floods and geological disasters in Hebei Province
县区 按灾害类型划分 按威胁对象划分 崩塌 滑坡 泥石流 地面塌陷 居民点 道路 其它 涞水县 66.5 138 925 0.05 1 059 70.5 0.05 易县 210 206 30.5 486 901.5 31 阜平县 261.5 49.7 405 296 20 400.2 满城区 82 221.6 31 62.6 272 曲阳县 180 20 20 180 涞源县 1 81.8 17 6 105.8 徐水区 0.6 0.5 0.7 25.2 26.5 0.5 唐县 10 10 涿鹿县 89 65.72 260.72 127.96 259.84 27.64 怀来县 34 26 8 赤城县 0.15 0.5 0.65 平山县 66 66 信都区 3.9 115.5 119.4 内丘县 5 36.5 41.5 沙河市 10.7 10.7 临城县 0.23 0.1 0.33 海港区 0.5 1 1.5 合计/万元 764.38 956.12 1 886.42 538.25 2 865.44 661.84 617.89 表 2 河北省极端降水引发地质灾害情况表
Table 2. Table of geological hazards caused by extreme rainfall in Hebei Province
极端降水年月 过程起止日期 小时最大雨强/(mm·h−1) 最大过程降雨量/mm 发生地质灾害数量/起 63•8 1963年8月1—10日 104.3 2 051.0 38 96•8 1996年8月3—6日 80.1 670.0 363 12•7 2012年7月21—22日 112.0 372.6 111 16•7 2016年7月19—21日 102.8 816.5 198 23•7 2023年7月29—8月2日 110.9 1 003.4 592 表 3 地质灾害气象风险预警等级与指数对应表
Table 3. Geological disaster meteorological risk warning level and index corresponding table
地质灾害气象风险预警等级 地质灾害预警指数 灾害概率/% 4级(蓝色预警) T<−2 <20 3级(黄色预警) −2≤T<0 20~50 2级(橙色预警) 0≤T<2 50~80 1级(红色预警) T≥2 >80 表 4 台风杜苏芮影响期间地质灾害预警预报成效情况表
Table 4. Table of the effect of geological disaster warning and forecast during the influence of Typhoon Doksuri
序号 日期 预警等级 红色预
警区地
质灾害
发生数
/处橙色预
警区地
质灾害
发生数
/处黄色预
警区地
质灾害
发生数
/处无预警
区地质
灾害发
生数
/处灾害发
生总数
/处预报
准确率
/%1 7月29日 红色预警 3 7 0 0 10 100 2 7月30日 红色预警 37 0 0 1 38 97 3 7月31日 红色预警 450 0 0 4 454 99 4 8月01日 红色预警 67 7 1 0 75 100 5 8月02日 橙色预警 0 3 0 0 3 100 6 8月03日 橙色预警 0 6 1 0 7 100 7 8月04日 橙色预警 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 8月05日 橙色预警 0 2 0 0 2 100 9 8月06日 橙色预警 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 8月07日 黄色预警 0 0 0 2 2 0 11 8月08日 黄色预警 0 0 0 1 1 0 -
[1] 河北省1∶5万地质灾害详细调查与研究报告[R]. 北省地质环境监测院,2016. [Detailed survey and research report on 1∶50,000 geological hazards in Hebei Province[R]. Hebei Environmental Geology Exploration Institute,2016. (in Chinese)]
Detailed survey and research report on 1∶50, 000 geological hazards in Hebei Province[R]. Hebei Environmental Geology Exploration Institute, 2016. (in Chinese)
[2] 刘艳辉,唐灿,李铁锋,等. 地质灾害与降雨雨型的关系研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(5):656 − 661. [LIU Yanhui,TANG Can,LI Tiefeng,et al. Statistical relations between geo-hazards and rain-type[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(5):656 − 661. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Yanhui, TANG Can, LI Tiefeng, et al. Statistical relations between geo-hazards and rain-type[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(5): 656 − 661. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 朱小龙,李玉龙,唐立强,等. 河北省保定地区“7•21” 群发地质灾害特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2014,25(1):90 − 96. [ZHU Xiaolong,LI Yulong,TANG Liqiang,et al. The analysis of geological hazard of the “7•21” rainstorm in Baoding in Hebei provinee[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2014,25(1):90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHU Xiaolong, LI Yulong, TANG Liqiang, et al. The analysis of geological hazard of the “7•21” rainstorm in Baoding in Hebei provinee[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2014, 25(1): 90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王海芝,曾庆利,许冰,等. 北京“7•21” 特大暴雨诱发的地质灾害类型及其特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):125 − 132. [WANG Haizhi,ZENG Qingli,XU Bing,et al. Types and characteristics of geological disasters induced by the “7•21” rainstorm in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):125 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Haizhi, ZENG Qingli, XU Bing, et al. Types and characteristics of geological disasters induced by the “7•21” rainstorm in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 125 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张江涛,何丽华,李江波,等,河北“23•7”极端暴雨过程特征及成因初探[J]. 大气科学学报,2023,46(6):884 − 903. [ZHANG Jiangtao,HE Lihua1,LI Jiangbo,et al. Preliminary study on the characteristics and causes of the "23•7" extreme rainstorm in Hebei[J].Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences,2023,46(6):884 − 903. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Jiangtao, HE Lihua1, LI Jiangbo, et al. Preliminary study on the characteristics and causes of the "23•7" extreme rainstorm in Hebei[J].Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2023, 46(6): 884 − 903. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 刘帅, 王涛, 刘甲美, 等. 基于优化随机森林模型的降雨群发滑坡易发性评价研究——以西秦岭极端降雨事件为例[J/OL]. 地质通报,(2024-01-19)[2024-03-09]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=Ma1nt2RbXaiCVYmTY10t4hBKE8E88KDCaireXxHDxs0AgciIbaQNWe-aW6MFZOAMZ4SHVmtNptvmVEyZQKhYHuCNFUSVuDpmascK0QsGWjP0A9CEQrFDO0lRiCabjCIbf6zdaz5jL-0=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS. [LIU Shuai, WANG Tao, LIU Jiamei, etal. A case study on susceptibility assessment of precipitation-induced mass landslides based on optimal random forest model, west Qinling Mountains[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin of China,(2024-01-19)[2024-03-09] (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Shuai, WANG Tao, LIU Jiamei, etal. A case study on susceptibility assessment of precipitation-induced mass landslides based on optimal random forest model, west Qinling Mountains[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin of China,(2024-01-19)[2024-03-09] (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王海芝,胡福根,于淼,等. 北京市房山区霞云岭“7•20” 坡面泥石流特点及形成因素浅析[J]. 城市地质,2021,16(4):399 − 403. [WANG Haizhi,HU Fugen,YU Miao,et al. Characteristics and formation factors of slope debris flow on “7•20” in Xiayunling,Fangshan District,Beijing[J]. Urban Geology,2021,16(4):399 − 403. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Haizhi, HU Fugen, YU Miao, et al. Characteristics and formation factors of slope debris flow on “7•20” in Xiayunling, Fangshan District, Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2021, 16(4): 399 − 403. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘佳意,陈春利,付昱凯,等. 降雨诱发的浅表堆积层滑坡成因机理与稳定性预测模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(2):183 − 191. [LIU Jiayi,CHEN Chunli,FU Yukai,et al. Mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow landslide and stability prediction model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(2):183 − 191. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jiayi, CHEN Chunli, FU Yukai, et al. Mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow landslide and stability prediction model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(2): 183 − 191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 孟生勇,江兴元,杨义,等. 降雨诱发堆积体滑坡水土响应与稳定性时空演化试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(1):104 − 112. [MENG Shengyong,JIANG Xingyuan,YANG Yi,et al. An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(1):104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Shengyong, JIANG Xingyuan, YANG Yi, et al. An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(1): 104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 潘元贵,伍中庚,孙东,等. 四川渠县“8•8” 特大暴雨引发的地质灾害分布特征与成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):125 − 133. [PAN Yuangui,WU Zhonggeng,SUN Dong,et al. Analysis on the distributive characteristics and causes of the geological disasters induced by the “8•8” heavy rainstorm in Qu County,Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):125 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
PAN Yuangui, WU Zhonggeng, SUN Dong, et al. Analysis on the distributive characteristics and causes of the geological disasters induced by the “8•8” heavy rainstorm in Qu County, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 125 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: