CENOZOIC TECTONIC SUBSIDENCE OF THE ZHU Ⅲ DEPRESSION IN THE PEARL RIVER MOUTH BASIN, NORTHERN SOUTH CHINA SEA
-
摘要:
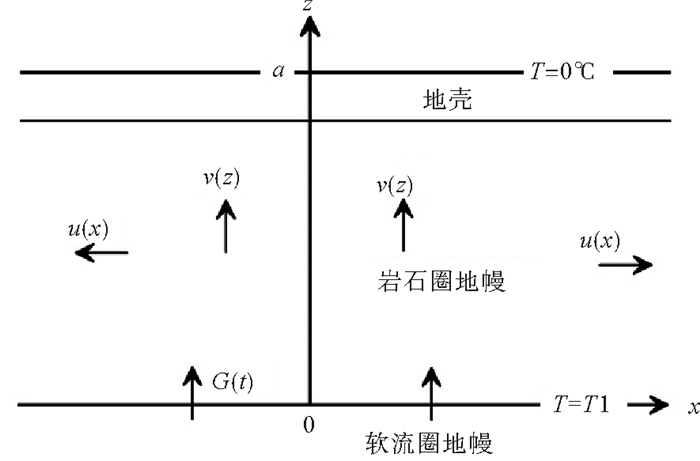
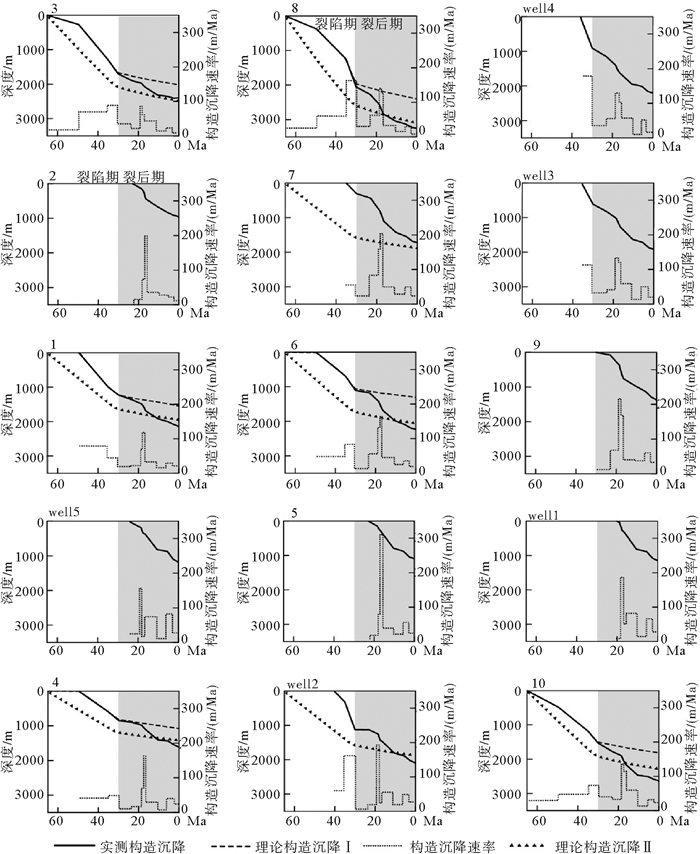
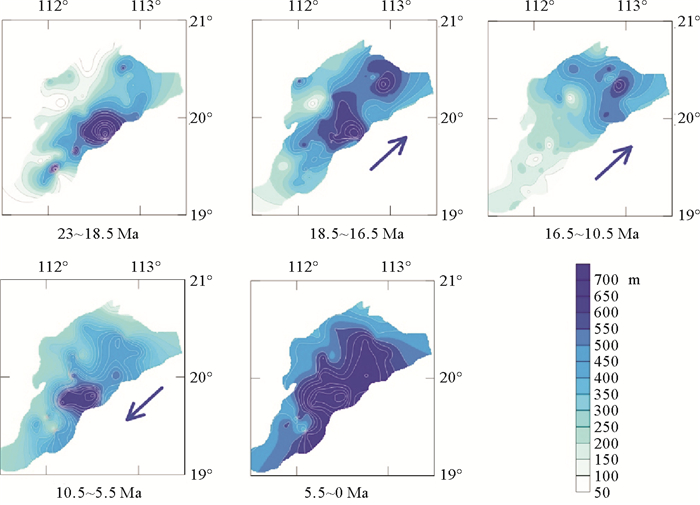
盆地的构造沉降史是盆地基底垂向升降的历史记录,不仅可以反映盆地形成演化历史,而且可能记录了深部地质过程的信息。近年来,越来越多的地球物理证据显示,雷琼地区深部存在延伸到下地幔的柱状低速异常体。为了揭示该深部异常体的活动信息,利用地震资料和钻孔资料,采用回剥和应变速率反演技术,计算了珠三坳陷各构造单元的构造沉降曲线和理论构造沉降曲线。结果显示,珠三坳陷新生代构造沉降可划分为5个阶段:初始张裂慢速沉降(65~49.5 Ma),张裂期快速沉降(49.5~30 Ma),裂后慢速热沉降阶段Ⅰ(30~23.03 Ma),裂后加速沉降(23.03~16.5 Ma),裂后慢速热沉降阶段Ⅱ(16.5~0 Ma)。珠三坳陷在裂陷期存在沉降亏损现象,裂后期存在300~800 m异常沉降可能是对前期沉降不足的补偿,可能与裂陷期软流圈热物质上涌和消退有关。研究结果还表明23.03~10.5 Ma珠三坳陷构造沉降中心发生北东向的迁移,是否与深部异常体活动有关或受区域应力场影响,还需进一步研究。
Abstract:The history of tectonic subsidence is the record of basement movement in vertical direction. It is not only the reflection of basin evolution, but also the record of deep geological process. More and more geophysical evidence accumulated in recent years suggest that there is a low velocity anomaly under the Leiqiong area and its adjacent. In order to reveal the movement information of this deep low velocity anomaly body, we calculated the real tectonic subsidence curves as well as the theoretical tectonic subsidence curves for each tectonic units of the Zhu Ⅲ depression by backstripping and strain rate inversion, based on seismic and drilling data. Results show that the Cenozoic tectonic subsidence of the Zhu Ⅲ depression can be divided into five stages: slow syn-rift tectonic subsidence (65~49.5 Ma), rapid syn-rift tectonic subsidence (49.5~30 Ma), slow post-rift thermal subsidence Ⅰ(30~23.03 Ma), accelerated post-rift subsidence (23.03~16.5 Ma), slow post-rift thermal subsidence Ⅱ(16.5~0 Ma). We find that the Zhu Ⅲ depression exists 300~800 m syn-rift subsidence deficit, and the rapid post-rift subsidence might be the compensation to the deficit probably caused by the dynamic support of the influx of warmer asthenosphere material. The results also show that the tectonic subsidence center of the Zhu Ⅲ depression migrated to the northeast during 23.03~10.5 Ma, together with the deep low velocity anomaly body.
-

-
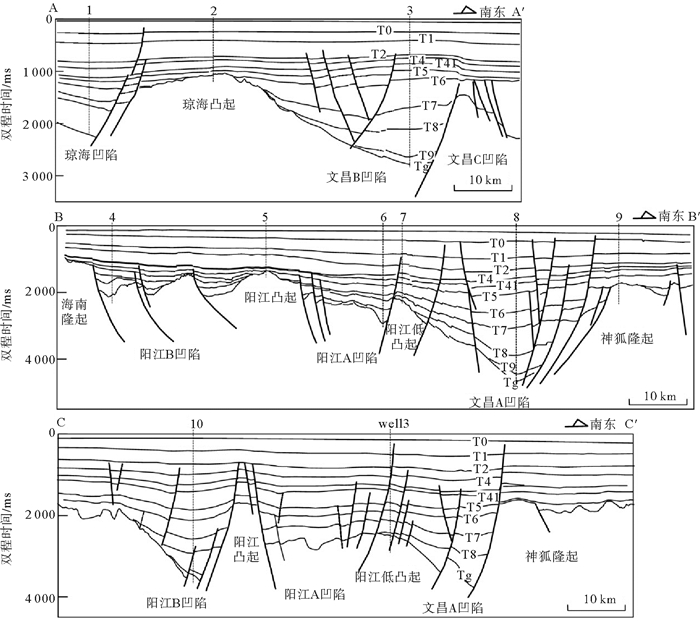
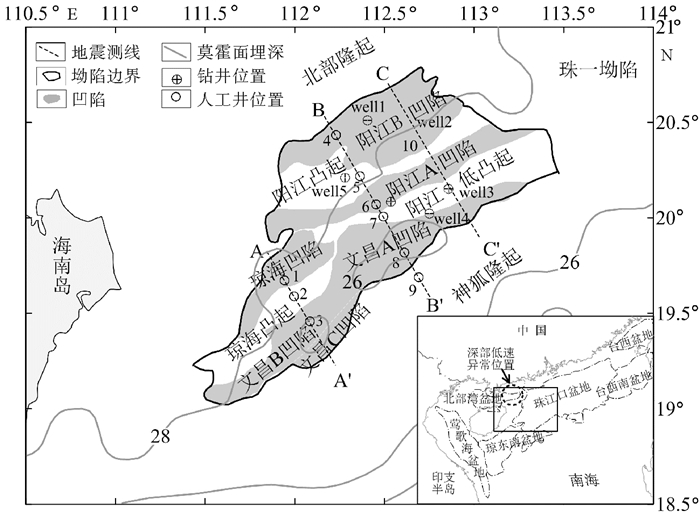
图 1 研究区构造划分及回剥点位置[15]
Figure 1.
表 1 珠三坳陷地层界面年龄及全球海平面变化(据Haq等,1987)
Table 1. Age of the sequence boundaries in Zhu Ⅲ depression(The ages used from CNOOC and sea level changes from Haq et al 1987)
地层界面 年龄/Ma 全球海平面/m 海底 0 0 T0 2.5 -30 T10 5.5 3 T20 10.5 -10 T40 16 95 T41 17.5 124 T50 18.5 128 T60 23.03 139 T70 30 100 T80 35 160 T9 49.5 148 Tg 65 212 参数物理含义 参考值 参数符号/单位 岩石圈初始厚度 125 a/km 地壳初始厚度 32 Tc/km 热膨胀系数 3.28×10-5 α/℃-1 地幔密度 3 330(0 ℃) ρm/(kg·m-3) 软流圈密度 3 185(1 350 ℃) ρa/(kg·m-3) 海水密度 1 030 ρw/(kg·m-3) 砂岩骨架密度 2 650 ρsand/(kg·m-3) 泥岩骨架密度 2 720 ρmud/(kg·m-3) 粉砂岩骨架密度 2 650 ρlime/(kg·m-3) 砂岩初始孔隙度 0.49 ϕ0 泥岩初始孔隙度 0.63 C 粉砂岩初始孔隙度 0.56 砂岩压实系数 0.27 泥岩压实系数 0.51 粉砂岩压实系数 0.39 -
[1] Huang J L, Zhao D P. High-resolution mantle tomography of China High-resolution mantle tomography of China and surrounding regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2006, 111(B9): B9305. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004066
[2] Lebedev S, Nolet G. Upper mantle beneath southeast Asia from S velocity tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2003, 108(B1): 2048. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0212209417/
[3] Montelli R, Nolet G, Dahlen F A, et al. A catalogue of deep mantle plumes: New results from finite-frequency tomography[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(11): Q11007. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-2006GC001248/
[4] Montelli R, Nolet G, Dahlen F A, et al. Finite-frequency tomography reveals a variety of plumes in the mantle[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5656): 338-343. doi: 10.1126/science.1092485
[5] Xia S H, Zhao D P, Sun J L, et al. Teleseismic imaging of the mantle beneath southernmost China: New insights into the Hainan plume[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 36: 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.05.003
[6] Zhao D P. Global tomographic images of mantle plumes and subducting slabs: insight into deep Earth dynamics[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2004, 146(1-2): 3-34. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2003.07.032
[7] Zhao D P. Seismic images under 60 hotspots: Search for mantle plumes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 12(14): 335-355. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.gr.2007.03.001/
[8] 雷建设, 赵大鹏, 沈繁銮, 等.海南地幔柱新的成像结果[J].国际地震动态, 2008(11): 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2008.11.032
LEI Jianshe, ZHAO Dapeng, SHEN Fanluan, et al. A new tomographic image of the Hainan plume in the upper mantle[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology, 2008(11): 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2008.11.032
[9] McKenzie D. Some remarks on the development of sedimentary basins[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 40(1): 25-32. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90071-7
[10] 张金川, 李桂群.盆地沉降分析及其应用[J].青岛海洋大学学报, 1995, 25(3): 391-399. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-QDHY503.022.htm
ZHANG Jinchuan, LI Guiqun. Subsidence analysis and its application to basins[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1995, 25(3): 391-399. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-QDHY503.022.htm
[11] 李超, 姜承鑫.盆地沉降分析中的两类沉降[J].中国科技信息, 2011(19): 48-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkjxx201119010
LI Chao, JIANG Chengxin. Tow kinds of subsidence in basin subsidence analysis[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2011(19): 48-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkjxx201119010
[12] 张功成, 金莉, 兰蕾, 等. "源热共控"中国油气田有序分布[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(5): 1-28. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.05.001
ZHANG Gongcheng, JIN Li, LAN Lei, et al. Analysis of the regular distribution of oil and gas fields in China based on the theory of hydrocarbon generation controlled by source rocks and geothermal heat[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 34(5): 1-28. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.05.001
[13] Xie H, Zhou D, LiYP, et al. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in deepwater sags in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 615: 182-198. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260028249_Cenozoic_Tectonic_Subsidence_in_Deepwater_Sags_in_the_Pearl_River_Mouth_Basin_Northern_South_China_Sea
[14] Nie F J, Li S T, Wang H, et al. Lateral migration pathways of petroleum in the Zhu Ⅲ subbasin, Pearl River Mouth basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2001, 18(5): 561-575. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(01)00013-7
[15] 宫贺晏.珠江口盆地珠三坳陷构造演化及其对煤系烃源岩的控制[D].徐州: 中国矿业大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10290-1014074215.htm GONG Heyan. Tectonic evolution and its control on coal-measure source rocks in Zhu-3 depression of pearl river mouth basin[D]. Xuzhou: Master's Thesis of China University of Mining and Technology, 2014.
[16] 刘志峰, 刘志鹏, 肖伶俐, 等.珠三坳陷北部珠海组—韩江组沉积演化及储盖组合[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(9): 25-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201309005
LIU Zhifeng, LIU Zhipeng, XIAO Lingli, et al. Facies evolution and reservoir-seal assemblages in the Zhuhai and Hanjiang formations, North of Zhu3 Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(9): 25-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201309005
[17] 张迎朝, 陈志宏, 李绪深, 等.珠江口盆地西部油气成藏组合和成藏模式[J].石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(1): 108-117, 123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201101013
ZHANG Yingzhao, CHEN Zhihong, LI Xushen, et al. Hydrocarbon plays and pool forming patterns in the western part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2011, 32(1): 108-117, 123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201101013
[18] 何光玉, 吴景富, 刘海滨, 等.南海珠三坳陷油气系统分析[J].石油实验地质, 2000, 22(1): 35-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2000.01.006
HE Guangyu, WU Jingfu, LIU Haibin, et al. Study on petroleum systems in Zhu Ⅲ subbasin of South China Sea[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 2000, 22(1): 35-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2000.01.006
[19] 张功成, 刘震, 米立军, 等.珠江口盆地—琼东南盆地深水区古近系沉积演化[J].沉积学报, 2009, 27(4): 632-641. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200904007
ZHANG Gongcheng, LIU Zhen, MI Lijun, et al. Sedimentary evolution of Paleogene series in deep water area of Zhujiangkou and Qiongdongnan basin[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(4): 632-641. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200904007
[20] 朱伟林.中国近海含油盆地古湖泊学研究[D].上海: 同济大学博士学位论文, 2002.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10247-2007224465.htm ZHU Wei. Oil-bearing basin offshore China: a paleolimnological perspective[D]. Shanghai: Doctor Dissertation of Tongji University, 2002.
[21] 张景茹.珠江口盆地珠二坳陷、珠三坳陷含油气系统及油气成藏模式[D].广州: 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2014.
http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/983246 ZHANG Jingru. Research on petroleum system and hydrocarbon pooling pattern in the Zhu-Ⅱand Zhu-Ⅲ Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Guangzhou: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014.
[22] White N. An inverse method for determining lithospheric strain rate variation on geological timescales[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 122(3-4): 351-371. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90008-6
[23] 李亚敏, 施小斌, 徐辉龙, 等.琼东南盆地构造沉降的时空分布及裂后期异常沉降机制[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(1): 47-57, 65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201201007
LI Yamin, SHI Xiaobin, XU Huilong, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of tectonic subsidence and discussion on formation mechanism of anomalous post-rift tectonic subsidence in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(1): 47-57, 65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201201007
[24] Sclater J G, Christie P A F. Continental stretching: an explanation of the post-mid-cretaceous subsidence of the central North Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1980, 85(B7): 3711-3739. doi: 10.1029/JB085iB07p03711
[25] 吕学菊, 肖力, 林正良, 等.珠江口盆地西部珠三坳陷沉降史分析[J].新疆石油地质, 2008, 29(2): 195-197, 205. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjsydz200802017
LV Xueju, XIAO Li, LIN Zhengliang, et al. Analysis of subsidence history of Zhusan Depression in Western Pearl River mouth basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2008, 29(2): 195-197, 205. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjsydz200802017
[26] Hap B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4793): 1156-1167. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156
[27] 杨军, 施小斌, 王振峰, 等.琼东南盆地张裂期沉降亏损与裂后期快速沉降成因[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(1): 81-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201501009
YANG Jun, SHI Xiaobin, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. Origin of syn-rift subsidence deficit and rapid post-rift subsidence in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(1): 81-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201501009
[28] Shi X B, Jiang H Y, Yang J, et al. Models of the rapid post-rift subsidence in the eastern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: implications for the development of the deep thermal anomaly[J]. Basin Research, 2017, 29(3): 340-362. doi: 10.1111/bre.12179
[29] 南海地质地球物理图系(1: 200万)[M].广州: 广州海洋地质调查局, 2016.
Atlas of geology and geophysics of the South China Sea (1: 2000000)[M]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, 2016.
[30] Dupré S, Bertotti G, Cloetingh S. Tectonic history along the South Gabon Basin: Anomalous early post-rift subsidence[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2007, 24(3): 151-172. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.11.003
[31] Morley C K, Westaway R. Subsidence in the super-deep Pattani and Malay Basins of Southeast Asia: a coupled model incorporating lower-crustal flow in response to post-rift sediment loading[J]. Basin Research, 2006, 18(1): 51-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2006.00285.x
[32] Zhao Z X, Sun Z, Sun L T, et al. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Basin Research, 2016, doi: 10.1111/bre.12220.
[33] Xie X N, Müller R D, Li S T, et al. Origin of anomalous subsidence along the Northern South China Sea margin and its relationship to dynamic topography[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(7): 745-765. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.03.004
[34] Zhao Z X, Sun Z, Wang Z F, et al. The dynamic mechanism of post-rift accelerated subsidence in Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geophysics Research, 2013, 34(3-4): 295-308. doi: 10.1007/s11001-013-9188-2
[35] Shi X B, Burov E, Leroy S, et al. Intrusion and its implication for subsidence: A case from the Baiyun Sag, on the northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2005, 407(1-2): 117-134. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2005.07.004
[36] 付洁, 黎明碧, 唐勇, 等.珠江口盆地白云凹陷裂后异常沉降研究及成因分析[J].海洋学研究, 2013, 31(1): 1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2013.01.001
FU Jie, LI Mingbi, TANG Yong, et al. Post-rift subsidence anomaly and its mechanism in the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Miuth Basin[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2013, 31(1): 1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2013.01.001
[37] 赵中贤, 周蒂, 廖杰, 等.珠江口盆地陆架区岩石圈伸展模拟及裂后沉降分析[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(8): 1135-1145. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201008006
ZHAO Zhongxian, ZHOU Di, LIAO Jie, et al. Lithospheric stretching modeling of the continental shelf in the pearl river mouth basin and analysis of post-breakup subsidence[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(8): 1135-1145. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201008006
[38] 秦国权.珠江口盆地新生代晚期层序地层划分和海平面变化[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2002, 16(1): 1-11, 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2002.01.001
QIN Guoquan. Late Cenozoic sequence stratigraphy and sea-level changes in Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2002, 16(1): 1-11, 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2002.01.001
[39] Haq B U, Jan H, Vail P. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4793): 1156-1166. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156
[40] Reston T J. The extension discrepancy and syn-rift subsidence deficit at rifted margins[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2009, 15(3): 217-237. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=68ae95bfda94dd4f631176ebc403bff2
[41] Wang C Y, Huang J L. Mantle transition zone structure beneath Hainan and adjacent areas derived from receiver function analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(6): 658-665. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.1760
[42] Wang X C, Li Z X, Li X H, et al. Identification of an ancient mantle reservoir and young recycled materials in the source region of a young mantle plume: Implications for potential linkages between plume and plate tectonics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 377-378: 248-259. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.07.003
[43] Zou H B, Fan Q C. U-Th isotopes in Hainan basalts: Implications for sub-asthenospheric origin of EM2 mantle endmember and the dynamics of melting beneath Hainan Island[J]. Lithos, 2010, 116(1-2): 145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.01.010
[44] 鄢全树, 石学法.海南地幔柱与南海形成演化[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(2): 311-322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.014
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa. Hainan mantle plume and the formation and evolution of the South China Sea[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(2): 311-322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.014
[45] Wang X C, Li Z X, Li X H, et al. Temperature, pressure, and composition of the mantle source region of late Cenozoic basalts in Hainan island, SE Asia: a consequence of a young thermal mantle plume close to subduction Zones?[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2012, 53(1): 177-233. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egr061
[46] Hoang N, Flower M. Petrogenesis of Cenozoic basalts from Vietnam: implication for origins of a 'Diffuse Igneous Province'[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(3): 369-395. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.3.369
[47] 邹和平, 李平鲁, 饶春涛.珠江口盆地新生代火山岩地球化学特征及其动力学意义[J].地球化学, 1995, 24(S1): 33-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX5S1.004.htm
ZOU Heping, LI Pinglu, RAO Chuntao. Geochemistry of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Zhujiangkou Basin and its geodynamic significance[J]. Geochimica, 1995, 24(S1): 33-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX5S1.004.htm
[48] Flower M F J, Zhang M, Chen C Y, et al. Magmatism in the South China Basin 2. Post-spreading quaternary basalts from Hainan Island, south China[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 97(1-2): 65-87. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90136-S
[49] Nguyen H, Flower M F J, Carlson R W. Major, trace element, and isotopic compositions of Vietnamese basalts: Interaction of hydrous EM1-rich asthenosphere with thinned Eurasian lithosphere[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(22): 4329-4351. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00247-5
[50] Tu K, Flower M F J, Carlson R W, et al. Sr, Nd, and Pb isotopic compositions of Hainan basalts (south China): Implications for a subcontinental lithosphere Dupal source[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(6): 567-569. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0567:SNAPIC>2.3.CO;2
[51] Zhou P B, Mukasa S B. Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic, and major- and trace-element geochemistry of Cenozoic lavas from the Khorat Plateau, Thailand: sources and petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 137(3-4): 175-193. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00162-3
[52] 王聪, 梅廉夫, 陈汉林, 等.珠江口盆地惠州凹陷裂后期沉降特征及成因分析[J].中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 47(3): 807-818. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zngydxxb201603014
WANG Cong, MEI Lianfu, CHEN Hanlin, et al. Post-rift subsidence history and mechanism of Huizhou depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2016, 47(3): 807-818. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zngydxxb201603014
-



 下载:
下载: