MIDDLE MIOCENE DEEP-WATER SEDIMENTS IN THE BEIKANG BASIN, SOUTHERN SOUTH CHINA SEA: TYPES, CHARACTERISTICS AND IMPLICATIONS
-
摘要:
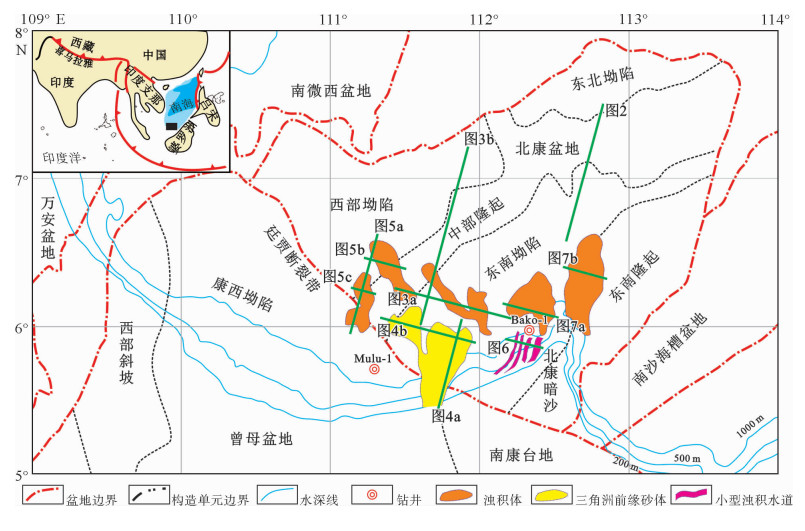
利用广州海洋地质调查局已有的2D地震资料,对南海南部北康盆地拗陷阶段中中新世地层内的地震反射结构进行了精细刻画。通过对地震反射同相轴振幅强度、连续性、接触关系、整体形态特征等要素的系统识别和总结,建立了5种典型的地震相类型。结合南海南部沉积盆地的构造-沉积演化特征,识别出了中中新世时期北康盆地内发育的深水沉积体类型,分别是半深海-深海细粒沉积体、三角洲前缘砂体、浊积体和小型浊积体水道。研究认为,三角洲前缘砂体和浊积体构成了研究区拗陷阶段的两大深水碎屑岩储集体类型,能够与下部断陷阶段的烃源岩和中中新世之后的深海-半深海细粒沉积体一起构成垂向上的生储盖组合,具有较好的油气勘探潜力。
Abstract:2D seismic data from Guangzhou Marine Geology Survey are used in this research for the internal seismic architectures of the Middle Miocene in the Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea. Based upon the integrated analyses of amplitude, continuity, contact relationship, and morphologies of the seismic reflections, five typical seismic facies have been identified. The study of the tectono-sedimentary evolution of the basins reveal that there occur bathyal-abyssal fine-grained sediments, deltaic front sandy bodies, turbidites and small-scale turbidite channels in the Middle Miocene of the study area, and deltaic front sandy bodies and turbidites dominate the deep-water clastic reservoirs in the depression stage of the Beikang Basin. The source-reservoir-cap assemblage is well developed by deep rifting stage source rocks, deep-water clastic reservoirs of Middle Miocene, and the bathyal-abyssal fine-grained deposits since Middle Miocene as covers, implying good hydrocarbon exploration potential.
-
Key words:
- deep-water sediment /
- Middle Miocene /
- Beikang Basin /
- southern South China Sea
-

-
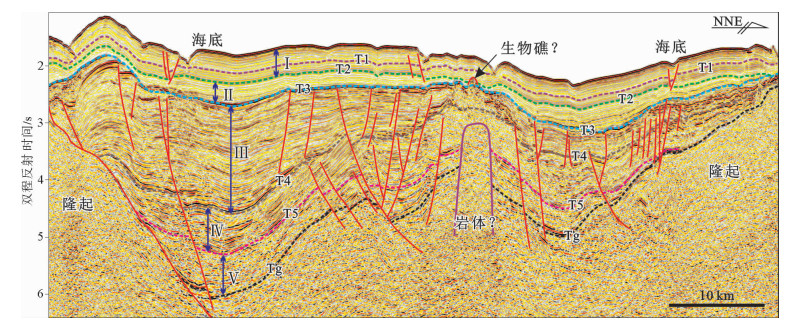
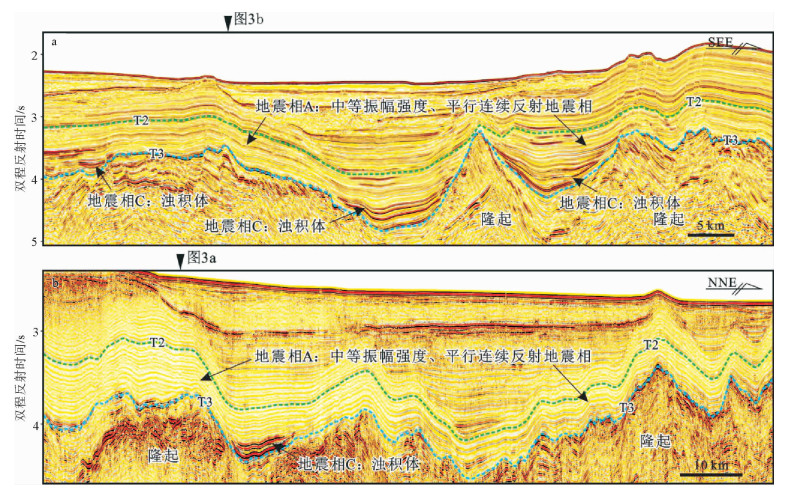
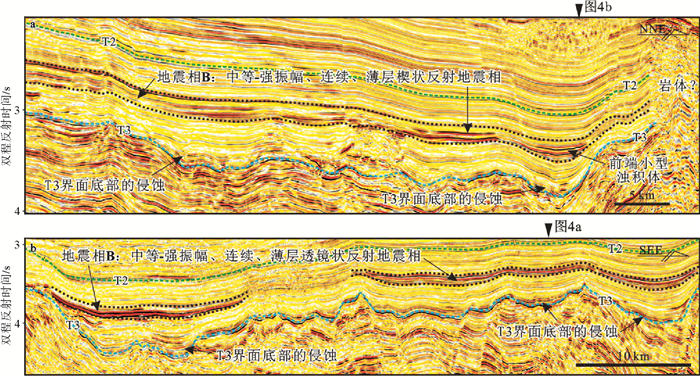
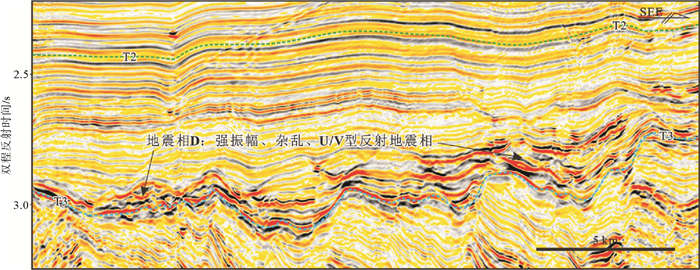
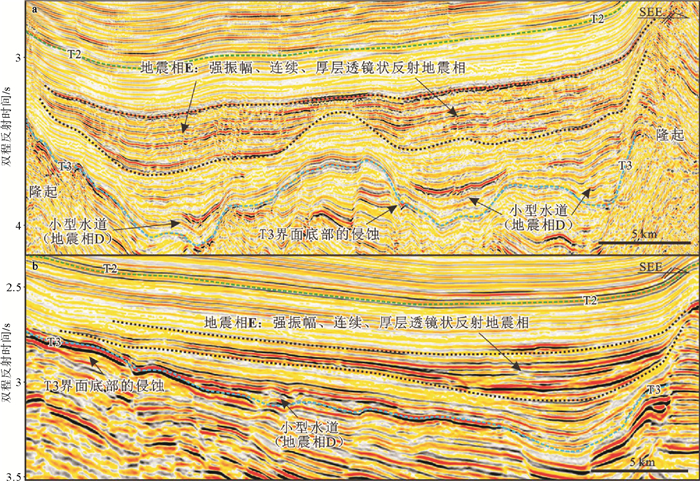
表 1 北康盆地中中新世地层中典型地震相类型及特征
Table 1. Types and characteristics of Mid-Miocene seismic facies in the Beikang Basin
地震相 振幅强度 连续性 接触关系 整体形态 分布范围 可能的解释 地震相A 中等强度 好 平行叠加 近似等厚状 全区都发育 半深海-深海细粒沉积 地震相B 中等—强振幅 中等—好 向北进积/两端上超 楔状/薄层透镜状,延伸范围大 东南坳陷的南部 三角洲前缘砂体 地震相C 强振幅 好 两端上超,底部小型侵蚀 透镜状,延伸范围较小 北康盆地南部 浊积体 地震相D 强振幅 差,杂乱 存在对下伏地层的侵蚀 U型-V型 东南坳陷的东南部 小型浊积水道 地震相E 强振幅 好 两端上超,底部侵蚀 透镜状,分布范围/厚度相对较大 北康盆地东南部 浊积体 -
[1] 刘宝明, 金庆焕.南海曾母盆地油气地质条件及其分布特征[J].热带海洋, 1997, 16(4): 18-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700820843
LIU Baoming, JIN Qinghuan. Hydrocarbon geological conditions and distribution characteristics of Zengmu Basin in southern South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1997, 96(4): 18-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700820843
[2] 王宏斌, 姚伯初, 梁金强, 等.北康盆地构造特征及其构造区划[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2): 49-54. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200102009
WANG Hongbin, YAO Bochu, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Tectonic characteristics and division of the Beikang Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology 2001, 21(2): 49-54. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200102009
[3] 王嘹亮, 吴能友, 周祖翼, 等.南海西南部北康盆地新生代沉积演化史[J].中国地质, 2002, 29(1): 96-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2002.01.016
WANG Liaoliang, WU Nengyou, ZHOU Zuyi, et al. History of the Cenozoic sedimentary evolution of the Beikang Basin, southwestern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 2002, 29(1): 96-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2002.01.016
[4] 张莉, 王嘹亮, 易海.北康盆地的形成与演化[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(4): 245-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200304005
ZHANG Li, WANG Liaoliang, YI Hai. The formation and evolution of Beikang Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(4): 245-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghsyq-dz200304005
[5] 孙珍, 赵中贤, 周蒂, 等.南沙海域盆地的地层系统与沉积结构[J].地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(5): 798-806. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2011.082
SUN Zhen, ZHAO Zhongxian, ZHOU Di, et al. The stratigraphy and the sequence achitecture of the Basins in Nansha Region[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(5): 798-806. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2011.082
[6] 谢晓军, 张功成, 赵志刚, 等.曾母盆地油气地质条件、分布特征及有利勘探方向[J].中国海上油气, 2015, 27(1): 19-26. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2015.01.003
XIE Xiaojun, ZHANG Gongcheng, ZHAO Zhigang, et al. Hydrocarbon geology, distribution and favorable exploration direction in Zengmu Basin, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(1): 19-26. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2015.01.003
[7] Warrlich G, Taberner C, Asyee W, et al. The impact of postdepositional processes on reservoir properties: two case studies of Tertiary carbonate buildup gas fields in Southeast Asia (Malampaya and E11)[M]//Morgan W A, George A D, Harris P M, et al. Cenozoic Carbonate Systems of Australasia. SEPM, 2010: 99-127.
[8] Zampetti V, Schlager W, Van Konijnenburg J H, et al. 3-D Seismic characterization of submarine landslides on a Miocene carbonate platform (Luconia Province, Malaysia)[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2004, 74(6): 817-830. doi: 10.1306/040604740817
[9] Wilson M E J. Development of equatorial delta-front patch reefs during the Neogene, Borneo[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2005, 75(1): 114-133. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2005.010
[10] 解习农, 任建业, 王振峰, 等.南海大陆边缘盆地构造演化差异性及其与南海扩张耦合关系[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 77-87. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.007
XIE Xinong, REN Jianye, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 77-87. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.007
[11] Madon M, Ly K C, Wong R. The structure and stratigraphy of deepwater Sarawak, Malaysia: implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76: 312-333. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.040
[12] Koŝa E. Sea-level changes, shoreline journeys, and the seismic stratigraphy of Central Luconia, Miocene-present, offshore Sarawak, NW Borneo[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 35-55. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.005
[13] 钟广见, 吴进民, 王嘹亮.南海西南走滑断裂特征及其与油气的关系[J].青岛海洋大学学报, 1995, 25(4): 495-502.
ZHONG Guangjian, WU Jinmin, WANG Liaoliang. Characteristics of strike-slip system and its relation to oil and gas in the south-west area of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1995, 25(4): 495-502.
[14] Mohammad A M, Wong R H F. 1995. Seismic sequence stratigraphy of the Tertiary sediments, offshore Sarawak deepwater area, Malaysia[C]//Teh G H, ed. Proceedings AAPG-GSM International Conference 1994-SE Asian Basins: Oil and Gas for the 21st Century. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: AAPG.
[15] Mat-Zin I C, Tucker M E. An alternative stratigraphic scheme for the Sarawak Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1999, 17(1-2): 215-232. doi: 10.1016/S0743-9547(98)00042-7
[16] Hassan M H A, Johnson H D, Allison P A, et al. Sedimentology and stratigraphic development of the upper Nyalau Formation (Early Miocene), Sarawak, Malaysia: A mixed wave-and tide-influenced coastal system[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76(1): 301-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.018
[17] Hutchison C S. Marginal basin evolution: the southern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(9): 1129-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.07.002
[18] Ismail M I, Eusoff A R, Mohamad A M. The geology of Sarawak deepwater and surrounding areas[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1995, 37: 165-178. doi: 10.7186/bgsm37199512
[19] 邱燕.南海南部主要含油气盆地沉积体系初步分析[J].海洋地质, 1996(2): 10-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199601018918
QIU Yan. Analysis of sedimentary system of major hydrocarbon-bearing basins in southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1996(2): 10-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199601018918
[20] 刘振湖.南海南沙海域沉积盆地与油气分布[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(3): 410-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2005.03.017
LIU Zhenhu. Distribution of sedimentary basins and petroleum potential in southern South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2005, 29(3): 410-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2005.03.017
[21] 姚伯初, 刘振湖.南沙海域沉积盆地及油气资源分布[J].中国海上油气, 2006, 18(3): 150-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.03.002
YAO Bochu, LIU Zhenhu. Sedimentary basins and petroleum resources in Nansha offshore area, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2006, 18(3): 150-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.03.002
[22] 张厚和, 刘鹏, 廖宗宝, 等.南沙海域北康盆地油气勘探潜力[J].中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(3): 40-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.005
ZHANG Houhe, LIU Peng, LIAO Zongbao, et al. Oil and gas exploration potential in Beikang Basin, Nansha Sea Area[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(3): 40-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.005
-



 下载:
下载: