Controlling factors and research prospect on creeping behaviors of marine natural gas hydrate-bearing-strata
-
摘要:
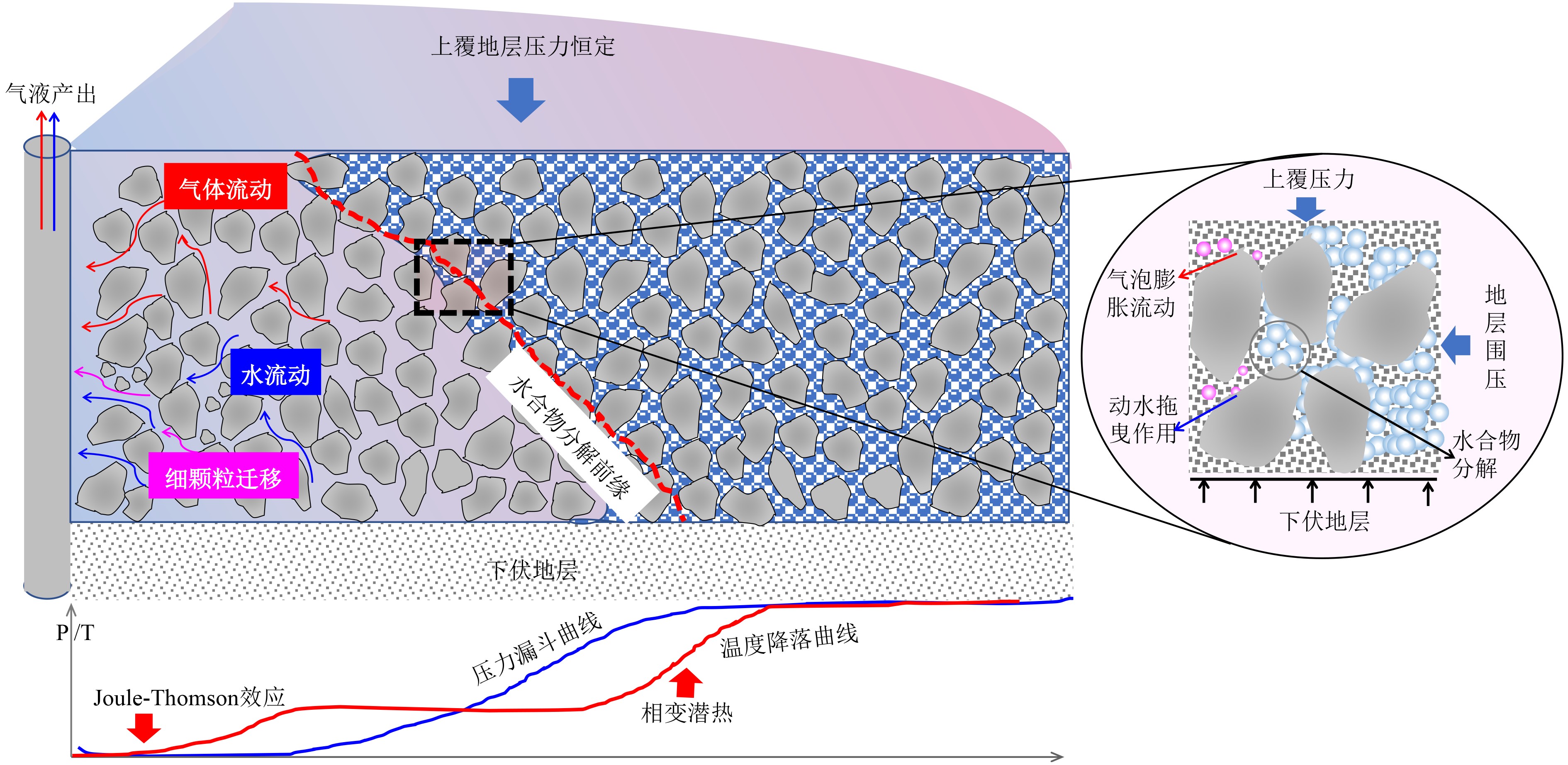
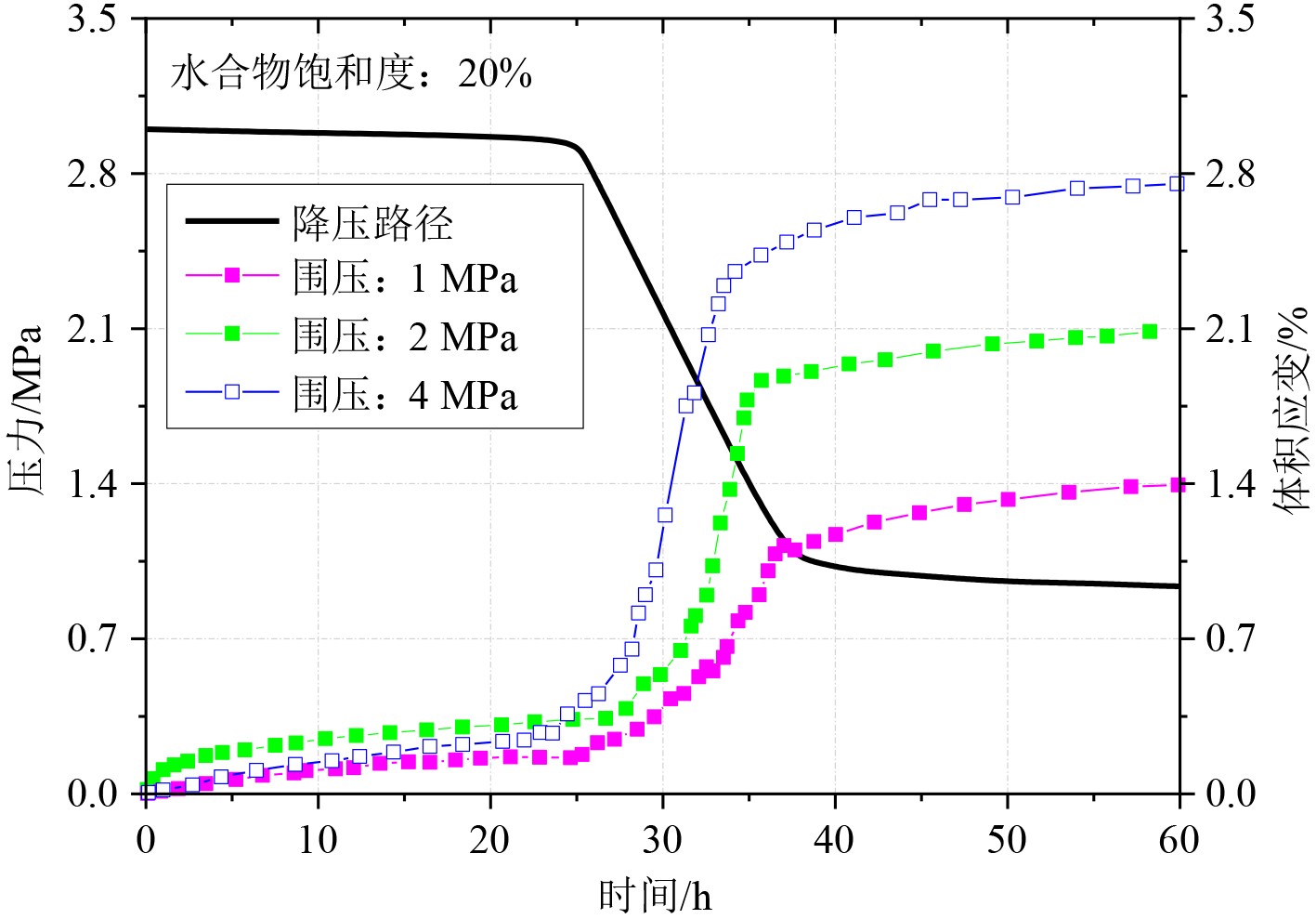
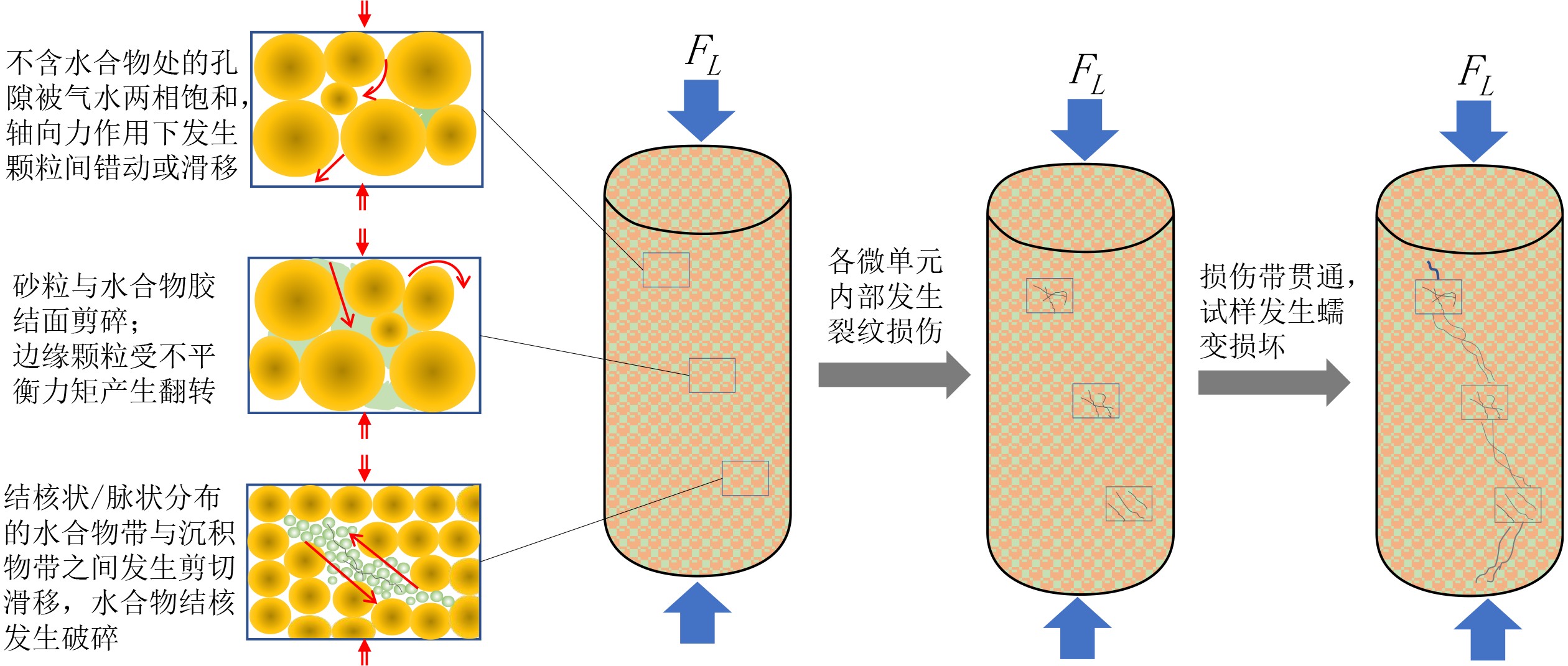
蠕变是指沉积物在特定应力状态下变形与时间的关系,属于沉积物的固有力学属性。厘清海洋天然气水合物开采过程中储层蠕变的主控因素及其控制机理,对量化评价潜在工程地质风险的发生和演变规律具有重要意义。本文将在综述海洋天然气水合物储层破坏特征的基础上,梳理海洋天然气水合物储层蠕变特征及主控因素,厘清关键科学问题;结合最新研究成果,阐述天然气水合物储层蠕变特征多尺度表征与探测技术体系的基本内涵,简要探讨该领域的未来研究方向。初步分析认为,海洋天然气水合物开采过程中储层蠕变行为是水合物本身及其分解产出过程中的应力、温度、渗流等动态因素综合作用的结果,现有蠕变本构模型无法完全反映上述相变-传热-渗流-应力多场多相多组分耦合过程。为建立适合南海北部水合物储层的蠕变本构,进而为后续开采工程安全设计提供理论支撑,建议从天然气水合物储层的力学性能弱化特征及蠕变各阶段的时效参数两方面入手,从分子尺度、纳微尺度、岩心尺度、中试尺度、矿藏尺度5个层面,建立天然气水合物储层蠕变行为的跨尺度研究方法体系;以南海实际储层样品为研究对象,剖析天然气水合物开采过程中储层蠕变行为的主控因素。
Abstract:Creeping of HBS is a common behavior of hydrate-bearing strata in the process of gas production and has great impact on the occurrence and development of engineering geohazards. In this paper, we summarized the main failure modes of HBS based on the investigation of a large number of literatures. Then the research thoughts and strategies on strata creeping behaviors during hydrate exploitation are comprehensively discussed, based on the key scientific issues expounded. Afterwards, a multi-scale creeping detection and characterization approach for HBS is put forward, together with its future research trends. It is supposed that creeping behaviors of HBS during gas extraction are the result of combination of hydrate distribution and its dissociation-induced changes in multi-physical fields such as phase transformation, heat exchange, seepage, and stress evolution. The current constitutive models for conventional soils are not effective enough to reflect such a complex dynamic multifield, multiphase and multicomponent coupling effect, which are doubtlessly inadaptable for evaluating the geotechnical issues during hydrate exploitation in the case of northern South China Sea. For this reason, a multi-scale detection and characterization system needs to be established to analyze the dynamic damage behaviors of HBS during hydrate production, which consists of the molecular scale, nano-to-micro scale, core scale, pilot scale, and field scales techniques. Using the sediments collected from the HBS at the northern South China Sea, the control mechanisms of different geological and engineering parameters on hydrate-bearing strata creeping should be quantitatively modeled.
-

-
[1] 吴能友, 黄丽, 胡高伟, 等. 海域天然气水合物开采的地质控制因素和科学挑战[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):1-11
WU Nengyou, HUANG Li, HU Gaowei, et al. Geological controlling factors and scientific challenges for offshore gas hydrate exploitation [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 1-11.
[2] Collett T. Gas hydrate production testing – knowledge gained[C]//Offshore Technology Conference. Houston, Texas: Offshore Technology Conference, 2019: 1-16.
[3] Yamamoto K, Terao Y, Fujii T, et al. Operational overview of the first offshore production test of methane hydrates in the Eastern Nankai Trough[C]//Offshore Technology Conference. Houston, Texas, USA: Offshore Technology Conference, 2014.
[4] Yamamoto K, Wang X X, Tamaki M, et al. The second offshore production of methane hydrate in the Nankai Trough and gas production behavior from a heterogeneous methane hydrate reservoir [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(45): 25987-26013. doi: 10.1039/C9RA00755E
[5] Li J F, Ye J L, Qin X W, et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea [J]. China Geology, 2018, 1(1): 5-16. doi: 10.31035/cg2018003
[6] Mao P X, Sun J X, Ning F L, et al. Effect of permeability anisotropy on depressurization-induced gas production from hydrate reservoirs in the South China Sea [J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2020, 8(8): 2690-2707.
[7] Wu N Y, Li Y L, Chen Q, et al. Sand production management during marine natural gas hydrate exploitation: review and an innovative solution [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(6): 4617-4632.
[8] Li Y L, Wu N Y, Ning F L, et al. A sand-production control system for gas production from clayey silt hydrate reservoirs [J]. China Geology, 2019, 2(2): 121-132. doi: 10.31035/cg2018081
[9] Jin Y R, Li Y L, Wu N Y, et al. Characterization of sand production for clayey-silt sediments conditioned to openhole gravel-packing: experimental observations [J]. SPE Journal, 2021: 1-18. doi: 10.2118/206708-PA
[10] Mu Y H, Ma W, Li G Y, et al. Long-term thermal and settlement characteristics of air convection embankments with and without adjacent surface water ponding in permafrost regions [J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 266: 105464. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105464
[11] Wang R H, Liu W G, Li Y H, et al. Effects of porosity on the creep behavior of hydrate-bearing sediments[C]//ASME 2012 31st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: ASME, 2012.
[12] Liu L L, Zhang Z, Li C F, et al. Hydrate growth in quartzitic sands and implication of pore fractal characteristics to hydraulic, mechanical, and electrical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 75: 103109. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2019.103109
[13] Li Y H, Liu W G, Song Y C, et al. Creep behaviors of methane hydrate coexisting with ice [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 33: 347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.05.042
[14] Yang J, Hassanpouryouzband A, Tohidi B, et al. Gas hydrates in permafrost: distinctive effect of gas hydrates and ice on the geomechanical properties of simulated hydrate-bearing permafrost sediments [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2019, 124(3): 2551-2563. doi: 10.1029/2018JB016536
[15] Pearson C F, Halleck P M, McGuire P L, et al. Natural gas hydrate deposits: a review of in situ properties [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1983, 87(21): 4180-4185. doi: 10.1021/j100244a041
[16] 张峰瑞, 姜谙男, 杨秀荣, 等. 冻融循环下花岗岩剪切蠕变试验与模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(2):509-519
ZHANG Fengrui, JIANG Annan, YANG Xiurong, et al. Experimental and model research on shear creep of granite under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(2): 509-519.
[17] 陈国庆, 万亿, 裴本灿, 等. 冻融循环作用下砂岩蠕变特性及损伤模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(1):19-28
CHEN Guoqing, WAN Yi, PEI Bencan, et al. The creep characteristics and damage model of sandstone under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(1): 19-28.
[18] Fan Z, Sun C M, Kuang Y M, et al. MRI analysis for methane hydrate dissociation by depressurization and the concomitant ice generation [J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 4763-4768. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1038
[19] 陈卫忠, 李翻翻, 雷江, 等. 热-水-力耦合条件下黏土岩蠕变特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(2):379-388 doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.0016
CHEN Weizhong, LI Fanfan, LEI Jiang, et al. Study on creep characteristics of claystone under thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(2): 379-388. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.0016
[20] Sun Y H, Ma X L, Guo W, et al. Numerical simulation of the short- and long-term production behavior of the first offshore gas hydrate production test in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 181: 106196. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106196
[21] Yang M J, Zhao J, Zheng J N, et al. Hydrate reformation characteristics in natural gas hydrate dissociation process: A review [J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 256: 113878. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113878
[22] Li Y L, Wu N Y, He C Q, et al. Nucleation probability and memory effect of methane-propane mixed gas hydrate [J]. Fuel, 2021, 291: 120103. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.120103
[23] Zhu Y M, Chen C, Luo T T, et al. Creep behaviours of methane hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Environmental Geotechnics, 2019: 1-11. doi: 10.1680/jenge.18.00196
[24] Bu Q T, Hu G W, Liu C L, et al. Acoustic characteristics and micro-distribution prediction during hydrate dissociation in sediments from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 65: 135-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2019.02.010
[25] 于超云, 唐世斌, 唐春安. 含水率对红砂岩瞬时和蠕变力学性质影响的试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(2):473-481
YU Chaoyun, TANG Shibin, TANG Chun'an. Experimental investigation on the effect of water content on the short-term and creep mechanical behaviors of red sandstone [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(2): 473-481.
[26] 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 廖华林, 等. 泥质粉砂沉积物—天然气水合物混合体系的力学特性[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):159-168 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.013
LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, LIAO Hualin, et al. Mechanical properties of the mixed system of clayey-silt sediments and natural gas hydrates [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 159-168. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.013
[27] 郝永卯, 黎晓舟, 李淑霞, 等. 天然气水合物降压开采半解析两相产能模型[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50(6):064701
HAO Yongmao, LI Xiaozhou, LI Shuxia, et al. The semi-analytical two-phase productivity model of natural gas hydrate by depressurization [J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2020, 50(6): 064701.
[28] 罗飞, 张元泽, 朱占元, 等. 一种青藏高原冻结砂土蠕变本构模型[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2020, 52(2):26-32 doi: 10.11918/201810053
LUO Fei, ZHANG Yuanze, ZHU Zhanyuan, et al. Creep constitutive model for frozen sand of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020, 52(2): 26-32. doi: 10.11918/201810053
[29] 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 刘乐乐, 等. 含甲烷水合物松散沉积物的力学特性[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(3):105-113
LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, LIU Lele, et al. Mechanical properties of methane hydrate-bearing unconsolidated sediments [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2017, 41(3): 105-113.
[30] Li Y L, Dong L, Wu N Y, et al. Influences of hydrate layered distribution patterns on triaxial shearing characteristics of hydrate-bearing sediments [J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 294: 106375. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106375
[31] Liu Z C, Dai S, Ning F L, et al. Strength estimation for hydrate-bearing sediments from direct shear tests of hydrate-bearing sand and silt [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(2): 715-723. doi: 10.1002/2017GL076374
[32] Li Y L, Hu G W, Wu N Y, et al. Undrained shear strength evaluation for hydrate-bearing sediment overlying strata in the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 38(3): 114-123. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1404-8
[33] 孔亮, 刘文卓, 袁庆盟, 等. 常剪应力路径下含气砂土的三轴试验[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(9):3319-3326
KONG Liang, LIU Wenzhuo, YUAN Qingmeng, et al. Triaxial tests on gassy sandy soil under constant shear stress paths [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(9): 3319-3326.
[34] 韦昌富, 颜荣涛, 田慧会, 等. 天然气水合物开采的土力学问题: 现状与挑战[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):116-132 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.009
WEI Changfu, YAN Rongtao, TIAN Huihui, et al. Geotechnical problems in exploitation of natural gas hydrate: Status and challenges [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 116-132. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.009
[35] 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 刘乐乐. 含水合物沉积物损伤统计本构模型及其参数确定方法[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(10):1273-1279 doi: 10.7623/syxb201610007
LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, LIU Lele. Damage statistic constitutive model of hydrate-bearing sediments and the determination method of parameters [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(10): 1273-1279. doi: 10.7623/syxb201610007
[36] 颜荣涛, 张炳晖, 杨德欢, 等. 不同温-压条件下含水合物沉积物的损伤本构关系[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(12):4421-4428
YAN Rongtao, ZHANG Binghui, YANG Dehuan, et al. Damage constitutive model for hydrate-bearing sediment under different temperature and pore pressure conditions [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(12): 4421-4428.
[37] Chen J, Liu C J, Zhang Z C, et al. Molecular study on the behavior of methane hydrate decomposition induced by ions electrophoresis [J]. Fuel, 2022, 307: 121866. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121866
[38] Zhang Z C, Kusalik P G, Guo G J, et al. Insight on the stability of polycrystalline natural gas hydrates by molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Fuel, 2021, 289: 119946. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119946
[39] Cao P Q, Wu J Y, Zhang Z S, et al. Mechanical properties of methane hydrate: intrinsic differences from ice [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(51): 29081-29093. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b06002
[40] Cladek B R, Everett S M, McDonnell M T, et al. Guest-host interactions in mixed CH4-CO2 hydrates: insights from molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(34): 19575-19583. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b05228
[41] Song W L, Sun X L, Zhou G G, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation study of N2/CO2 displacement process of methane hydrate [J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(44): 1393613950.
[42] Zhang Y C, Liu L L, Wang D G, et al. Application of Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LFNMR) in characterizing the dissociation of gas hydrate in a porous media [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(3): 2174-2182.
[43] 张永超, 刘昌岭, 刘乐乐, 等. 水合物生成导致沉积物孔隙结构和渗透率变化的低场核磁共振观测[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(3):193-202
ZHANG Yongchao, LIU Changling, LIU Lele, et al. Sediment pore-structure and permeability variation induced by hydrate formation: Evidence from low field nuclear magnetic resonance observation [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(3): 193-202.
[44] 吴能友, 李彦龙, 刘昌岭, 等. 一种基于低场核磁分析水合物沉积物力学特性的装置及方法: 中国, 202010147539.5[P]. 2021-02-26
.WU Nengyou, LI Yanlong, LIU Changling, et al. Dwtection device and method for mechanical properties of hydrate-bearing sediment based on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance: CN, 202010147539.5[P]. 2021-02-26. ]
[45] Seol Y, Lei L, Choi J H, et al. Integration of triaxial testing and pore-scale visualization of methane hydrate bearing sediments [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90(12): 124504. doi: 10.1063/1.5125445
[46] 张诚成, 施斌, 朱鸿鹄, 等. 分布式光纤探测地裂缝的理论基础探讨[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(6):1473-1482
ZHANG Chengcheng, SHI Bin, ZHU Honghu, et al. A theoretical framework for detecting and monitoring ground fissures using distributed fiber optic sensing [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(6): 1473-1482.
[47] Zhang C C, Zhu H H, Liu S P, et al. A kinematic method for calculating shear displacements of landslides using distributed fiber optic strain measurements [J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 234: 83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.002
[48] 万义钊, 吴能友, 胡高伟, 等. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物降压开采过程中储层的稳定性[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(4):117-128 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.04.014
WAN Yizhao, WU Nengyou, HU Gaowei, et al. Reservoir stability in the process of natural gas hydrate production by depressurization in the Shenhu area of the South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(4): 117-128. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.04.014
[49] Jin G R, Lei H W, Xu T F, et al. Simulated geomechanical responses to marine methane hydrate recovery using horizontal wells in the Shenhu area, South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 424-436. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.11.007
-



 下载:
下载: