The relation between mineral morphology and metallogenic process of celestite in the Aijingshan strontium deposit in Lishui, Jiangsu Province
-
摘要:
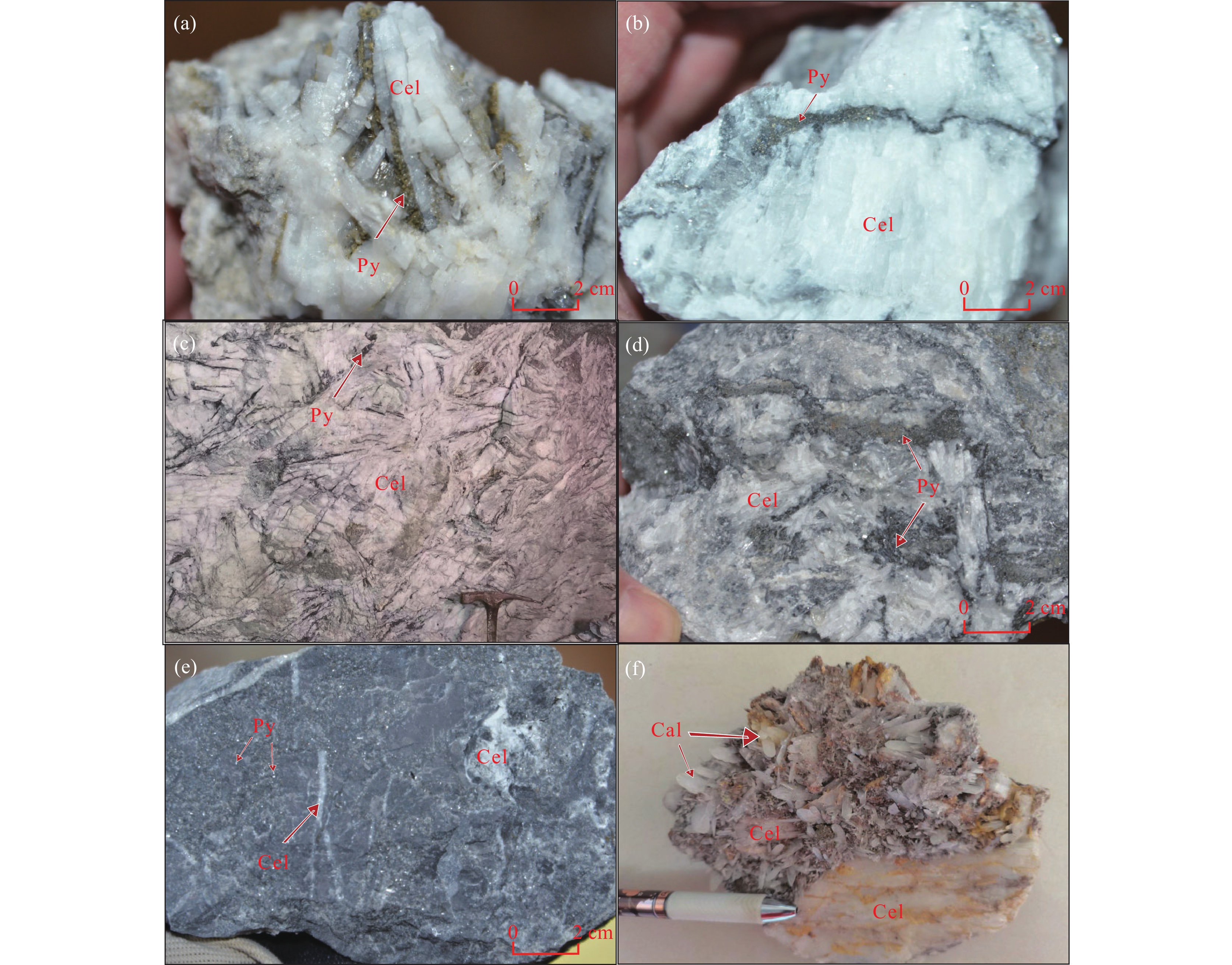
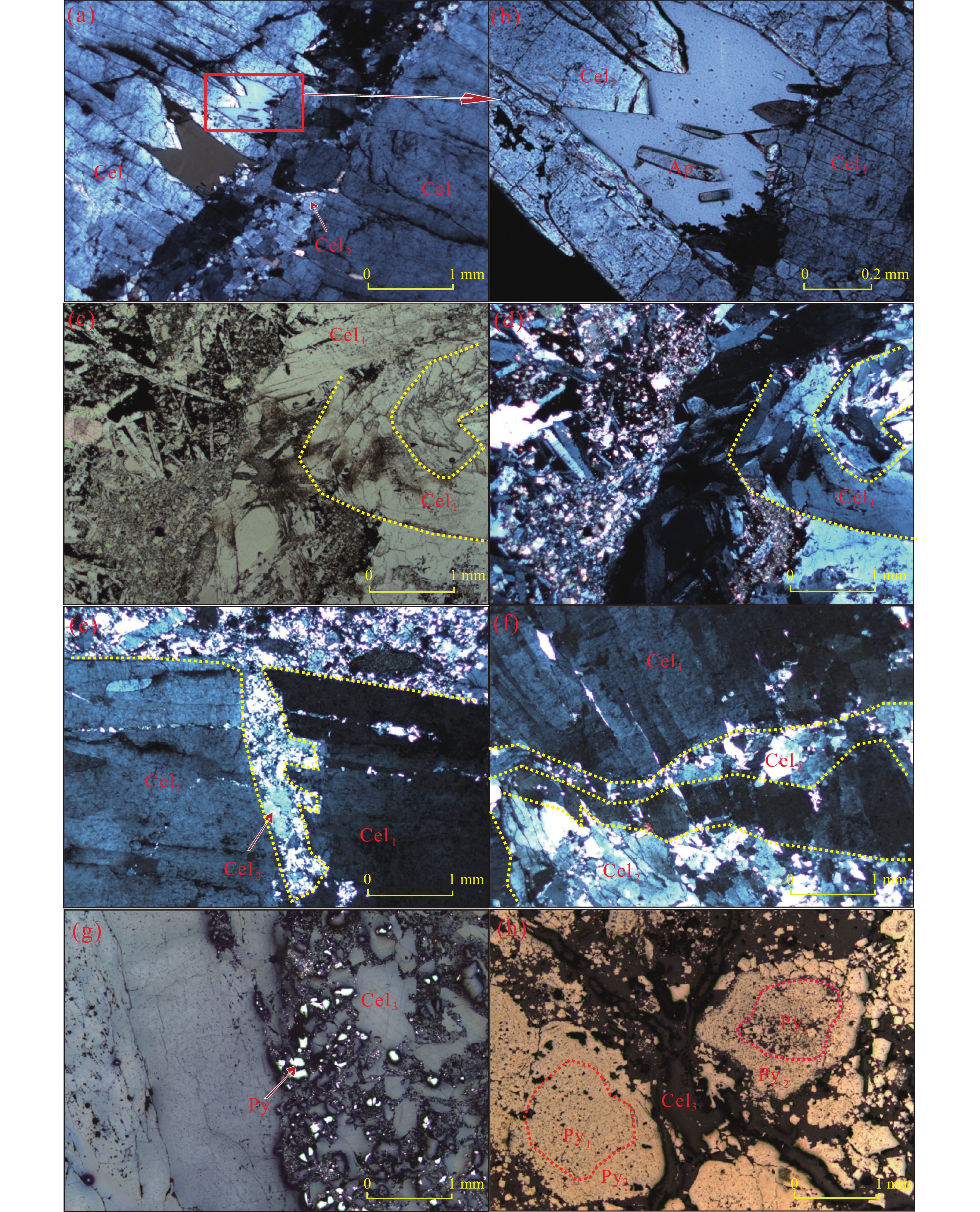
江苏溧水爱景山锶矿床位于长江中下游成矿带溧水盆地东段,是我国火山热液型锶矿床的典型代表。文章对该矿床的矿石样品进行了天青石矿物宏观形态学与微观形态学分析,探讨了天青石矿物形态学与成矿过程的关系。研究表明:天青石主要有板状、片状−薄片状、他形细粒状、晶簇状4种宏观形态和板状、细粒状−薄片状、无定型状3种微观形态。该锶矿床的热液成矿过程可分为早期成矿过程和中晚期成矿过程,进一步分为天青石、黄铁矿−天青石、高岭土−天青石和方解石−天青石4个矿化阶段。天青石的矿物形态与矿化阶段相对应,表现为宏观及微观形态中的板状天青石主要形成于早期成矿过程中的天青石和黄铁矿−天青石矿化阶段,其余形态的天青石多数形成于中晚期成矿过程,其中宏观形态中的片状−薄片状、它形粒状和微观形态中的薄片−细粒状多数形成于高岭土−天青石矿化阶段,宏观形态中的晶簇状天青石常形成于方解石−天青石矿化阶段,微观形态中的无定型状天青石在高岭土−天青石矿化阶段和方解石−天青石矿化阶段均可形成。
Abstract:The Aijingshan strontium deposit in Lishui of Jiangsu Province, located in the eastern section of the Lishui Basin in the middle-lower reaches of Yangtze Basin metallogenic belt, is a representative of volcanic hydrothermal strontium deposits in China. The relation between the morphological characteristics of celestite and its mineralization stages is discussed in the paper by analyzing the macroscopic and microscopic morphology of celestite samples gathered from the strontium deposit. The macro morphological characteristics of celestite mainly include four forms: tabular, platy-flaky, xenomorphic fine granular and drusy. The microscopic morphology of celestite is characterized with three shapes: tabular, fine granular-flaky and amorphous. The hydrothermal metallogenesis of the Aijingshan strontium deposit undergone early and mid-late metallogenic processes in sequence, which can be further divided into four stages: celestite, pyrite-celestite, kaolinite-celestite and calcite-celestite. The mineral morphology of celestite corresponds to the metallogenic process, which shows that the tabular celestite in the macro and micro morphology is mainly formed in the celestite and pyrite-celestite mineralization stages during the early metallogenic process, while the other shapes of celestite are mostly formed during the mid-late process, i.e. platy-flaky, xenomorphic fine-granular celestite in the macro morphology, and flaky-fine granular celestite in the micro morphology are mostly formed in the kaolinite-celestite mineralization stage, drusy celestite in the macro morphology is formed in the calcite-celestite mineralization stage, while amorphous celestite in the micro morphology can be formed both in the kaolinite-celestite and calcite-celestite mineralization stages.
-

-
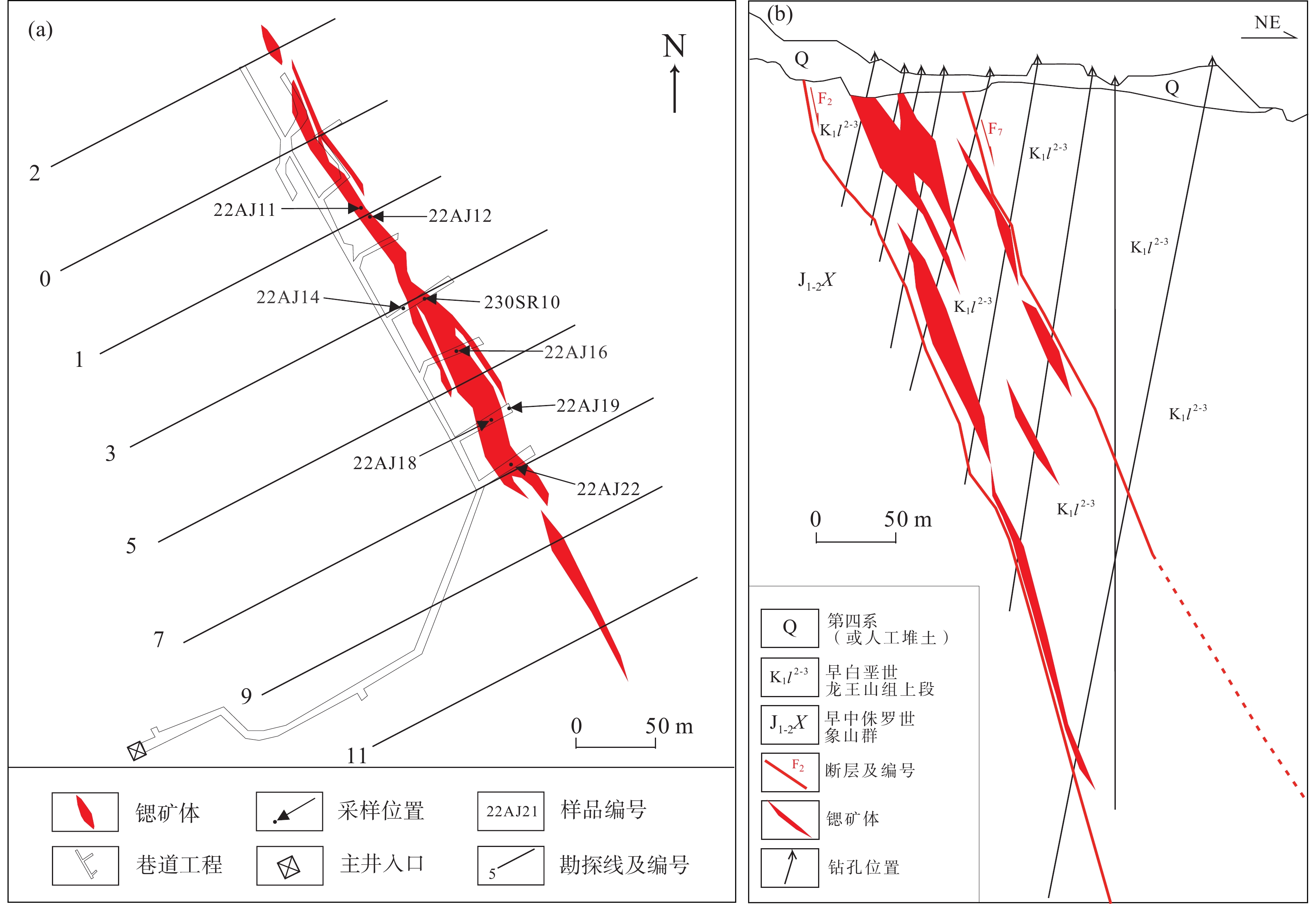
图 1 爱景山锶矿床地质简图(江苏省地质调查研究院,2013)
Figure 1.
表 1 爱景山锶矿床的矿体特征(江苏省地质调查研究院,2013)
Table 1. Ore body characteristics of the Aijingshan strontium deposit(Geology Survey of Jiangsu Province,2013)
编号 产状/(°) 控制长/m 延深/m 厚度(最大厚度)/m SrSO4平均品位/% SrI 50∠54~70 150 170 1~4 43.79 SrII 55∠65~75 1 150 380 4~12(31) 33.73 SrIII 68∠80 100 135 1~2 17.02 SrIV 60∠61~85 100 100 1.5~3 已采空 表 2 爱景山锶矿床的矿石及围岩样品
Table 2. Strontium ore and wall-rock samples from the Aijingshan strontium deposit
样品编号 样品名称 样品编号 样品名称 22AJ11 黄铁矿化天
青石矿石22AJ19 黄铁矿化天青
石化凝灰岩22AJ12 黄铁矿化天
青石矿石22AJ22 天青石化黄
铁矿矿石22AJ14 黄铁矿化天
青石矿石230SR10 黄铁矿化天
青石矿石22AJ16 黄铁矿化天
青石矿石150SR2 天青石方
解石晶簇22AJ18 黄铁矿化天
青石矿石注: 150SR2样品采自−150 m中段(手标本)。 表 3 爱景山锶矿床的矿石及围岩样品
Table 3. Strontium ore and wall-rock samples from the Aijingshan strontium deposit

-
[1] CHEN D, LI X, MIAO B H, SUN Q Z, CAI L M, HU F P. 2016. Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of Wolongshan strontium deposit in Lishui area, Jiangsu Province[J]. Mineral Deposits,35(4):709-723 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] DOU Z J. 2015. Relationship studies of volcanic activity and strontium Mineralization of Lishui volcano-tectonic depression[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] DOU Z J, YANG Z L, CHEN Z H, ZHANG B S. 2015. Geochronology and significance of Lishui basin (sub) volcanic rocks of the Yangtze River metallogenic belt[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,35(2):25-31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] GAO S Y, WANG L J, LU J J, MA D S, SONG G W. 2017. Geochemical comparison of ore-bearing rocks associated with iron mineralization in the Ningwu and Luzong basins[J]. East China Geology,38(1):21-27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF JIANGSU PROVINCE. (2024-01-02)[2024-04-13]. A large-scale strontium deposit discovered by the strontium mining survey project in Mashantou—Xihu village, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province[EB/OL]. http://www.jsgs.com.cn (in Chinese).
[6] GEOLOGY SURVEY OF JIANGSU PROVINCE. 2013. The deep geological survey of Sr-deposit in Aijingshan, Lishui district, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province[R]. Nanjing: Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province (in Chinese).
[7] GUAN B C, CAO C J. 1989. Exploration and origin of Aijingshan strontium deposit[J]. Jiangsu Geology, 13(1): 3-7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] HUANG Z L, CUI N F, LENG S Q, YANG Y L. 1994. Geochemistry and origin of the Lishui strontium deposit[J]. Journal of Wuhan Institute of Chemical Technology,16(4):60-65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] HUANG Z, JIANG L, WANG H X, LAI Y D, WEI F. 2015. Metallogenic models of pyrite deposits in the middle and lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt, Jiangsu Province[J]. Resources Survey and Environment,36(3):165-171 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] JINYAN STRONTIUM INDUSTRY Co., LTD of NANJING. 2023. The instruction for the annual change table of the mine resource reserves of Nanjing strontium deposit in 2023[R]. Nanjing:Jinyan Strontium Industry Co., Ltd of Nanjing (in Chinese).
[11] LI Y C, LIU Z H. 1986. Geological characteristics and genesis of strontium deposit in Lishui, Jiangsu Province[J]. Chemical Geology, (2): 48-57 (in Chinese).
[12] LIU Z H. 1990. Characteristics and metallogenesis of strontium deposit in the middle and lower Yangtze Reaca[J]. Jiangsu Geology,14(2):31-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] LU Z Y, LIU X G, LUO G X, WU Z B, ZHU D S. 2024. Discussion on morphological characteristics of celestite and metallogenic processes of Aijingshan strontium deposit in Lishui county, Jiangsu province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research,39(1):73-79 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] SHENG X Z, XING C. 1988. The geology and origin of Wolongshan strontium deposit[J]. Jiangsu Geology,12(3):11-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] THE 2TH GEOLOGICAL BRIGADE, JIANGSU PROVINCIAL BUREAU OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL RESOURCES. 1986. 1: 50000 regional geological survey report in Lishui, Jiangsu Province[R]. Changzhou: The 2th Geological Brigade, Jiangsu Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (in Chinese).
[16] WANG Z Q, ZHOU M J, LI X F, DA H X. 2024. Identification and significance of fluid exsolution in high silica granite[J]. East China Geology,45(1):26-48.
[17] XU X G, GU X L. 1999. Strontium deposits in China[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press (in Chinese).
[18] XUE T X. 1999. Celestite (Sr) deposits in China[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,21(3):141-148 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] XUE P D, ZHOU Y Q. 1985. A preliminary discussion on the genetic type of Aijingshan strontium ore deposit in Jiangsu province[J]. Journal of Hebei Geological College,(4):41-49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] YAN J. 2022. Characteristics and petrogenesis of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt and the Dabie Orogen[J]. East China Geology,43(4):375-390 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] YANG W C. 2023. Origin of the Mid—Lower-Yangtze tectonic belt and Yanshanian ocean subduction[J]. Geological Review,69(5):1619-1627 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] YANG S P, ZHANG F Z. 2013. Geological characteristics and prospecting of Aijingshan strontium deposit in Lishui County, Jiangsu Province[C]//Chinese Geological Society, Compilation of Abstracts from Papers at the 2013 Academic Annual Conference. Kunming: Geological Society of China, 681-684 (in Chinese).
[23] ZHANG F Z, LIAN H Q. 1997. Aijingshan strontium deposit in Lishui, Jiangsu: a multi-parameter ore-hunting model[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,19(3):193-196 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] ZHANG S Q, WANG L J, YANG Y H. 2015. Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks in the Lishui Basin in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River and its geological implications[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,21(1):15-30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] ZHOU Y Q. 1984. Geological characteristics and genesis of a strontium deposit in east China[J]. Geology and Prospecting,(10):14-16.
[26] ZHOU T F, FAN Y, YUAN F, ZHONG G X. 2012. Progress of geological study in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley Metallogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(10):3051-3066 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] ZHOU S G, CAI Y , DU J G, WU S, SHI K, LI Z T. 2023.Skarn mineralogical characteristics and ore sulfur isotope geochemistry of Tianmashan sulfur-gold deposit, Tongling area[J]. East China Geology, 44(1): 51-66(in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] ZHU G L, YIN Y D, LIU Z H. 1990. Geology and prospecting of strontium deposit in Lishui district[J]. Jiangsu Geology,14(4):27-32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] 陈冬, 李鑫, 缪柏虎, 孙清钟, 蔡露明, 胡福培. 2016. 江苏溧水卧龙山锶矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质,35(4):709-723.
[30] 窦志娟. 2015. 溧水火山构造洼地火山活动及与锶成矿作用关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院.
[31] 窦志娟, 杨祝良, 陈志洪, 张宝松. 2015. 长江中下游成矿带溧水盆地(次)火山岩的年代学及其意义[J]. 矿物岩石,35(2):25-31.
[32] 高守业, 王丽娟, 陆建军, 马东升, 宋革文. 2017. 宁芜和庐枞盆地含矿岩体地球化学特征对比[J]. 华东地质,38(1):21-27.
[33] 管保成, 曹纯洁. 1989. 试论爱景山锶矿床成因及其找矿方向[J]. 江苏地质, 13(1): 3-7.
[34] 黄志良, 崔南方, 冷盛强, 阳岳龙. 1994. 溧水锶矿成矿地球化学及矿床成因研究[J]. 武汉化工学院学报,16(4):60-65.
[35] 黄震, 姜丽, 王海欧, 来又东, 魏芳. 2015. 长江中下游成矿带(江苏段)硫铁矿床成矿模式[J]. 资源调查与环境,36(3):165-171.
[36] 江苏省地质调查研究院. 2013. 江苏省溧水县爱景山矿区锶矿深部详查地质报告[R]. 南京: 江苏省地质调查研究院.
[37] 江苏省地质调查研究院. (2024-01-02)[2024-04-13]. 江苏省南京市溧水区麻山头-西湖村锶矿普查项目发现一大型锶矿床[EB/OL]. http://www.jsgs.com.cn.
[38] 江苏省地质矿产局第二地质大队. 1986. 江苏省溧水地区1∶5万区域地质调查报告[R]. 常州: 江苏省地质矿产局第二地质大队.
[39] 黎永才, 刘振红. 1986. 江苏溧水天青石矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 化工地质,(2):48-57.
[40] 刘振红. 1990. 苏南锶矿成矿作用讨论[J]. 江苏地质, 14(2): 31-34.
[41] 陆振云, 刘新光, 骆光新, 吴正兵, 朱冬生. 2024. 江苏溧水爱景山锶矿床天青石形态特征及成矿过程探讨[J]. 地质找矿论丛,39(1):73-79. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2024.01.009
[42] 南京金焰锶业有限公司. 2023. 南京锶矿2023年矿山资源储量年度变化表说明书[R]. 南京:南京金焰锶业有限公司.
[43] 盛杏中, 邢瑃. 1988. 溧水县卧龙山锶矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 江苏地质, 12(3): 11-14.
[44] 王志强, 周美娟, 黎训飞, 笪昊翔. 2024.高硅花岗岩流体出溶作用的识别和意义[J]. 华东地质, 45(1): 26-48.
[45] 徐兴国, 谷秀兰. 1999. 中国的锶矿床[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社.
[46] 薛天星. 1999. 中国(天青石)锶矿床概述[J]. 化工矿产地质,21(3):141-148.
[47] 薛丕东, 周有庆. 1985. 江苏爱景山锶矿床成因类型初探[J]. 河北地质学院学报,(4):41-49.
[48] 闫峻. 2022. 长江中下游—大别造山带中生代火山岩特征及成因[J]. 华东地质,43(4):375-390.
[49] 杨文采. 2023. 长江中下游构造带成因与燕山期的大洋俯冲[J]. 地质论评,69(5):1619-1627.
[50] 杨善坪, 张福祯. 2013. 江苏省溧水县爱景山锶矿床地质特征及找矿[C]//中国地质学会2013年学术年会论文摘要汇编——S10非金属矿产地质专业委员会换届暨2013年学术研讨会分会场. 昆明: 中国地质学会, 681-684.
[51] 张福桢, 练洪奇. 1997. 江苏溧水爱景山锶矿综合技术方法找矿模型[J]. 化工矿产地质,19(3):193-196.
[52] 张少琴, 王丽娟, 杨颍鹤. 2015. 长江中下游溧水盆地火山岩的时代、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报,21(1):15-30.
[53] 周有庆. 1984. 华东某锶矿床地质特征及其成因初探[J]. 地质与勘探,(10):14-16.
[54] 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰, 钟国雄. 2012. 长江中下游成矿带地质与矿产研究进展[J]. 岩石学报,28(10):3051-3066.
[55] 周曙光, 蔡杨, 杜建国, 吴硕, 施珂, 李孜腾. 2023.铜陵天马山硫金矿床矽卡岩矿物学特征及矿石硫同位素地球化学研究[J]. 华东地质, 44(1): 51-66.
[56] 朱根林, 殷友东, 刘振红. 1990. 溧水地区锶矿地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 江苏地质, 14(4): 27-32.
-




 下载:
下载: