Remote sensing interpretation and metallogenic prediction in the Bairendaba-Weilasituo silver-tin polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
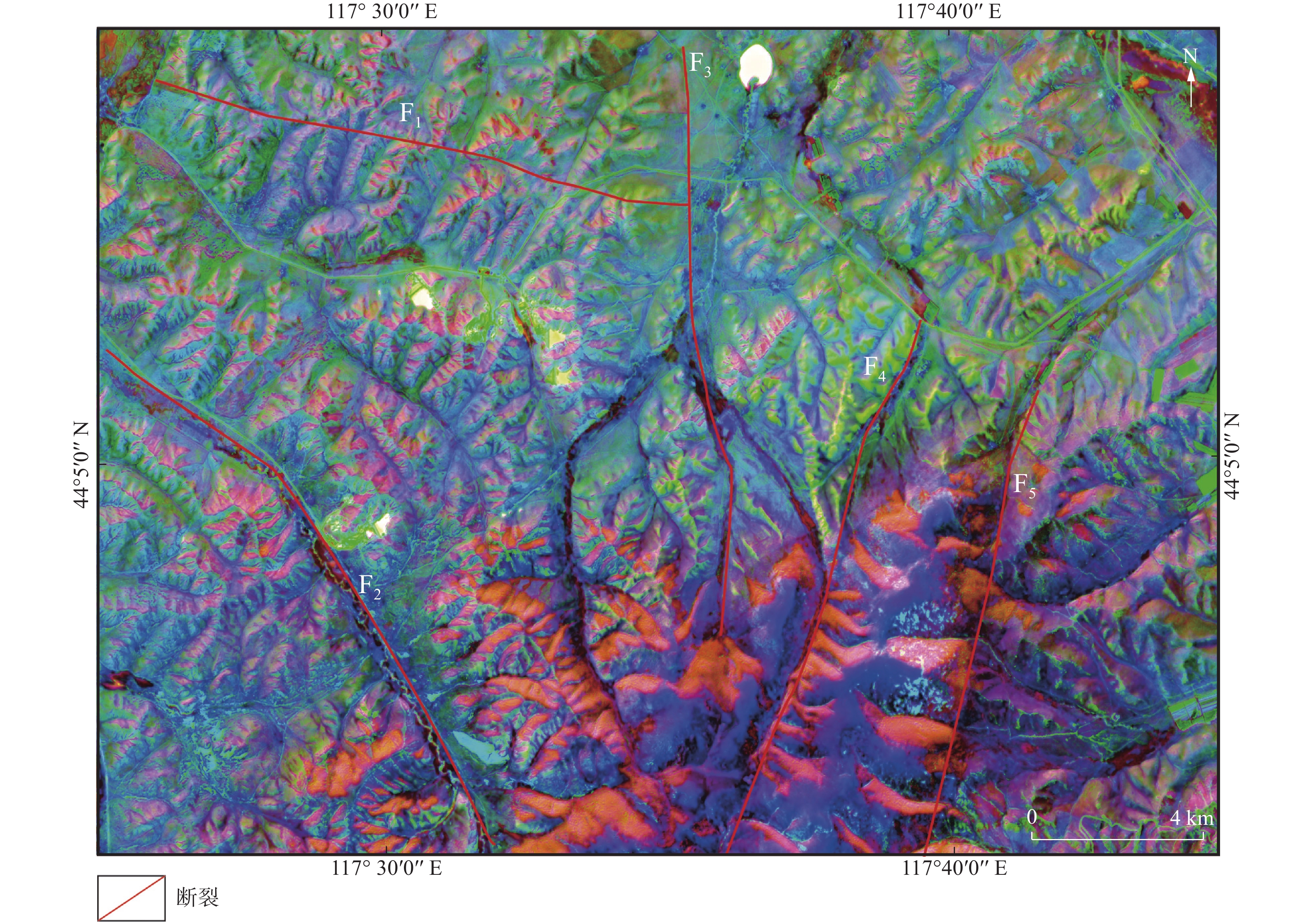
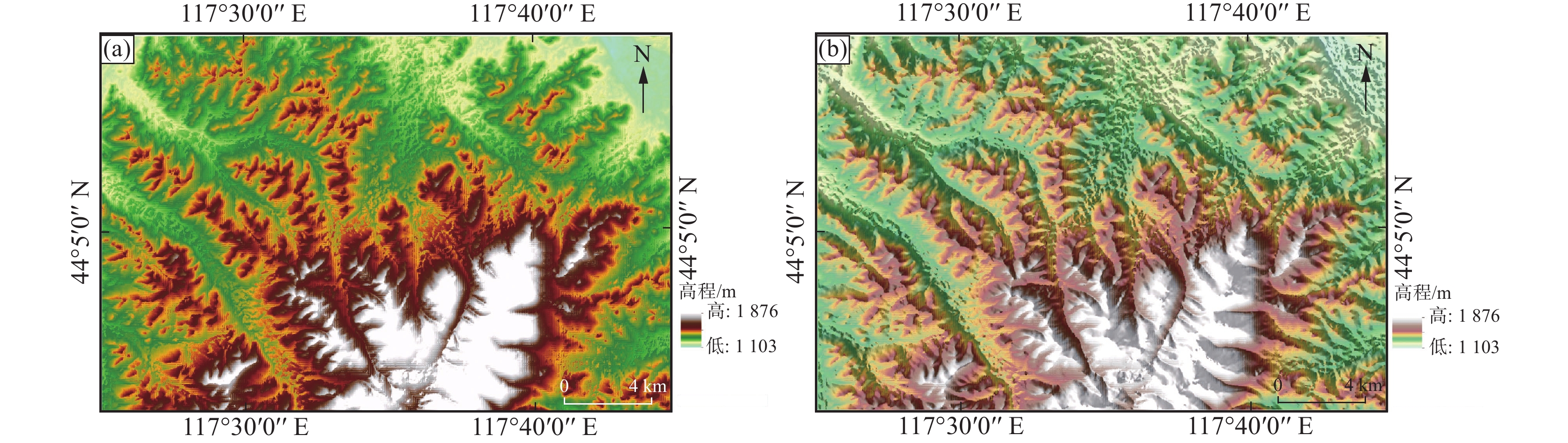
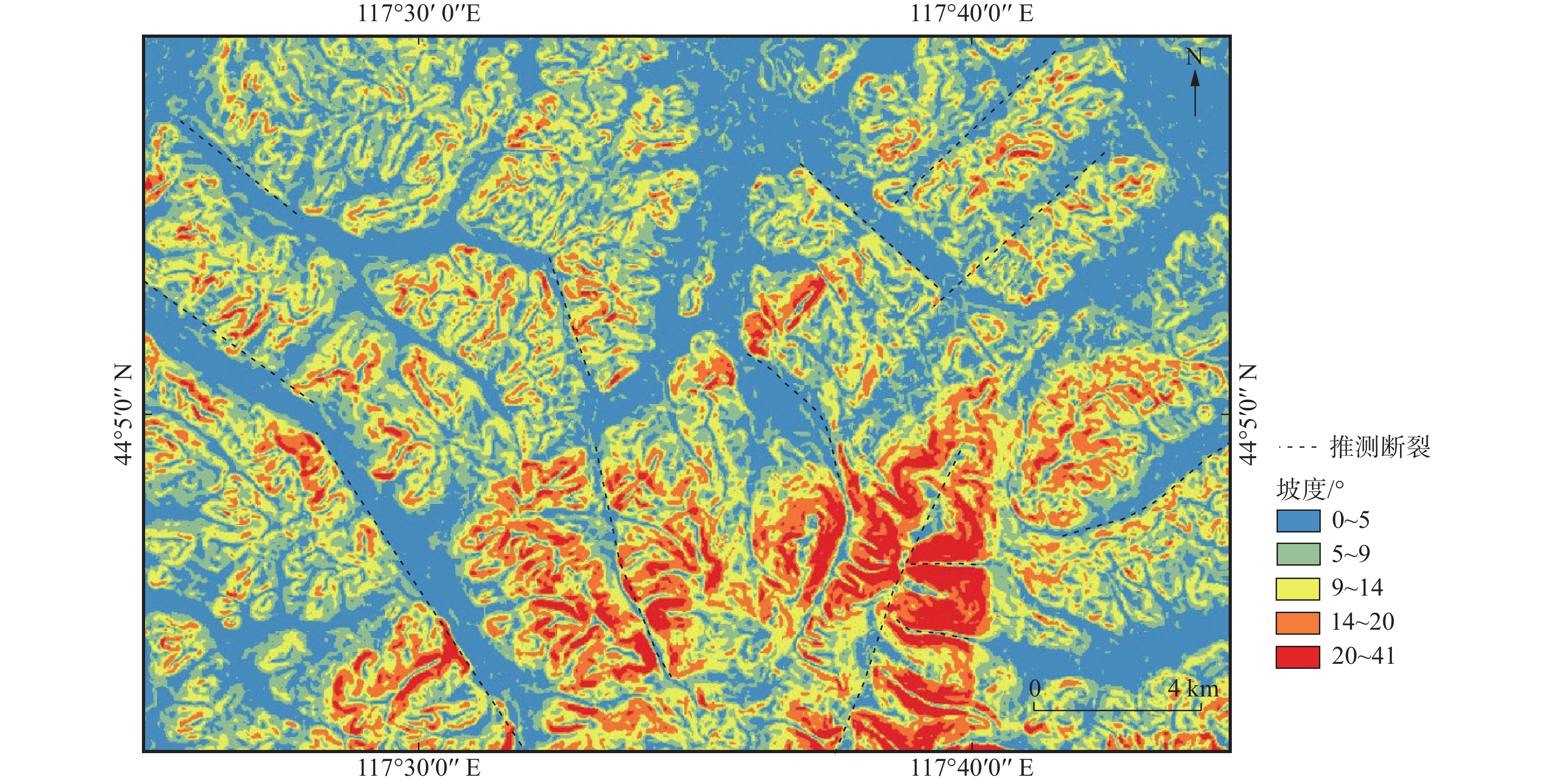
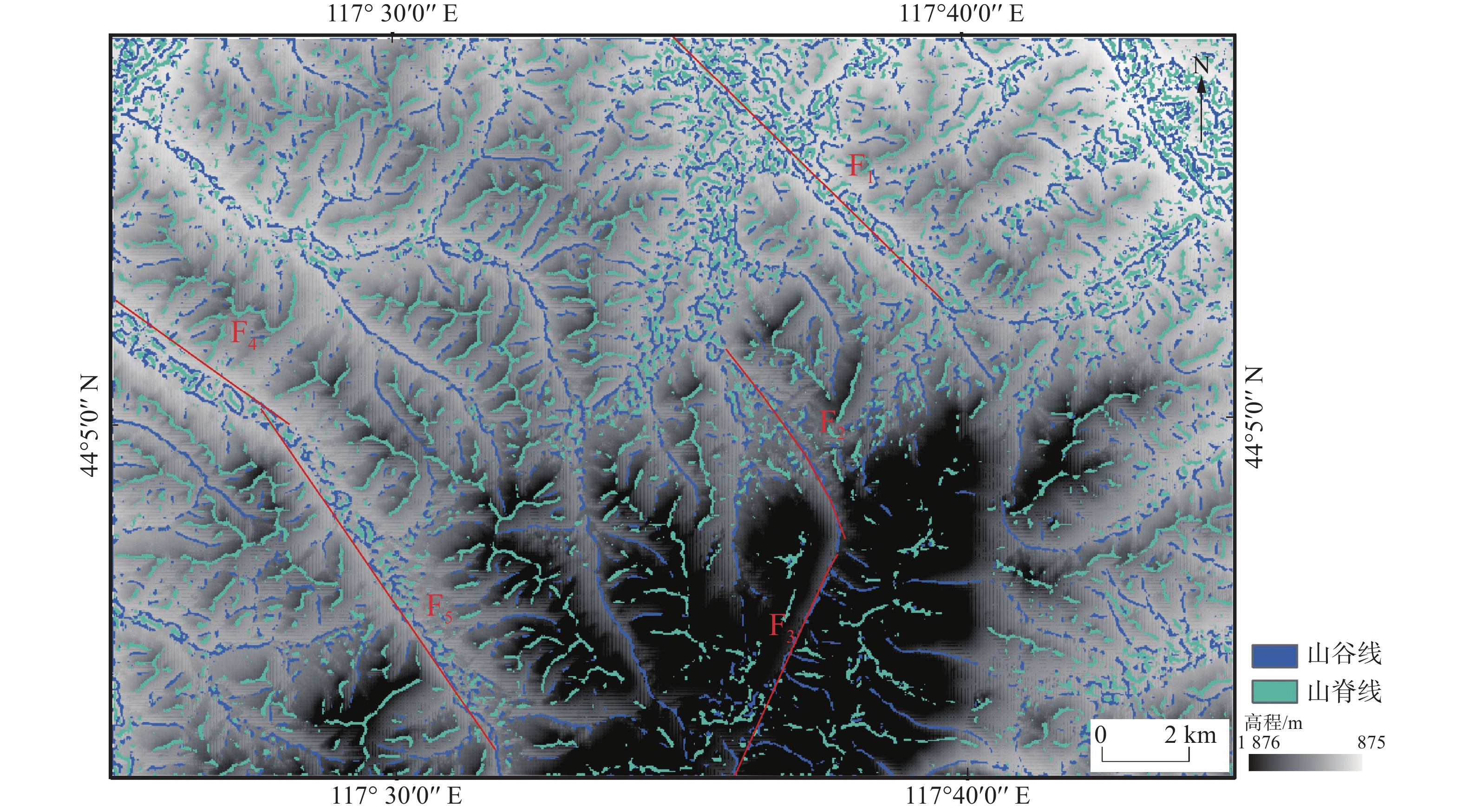
内蒙古拜仁达坝—维拉斯托地区成矿条件优越,银、锡等矿产资源富集,矿化蚀变广泛发育,且地质构造控矿作用明显。文章利用ASTER、Landsat-8 OLI和DEM等数据,采用DEM山体阴影渲染、坡度分析、高通滤波和方向滤波等方法,结合主成分分析等数字图像处理技术,在拜仁达坝—维拉斯托地区解译出329条线性构造和4个环形构造。同时,利用ASTER数据,采用主成分分析方法,提取了Fe3+、Al-OH、Mg-OH、碳酸盐化、硅酸盐化和泥化蚀变信息,依据蚀变信息与构造信息圈出3处找矿有利区。结果表明:采用基于DEM、Landsat-8 OLI和ASTER数据的构造解译和蚀变信息提取方法进行找矿预测,可以准确指示构造和蚀变的关键找矿标志,在内蒙古中部地区具有一定的适用性,是快速有效找矿勘查的重要手段,也可为区带内银锡多金属矿床研究提供借鉴。
Abstract:The Bairendaba-Weilasituo area in Inner Mongolia is characterized with favorable metallogenic conditions, where the silver and tin mineral resources are enriched, mineralization alterations extensively developed and prominent geo-structures control ore deposits. By utilizing ASTER, Landsat-8 OLI, and DEM data, applying methods such as DEM hill shading, slope analysis, high-pass filtering, and directional filtering, in combination with principal component analysis and other digital image processing methods, this study finally identified a total of 329 linear structures and 4 circular structures of the Bairendaba-Weilasituo area. Additionally, ASTER data and the principal component analysis method were employed to extract alteration information related to Fe3+, Al-OH, Mg-OH, carbonation, silicification, and clay alteration. Based on alteration and structural data, three prospects favorable for mineral exploration were delineated. The results indicate that structural interpretation and alteration information extraction based on DEM, Landsat-8 OLI, and ASTER data can accurately identify key structural and alteration-related exploration markers. This approach is applicable in central Inner Mongolia, providing a rapid and effective method for mineral exploration and offering valuable insights for the study of silver-tin polymetallic deposits within the region.
-

-
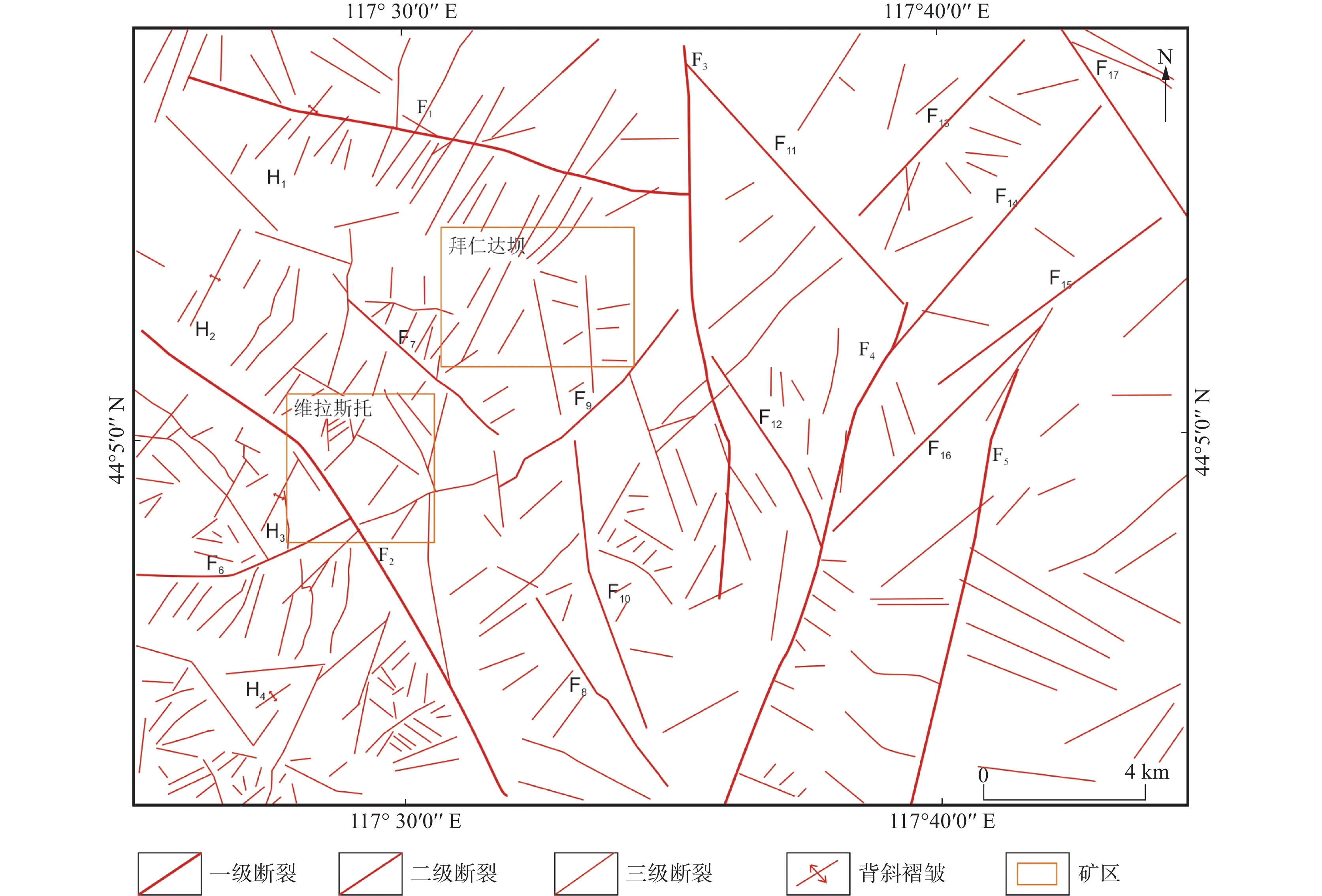
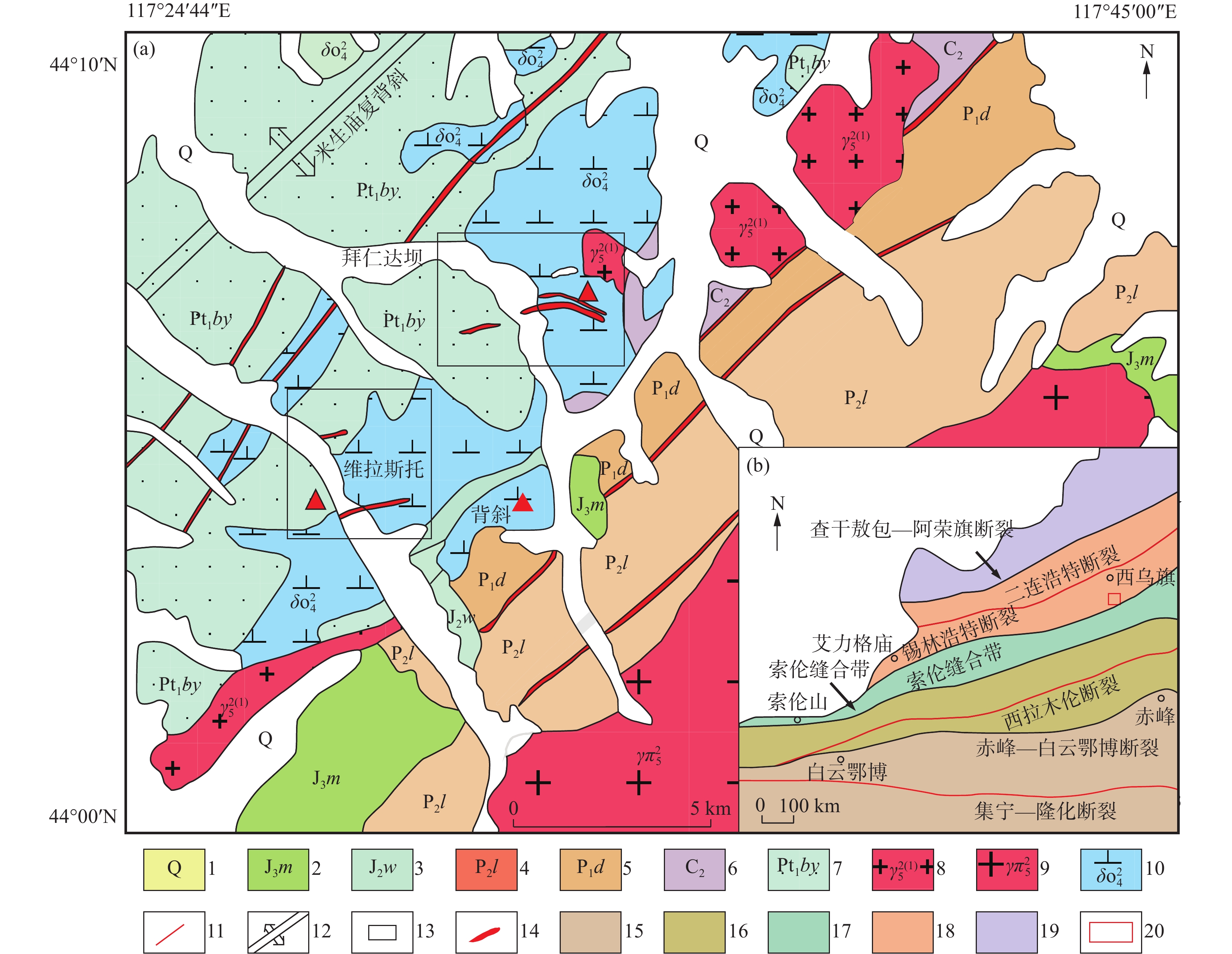
图 1 内蒙古拜仁达坝—维拉斯托地区地质简图(a)及大地构造位置图(b)(赵保具等,2021)
Figure 1.
表 1 ASTER、Landsat-8 OLI和ASTER DEM数据参数表
Table 1. The data parameter for ASTER, Landsat-8 OLI and ASTER DEM
卫星名称 最大空间
分辨率/m波谱范
围/μm波段数 采集时间 ASTER 15 520~2 430 14 2004.04.09 Landsat-8 OLI 15 433~1 390 9 2013.10.03 ASTER DEM 30 表 2 ASTER数据各类干扰地物去除方法(唐超等,2013)
Table 2. The removal of various interfering ground objects in ASTER data(Tang et al.,2013)
干扰因素 去除方法 干扰因素 去除方法 冰雪 band9或band1高端剪切 阴影 band9/band1 植被 (band3-band2)/(band3+band2) 盐碱地 band9/band1或band7、9高端剪切 云 band7、9高端剪切 水体 band9/band1 表 3 蚀变提取主成分特征向量矩阵
Table 3. Eigenvector matrix of the principal components by alteration mineral extraction
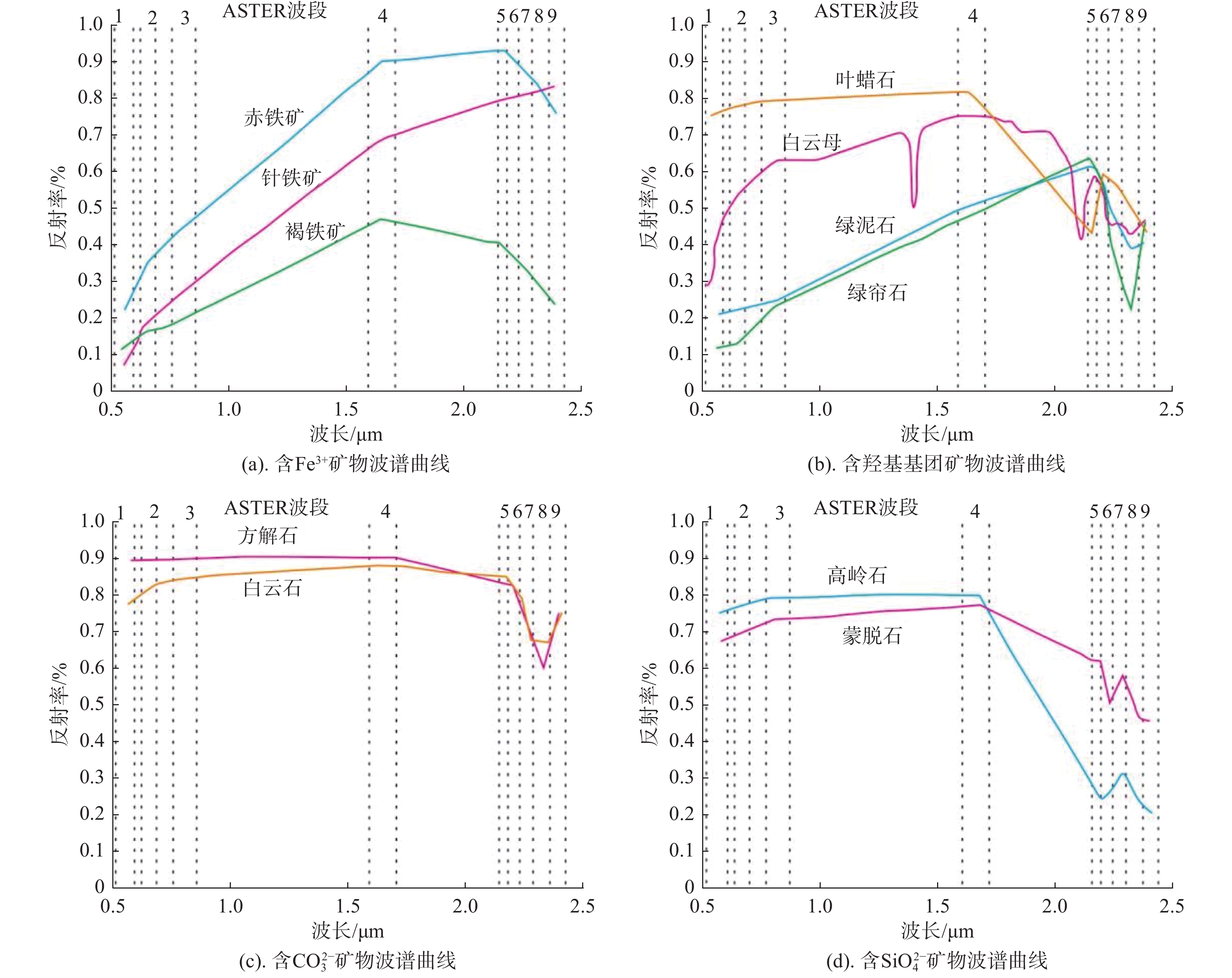
蚀变类别 特征向量 Band2 Band3 Band4 Band5 蚀变类别 特征向量 Band1 Band3 Band4 Band5 Fe3+ eig1 0.37 0.49 0.52 0.59 CO32− eig1 0.35 0.51 0.67 0.41 eig2 0.39 0.38 0.25 −0.80 eig2 0.57 0.54 −0.54 −0.29 eig3 0.55 0.25 −0.79 0.14 eig3 0.71 −0.65 −0.04 0.27 eig4 0.64 −0.74 0.22 0.03 eig4 −0.20 0.15 −0.51 0.82 蚀变类别 特征向量 Band1 Band3 Band4 Band6 蚀变类别 特征向量 Band1 Band4 Band5 Band8 Al-OH eig1 −0.35 −0.51 −0.67 −0.42 SiO42− eig1 −0.33 −0.73 −0.45 −0.39 eig2 −0.58 −0.55 0.52 0.31 eig2 −0.94 0.30 0.11 0.09 eig3 −0.73 0.66 0.00 −0.19 eig3 0.07 0.60 −0.49 −0.62 eig4 −0.13 0.10 −0.53 0.83 eig4 0.00 0.09 −0.74 0.67 蚀变类别 特征向量 Band1 Band3 Band4 Band8 蚀变类别 特征向量 Band1 Band4 Band6 Band7 Mg-OH eig1 0.36 0.53 0.68 0.36 高岭土-绢云母 eig1 −0.32 −0.73 −0.46 −0.40 eig2 0.57 0.53 −0.57 −0.26 eig2 −0.94 0.29 0.14 0.08 eig3 0.71 −0.65 −0.02 0.27 eig3 0.06 0.60 −0.40 −0.69 eig4 −0.20 0.14 −0.46 0.85 eig4 −0.01 0.17 −0.78 0.60 -
[1] BAI H Q, LI J. 2018. Application of remote sensing technology in geological structure and prospecting[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,41(5):99-101 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] CHEN W K, ZHANG J F, JIANG W L, YANG Y H. 2007. Active fault interpretation of Mao Mountain Area based on the TM image and DEM data[J]. Bulletin of the Institute of Crustal Dynamics,(1):67-75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] CHEN Q, ZHAO Z F, ZHOU J X, ZHU R F, XIA J S, SUN T, ZHAO X, CHAO J Q. 2022. ASTER and GF-5 satellite data for mapping hydrothermal alteration minerals in the Longtoushan Pb-Zn deposit, SW China[J]. Remote Sensing,14(5):1253. doi: 10.3390/rs14051253
[4] CHENG G, ZENG L Y, CHEN S L. 2014. Comparative study of sedimentary bauxite resources in Western Henan Province by OLI data and ETM+data[J]. Light Metals,(11):7-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] FAN X Y, FU C L, SHI J H, WU L J. 2006. Remote-sensing simulative true-color fusion method based on principal components[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology,23(4):287-289,292 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] GUO L J. 2009. Detailed investigation report of zinc copper polymetallic ore in Velasto Mine area, Hexigten Banner, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[R]. Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region: Inner Mongolia Geological Exploration Co. , LTD (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] HAN Y H, WANG C Z, WU Z J, LÜ G X, ZHANG B L, ZHANG Q P. 2024. Remote sensing geological interpretation, alteration information extraction, and mineral prospecting prediction in the Chaihulanzi Gold Field, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience,38(4):1076-1091 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] JIANG S H, NIE F J, LIU Y F, YUN F. 2010. Sulfur and lead isotopic compositions of Bairendaba and Weilasituo silver-polymetallic deposits, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits,29(1):101-112 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] LI K, CHEN H P, WAN H, YANG X H, LI Y X. 2023. Control effect of ductile shear zone on gold mineralization and its ore-searching prospects in Yongshan area, Leping City, Jiangxi Province[J]. East China Geology,44(4):376-385 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] LI H, CHEN X L, ZHANG L H, LI C A. 2009. Depression removal method for grid DEM based on three-direction search[J]. Advances in Water Science,20(4):473-479 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] LIU Y F, FAN Z Y, JIANG H C, NIE F J, JIANG S H, DING C W, WANG F X. 2014. Genesis of the weilasituo-bairendaba porphyry-hydrothermal vein type system in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,88(12):2373-2385 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] LIU Z H, ZHOU S P, YU H, WU T T, HAN L. 2023. Geological fault detection by fusing DEM and remote sensing images in loess covered area[J]. Remote Sensing Information,38(4):57-65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] MIAO C. 2015. Comprehensive application of geochemical prospecting and remote sensing information in prospecting prediction of the southern of Bogda, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology,48(1):213-220 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] OLLIER C. 2009. Tectonic geomorphology of mountains: a new approach to paleoseismology‐ by William B. Bull[J]. Geographical Research,47(1):84-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-5871.2008.00564.x
[15] OUYANG H G. 2013. Metallogenesis of Bairendaba-Weilasituo silver-polytmetallic deposit and its geodynamic setting, in the southern segment of Great Xing’an Range, NE China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] SU H, CHEN M Y, ZHANG D Q, JIN Z E, YANG J. 2020. Study on the method of extracting information of mineralization alteration by using remote sensing in high vegetation coverage area——Taking Daqiao-Shixia area of Xihe county, Gansu Province for example[J]. Northwestern Geology,53(1):146-161 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] SUN J D, XU M C, TAN G L, LÜ J S, WU B, ZHANG Y, JIANG X Q. 2023.Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic significance of Huangshan Nb-Ta deposit in northeast Jiangxi Province[J]. East China Geology, 44(1): 28-38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] TANG C, CHEN J P, ZHANG R S, PEI Y R. 2013. Alteration from aster remote sensing data in Ban Nu Metallogenic Belt, Gaize, Tibet[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application,28(1):122-128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] WANG Y X, LIU X X, ZHANG J, CHENG J W, LU K X, YANG J F. 2023. Remote sensing exploration of fluorite ore based on TM and ASTER data——A case study of the North-Central Region of Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Hebei GEO University,46(2):1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] XU Z, ZHANG F R, ZHANG F S, LOU F S, ZHANG Y, PAN J Y, WU Z C, HE B, ZHOU Y, FU H M. 2024. Classification of hard rock lithium deposits in Jiangxi Province and its implication for prospecting[J]. East China Geology,45(1):62-77 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] ZHANG G Z, YAN E P, HONG Y F, CHEN L, MO D K. 2013. Study on the hydrological analysis of Dongjiang lake scenic area based on DEM[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,29(2):172-177 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] ZHAO B J, YAN K, XIAO R G. 2021. A novelty method of REE parameter diagrams: a case study of petrogenesis of bairendaba-weilasituo dioritoids in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience,35(3):608-624 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] ZHOU Z H, YANG Z, LI X F, XU Q D. 2023. Pre-metallogenic wall-rock alterations and element migration features of Bairendaba Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits,42(3):548-564 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 白鸿起, 李建. 2018. 遥感技术在地质构造及找矿中的应用[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息,41(5):99-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2018.05.031
[25] 陈文凯, 张景发, 姜文亮, 杨映红. 2007. 基于TM和DEM的茅山地区断裂构造解译[J]. 地壳构造与地壳应力文集,(1):67-75.
[26] 成功, 曾令瑶, 陈松岭. 2014. OLI与ETM+数据在豫西沉积型铝土矿找矿中的对比研究[J]. 轻金属,(11):7-11.
[27] 樊旭艳, 付春龙, 石继海, 武丽娟. 2006. 基于主成分分析的遥感图像模拟真彩色融合法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报,23(4):287-289,292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2006.04.016
[28] 郭利军. 2009. 内蒙古自治区克什克腾旗维拉斯托矿区锌铜多金属矿详查报告[R]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古地质勘查有限责任公司.
[29] 韩燿徽, 王翠芝, 吴志杰, 吕古贤, 张宝林, 张启鹏. 2024. 内蒙古赤峰柴胡栏子金矿田遥感地质解译和蚀变信息提取与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质,38(4):1076-1091.
[30] 江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 云飞. 2010. 内蒙古拜仁达坝及维拉斯托银多金属矿床的硫和铅同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质,29(1):101-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.010
[31] 李凯, 陈浩鹏, 万欢, 杨细浩, 李业兴. 2023. 江西乐平涌山地区韧性剪切带对金矿化的控制及找矿远景[J]. 华东地质,44(4):376-385.
[32] 李辉, 陈晓玲, 张利华, 李长安. 2009. 基于三方向搜索的DEM中洼地处理方法[J]. 水科学进展,20(4):473-479. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2009.04.003
[33] 刘翼飞, 樊志勇, 蒋胡灿, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 丁成武, 王丰翔. 2014. 内蒙古维拉斯托-拜仁达坝斑岩-热液脉状成矿体系研究[J]. 地质学报,88(12):2373-2385.
[34] 刘志恒, 周绥平, 余航, 吴婷婷, 韩玲. 2023. 融合DEM和遥感影像的黄土区断裂构造识别[J]. 遥感信息,38(4):57-65.
[35] 妙超. 2015. 新疆博格达南缘化探与遥感信息综合应用及找矿预测[J]. 西北地质,48(1):213-220.
[36] 欧阳荷根. 2013. 大兴安岭南段拜仁达坝—维拉斯托银多金属矿床成矿作用及动力学背景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
[37] 宿虎, 陈美媛, 张丹青, 靳仲娥, 杨菁. 2020. 高植被覆盖区遥感矿化蚀变信息提取方法研究——以甘肃省西河县大桥-石峡地区为例[J]. 西北地质,53(1):146-161.
[38] 孙建东, 徐敏成, 谭桂丽, 吕劲松, 武彬, 张勇, 江小强.2023.赣东北黄山铌钽矿床成矿岩体地球化学特征及成矿意义[J].华东地质, 44(1): 28-38.
[39] 唐超, 陈建平, 张瑞丝, 裴英茹. 2013. 基于Aster遥感数据的班怒成矿带矿化蚀变信息提取[J]. 遥感技术与应用,28(1):122-128. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2013.1.122
[40] 王瑛雪, 刘新星, 张娟, 成嘉伟, 卢克轩, 杨俊峰. 2023. 基于TM和ASTER数据的萤石矿的遥感找矿研究——以内蒙古中北部地区为例[J]. 河北地质大学学报,46(2):1-11.
[41] 徐喆, 张芳荣, 张福神, 楼法生, 张勇, 潘家永, 吴正昌, 贺彬, 周渝, 符海明. 2024. 江西硬岩型锂矿类型划分及其找矿启示[J]. 华东地质,45(1):62-77.
[42] 张国珍, 严恩萍, 洪奕丰, 陈利, 莫登奎. 2013. 基于DEM的东江湖风景区水文分析研究[J]. 中国农学通报,29(2):172-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2013.02.030
[43] 赵保具, 颜开, 肖荣阁. 2021. 一种稀土参数图解新方法: 以内蒙古拜仁达坝-维拉斯托闪长岩成因研究为例[J]. 现代地质,35(3):608-624.
[44] 周增辉, 杨振, 李晓峰, 徐启东. 2023. 内蒙古拜仁达坝银铅锌矿区成矿前围岩蚀变与元素迁移规律[J]. 矿床地质,42(3):548-564.
-



 下载:
下载: