Distribution characteristics and source identification of nitrate in the underground water of coastal areas of South China: A case study of Zhuhai City
-
摘要:
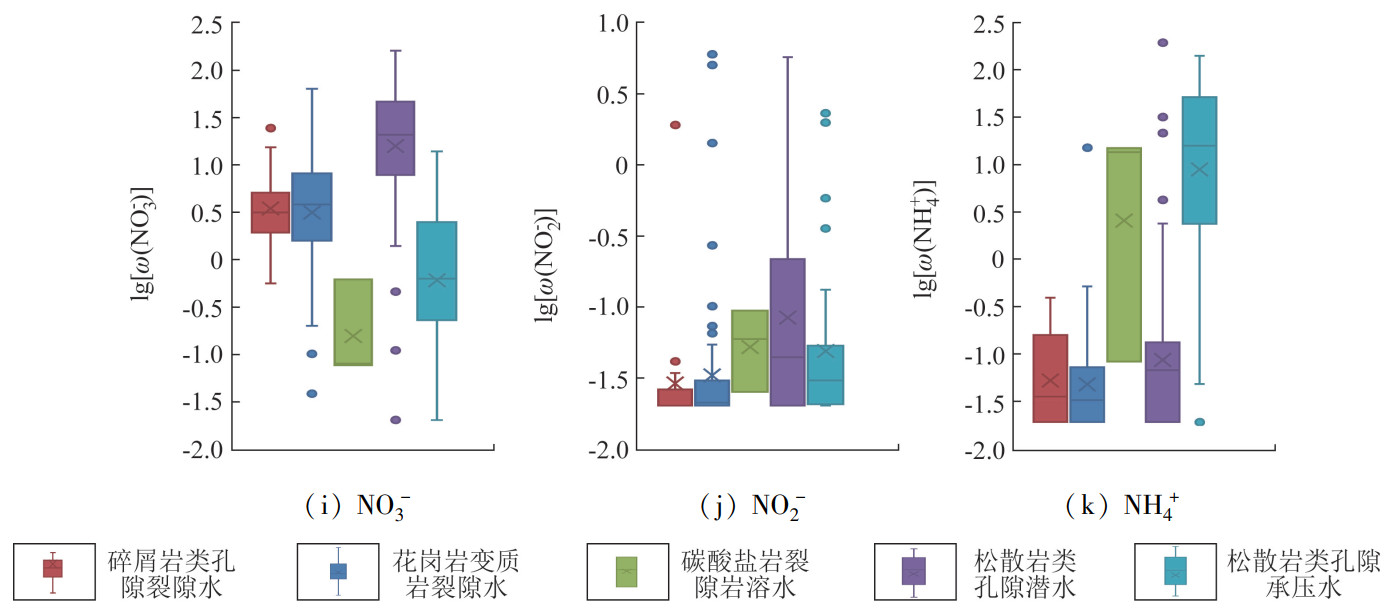
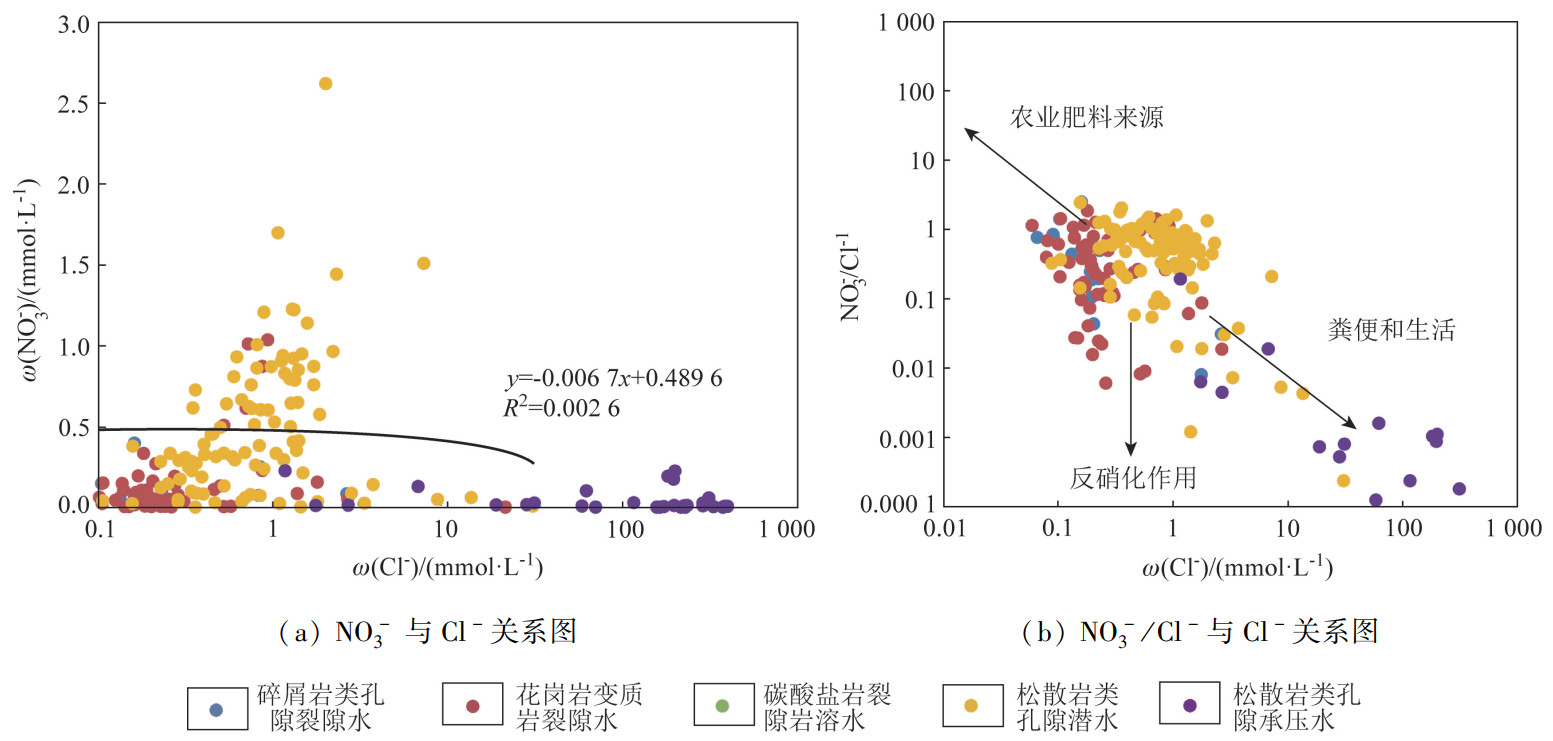
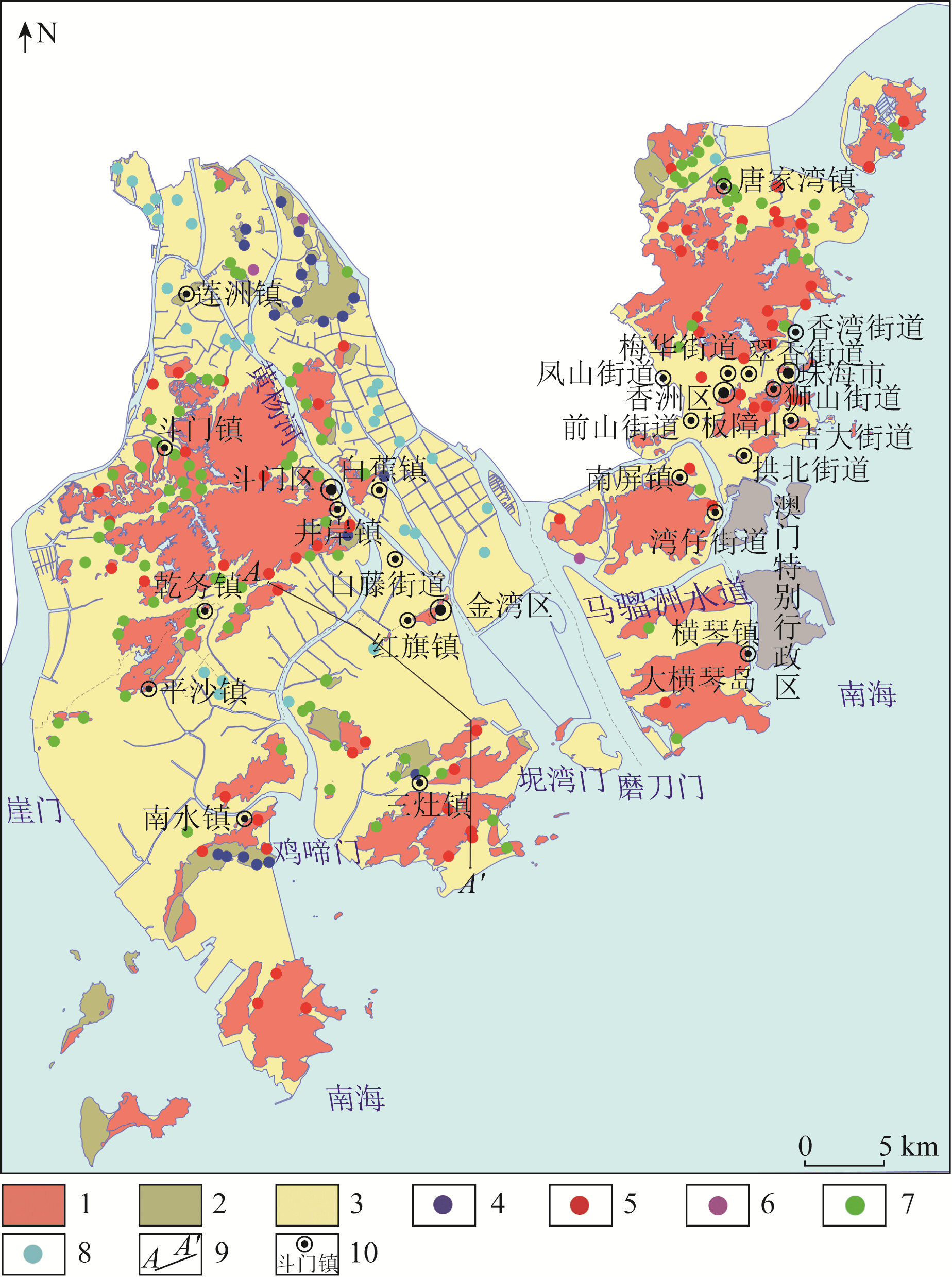
沿海地区农业、工业、生活和海水养殖多重作用下的人类活动可能会导致地下水硝酸盐污染,为查明我国华南沿海地区地下水硝酸盐的分布特征及其来源,以典型的沿海城市珠海市为例,综合运用数理统计、离子关系比值、主成分分析等方法研究不同类型地下水水化学及硝酸盐、亚硝酸盐和氨氮的分布特征,识别地下水硝酸盐来源。结果表明。研究区地下水以弱酸性水为主,深层承压水电导率明显高于浅层地下水,主要的地下水化学类型为Ca2+·Mg2+-HCO3-型和Na+-Cl-·SO42-型。松散岩类孔隙承压水的溶解性无机氮(dissolved inorganic nitrogen, DIN)组成以NH4+为主,其他类型地下水以NO3-为主。个别水样的硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐超标,丘陵台地区和山间沟谷地区水样的硝酸盐浓度相对较高。研究区18.01%的地下水样品氨氮超标,高氨地下水主要分布于滨海平原区。硅酸盐、硫酸盐矿物的风化作用、蒸发作用和海水混合作用是控制研究区地下水化学特征的主要因素。地下水硝酸盐主要来源于大气降水和人类活动,其中碎屑岩类孔隙裂隙水、花岗岩变质岩裂隙水和孔隙潜水中的硝酸盐主要来大气降水和农业活动,松散岩类孔隙承压水和碳酸盐岩裂隙岩溶水中的硝酸盐则来自于生活污水和养殖废水。研究成果可为华南沿海地区地下水开发利用与保护提供科学依据。
Abstract:Nitrate pollution could present in the underground water due to the human activities like agriculture, industry, residents and mariculture in coastal areas. In order to find out the distribution characteristics and sources of nitrate in the underground water of the coastal areas of South China, the authors in this paper took a typical coastal city-Zhuhai as an example. The mathematical statistics, ion ratio and principal component analysis were adopted to study the distribution characteristics of water chemical, nitrate, nitrite and ammonia nitrogen, and the sources of nitrate in the underground water. The results show that the underground water is mainly weak acid, and conductivity of deep confined underground water is obviously higher than that of shallow underground water. The chemical type of underground water is mainly Ca2+·Mg2+-HCO3- and Na+-Cl-·SO42- type. The dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) of pore confined groundwater in loose rocks is mainly composed of NH4+, and the DIN of other types of underground water is mainly NO3-. Nitrate and nitrite exceed the standard in sporadic water samples, and the concentration of nitrate is relatively high in the water samples of hilly areas and intermountain valleys. The ammonia nitrogen of 18.01% underground water samples in loost rocks exceeds the standard, and the high concentration ammonia nitrogen water samples are mainly distributed in the coastal plain area. The chemical characteristics of underground water in the study area is mainly controlled by the weathering, evaporation and seawater mixing of silicate and sulfate minerals. Nitrate in the underground water is mainly from atmospheric precipitation and human activities. Nitrate in clastic pore fissure groundwater, granite metamorphic rook fissure groundwater and pore unconfined groundwater mainly comes from atmospheric precipitation, and agricultural activities. Nitrate in pore confined groundwater in loose rocks and carbonate fissure karst water comes from domestic sewage and mariculture wastewater. This research results could provide scientific basis for the development, utilization and protection of the underground water in the coastal areas of South China.
-
Key words:
- coastal zone /
- underground water /
- nitrate /
- hydrochemistry /
- genesis
-

-
表 1 研究区地下水主要离子主成分分析荷载矩阵
Table 1. Load matrix for principal component analysis of the major ions in the underground water of the study area
PC1 PC2 PC3 pH值 0.368 0.215 0.572 Eh -0.761 -0.259 0.085 DO -0.515 -0.022 0.357 EC 0.803 0.579 -0.064 总硬度 0.761 0.618 -0.027 TDS 0.809 0.569 -0.047 SO42- -0.063 0.868 -0.035 Cl- 0.803 0.572 -0.069 CODMn 0.842 -0.028 -0.043 NH4+ 0.905 0.248 -0.040 K+ 0.556 0.736 -0.042 Na+ 0.831 0.530 -0.060 Ca2+ 0.385 0.812 0.000 Mg2+ 0.841 0.461 -0.036 NO3- -0.362 -0.209 0.716 NO2- -0.009 -0.049 0.658 HCO3- 0.825 0.094 0.361 方差贡献率/% 60.51 9.28 8.50 累计方差贡献率/% 60.51 69.79 78.29 -
[1] Adimalla N, Dhakate R, Kasarla A, et al. Appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in central Telangana, India[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2020, 10: 100334. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100334
[2] Salehi S, Chizari M, Sadighi H, et al. Assessment of agricultural groundwater users in Iran: a cultural environmental bias[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(1): 285-295. doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1634-9
[3] 张列宇, 马阳阳, 李国文, 等. 稳定同位素技术在水体硝酸盐污染源解析中的研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(4): 1373-1383.
Zhang L Y, Ma Y Y, Li G W, et al. Research progress of stable isotopes in source analysis of nitrate pollution in water[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2023, 13(4): 1373-1383.
[4] Paladino O, Seyedsalehi M, Massabò M. Probabilistic risk assessment of nitrate groundwater contamination from greenhouses in Albenga plain (Liguria, Italy) using lysimeters[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 634: 427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.320
[5] Wu J, Zhao W D, Lu J, et al. Geographic information system based approach for the investigation of groundwater nitrogen pollution near a closed old landfill site in Beijing, China[J]. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2018, 17(5): 1095-1101. doi: 10.30638/eemj.2018.108
[6] 程焰, 王亚, 周永章, 等. 珠海市地下水系统中重金属和类金属污染状况与污染来源分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(3): 595-603.
Cheng Y, Wang Y, Zhou Y Z, et al. Status and sources of heavy metal/metalloid pollution in the groundwater system of Zhuhai City[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(3): 595-603.
[7] 姚普. 珠海西部海岸带地下水锰的分布与成因[J]. 地下水, 2015, 37(4): 1-3, 31.
Yao P. Distribution and origin of manganese in groundwater in the west Zhuhai coastal zone[J]. Ground Water, 2015, 37(4): 1-3, 31.
[8] 王双, 严学新, 揭江, 等. 珠江三角洲平原区地面沉降影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2019, 30(5) 98-104, 112.
Wang S, Yan X X, Jie J, et al. Analysis on factors affecting ground settlement in plain area of Pearl River Delta[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5): 98-104, 112.
[9] 赵新锋, 陈法锦, 陈建耀, 等. 城市地下水硝酸盐污染及其成因分析——以珠海香洲区为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2008, 35(3): 87-92.
Zhao X F, Chen F J, Chen J Y, et al. Using nitrogen isotope to identify the sources of nitrate contamination in urban groundwater: A case study of Zhuhai City[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2008, 35(3): 87-92.
[10] Kang P P, Xu S G. The impact of mariculture on nutrient dynamics and identification of the nitrate sources in coastal waters[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(2): 1300-1311. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5363-0
[11] 魏凤英. 珠海市应急供水地下水水质评价[J]. 地下水, 2014, 36(5): 126-128.
Wei F Y. Groundwater quality evaluation of emergency water supply in Zhuhai City[J]. Ground Water, 2014, 36(5): 126-128.
[12] 文冬光, 孙继朝, 何江涛, 等. GB/T 14848—2017地下水质量标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
Wen D G, Sun J C, He J T, et al. GB/T 14848—2017 Standard for Groundwater Quality[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[13] 於昊天, 马腾, 邓娅敏, 等. 江汉平原东部地区浅层地下水水化学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 685-692.
Yu H T, Ma T, Deng Y M, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in eastern Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 685-692.
[14] 沈贝贝, 吴敬禄, 吉力力·阿不都外力, 等. 巴尔喀什湖流域水化学和同位素空间分布及环境特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 173-182.
Shen B B, Wu J L, Abuduwaili J, et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of the Lake Balkhash catchment, Kazakhstan[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 173-182.
[15] 徐进, 何江涛, 彭聪, 等. 柳江盆地浅层地下水硝酸型水特征和成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 4142-4149.
Xu J, He J T, Peng C, et al. Characteristics and genesis of NO3 type water in shallow groundwater in Liujiang Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4142-4149.
[16] 张勇, 郭纯青, 朱彦光, 等. 云南荞麦地流域地下水水化学特征及物质来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2686-2695.
Zhang Y, Guo C Q, Zhu Y G, et al. Chemical characteristics of groundwater and material sources analysis in Buckwheat field, Yunnan Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2686-2695.
[17] 涂春霖, 陈庆松, 尹林虎, 等. 我国地下水硝酸盐污染及源解析研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(6): 3129-3141.
Tu C L, Chen Q S, Yin L H, et al. Research advances of groundwater nitrate pollution and source apportionment in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(6): 3129-3141.
[18] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090.
[19] Halder S, Jha M K. Hydrogeologic and geochemical investigations in a coastal basin of West Bengal[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2023, 16(7): 420.
[20] 杜新强, 方敏, 冶雪艳. 地下水"三氮"污染来源及其识别方法研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(11): 5266-5275.
Du X Q, Fang M, Ye X Y. Research progress on the sources of inorganic nitrogen pollution in groundwater and identification methods[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(11): 5266-5275.
[21] 陈雯, 吴亚, 张宏鑫, 等. 合浦盆地西部地区地下水水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(1): 194-206.
Chen W, Wu Y, Zhang H X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in the western region of Hepu Basin, Beihai City[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(1): 194-206.
[22] Puig R, Soler A, Widory D, et al. Characterizing sources and natural attenuation of nitrate contamination in the Baix Ter aquifer system (NE Spain) using a multi-isotope approach[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 580: 518-532.
[23] 张宏鑫, 吴亚, 罗炜宇, 等. 雷州半岛岭北地区地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(11): 4924-4935.
Zhang H X, Wu Y, Luo W Y, et al. Hydrogeochemical investigations of groundwater in the Lingbei Area, Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(11): 4924-4935.
[24] Liu J T, Peng Y M, Li C S, et al. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115947.
[25] 袁宏颖, 杨树青, 张万锋, 等. 河套灌区浅层地下水NO3--N时空变化及驱动因素[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 1898-1907.
Yuan H Y, Yang S Q, Zhang W F, et al. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and driving factors of nitrogen of shallow groundwater in Hetao irrigation district[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 1898-1907.
[26] Xiao J, Zhang F, Jin Z D. Spatial characteristics and controlling factors of chemical weathering of loess in the dry season in the middle Loess Plateau, China[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2016, 30(25): 4855-4869.
[27] Panno S V, Hackley K C, Hwang H H, et al. Characterization and identification of Na-Cl sources in ground water[J]. Ground Water, 2006, 44(2): 176-187.
[28] 吕晓立, 刘景涛, 韩占涛, 等. 快速城镇化进程中珠江三角洲硝酸型地下水赋存特征及驱动因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(10): 4761-4771.
Lü X L, Liu J T, Han Z T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and driving factors of NO3-type groundwater in the rapidly urbanizing Pearl River Delta[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(10): 4761-4771.
-



 下载:
下载: