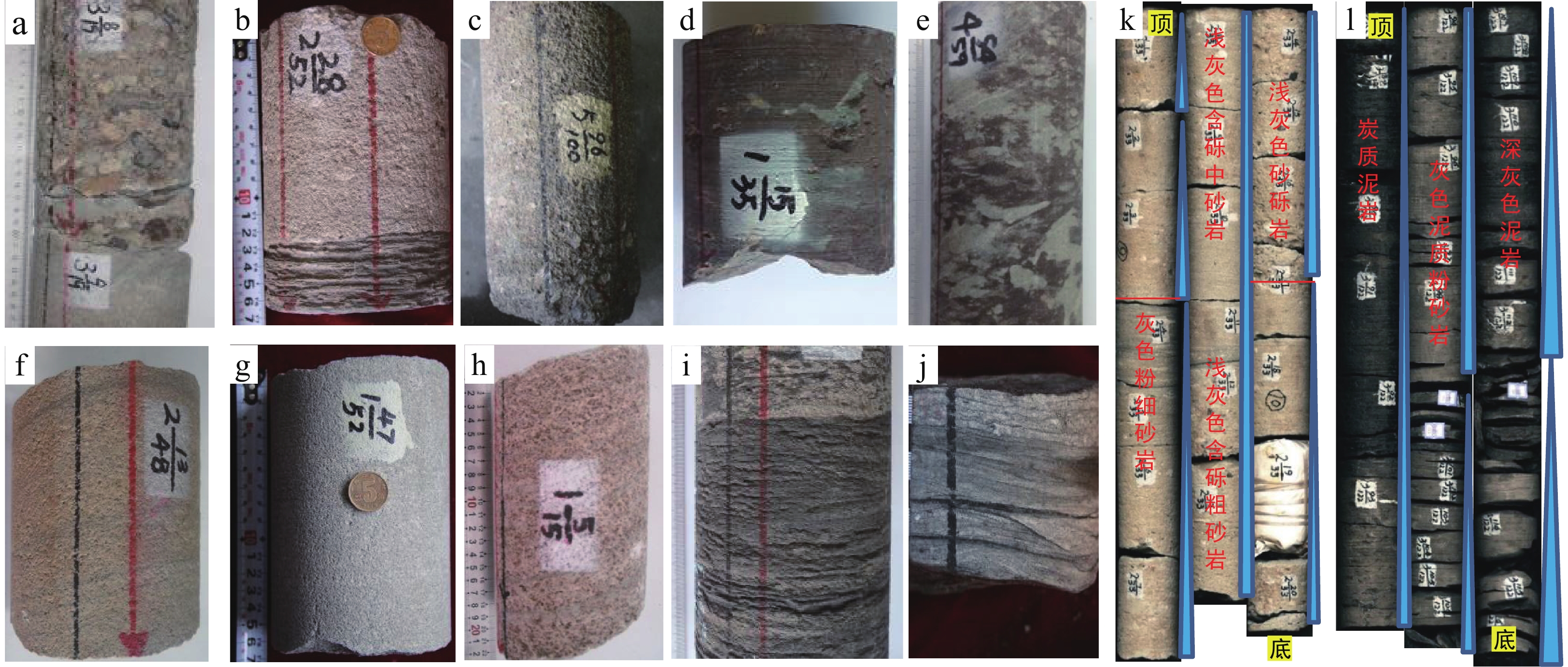
Sub-layer division and correlation based on well-seismic combination and step-by-step interface constraint: A case study of the Taiyuan-Lower Shihezi Formation in the Shilijiahan of the Hangjinqi area
-
摘要:
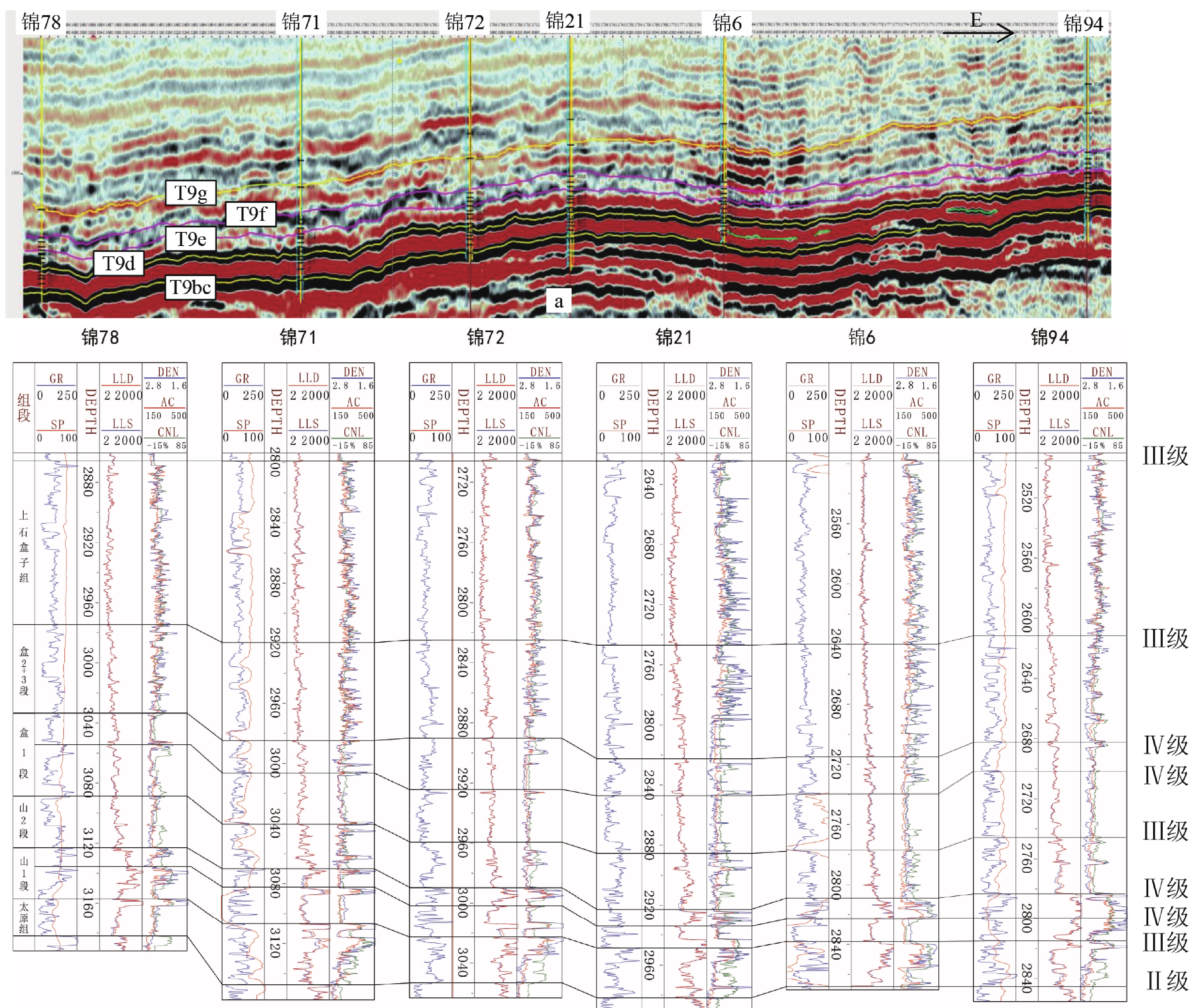
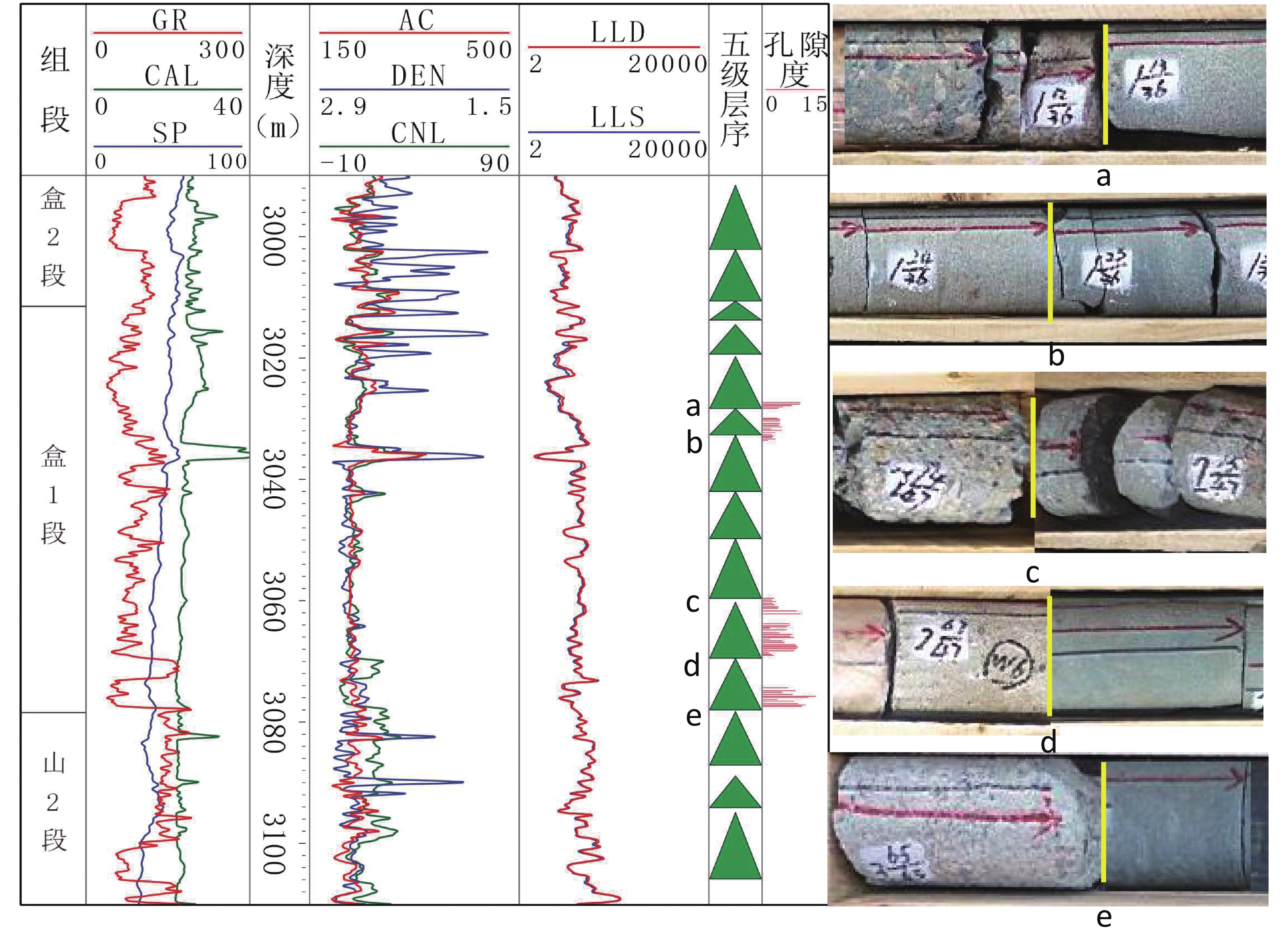
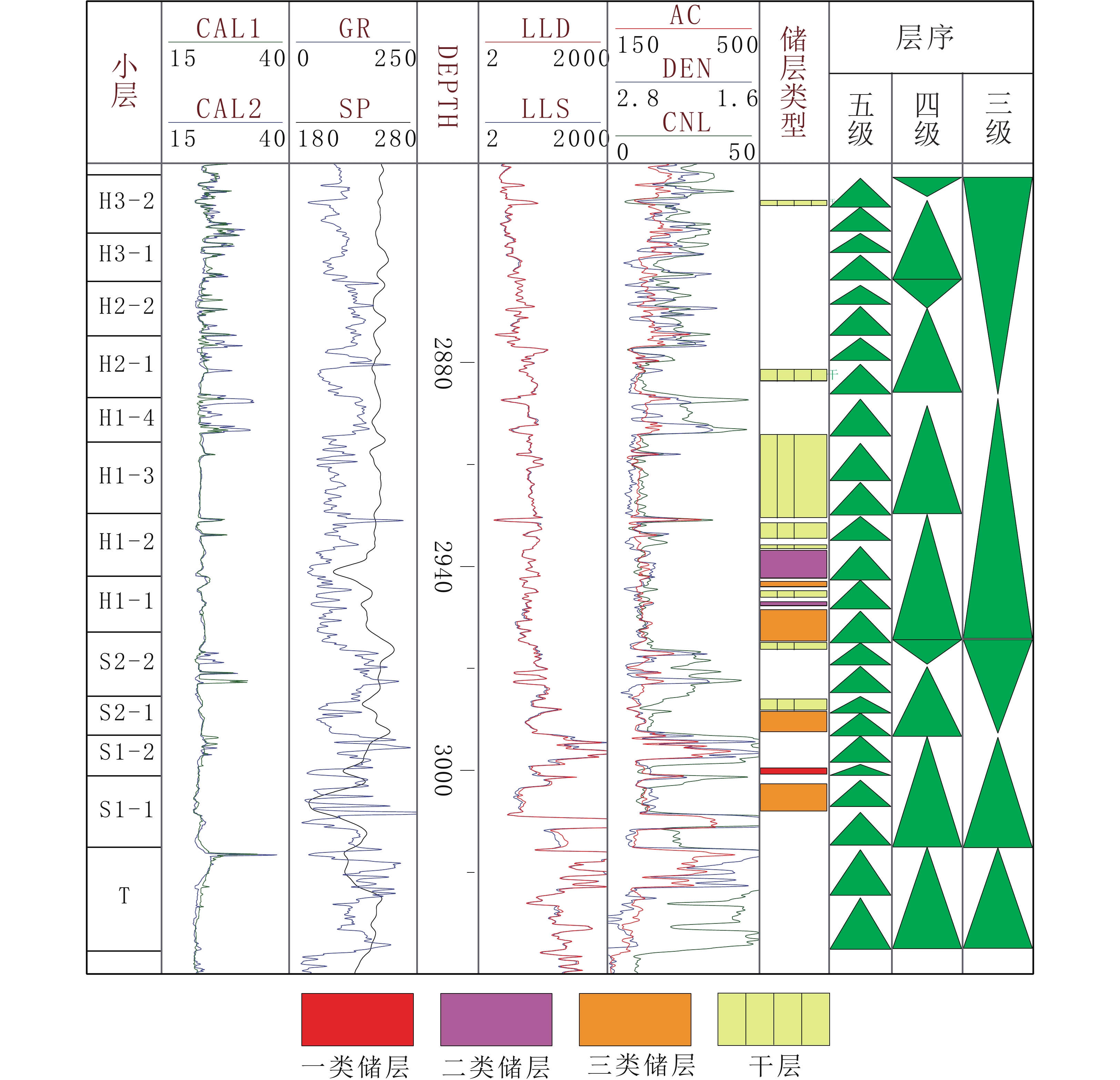
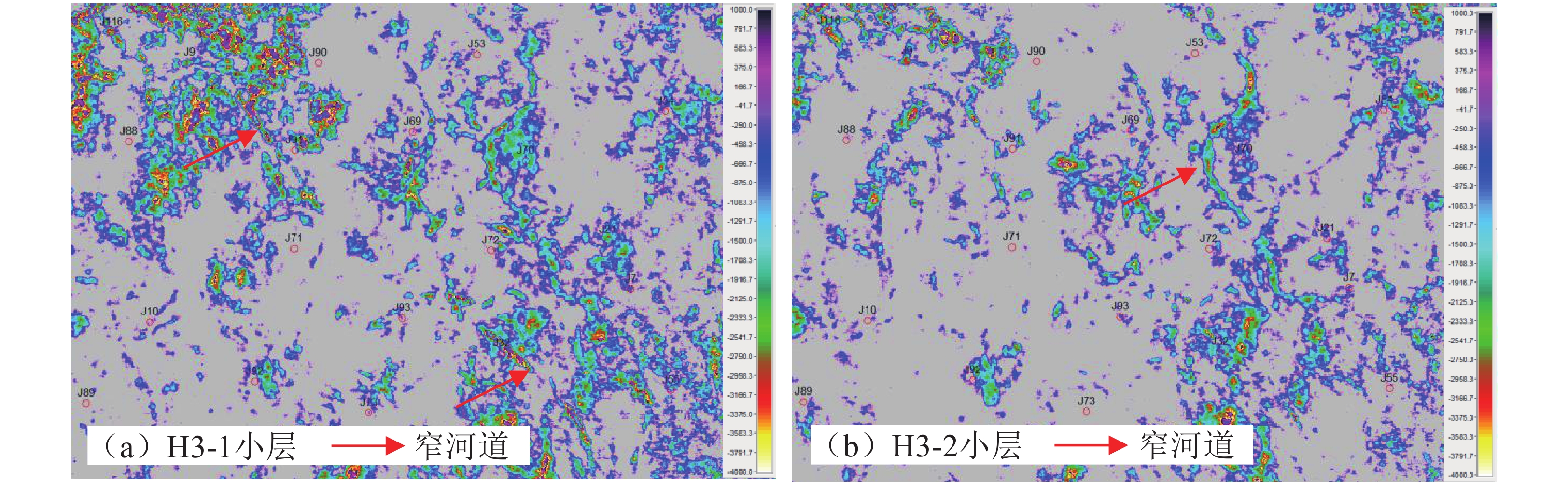
为了实现鄂尔多斯盆地北部杭锦旗十里加汗太原组—下石盒子组小层精细对比,通过详细的岩心观察,岩心–测井–地震紧密结合,利用岩心标定测井曲线,总结不同级次标志层序界面特征,利用逐级标志层序约束,井震结合进行高频层序划分,结合开发实际,进行小层划分对比。结果表明,研究区太原组—下石盒子组地层厚度在230 m左右,自下而上,由海陆过渡环境的潮坪相—三角洲相沉积,逐渐演变为山西组的辫状河三角洲相沉积,至下石盒子组则主要发育辫状河沉积。依据层序界面类型,将目的层识别出Ⅱ级界面1个,Ⅲ级界面3个,Ⅳ级界面4个。将Ⅱ-Ⅳ级层序界面按照岩心–测井曲线–地震响应特征的难易识别程度,划分了4个级次,进一步通过岩心–测井详细标定,识别V级界面25个。在地震剖面约束和沉积认识指导下,开展不同级别标志界面井间对比,进而逐级约束,实现高频层序对比,结合现场开发实际,将目的层划分为13个小层,各小层厚度较为稳定,主要反映了平原三角洲—辫状河沉积特征。高频层序一定程度上控制着沉积储层的发育与分布。通过井震结合、逐级约束的方法,可提高小层划分对比的准确度和精细度,为该区进一步的气藏地质研究与评价提供基础。
Abstract:This study aims to achieve fine correlation of sub-layers between wells in the Taiyuan-Lower Shihezi Formations in the Shilijiahan of the Hangjinqi area. Based on detailed core observations and core-log-seismic integration, calibrated logging curves are used to summarize the interface characteristics of different levels of marker beds, and high-frequency sequence division is performed by using step-by-step marker bed constraints and well-seismic combination. In combination with development practice, sub-layers division and comparison are carried out. The results indicate that the stratum thickness from the Taiyuan Formation to the Lower Shihezi Formation in the study area is about 230 meters. From bottom to top, the tidal flat facies and delta facies in the transitional environment between sea and land gradually evolved into the braided river delta facies of the Shanxi Formation, and the braided river deposits are mainly developed in the Lower Shihezi Formation. According to the sequence interface types, the target layer is identified as one second-order interface, three third-order interfaces and four fourth-order interfaces. Based on core, logging curve, and seismic response characteristics, the second-fourth order sequence interfaces are divided into four levels. Through detailed core-log calibration, 17-18 fifth-order interfaces are further identified. Under the constraint of seismic profile and the guidance of sedimentary characteristics, the inter-well correlation of different marker interface levels is conducted, and then the high-frequency sequence correlation is achieved by level-by-level constraint. In combination with the actual field development, the Taiyuan Formation to the Lower Shihezi Formation can be further divided into 13 sub-layers. The thickness of each sub-layer is relatively stable, primarily reflecting the sedimentary characteristics of plain braided rivers. High-frequency sequences control the development and distribution of sedimentary reservoirs to a certain extent. The well-seismic combination and step-by-step constraint method enhance the accuracy and fineness of sub-layer division and correlation, providing a foundation for further gas reservoir geological research and evaluation in this area.
-

-
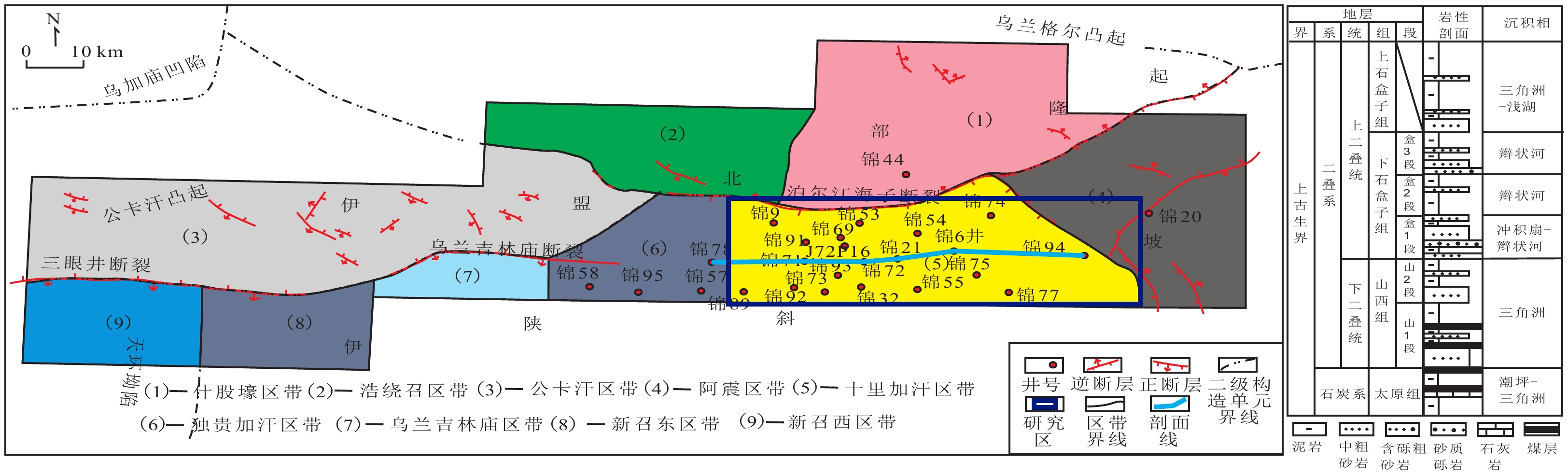
图 1 杭锦旗地区区域构造划分及研究区位置(据曹桐生等,2021修改)
Figure 1.
-
[1] Brett C E,Goodman W M,Loduuca S T. 1990. Sequences,cycles and basin dynamics in the Silurian of the Appalactian foreland basin [J]. Sedimentary Geology,69:191 − 224.
[2] China National Petroleum Corporation. 1997. SY/T 6285-1997 Evaluating methods of oil and gas reservoirs[S]. The People Republic of China petroleum natural gas profession standard,.
[3] Fu S,Liu Z,Guo Y R,et al.,2019. Lacustrine paleoshoreline determination under established sequence stratigraphic framework and its controls on sand bodies and hydrocarbon accumulations[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,110:497 − 51. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.041
[4] Mitchum R M,Van Wagoner J C,1991. High-frequency sequences and their stacking patterns:sequence-statigraphic evidences of high-frequency eustatic cycles[J]. Sedimentary Geology,70(2):131 − 160.
[5] Nunes R,Soares A,Azevedo L,et al.,2017. Geostatical seismic inversion with direct sequential simulation and co-simulation with mutli-local distribution functions[J]. Mathematical geosciences,49(5):583 − 601. doi: 10.1007/s11004-016-9651-0
[6] Vail P R,Audemard F,Bowman S A,et al.,1991. The stratigraphic signatures of tectonics,eustasy and sedimentology—an overview [C]. In:Einsele G,Ricken W,Seilacher A eds. Cycles and event s in stratigraphy. Berlin,Heidberg:Springer-Verlag. 617 − 659.
[7] Vail P R,Todd R G,SangreeJB,1977. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level,part5:chronostratigraphic significance of seismic reflections[C]//Payton CE. Seismic stratigraphy–applications to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Memoir,26:99 − 116.
[8] 曹桐生,罗龙,谭先锋,等,2021. 致密砂岩储层成因及其孔隙演化过程:以杭锦旗十里加汗地区下石盒子组为例[J]. 断块油气田,28(5):598 − 603.
Cao T S,Luo L,Tan X F,et al.,2021. Genesis and pore evolution of tight sandstone reservoir:taking Lower Shihezi Formation in the Shilijiahan block of Hangjinqi area as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,28(5):598 − 603 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] 陈安清,陈洪德,徐胜林,等,2011. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部晚古生代物源体系及聚砂规律[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),35(6):1 − 7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.06.001
Chen A Q,Chen H D,Xu S L,et al.,2011. Provenance and sandy accumulation regularity of Neopaleozoic in North Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum,35(6):1 − 7 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.06.001
[10] 陈留勤, 2008. 准层序到米级旋回——层序地层学与旋回地层学相互交融的纽带[J]. 地层学杂志, 32(4): 447 − 454.
Chen L Q,2008. From parasequences to meter-scale cycles:the connection between sequence stratigraphy and cyclostratigraphy[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,32(4):447 − 454 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] 邓宏文,1995. 美国层序地层研究中的新学派——高分辨率层序地层学[J]. 石油天然气地质,16(2):89 − 97.
Deng H W,1995. A new school of thought in sequence stratigraphic studiesin U. S. :high-resolution sequence stratigraphy[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,16(2):89 − 97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] 邓宏文,王红亮,宁宁,2000. 沉积物体积分配原理——高分辨率层序地层学的理论基础[J]. 地学前缘,7(4):305 − 313.
Deng H W,Wang H L,Ning N,2000. Sediment volume partition principle:theory basis for high-resolution sequence stratigraphy[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,7(4):305 − 313 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] 段治有,李贤庆,陈纯芳,等,2019. 杭锦旗地区 J58 井区下石盒子组气水分布及其控制因素[J]. 岩性油气藏,31(3):45 − 54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.001
Duan Z Y,Li X Q,Chen C F,et al,2019. Gas and water distribution and its controlling factors of Xiashihezi Formation in J58 well area,Hangjinqi area[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,31(3):45 − 54 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.001
[14] 郭军,陈洪德,王峰,等,2012. 鄂尔多斯盆地太原组砂体展布主控因素[J]. 断块油气田,19(5):568 − 571.
Guo J,Chen H D,Wang F,et al.,2012. Main controlling factors of Taiyuan Formation sand body distribution in Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,19(5):568 − 571 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] 郭顺,闫继福,郭 兰,等,2009. 鄂北杭锦旗地区太原组沉积微相分析[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),39(2):283 − 287.
Guo S,Yan J F,Guo L,et al.,2009. The sedimentary microfacies of Taiyuan formation in the Hangjinqi area,the north of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),39(2):283 − 287 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] 韩兴刚,肖峰,张伟,等,2018. 辫状河沉积储层小层精细划分对比——以苏里格气田苏X加密井区为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),48(1):76 − 84.
Han X G,Xiao F,Zhang W,et al.,2018. Stratigraphic division and correlation of braid river reservoir——An example from SuX dense wellarea, Sulige Gas Filed[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,48(1):76 − 84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] 何发岐,王付斌,张威,等,2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘勘探思路转变与天然气领域重大突破[J]. 中国石油勘探,25,(6):39 − 49.
He F Q,Wang F B,Zhang W,et al.,2020. Transformation of exploration ideas and major breakthrough in natural gas discovery in the northern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,25,(6):39 − 49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] 李宏涛,马立元,史云清,等,2020. 基于井−震结合的水下分流河道砂岩储层展布分析与评价:以什邡气藏 JP35 砂组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏,32(2):78 − 89.
Li H T,Ma L Y,Shi Y Q,et al.,2020. Distribution and evaluation of underwater distributary channel sandstone reservoir based on well-seismic combination:A case study of JP35 sand group in Shifang gas reservoir[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,32(2):78 − 89 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] 李宏涛,史云清,肖开华,等,2016. 元坝气田须三段气藏层序沉积与储层特征[J]. 天然气工业,36(9):20 − 34.
Li H T,Shi Y Q,Xiao K H,et al.,2016. Sequence,sedimentary and reservoir characteristics of Xu 3 gas reservoir in the Yuanba Gasfield,NE Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,36(9):20 − 34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] 李军,宋新民,薛培华,等,2010. 扶余油田杨大城子组曲流河相油藏单砂体层次细分及成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质,31(1):119 − 125. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.09.003
Li J. Song X M. Xue P H,et al.,2010. Hierarchical subdivision and origin of single sandbody in the reservoirs of meandering river facies in the Yangdachengzi Formation of Fuyu oilfield[J]. Oil & gas geology,31(1):119 − 125 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.09.003
[21] 凌云,孙德胜,高军,等,2006. 叠置薄储层的沉积微相解释研究[J]. 石油物探,45(4):329 − 341. doi: 10.11743/ogg20100119
Lin Y,Sun D S,Gao J,et al.,2006. Interpretation research into continental microfacies of superposed thin reservoirs[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,45(4):329 − 34 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11743/ogg20100119
[22] 刘波,赵翰卿,于会宇,2000. 储集层的两种精细对比方法讨论[J]. 石油勘探与开发,27(6):94 − 96.
Liu B,Zhao H Q,Yu H Y,2000. Discussion on the two methods of detailed reservoir correlation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,27(6):94 − 96 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] 刘晓晨,陆永潮,杜学斌,等,2020. 层序格架约束下的地质统计学反演在薄砂体预测中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报,39(3):99 − 109.
Liu X C,Lu Y C,Du X B,et al.,2020. Application of geostatistical inversion constrained by sequence framework in thin-bedded sandbody prediction[J],Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,39(3):99 − 109 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 刘震,王大伟,吴辉,等,2008. 利用地震资料进行陆相储层小层等时对比的方法研究——以绥中 36-1 油田为例[J]. 地学前缘 (中国地质大学(北京); 北京大学),15(1):133 − 139.
Liu Z,Wang D W,Wu H,et al.,2008. Research on isochronic subzone correlation of non-marine reservoir by seismic data:a case study in SZ36-1 oil-field,Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,15(1):133 − 139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] 罗开平,杨帆,陆永德,等,2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区关键构造期与二叠系致密气成藏响应[J]. 石油实验地质,43(4):557 − 568.
Luo K P,Yang F,Lu Y D,et al.,2021. Key structural periods and Permian tight gas accumulation response in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,43(4):557 − 568 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] 梅冥相,2011. 从旋回的有序叠加形式到层序的识别和划分:层序地层学进展之三[J]. 古地理学报,13(1):37 − 54.
Mei M X,2011. From vertical stacking pattern of cycles to discerning and division of sequences:The third advance in sequence stratigraphy[J]. Journal of palaeogeography,13(1):37 − 54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] 梅冥相,徐德斌,周洪瑞,2000. 米级旋回层序的成因类型及其相序组构特征[J]. 沉积学报,18(1):43 − 49.
Mei M X,Xu D B,Zhou H R,2000. Genetic Types of Meter—Scale Cyclic Sequences and Their Fabric Features of Facies—Succession[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,18(1):43 − 49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] 牟传龙,2022. 关于相的命名及其分类的建议[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,DOI:10.19826/j.cnki.1009.3850.03001.
MOU C L,2022. Suggested naming and classification of the word facies [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,42(3) :331 − 339(in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] 齐荣,李良,秦雪霏,2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘近源砂砾质辫状河砂体构型与含气性[J]. 石油实验地质,41(5):682 − 690.
Qi R,Li L,Qin X F,2019. Sand body configuration and gas-bearing properties of near source sand-gravel braided river on the northern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,41(5):682 − 690 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] 裘亦楠,张志松,唐美芳,等,1987. 河流砂岩储层的小层对比问题[J]. 石油勘探与开发,14(2):46 − 52.
Qiu Y N,Zhang Z S,Tang M F,et al.,1987. The detailed correlation of fluvial sandbody reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,14(2):46 − 52(in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] 沈玉林,郭英海,李壮,2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格庙地区二叠系山西组及下石盒子组盒八段沉积相[J]. 古地理学报,8(1):53 − 62.
Sheng Y L,Guo Y H,Li Z,2006. Sedimentary facies of the Shanxi Formation and Member 8 of Xiashihezi Formation of Permian in Suligemiao area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),8(1):53 − 62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] 王西文,苏明军,王大兴,等,2003. 相控−等时小层对比方法及应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,30(6):78 − 80. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2006.01.006
Wang X W,Su M J,Wang D X,et al.,2003. Method and application of facies controlling isochrones oil-layer[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,30(6):78 − 80 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2006.01.006
[33] 卫延召,薛良清,池英柳,等,2002. 在高频层序格架约束下的地震岩性反演及储层预测[C]. 2002低渗透油气储层研讨会论文摘要集,47.
Wei Y Z,Xue L Q,Chi Y L,et al.,2002. Seismic lithology inversion and reservoir prediction under high-frequency sequence framework constraints [J]. Summary of 2002 Low Permeability Oil and Gas Reservoir Symposium Papers,47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] 魏华芝,2018. 井震结合刻画水下分流河道砂体[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,37(6):132 − 139.
Wei H Z,2018. Characterization of the underwater distributary channel sandbodies by integrating the well log and seismology[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing,37(6):132 − 139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 薛会,王毅,毛小平,等,2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部上古生界天然气成藏期次:以杭锦旗探区为例[J]. 天然气工业,29(12): 9 − 12.
Xue H,Wang Y,Mao X P,et al.,2009. The timing of gas pooling in the Upper Paleozoic in the northern Ordos Basin:a case study of the Hangjinqi block[J]. Natural Gas Industry,29(12):9 − 12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] 杨云,余逸凡,毛平,等,2010. 复杂地层精细对比方法——以奈斯N1-N21油藏为例[J]. 石油地质与工程,24(4):22 − 25. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.12.003
Yang Y,Yu Y F,Mao P,et al.,2010. Fine stratigraphic correlation and its application in complicated formation- a case study of gas N1-N12 reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering,24(4):22 − 25 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.12.003
[37] 袁志祥,2001. 鄂北塔巴庙、杭锦旗地区古生界天然气勘探前景分析[J]. 天然气工业,21(增刊1):5 − 9.
Yuan Z X,2001. An analysis of the natural gas exploration potential of Paleozoic at Tabamiao and Hangjin banner regions in north Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,21(Suppl 1):5 − 9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] 张广权,2013. 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田本溪组—太原组高分辨率层序地层学研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,24(5):915 − 922.
Zhang G Q,2013. Study on the high-resolution sequences stratigraphy of Benxi Formation to Taiyuan Formation in Daniudi Gasfield,Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,24(5):915 − 922 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] 张满郎,李熙喆,谷江锐,等,2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界层序地层划分及演化[J]. 沉积学报,27(2):289 − 298.
Zhang M L,Li X Z,Gu J R,et al.,2009. Sequence division and evolution of Upper Paleozoic in the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,27(2):289 − 298 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] 张威,何发岐,闫相宾,等,2021. 大型辫状河席状复合河道岩性圈闭识别描述方法及应用[J]. 石油实验地质,43(3):432 − 442.
Zhang W,He F Q,Yan X B,et al.,2021. Study and application of identification and description methods for lithologic traps in large braided river sheet composite channels[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,43(3):432 − 442 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] 张威,李良,贾会冲,等,2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区十里加汗区带下石盒子组 1 段岩性圈闭成藏动力及气水分布特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,37(2):189 − 196.
Zhang W,Li L,Jia H C,2016. Reservoir-forming dynamics and gas-water distribution characteristics of lithologic traps in the first member of Xiashihezi Formation in the Shilijiahan zone,Hangjinqi area,Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,37(2):189 − 196 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] 张倚安,田景春,张翔,等. 构造−沉积格局控制下的砂体展布规律:以杭锦旗地区二叠系为例[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(2):187 − 193,229.
Zhang Y A,Tian J C,Zhang X,et al.,2021. The sand body distribution law controlled by tectonic-sedimentary pattern:a case study of Permian in Hangjinqi area [J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,28(2):187 − 193,229 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] 赵翰卿,1988. 大庆油田河流−三角洲沉积的油层对比方法[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,7(4):25 − 31.
Zhao H Q,1988. Formation correlation of fluvial-deltaic deposition in Daqing oil field[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oil field Development in Daqing,7(4):25 − 31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] 赵翰卿,2005. 高分辨率层序地层对比与我国的小层对比[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,24(1):5 − 9.
Zhao H Q,2005. High-resolution sequential stratigraphy correlation and Chinese subzone correlation[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,24(1):5 − 9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] 赵靖舟,付金华,姚泾利,等,2012. 鄂尔多斯盆地准连续型致密砂岩大气田成藏模式[J]. 石油学报,33(增刊1):37 − 52.
Zhao J Z,Fu J H,Yao J L,et al.,2012. Reservoir formation model for large gas fields of quasi-continuous compact sandstone in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,33(Suppl 1):37 − 52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] 郑荣才,柯光明,文华国,等,2004. 高分辨率层序分析在河流相砂体等时对比中的应用[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版,31(6):641 − 647.
Zheng R C,Ke G M,Wen H G,et al,2004. Isochronic correlation of fluvial sandbodies by high-resolution sequence technique[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition,31(6):641 − 647 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] 郑荣才,吴朝容,叶茂才,2000. 浅谈陆相盆地高分辨率层序地层研究思路[J]. 成都理工学院学报,27(3):241 − 244.
Zheng R C,Wu C R,Ye M C,2000. Research thinking of high-resolution sequence stratigraphy about a terrigenous basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,27(3):241 − 244 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] 朱筱敏,董艳蕾,曾洪流,等,2019. 沉积地质学发展新航程——地震沉积学[J]. 古地理学报,21(2):189 − 201.
Zhu X M,Dong Y L,Zeng H L,et al.,2019. New development trend of sedimentary geology:Seismic Sedimentology[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),21(2):189 − 201 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] 朱宗良,李文厚,李克永,等,2010. 杭锦旗地区上古生界层序及沉积体系发育特征[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),40(6):1050 − 1054.
Zhu Z L,Li W H,Li K Y,Et al.,2010. The characteristic of sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary systems of Taiyuan—Xiashihezi formation in Hangjinqi area[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),40(6):1050 − 1054 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] 陈留勤,2008. 准层序到米级旋回——层序地层学与旋回地层学相互交融的纽带[J]. 地层学杂志,32(4):447 − 454.
Zhu X M, Dong Y L, Zeng H L, et al., 2019. New development trend of sedimentary geology: Seismic Sedimentology[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 21(2): 189 − 201 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] 中国石油天然气总公司,1997. SY/T 6285-1997 油气储层评价方法. 中华人民共和国石油天然气行业标准.
Zhu Z L, Li W H, Li K Y, Et al., 2010. The characteristic of sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary systems of Taiyuan—Xiashihezi formation in Hangjinqi area[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 40(6): 1050 − 1054.
-



 下载:
下载: