Influencing Factors of NO Removal from Sintering Flue Gas Based on Microwave Treatment
-
摘要:
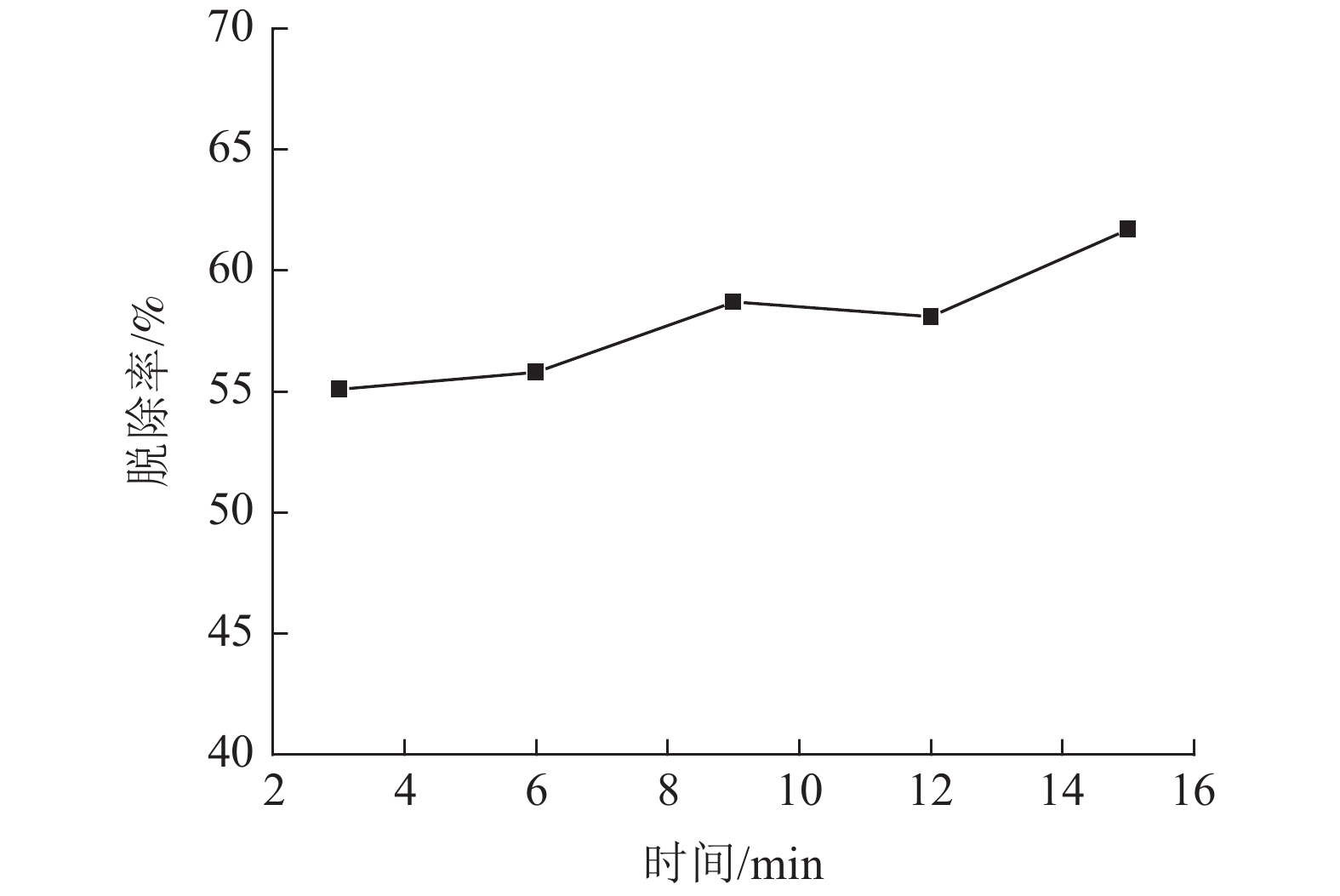
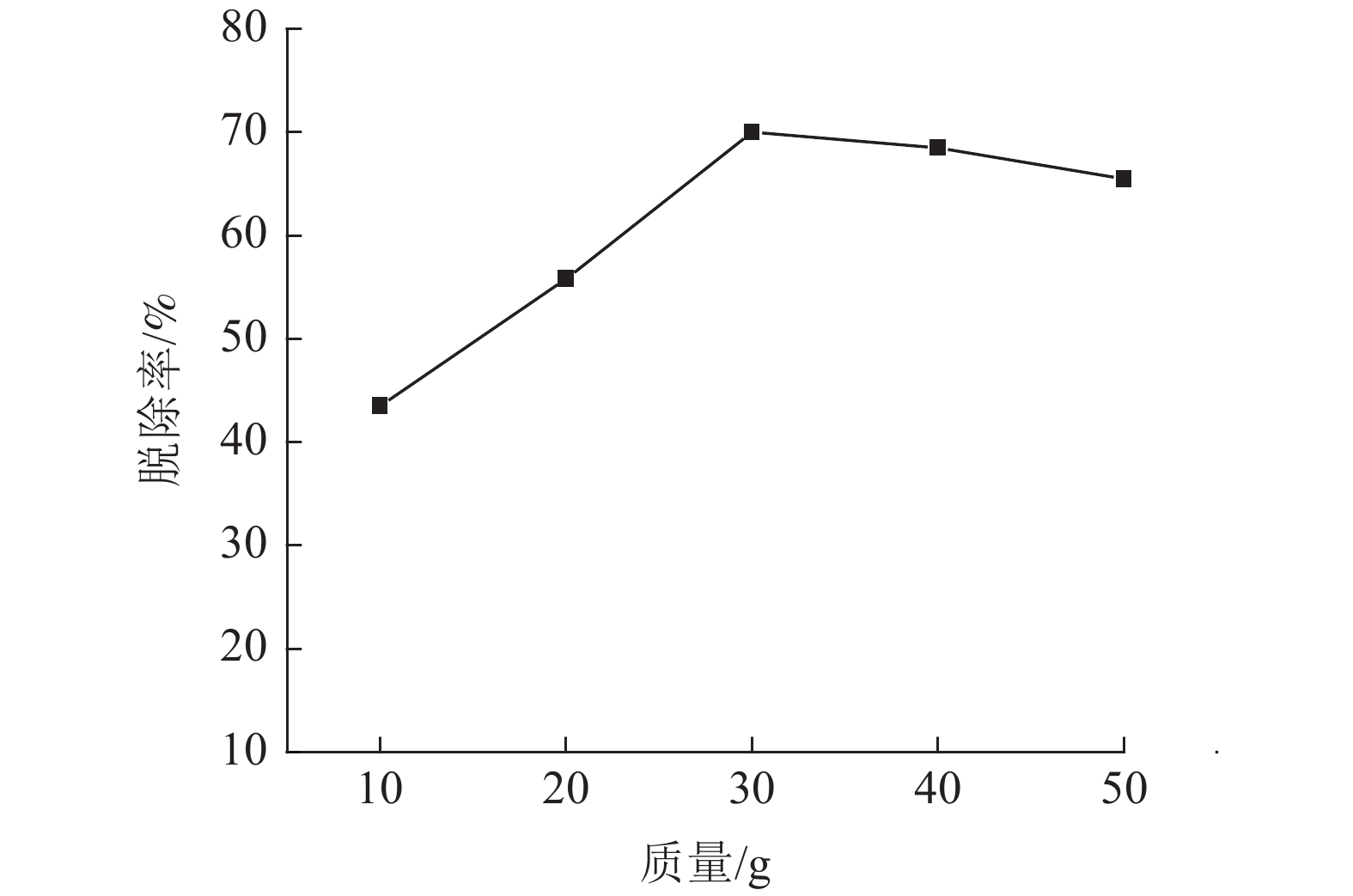
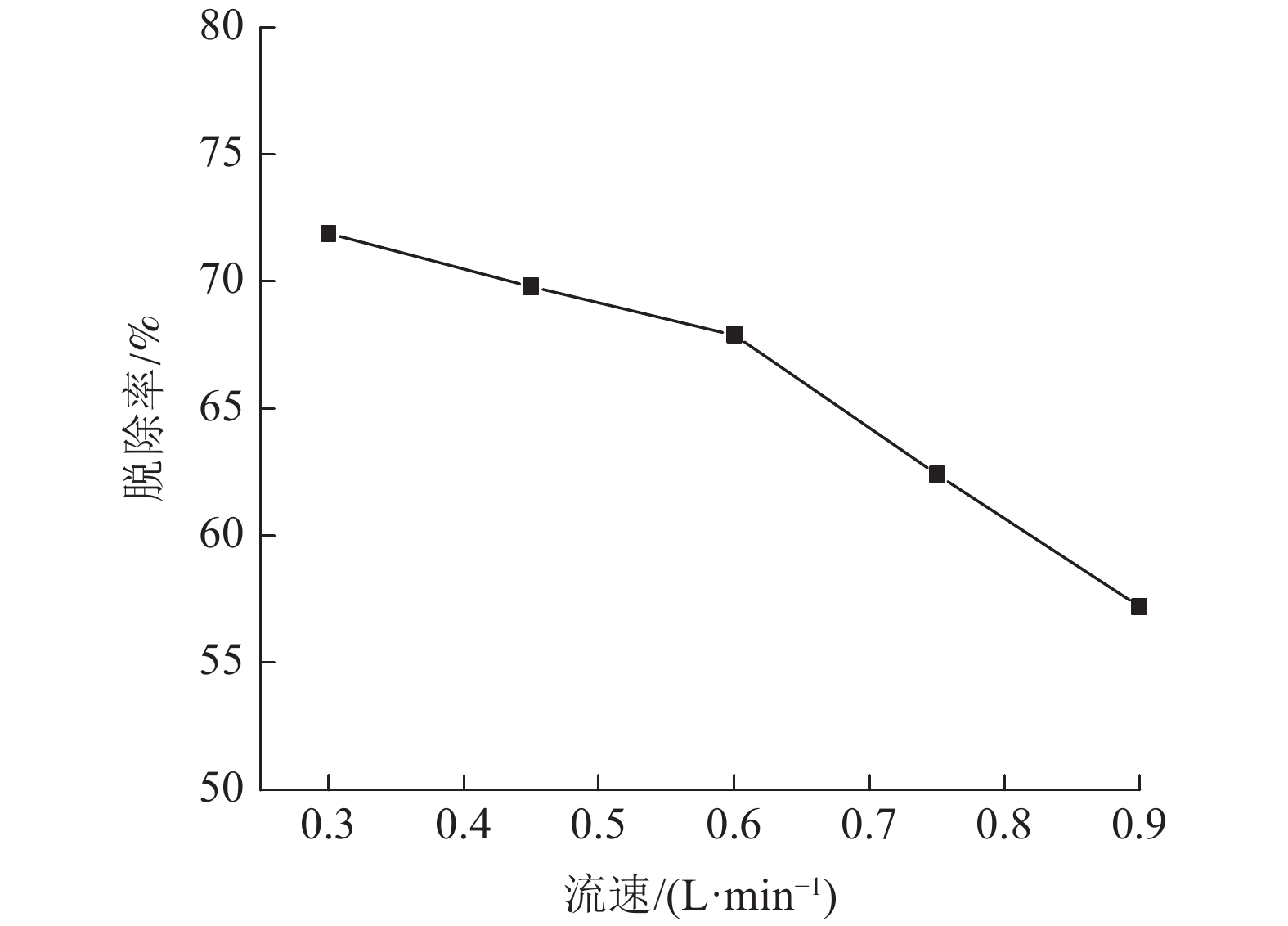
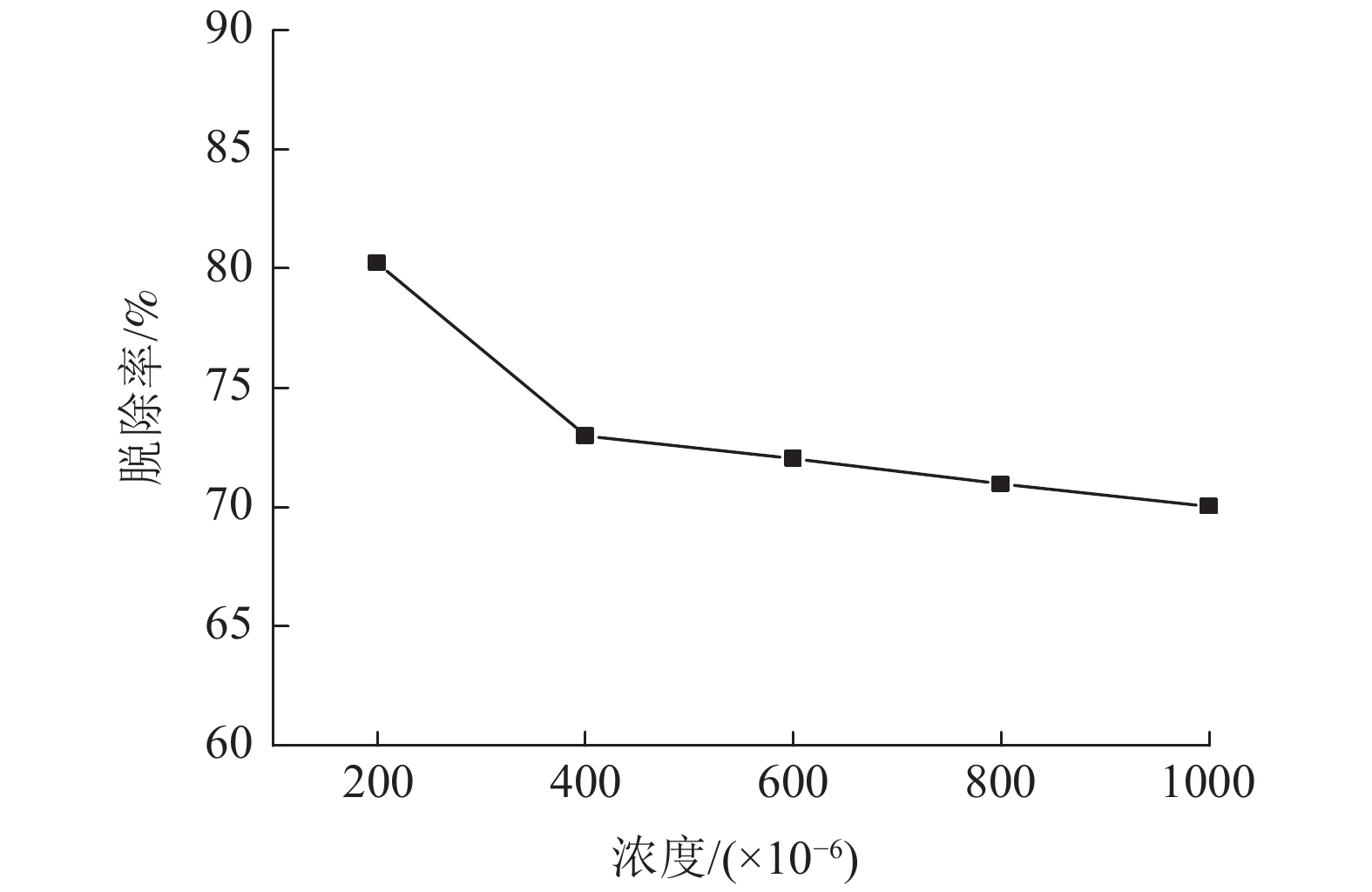
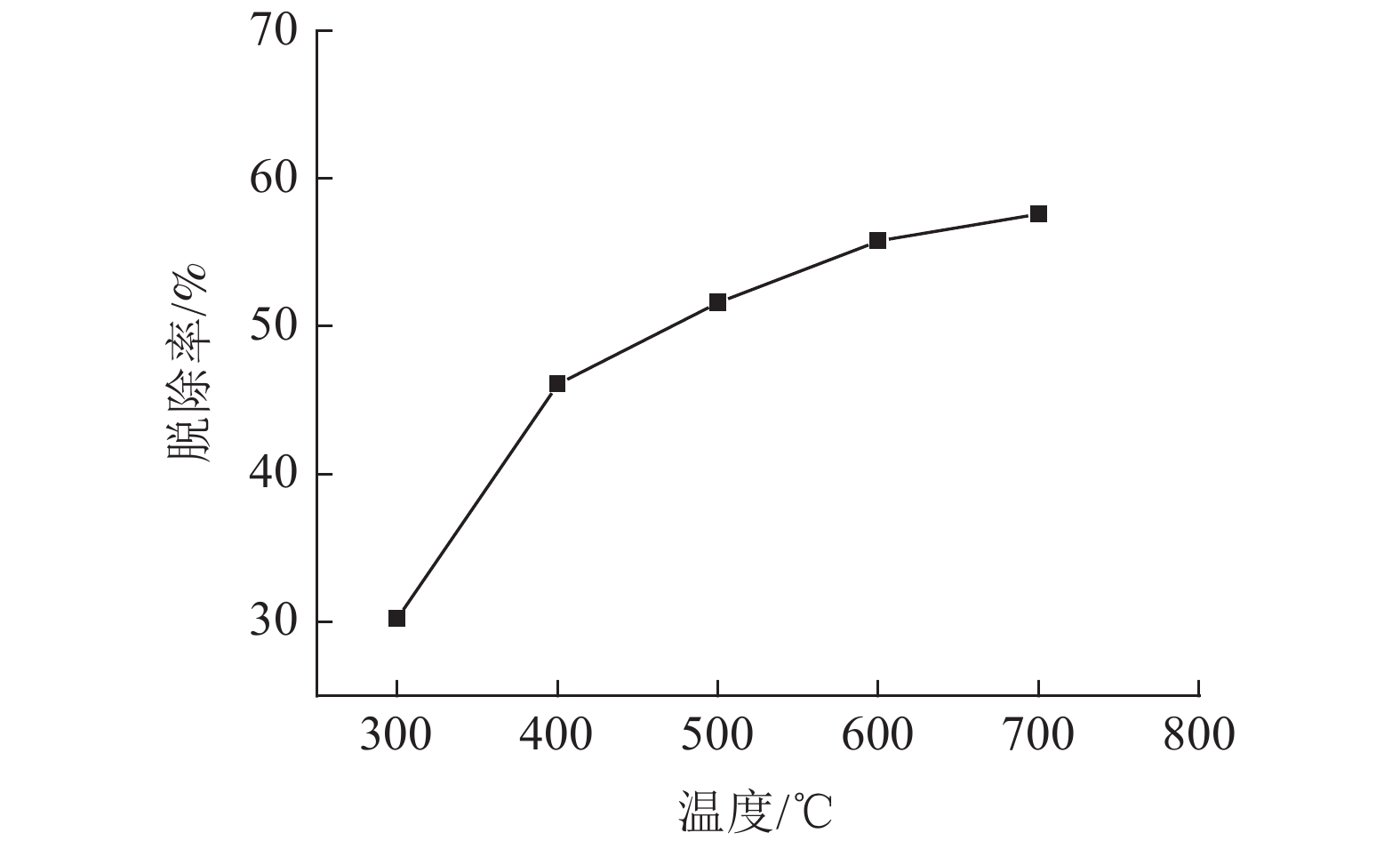
以实验室模拟的烧结烟气为研究对象,研究微波加热温度、微波处理时间、活性炭用量、烟气流量以及气体浓度等因素对微波脱硝效果的影响。试验结果表明,增大微波加热温度和提高活性炭的加入量可显著提高微波脱硝效率,微波加热温度为700℃和活性炭用量为30 g/L时,脱硝效率分别为57.6%和70.02%;微波加热时间从3 min增加到15 min,脱硝效率由55.45%增大到62.8%,影响不明显;烟气流速为0.3 L/min时,可获得71.9%的脱硝效率,并随着烟气流速增大表现出对脱硝效果的不利影响;受活性炭吸附的影响,随着烟气中NO浓度增大,NO脱除效率逐渐降低,NO浓度为200 ×10-6时,脱硝效率达到最大值80.25%。
Abstract:Taking sintering flue gas simulated in the laboratory as the research object, the effects of microwave heating temperature, microwave treatment time, modified activated carbon dosage, flue gas flow rate and gas concentration on microwave denitration were studied. The test results showed that increasing the microwave heating temperature and increasing the amount of activated carbon can significantly improve the microwave denitration efficiency. When the microwave heating temperature is 700℃ and the activated carbon dosage is 30 g/L, the denitration efficiency is 57.6% and 70.02%, respectively. When the microwave heating time is increased from 3min to 15min, the denitration efficiency is increased from 55.45% to 62.8%, but the effect is not obvious. When the flue gas flow rate is 0.3 L/min, 71.9% denitration efficiency can be obtained, and detrimental effects on denitration is shown as the flue gas flow rate increases. Being affected by the adsorption of activated carbon, as the NO concentration in the flue gas increases, the NO removal efficiency gradually decreases. When the NO concentration is 200 ×10-6, the denitration efficiency reaches the maximum of 80.25%.
-
Key words:
- Microwave /
- Activated carbon /
- Denitration /
- Sintering flue gas
-

-
[1] 杨光, 张淑会, 杨艳双. 烧结烟气中气态污染物的减排技术现状及展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):45-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.007
YANG G, ZHANG S H, YANG Y S. Current status and prospects of emission reduction technology for gaseous pollutants in sintering flue gas[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):45-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.007
[2] 刘正强, 唐铁龙, 刘威尔. 火法次氧化锌生产烟气适用排放标准的探讨[J]. 中国环保产业, 2018(6):53-54+57.
LIU Z Q, TANG T L, LIU W E. Discussion on the applicable emission standard of flue gas in pyrometallurgical zinc oxide production[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2018(6):53-54+57.
[3] 王世磊, 章贤臻, 李运姣, 等. 天然锰矿低温NH3-SCR烟气脱硝催化活性研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):76-82.
WANG S L, ZHANG X Z, LI Y J, et al. Performance of low temperature no catalytic oxidation activity of natural manganese ore catalysts[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):76-82.
[4] 肖德超, 张军红, 何志军, 等. 微波制备高效脱硫脱硝吸附剂及性能[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):71-76.
XIAO D C, ZHANG J H, HE Z J, et al. Microwave preparation and properties of high- efficiency desulfurization and denitrification adsorbent[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):71-76.
[5] 佟志芳, 毕诗文, 杨毅宏. 微波加热在冶金领域中应用研究现状[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2004(02):117-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2004.02.008
TONG Z F, BIS W, YANG Y H. Research status of application of microwave heating in metallurgical field[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2004(02):117-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2004.02.008
[6] 鲍瑞, 易健宏. 微波烧结技术在硬质合金制备中的应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(6):1544-1561.
BAO R, YI J H. Application of microwave sintering technology in the preparation of cemented carbide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(6):1544-1561.
[7] 唐军旺. 微波辐射下NO转化的研究[D]. 大连: 中国科学院大连化学物理研究所, 2001.
TANG J W. Study on NO conversion under microwave irradiation [D]. Dalian: Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2001.
[8] 朱政. 微波—煤基炭脱除焦炉烟气NOx的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2015.
ZHU Z. Study on the removal of NOx from coke oven flue gas by microwave and coal-based charcoal [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[9] 石焱, 孔征, 赵莹, 等. 微波辐照活性炭处理烧结烟气质量损失影响因素[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019, 40(4):74-78.
SHI Y, KONG Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Influence factors on quality loss of sintering flue gas treated by microwave irradiation activated carbon[J]. Iron and Steel Vanadium and Titanium, 2019, 40(4):74-78.
[10] 马双忱, 姚娟娟, 金鑫, 等. 微波辐照活性炭床脱硫脱硝动力学研究[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2011, 41(09):1234-1239.
MA S C, YAO J J, JIN X, et al. Microwave-irradiated activated carbon for desulfurization and denitrification[J]. Science China:Technical Science, 2011, 41(09):1234-1239.
[11] 叶春松, 胡爱辉, 张弦, 等. 微波改性活性炭深度处理高盐废水性能研究[J]. 现代化工, 2016, 36(8):133-137.
YE C S, HU A H, ZHANG X, et al. Research on the advanced treatment of high-salt wastewater by microwave modified activated carbon[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2016, 36(8):133-137.
[12] 石焱, 赵鑫, 冯英英, 等. 微波-吸波介质处理炼焦烟气中五环多环芳烃[J]. 现代化工, 2017, 37(12):76-78+80.
SHI Y, ZHAO X, FENG Y Y, et al. Treatment of pentacyclic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coking flue gas by microwave and absorbing medium[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2017, 37(12):76-78+80.
-



 下载:
下载: