Research on Boiling Roasting Behavior of Complex Zinc Concentrate
-
摘要:
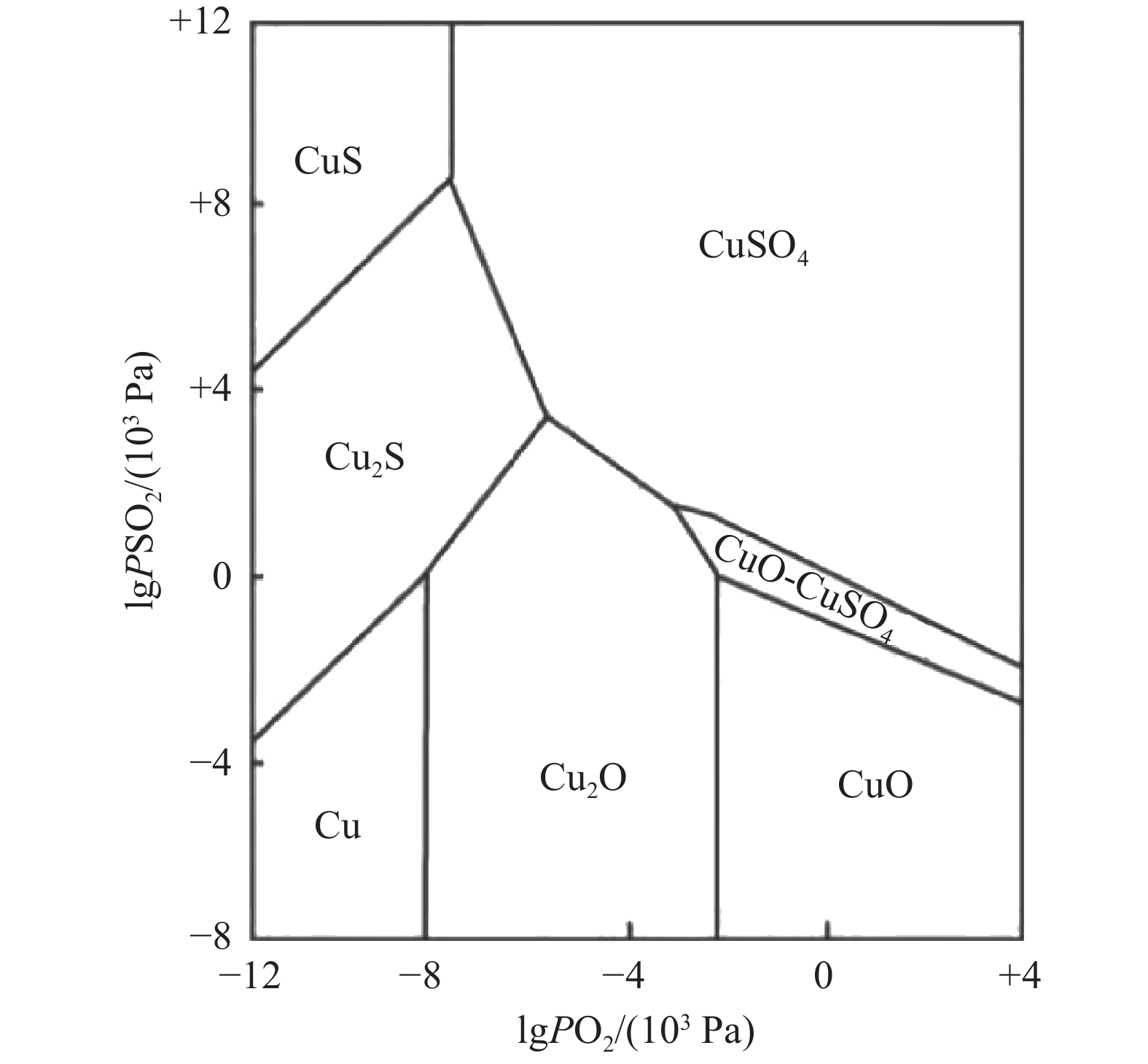
随着国内锌资源的不断匮乏以及市场的快速变化,锌冶炼企业入选的锌精矿成分也越来越复杂,高硅、高铜、高铅、高铁矿源已逐渐成为常态,这些高杂质矿使得沸腾焙烧炉炉况严重恶化,极大影响焙烧工序的正常进行。锌冶炼企业要想在日益复杂的市场竞争中获得长足发展,除了需要以最低的成本组织生产外,还需要能够适应各种复杂矿源,特别是能够处理高附加值的锌精矿。因此本文对复杂锌精矿中的重点杂质Cu、Pb、SiO2、Fe在沸腾焙烧中的行为以及影响进行了系统的研究,旨在为锌冶炼企业处理复杂锌精矿提供一定的理论与实践指导。
Abstract:With the continuous scarcity of domestic zinc resources and the rapid changes in the market, the composition of zinc concentrates selected by zinc smelting companies has become more and more complex. High-silicon, high-copper, high-lead, and high-iron mineral sources have gradually become the norm. These high impurities ore seriously deteriorates the conditions of the fluidized roaster, which greatly affects the normal progress of the roasting process. In order for zinc smelting companies to achieve rapid development in the increasingly complex market competition, in addition to organizing production at the lowest cost, they also need to be able to adapt to various complex mineral sources, especially to be able to handle high value-added zinc concentrates. Therefore, this article systematically studies the behavior and influence of Cu, Pb, SiO2 and Fe, the key impurities in complex zinc concentrates, during boiling roasting, and aims to provide certain theoretical and practical guidance for zinc smelting enterprises to deal with complex zinc concentrates.
-
Key words:
- Zinc concentrate /
- Impurities /
- Boiling roasting /
- Sintering
-

-
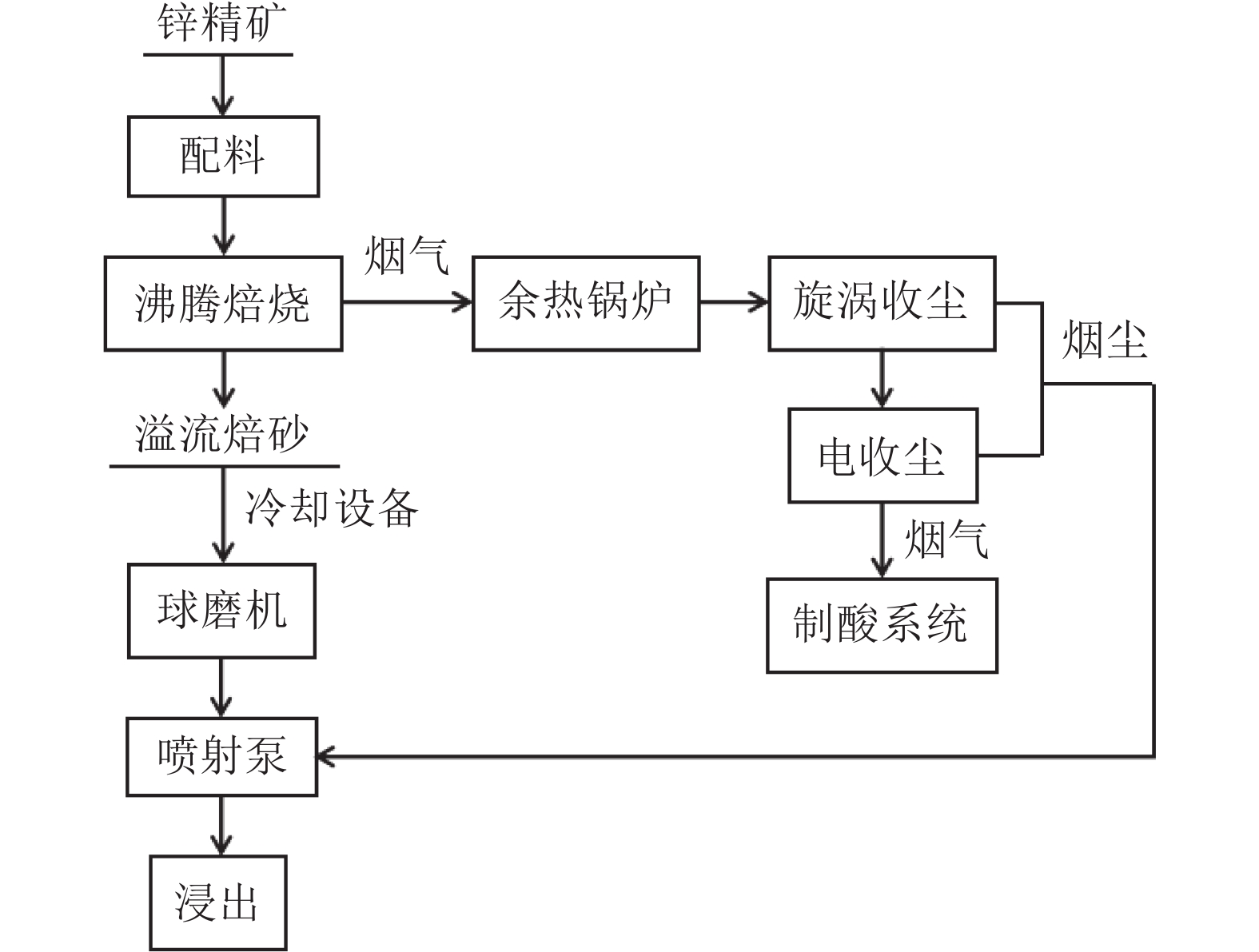
表 1 沸腾焙烧炉入炉料成分/%
Table 1. Requirements for the composition of the charging of the fluidized roaster
Zn S SiO2 Cu Pb Fe H2O >46 26~32 <3 <1 <1.7 <10 8~11 -
[1] 谢华涛. 沸腾焙烧炉处理高杂锌精矿的生产实践[C]//中国首届熔池熔炼技术及装备专题研讨会论文集. 昆明: 中国有色金属学会, 2007: 242.
XIE H T. Production practice of fluidized roaster for high-impurity zinc concentrate[C]//Proceedings of China's First Seminar on Melting Technology and Equipment for Molten Pool. Kunming: China Nonferrous Metals Society, 2007: 242.
[2] 王康. 沸腾炉面对几种复杂锌精矿的处理办法[C]. 中国有色金属学会第七届学术年会. 北京: 中国有色金属学会, 2009: 426.
WANG K. Fluidized bed furnace facing several complex zinc concentrate treatment methods [C]. The 7th Annual Conference of China Nonferrous Metals Society. Beijing: China Nonferrous Metals Society, 2009: 426.
[3] 彭容秋. 铅锌冶金学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
PENG R Q. Lead and zinc metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003.
[4] 鲍超, 唐三川, 张寿年, 等. 铅锌混合精矿的沸腾焙烧研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 1991(1):55-58.
BAO C, TANG S C, ZHANG S N, et al. Research on boiling roasting of lead-zinc mixed concentrate[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 1991(1):55-58.
[5] 孙成余, 罗永光. 锌冶金技术问答[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2015.
SUN C Y, LUO Y G. Questions and answers on zinc metallurgy technology [M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2015.
[6] 王利君. 锌精矿沸腾焙烧过程中SiO2的行为[J]. 矿冶工程, 1995, 15(1):48-52.
WANG L J. The behavior of SiO2 during boiling and roasting of zinc concentrate[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 1995, 15(1):48-52.
-



 下载:
下载: